Abstract
Objective
Anxiety, depression, and pain are highly interactive with each other in adolescent and young adult (AYA) cancer patients. This study aims to map out the connectivity between anxiety, depression and pain symptoms amongst Chinese AYA cancer patients from the perspective of a network model.
Methods
Two hundred and eighteen AYA patients, aged between 15 and 39 years at diagnosis; completed the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ), Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), and McGill Pain Questionnaire-Visual Analogue Scale (MPQ-VAS). Network analyses were performed.
Results
In all, 38.07% (95% CI = 31.58–44.57%) of the participants reported depression, 30.73% (95% CI = 24.56–36.91%) reported anxiety, and 14.22% (95% CI = 9.55–18.89%) reported current pain. The generated network illustrated that anxiety, depression and pain community were well connected. In the network, “having trouble relaxing” (GAD4, node strength = 1.182), “uncontrollable worry” (GAD2, node strength = 1.165), and “sad mood” (PHQ2, node strength = 1.144) were identified as the most central symptoms, while “uncontrollable worry” (GAD2, bridge strength = 0.645), “guilty” (PHQ6, bridge strength = 0.545), and “restlessness” (GAD5, bridge strength = 0.414) were the key bridging symptoms that connected different communities.
Conclusion
Anxiety, depression and pain symptoms are highly interactive with each other. Alleviating AYA cancer patient’s excessive worries might be helpful in improving the patient’s co-occurring anxiety, depression and pain symptoms.
Keywords: adolescent, anxiety, cancer, depression, network, pain, young adult
Introduction
Cancer is the leading cause for disease-related deaths in adolescents and young adults (AYAs).1 AYA cancer patients, defined as age 15–39 years by the National Cancer Institute,2 face a crucial period in their lives due to the inevitable changes in their physiology, social situation, and psychological well-being.1 In China, the prevalence of cancer has been estimated to be around 87.56 per million person-years among AYAs.3 A cancer diagnosis can lead to psychological distress, and AYA patients with cancer are specifically vulnerable to psychological distress due to the intersection of disease and young age.4 Consequently, AYA cancer patients are more likely to report treatment disengagement, lower quality of life, and even suicidality.5,6
Psychological disturbances are common in AYA cancer patients.1,7,8 A meta-analysis indicated that approximately 32% of cancer patients experience some type of psychological distress during active treatment,9 and a review reported a significant association between younger age and greater psychological distress during cancer trajectory.10 In China, a study found that about 75% of the AYA cancer patients reported anxiety, and 90% of them reported depression.11 Emotional disturbances can compromise cancer patients’ emotional and role functioning,12 lower their quality of life, and may lead to higher risk of mortality.13–15
As a complex symptom, pain is prevalent in cancer population.16,17 A recent cross-sectional study found that 66% of the cancer patients reported moderate-to-severe pain,18 while another study showed that 42.1% of the adult cancer patients reported pain.12 Previous studies have found that age, gender, genetic predisposition, and cognitive and/or emotional process around pain could significantly affect one’s perceived pain level.19,20 Inappropriate management of pain could result in negative consequences for patients’ emotions and cognitive function, and their quality of life.21
Anxiety, depression, and pain are prevalent, and highly interactive with each other in AYA cancer patients.22 Individuals with comorbid anxiety and depression tend to respond more slowly to treatment and have a higher probability of suicide and recurrences.23 Moreover, pain often co-occurs with anxiety and depression, and together leads to considerable social and economic burden.24 The pain related to the oncological process may be accompanied by anxiety about medical procedures and hospitalization, separation anxiety and psychological stress.22 The presence of pain is also associated with more depressive symptoms and worse outcome, such as lower quality of life, poorer work performance, and higher health service utilization.19
In a randomized controlled trial, patients with increased pain were more likely to report higher levels of anxiety, fatigue, and depression.25 On the other hand, fatigue, anxiety and depression also have significant influence on pain in patients with cancer.25 A previous study showed that compared to non-depressed patients with pain, patients with comorbid depression and pain tend to experience more pain-related complaints, more severe pain symptoms, and greater impairments.26 Subsequently, even though anxiety, depression, and pain are prevalent, and highly interactive with each other, the interaction amongst these conditions has not been fully investigated. To the best of our knowledge, no study has examined the comorbidity of anxiety, depression and pain in cancer population from the perspective of network analysis.
Network analysis is an alternative novel approach to examine the comorbidity of two or more disorders.27 In network analysis, it is believed that comorbidity occurs when symptoms from different disorders are directly linked to each other.28 It estimates the unique associations between each pair of measured symptoms while controlling for all other symptoms and shrinking potentially spurious associations to zero.29 In this study, 1) network analysis was applied to assess the connectivity between anxiety, depression and pain symptoms in a Chinese AYA cancer sample; 2) the prevalence of anxiety, depression and pain in AYAs was also investigated.
Methods
Participants
This study’s participants were consecutively seen at the outpatient units of Southern Medical University Nanfang Hospital and Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital. Participants were recruited from 1 January 2018 to 30 November 2018. To be eligible, patients needed to: 1) have a cancer diagnosis within the last 6 months; 2) have ages between 15 and 39 years; 3) be able to understand Chinese. Those with disturbances of consciousness were excluded.
Study Procedure
This study was performed in accordance with the Helsinki standard and the study protocol was approved by the Nanfang Hospital Ethics Committee (ref No: NFEC-2018-038) and Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital Research Ethics Committee (ref No. 2018295H(R1)). All participants were approached in the waiting room by trained research assistants. For those patients (adults), showing an interest in participating; were asked to provide a written informed consent form. Simultaneously, approval was also required from a parent/legal guardian for participants under the age of 18 years. All recruited participants were asked to complete a personal information collection form and a set of scales after which they were sent back to the research assistants immediately. The recruitment and assessment procedure was supervised by a licensed psychiatrist.
Measures
Basic Demographic and Clinical Data
Participants’ basic demographic and clinical data (such as, gender, age, cancer site, comorbidities, and family cancer history) were collected using a specially designed case record form.
Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9)
The PHQ is a self-rating scale that measures depression-related symptoms of patients. PHQ contains 9 items, each item uses a four-level score of 0 to 3, with a total score of 0 to 27. A total score of 5 or more indicates depressive symptoms.30 The Chinese PHQ-9 showed good psychometrics properties,31 and the internal consistency of PHQ-9 was 0.802 in Chinese AYA cancer patients.32
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-7)
The GAD is a 7-item self-report scale used to assess an individual’s anxiety symptoms. Response options available are rated from 0 to 3, and a total score of 5 or more indicates anxiety symptoms.33 The Chinese GAD-7 showed satisfactory psychometrics properties,34 and the Cronbach’s alpha of GAD-7 was 0.883 among Chinese AYA cancer patients.32
McGill Pain Questionnaire-Visual Analogue Scale (MPQ-VAS)
The McGill Pain Questionnaire-Visual Analogue Scale (MPQ-VAS) is one of the most widely used tests for the measurement of pain,35 and has been validated in the Chinese language in 2013.36 The score for VAS ranges from 0 (no pain) to 100 (worst possible pain), and a total score of 40 or more indicates that the patient is currently suffering from pain.36
Sample Size Estimation
The sample size (N) was calculated with the formula: 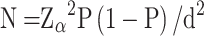 37 where Z is the statistic of the significance test, alpha is the significance level, P is the prevalence, and d is the allowable error. In this study, alpha was set at 0.05, Zα was set at 1.96, and d was 0.1P. Based on a previous finding that about 75% of the AYA cancer patients reported anxiety, and 90% of them reported depression in China.11 We, therefore, assume the prevalence as 75% and to enable further analyses, we increased the expected sample size by 50%. Finally, at least 192 participants were recruited in this study.
37 where Z is the statistic of the significance test, alpha is the significance level, P is the prevalence, and d is the allowable error. In this study, alpha was set at 0.05, Zα was set at 1.96, and d was 0.1P. Based on a previous finding that about 75% of the AYA cancer patients reported anxiety, and 90% of them reported depression in China.11 We, therefore, assume the prevalence as 75% and to enable further analyses, we increased the expected sample size by 50%. Finally, at least 192 participants were recruited in this study.
Statistical Analysis
Network Analysis
First, we estimated the network using the R “bootnet” and “qgraph” packages,38 with “EBICglasso” (ie, the Extended Bayesian Information Criterion combined with the Graphical Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator method) as the default method.29 A network is a graphical representation of variables (nodes), and their correlations are depicted as edges.39 In the network, thicker and more saturated edges represent stronger correlations, green lines represent positive correlations, and red lines represent negative correlations.
Secondly, to quantify the importance of each node in the network, we computed the centrality indices of Strength, Betweenness, and Closeness. Higher centrality index values are representative of greater importance within the network, and symptoms with high centrality measures might be important as potential targets for further treatment interventions.40 Additionally, to identify the bridge symptoms that connect different communities, we computed the bridge centrality (Bridge Strength, Bridge Betweenness, and Bridge Closeness). Recent studies have recommended that both Betweenness, Bridge Betweenness, Closeness, and Bridge Closeness indices might not be robust in psychological networks.41 Therefore, in the subsequent network analysis, we mainly focused on Strength42 and Bridge Strength.43,44 Strength means the sum of the absolute value of a node’s correlations with other nodes in the structure, while Bridge Strength refers to the sum of absolute edge weight values of all intercommunity edges.43,44 Centrality plots were created to represent these indices.
Thirdly, to examine the stability and accuracy of the networks,29 a case-dropping bootstrap procedure was performed to compute the correlation stability coefficient (CS-C). The CS-C is required to be above 0.25.29 Also, a non-parametric bootstrapping method was used to estimate the accuracy of edge-weights by computing confidence intervals (CIs). This means that larger CIs indicated poorer precision in the estimation of edges, while narrower CIs indicated a more trustworthy network.42 Additionally, to examine the possible influence of age and gender on cancer patient’s emotional disturbances, the network model and the local structure indexes were re-estimated, after controlling for age and gender.
Results
Patient Characteristics
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the included participants are reported in Table 1. The study sample consisted of 218 patients with complete data on the 17 variables (7 anxiety nodes, 9 depression nodes, and 1 pain node) used to construct the network. Comparison of patients with complete data vs the rest of the recruited sample (n = 31) revealed no significant differences in sex and age, which indicates that the subgroup of participants included in the network analysis can be considered to be representative of the overall sample. The mean age of the AYA patients was 30.22 years (SD = 4.82). In total, 38.07% (95% CI = 31.58–44.57%) of the participants reported depression, 30.73% (95% CI = 24.56–36.91%) reported anxiety, and 14.22% (95% CI = 9.55–18.89%) reported current pain.
Table 1.
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Sample
| N | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 75 | 34.4 |
| Female | 143 | 65.6 |
| Cancer Site | ||
| Breast | 121 | 55.5 |
| Leukemia | 67 | 30.7 |
| Colorectal | 20 | 9.2 |
| Nasopharynx | 10 | 4.6 |
| Physical comorbidities | ||
| No | 41 | 18.8 |
| Yes | 177 | 81.2 |
| Current Smoker | ||
| No | 215 | 98.6 |
| Yes | 3 | 1.4 |
| Daily Exercise Time | ||
| None | 27 | 12.4 |
| Less than 60min | 171 | 78.4 |
| More than 60min | 20 | 9.2 |
| Childhood Adversity Experience (eg, bullying) | ||
| None | 204 | 93.6 |
| Yes | 14 | 6.4 |
| Family Cancer History | ||
| None | 167 | 76.6 |
| Yes | 51 | 23.4 |
| Depression | ||
| Negative (PHQ total score <5) | 135 | 61.9 |
| Positive (PHQ total score ≧5) | 83 | 38.1 |
| Anxiety | ||
| Negative (GAD total score <5) | 151 | 69.3 |
| Positive (GAD total score ≧5) | 67 | 30.7 |
| Current Pain | ||
| Negative (VAS total score <40) | 187 | 85.8 |
| Positive (VAS total score ≧40) | 31 | 14.2 |
Abbreviations: GAD, General Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire; PHQ, Patient Health Questionnaire.
Network Analysis
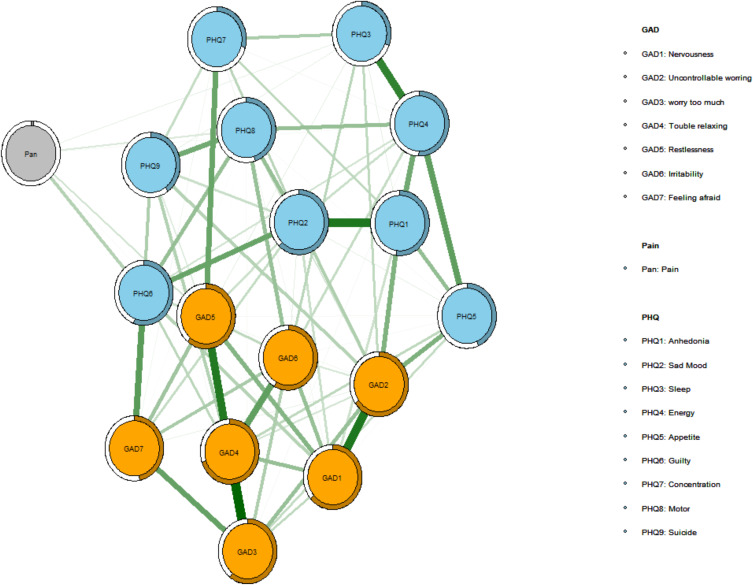
Figure 1 presents the association network. The generated network illustrated that the anxiety, depression and pain community were well connected (with no isolated node). Out of 136 edges, 87 (63.97%) of them were estimated to be non-zero. This model and edge weight matrix revealed that the edges between “excessive worry” and “trouble relaxing” (GAD3 - GAD4, edge weight = 0.3031),“nervousness” and “uncontrollable worry” (GAD1 - GAD2, edge weight = 0.2676), and “anhedonia” and “sad mood” (PHQ1 - PHQ2, edge weight = 0.2671) were the strongest positive edges in the model.
Figure 1.
Network structure of anxiety, pain and depression.
Notes: In the diagram, orange nodes represent anxiety symptoms, light blue nodes represent depression symptoms, and grey node represents pain symptom. Nodes with stronger correlations are closer to each other. The thickness of an edge indicates the strength of the correlation. Green lines represent positive connections.
Abbreviations: PHQ, Patient Health Questionnaire; GAD, General Anxiety Disorder.
Three important bridges between anxiety and depression communities emerged to be: “afraid” and “guilty” (GAD7 - PHQ6, edge weight = 0.1965), “restlessness” and “concentration difficulties” (GAD5 - PHQ7, edge weight = 0.1784), and “uncontrollable worry” and “appetite change” (GAD2 - PHQ5, edge weight = 0.1548). Additionally, there were three bridges between pain and depression: “pain” - “guilty” (PHQ6) (edge weight = 0.0894), “pain” - “motor change” (PHQ8) (edge weight = 0.0452), and “pain” - “sleep problems” (PHQ3) (edge weight = 0.0326). The only bridge that links the pain and anxiety community was “pain” - “restlessness” (GAD5) (edge weight = 0.0576).
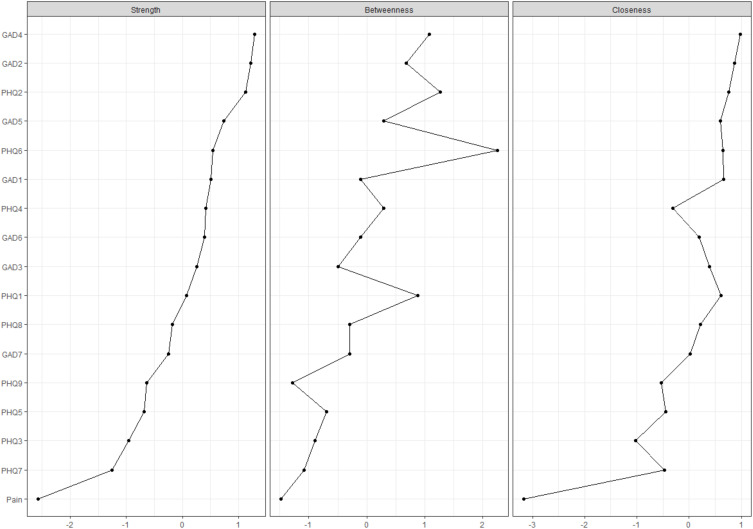
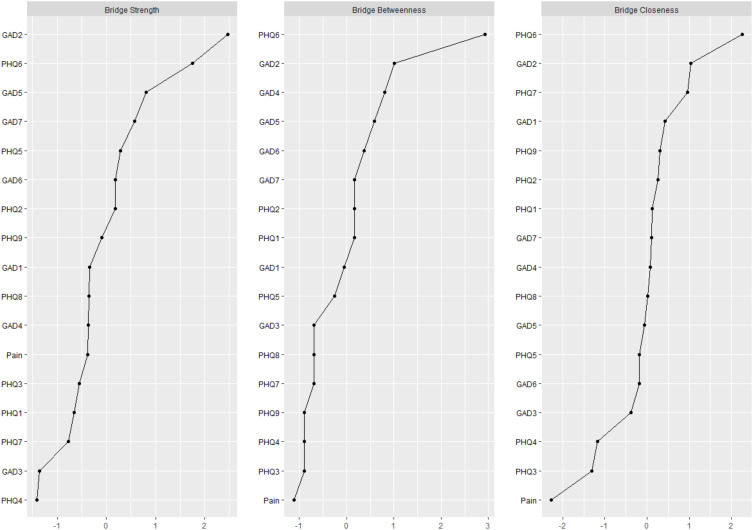
Central Symptoms and Bridging Symptoms
Figure 2 shows the network centrality indices, and Figure 3 shows the network bridge centrality indices. The node “having trouble relaxing” (GAD4, node strength = 1.182), was the most central node within the network, followed by “uncontrollable worry” (GAD2, node strength = 1.165), and “sad mood” (PHQ2, node strength = 1.144). Additionally, “uncontrollable worry” (GAD2, bridge strength = 0.645) was also the strongest bridge symptom in the network that connected the anxiety, depression, and pain clusters, followed by “guilty” (PHQ6, bridge strength = 0.545), and “restlessness” (GAD5, bridge strength = 0.414) (Table 2).
Figure 2.
Centrality Indices of all symptoms within the network.
Abbreviations: PHQ, Patient Health Questionnaire; GAD, General Anxiety Disorder.
Figure 3.
Bridge Centrality Indices of all symptoms within the network.
Abbreviations: PHQ, Patient Health Questionnaire; GAD, General Anxiety Disorder.
Table 2.
Centrality and Bridge Centrality Estimates of Nodes in the Network
| Centrality | Bridge Centrality | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Betweenness | Closeness | Expected Influence | Predictability | Strength | Betweenness | Closeness | |
| Pain | 0.249 | 0 | 0.003 | 0.045 | 0.016 | 0.249 | 0 | 0.046 |
| PHQ1 | 0.888 | 12 | 0.005 | 0.888 | 0.520 | 0.212 | 6 | 0.066 |
| PHQ2 | 1.144 | 14 | 0.005 | 1.144 | 0.620 | 0.327 | 6 | 0.068 |
| PHQ3 | 0.639 | 3 | 0.004 | 0.573 | 0.310 | 0.227 | 1 | 0.054 |
| PHQ4 | 0.972 | 9 | 0.004 | 0.949 | 0.504 | 0.106 | 1 | 0.055 |
| PHQ5 | 0.705 | 4 | 0.004 | 0.705 | 0.435 | 0.342 | 4 | 0.064 |
| PHQ6 | 1.003 | 19 | 0.005 | 1.003 | 0.559 | 0.545 | 19 | 0.085 |
| PHQ7 | 0.566 | 2 | 0.004 | 0.566 | 0.293 | 0.196 | 2 | 0.074 |
| PHQ8 | 0.829 | 6 | 0.005 | 0.738 | 0.450 | 0.254 | 2 | 0.066 |
| PHQ9 | 0.718 | 1 | 0.004 | 0.718 | 0.402 | 0.290 | 1 | 0.068 |
| GAD1 | 0.993 | 7 | 0.005 | 0.969 | 0.635 | 0.255 | 5 | 0.069 |
| GAD2 | 1.165 | 11 | 0.005 | 1.165 | 0.651 | 0.645 | 10 | 0.074 |
| GAD3 | 0.933 | 5 | 0.005 | 0.933 | 0.604 | 0.114 | 2 | 0.062 |
| GAD4 | 1.182 | 13 | 0.005 | 1.182 | 0.696 | 0.252 | 9 | 0.066 |
| GAD5 | 1.050 | 9 | 0.005 | 1.050 | 0.609 | 0.414 | 8 | 0.065 |
| GAD6 | 0.967 | 7 | 0.005 | 0.967 | 0.577 | 0.328 | 7 | 0.064 |
| GAD7 | 0.812 | 6 | 0.005 | 0.812 | 0.471 | 0.382 | 6 | 0.066 |
Abbreviations: GAD, General Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire; PHQ, Patient Health Questionnaire.
Network Stability
Supplementary Figure 1 shows the results of the case-dropping subset bootstrapping test. The CS-coefficient for Strength and Bridge Strength was 0.518, and 0.284, both exceeding the recommended threshold of 0.25. This indicates that the network model is relatively robust. The bootstrapped 95% CIs for the estimated edge-weights were relatively narrow, suggesting that the estimates were accurate (Supplementary Figure 2). The edge weight matrix is presented in Supplementary Table 1. After controlling for age and gender, the network model and local structure indexes were re-estimated. When compared with the original network model, an almost identical network was obtained with respect to magnitude (r = 0.986 [0.971, 0.996]), and strength (r = 0.994 [0.970, 0.998]) of edges.
Discussion
This was the first study that explored the connectivity between anxiety, depression and pain symptoms in Chinese AYA cancer patients, using a network approach. In this study, we found that the prevalence of depression (38.07%) and anxiety (30.73%) in AYA cancer patients is lower than that in a previous AYA study in China.11 However, the prevalence found in the current study is significantly higher than that in Chinese general cancer population.3 A recent investigation has reported that about 13.9% and 15.1% of the Chinese cancer patients have significant symptoms of depression and anxiety, respectively.3 Although several relevant studies have been conducted in China, generalizations to the larger population cannot be made due to several limitations, such as small sample sizes and single-site study designs. In addition, we found that around 14.22% of the AYA patients reported being in current pain. A previous study revealed that about 81.8% of the AYA cancer survivors reported some pain,45 while another study reported that 36.2% of the AYA cancer survivors reported pain.46 The difference in results could be partially explained by the difference in study sample, patient’s sociocultural background, cancer type, and the use of various measurement tools and cutoff values.
In this study, we found that the three communities (ie, anxiety, depression, and pain) were well connected with each other, particularly anxiety and depression. Previous studies have consistently proved that anxiety and depressive symptoms are highly correlated with each other in different populations,39,47–49 including cancer patients.32 Anxiety and depression often share a high degree of comorbidity amongst cancer patients.7,50 The possible underlying mechanisms behind the anxiety–depression interaction could be the polymorphic variation at the serotonin 1-A receptor gene,51 or the alteration of activation and connectivity of amygdala and ventral cingulate.52
Besides the strong associations between anxiety and depression, several positive edges were identified between pain and anxiety/depression. In the network model, pain was positively linked to “guilty”, “motor change”, “sleep problems”, and “restlessness”. Pain is recognized to have both a sensory dimension (ie intensity) and an affective dimension, such as, unpleasantness, anxiety, sadness, and annoyance.53 It has a profound impact on a patient’s physical, psychological, and social quality of life.54 The network model confirmed results from previous studies that emotional disturbances significantly influence the prognosis and treatment of pain, and vice versa.19,53 For example, studies have proved that depression, anxiety, and fear of cancer progression play important roles in the association between objective pathophysiology and patient’s subjective experience of pain.8 Simultaneously, the presence of pain is associated with worse psychological and health-related outcomes, such as higher depression, poorer work performance, and lower quality of life.19 Meanwhile, our findings are in accordance with previous studies which indicated that insomnia at baseline predicted the development of pain, and anxiety symptoms partially mediated that association between insomnia and pain.55 As suggested by the biopsychosocial models, an increasing number of researchers have delineated psychosocial variables to be important correlates of pain.
In this study, the node “having trouble relaxing” was the most central node within the network, followed by “uncontrollable worry” and “sad mood”. Our findings were consistent with previous similar studies which identified “persistent worrying or anxiety”, and “inability to relax” as core symptoms for the diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder, and “sad mood” as the hallmark symptom of major depressive disorder.39,48 Also, “uncontrollable worry” was the strongest bridging symptom in the network. Previous studies have indicated that the activation of bridging symptoms is likely to result in the development and maintenance of different disorders.56 Therefore, “uncontrollable worry”, “guilty”, and “restlessness”, which were the key bridging symptoms that linked one cluster to other clusters in the current study, should be considered as potential targets for future intervention. In particular, in this study, “uncontrollable worry” acts as both central symptom and bridging symptom, indicating that alleviating cancer patient’s excessive worries might be helpful in improving the patient’s co-occurring anxiety, depression and pain symptoms.
This study contributes to the literature in several ways. First, we specifically targeted the AYA population, as they have unique biological and psychological needs. However, health care services in this population have not shown any significant improvement in over two decades, and in China, AYA cancer patients are often ignored.32 The current study helped fill the gap between pediatric and adult psycho-oncology. Second, this was the first study that examined the connectivity between anxiety, depression and pain symptoms in Chinese AYA cancer population. Pain and emotional distress (eg, anxiety, and depression) have been considered as the fifth and sixth vital signs for a cancer patient’s well-being, along with signs of blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, and respiration. Thus, investigating the connectivity between emotional distress and pain provided us better insights into the AYA population. Third, this study used sophisticated network analysis approach, which is a novel approach to examine the comorbidity of two or more disorders.
Study Limitations
There are several limitations that should be acknowledged, however. First, due to the cross-sectional design of the study, no causal relationship could be derived. Second, the sample size of the current study was relatively small; thus, our findings may not be generalizable to the entire AYA population in China. In addition, the sample size calculation formula for cross-sectional study might not be applicable to network analysis. Third, cancer pain was assessed by one-item question, and anxiety and depression symptoms were measured by self-rating scales, thus, recall bias and measurement bias may exist. Fourth, certain factors that may influence an individual’s anxiety, depression and pain, such as, family/social support, time since diagnosis, disease severity, and substance use were not examined in this study. A further multicenter, large-sample, longitudinal investigation using validated objective instruments is needed.
Clinical Implications
This is the first network study to assess the bridge symptoms/items that mediate the interaction among different disorders/syndromes (eg, anxiety, and depression) in AYA cancer populations. Examining patient’s anxiety, depression, and pain symptoms as dynamic systems may provide new insights into the maintenance of these psychosomatic problems. As “uncontrollable worry” was the strongest bridge symptom that linked one symptom cluster to other symptom clusters, this finding suggested that interventions aimed at alleviating patients’ worries and fostering a sense of control (eg, Acceptance – commitment therapy and Mindfulness – base stress reduction) might have utility. Further longitudinal studies could also help to better understand the directionality of these bridge pathways.
Conclusion
In conclusion, anxiety, depression, and pain are highly interactive with each other in Chinese adolescent and young adult cancer patients. In the anxiety-depression-pain network model, “having trouble relaxing”, “uncontrollable worry”, and “sad mood” were identified as the most central symptoms, while “uncontrollable worry”, “guilty”, and “restlessness” were the key bridging symptoms that linked one cluster to other clusters. Alleviating AYA cancer patient’s excessive worries might be helpful in improving a patient’s co-occurring anxiety, depression and pain symptoms.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the patients who participated in this study.
Funding Statement
This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (72101107); the Clinical Research Program of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University (2021CR014), and the Start-up Funds of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (KY0120211134).
Data Sharing Statement
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included within the article and its additional file.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was performed in accordance with the Helsinki standard, and the study’s protocol was approved by the Nanfang Hospital Ethics Committee (ref No: NFEC-2018-038) and Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital Research Ethics Committee (ref No. 2018295H(R1)). The informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s).
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Shay LA, Carpentier MY, Vernon SW. Prevalence and correlates of fear of recurrence among adolescent and young adult versus older adult post-treatment cancer survivors. Support Care Cancer. 2016;24(11):4689–4696. doi: 10.1007/s00520-016-3317-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization. Adolescent health. Available from: https://www.who.int/topics/adolescent_health/en/. Accessed August 19, 2022.
- 3.Duan Y, Wang L, Sun Q, et al. Prevalence and determinants of psychological distress in adolescent and young adult patients with cancer: a multicenter survey. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2021;8(3):314–321. doi: 10.4103/2347-5625.311005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tsiouris A, Mayer A, Nolke C, et al. An emotion-based online intervention for reducing anxiety and depression in cancer patients: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Internet Interv. 2021;25:100410. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2021.100410 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang A, Ji Q, Zhang K, et al. Solution-focused brief therapy for adolescent and young adult cancer patients in China: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Psychosoc Oncol. 2021;1–18. doi: 10.1080/07347332.2021.1931627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tremolada M, Taverna L, Bonichini S, Pillon M, Biffi A. Psychological well-being, cognitive functioning, and quality of life in 205 adolescent and young adult childhood cancer survivors compared to healthy peers. Front Psychol. 2022;13:860729. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.860729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yang Y, Li W, Wen Y, et al. Fear of cancer recurrence in adolescent and young adult cancer survivors: a systematic review of the literature. Psychooncology. 2019;28(4):675–686. doi: 10.1002/pon.5013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhang Y, Tan X, Li W, et al. Self-perceived pain in Chinese patients with cancer. Front Psychol. 2019;10:1994. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Singer S, Das-Munshi J, Brahler E. Prevalence of mental health conditions in cancer patients in acute care–a meta-analysis. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(5):925–930. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lang MJ, David V, Giese-Davis J. The age conundrum: a scoping review of younger age or adolescent and young adult as a risk factor for clinical distress, depression, or anxiety in cancer. J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol. 2015;4(4):157–173. doi: 10.1089/jayao.2015.0005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Xie J, Ding S, He S, Duan Y, Yi K, Zhou J. A prevalence study of psychosocial distress in adolescents and young adults with cancer. Cancer Nurs. 2017;40(3):217–223. doi: 10.1097/NCC.0000000000000396 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Góes SM, Pereira MCS, Teixeira DSC, Da SAM. Prevalence of symptoms and quality of life of cancer patients. Rev Bras Enferm. 2020;73(2):1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.DiMatteo MR, Lepper HS, Croghan TW. Depression is a risk factor for noncompliance with medical treatment: meta-analysis of the effects of anxiety and depression on patient adherence. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(14):2101–2107. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.14.2101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Greer JA, Pirl WF, Park ER, Lynch TJ, Temel JS. Behavioral and psychological predictors of chemotherapy adherence in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Psychosom Res. 2008;65(6):549–552. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2008.03.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pinquart M, Duberstein PR. Depression and cancer mortality: a meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2010;40(11):1797–1810. doi: 10.1017/S0033291709992285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Breivik H, Cherny N, Collett B, et al. Cancer-related pain: a pan-European survey of prevalence, treatment, and patient attitudes. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(1):1420–1433. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tremolada M, Tasso G, Bonichini S, et al. Pain coping strategies in pediatric patients newly diagnosed with leukaemia compared with healthy peers. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2022;31:e13575. doi: 10.1111/ecc.13575 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kong H, Liu Y, Wu K, Cui S, Bai J, Fan X. Pain and self-management status among Chinese patients with cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pain Manag Nurs. 2021;9(4):1–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bair MJ, Robinson RL, Katon W, Kroenke K. Depression and pain comorbidity: a literature review. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(20):2433–2445. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.20.2433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Michaelides A, Zis P. Depression, anxiety and acute pain: links and management challenges. Postgrad Med. 2019;131(7):438–444. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2019.1663705 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Caraceni A, Shkodra M. Cancer pain assessment and classification. Cancers. 2019;11(4):510–523. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040510 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lopez-Rodriguez MM, Fernández-Millan A, Ruiz-Fernández MD, Dobarrio-Sanz I, Fernández-Medina IM. New technologies to improve pain, anxiety and depression in children and adolescents with cancer: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(10):3563–3576. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103563 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Galyamina AG, Kovalenko IL, Smagin DA, Kudryavtseva NN. Interaction of depression and anxiety in the development of mixed anxiety/depression disorder. experimental studies of the mechanisms of comorbidity (review). Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2017;47(6):699–712. doi: 10.1007/s11055-017-0458-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Khan AAM, Islam MR, Sumon MA, Alam MJ, Hasan ATMK. Prospective outcomes of adolescent and young adult (AYA) patients received treatment from a tertiary cancer hospital in Bangladesh. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:144–145. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz434.014 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cheville AL, Moynihan T, Herrin J, Loprinzi C, Kroenke K. Effect of collaborative telerehabilitation on functional impairment and pain among patients with advanced-stage cancer: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5(5):644–652. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bair MJ, Robinson RL, Eckert GJ, Stang PE, Croghan TW, Kroenke K. Impact of pain on depression treatment response in primary care. Psychosom Med. 2004;66(1):17–22. doi: 10.1097/01.PSY.0000106883.94059.C5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Borsboom D. A network theory of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):5–13. doi: 10.1002/wps.20375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cramer AOJ, Waldorp LJ, van der Maas HLJ, Borsboom D. Complex realities require complex theories: refining and extending the network approach to mental disorders. Behav Brain Sci. 2010;33(2–3):178–193. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X10000920 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Epskamp S, Borsboom D, Fried EI. Estimating psychological networks and their accuracy: a tutorial paper. Behav Res Methods. 2018;50(1):195–212. doi: 10.3758/s13428-017-0862-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Lowe B. The patient health questionnaire somatic, anxiety, and depressive symptom scales: a systematic review. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2010;32(4):345–359. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.03.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chen M, Sheng L, Qu S. Diagnostic test of screening depressive disorder in general hospital with the patient health questionnaire (in Chinese). Chin Ment Health. 2015;29(4):241–245. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sun H, Yang Y, Zhang J, et al. Fear of cancer recurrence, anxiety and depressive symptoms in adolescent and young adult cancer patients. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019;15:857–865. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S202432 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Lowe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(10):1092–1097. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zheng Q. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of generalized anxiety disorder 7-item (GAD-7) scale in screening anxiety disorder in outpatients from traditional Chinese internal department (in Chinese). Chin Ment Health. 2013;27(3):163–168. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Melzack R. The short-form McGill pain questionnaire. Pain. 1987;30(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(87)91074-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Peng L, Zhang JY. Applicability of the Chinese version of short form-McGill pain questionaire among patients with sciatica disease caused by lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion [in Chinese]. Chin J Rehabil Med. 2013;28(11):1035–1040. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hajian-Tilaki K. Sample size estimation in epidemiologic studies. Caspian J Intern Med. 2011;2(4):289–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Team RC. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Available from: https://www.r-project.org/. Accessed August 19, 2022.
- 39.Beard C, Millner AJ, Forgeard MJ, et al. Network analysis of depression and anxiety symptom relationships in a psychiatric sample. Psychol Med. 2016;46(16):3359–3369. doi: 10.1017/S0033291716002300 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Epskamp S, Cramer AO, Waldorp LJ, Schmittmann VD, Borsboom D. qgraph: network visualizations of relationships in psychometric data. J Stat Softw. 2012;48(4):1–18. doi: 10.18637/jss.v048.i04 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bringmann LF, Elmer T, Epskamp S, et al. What do centrality measures measure in psychological networks? J Abnorm Psychol. 2019;128(8):892. doi: 10.1037/abn0000446 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mullarkey MC, Marchetti I, Beevers CG. Using network analysis to identify central symptoms of adolescent depression. J Clin Child Adolesc. 2019;48(4):656–668. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2018.1437735 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jones PJ, Ma R, McNally RJ. Bridge centrality: a network approach to understanding comorbidity. Multivariate Behav Res. 2019;56:1–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Garabiles MR, Lao CK, Xiong Y, Hall BJ. Exploring comorbidity between anxiety and depression among migrant Filipino domestic workers: a network approach. J Affect Disord. 2019;250:85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.02.062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tanna V, Cunningham SJ, Simon P, et al. Pain and intolerance of uncertainty among adolescent and young adult cancer survivors. J Pain. 2021;22(5):611. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2021.03.132 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mohile SG, Heckler C, Fan L, et al. Age-related differences in symptoms and their interference with quality of life in 903 cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy. J Geriatr Oncol. 2011;2(4):225–232. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2011.08.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. National comorbidity survey R: the epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). JAMA. 2003;289(23):3095–3105. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.23.3095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Park SC, Kim D. The centrality of depression and anxiety symptoms in major depressive disorder determined using a network analysis. J Affect Disord. 2020;271:19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.03.078 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rouquette A, Pingault JB, Fried EI, et al. Emotional and behavioral symptom network structure in elementary school girls and association with anxiety disorders and depression in adolescence and early adulthood: a network analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75(11):1173–1181. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yang Y, Sun H, Liu T, et al. Factors associated with fear of progression in Chinese cancer patients: sociodemographic, clinical and psychological variables. J Psychosom Res. 2018;114:18–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2018.09.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bui E, Fava M. From depression to anxiety, and back. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;136(4):341–342. doi: 10.1111/acps.12801 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Niu M, Wang Y, Jia Y, et al. Common and specific abnormalities in cortical thickness in patients with major depressive and bipolar disorders. EBioMedicine. 2017;16:162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.01.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Doan L, Manders T, Wang J. Neuroplasticity underlying the comorbidity of pain and depression. Neural Plast. 2015;2015:504691. doi: 10.1155/2015/504691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Li Z, Aninditha T, Griene B, et al. Burden of cancer pain in developing countries: a narrative literature review. CEOR. 2018;10:675–691. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S181192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Dunietz GL, Swanson LM, Jansen EC, et al. Key insomnia symptoms and incident pain in older adults: direct and mediated pathways through depression and anxiety. Sleep. 2018;41(9):zsy125. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsy125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fried EI, Cramer AOJ. Moving forward: challenges and directions for psychopathological network theory and methodology. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2017;12(6):999–1020. doi: 10.1177/1745691617705892 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]