Abstract
Objective
The aim of this article is to compare the efficacy and safety of doripenem for bacterial infections.
Methods
We included six randomized clinical trials identified from PubMed and Embase up to July 31, 2014. The included trials compared efficacy and safety of doripenem for complicated intra-abdominal infections, complicated urinary tract infection, nosocomial pneumonia, and acute biliary tract infection. The meta-analysis was carried on by the statistical software of Review Manager, version 5.2.
Results
Compared with empirical antimicrobial agents on overall treatment efficacy, doripenem was associated with similar clinical and microbiological treatment success rates (for the clinical evaluable population, odds ratio [OR] = 1.26, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.93–1.69, p = 0.13; for clinical modified intent-to-treatment population, OR = 0.88, 95% CI 0.55–1.41, p = 0.60; for microbiology evaluable population, OR = 1.16, 95% CI 0.90–1.50, p = 0.26; for microbiological modified intent-to-treatment (m-mITT), OR = 0.98, 95% CI 0.81–1.20, p = 0.87). We compared incidence of adverse events and all-cause mortality to analyze treatment safety. The outcomes suggested that doripenem was similar to comparators in terms of incidence of adverse events and all-cause mortality on modified intent-to-treatment population (for incidence of AEs, OR = 1.10, 95% CI 0.90–1.35, p = 0.33; for all-cause mortality, OR = 1.08, 95% CI 0.77–1.51, p = 0.67). In nosocomial pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia treatment, doripenem was not inferior to other antibacterial agents in terms of efficacy and safety.
Conclusion
From this meta-analysis, we can conclude that doripenem is as valuable and well-tolerated than empirical antimicrobial agents for complicated intra-abdominal infections, complicated urinary tract infection, acute biliary tract infection and nosocomial pneumonia treatment.
Keywords: Doripenem, Meta-analysis, Efficacy, Safety, Infection
Introduction
Antibacterial agents of the carbapenem class are assuming a more important role in the treatment of severe bacterial infections. Doripenem, a new parenteral carbapenem, has been recognized as a valuable addition to the currently available carbapenems in the treatment of serious infections. Doripenem has a broad spectrum of in vitro activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including multi-drug resistant bacteria that have been a significant cause of morbidity and mortality.1 In the USA, doripenem is the most recent US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved carbapenem for the treatment of patients with complicated intra-abdominal infection (cIAI), complicated urinary tract infection (cUTI) and pyelonephritis. Doripenem is approved in Europe and in other countries for the treatment of patients with cIAI, cUTI and nosocomial pneumonia (NP), including ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).2 However, a statement about doripenem was issued from the FDA, in May 2012, stating that the clinical trial for VAP treatment with doripenem had been terminated early due to significant safety concerns. The trial initiated by Kollef et al. was aimed at evaluating the effects of doripenem on treatment of patients with VAP, demonstrated excess mortality and a numerically poorer clinical cure rate among doripenem-treated subjects compared to those treated with imipenem–cilastatin.3, 4 In March 2014, the FDA issued further safety information stating the approved doripenem label changes for highlighting the increased risk of death for ventilator patients with pneumonia.5 By now, several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have assessed doripenem efficacy and safety compared to some empirical antimicrobial agents, including three trials evaluating NP and VAP treatment. So far, however, there is no systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the efficacy and safety of doripenem and comparators for treating bacterial infections. Although a meta-analysis was published by Jenkins in 2009, it was limited to patients with Pseudomonas infections enrolled in four clinical trials.6 Therefore, we performed a comprehensive and updated meta-analysis to provide better evidence of the efficacy and safety doripenem on treating bacterial infections, especially focused on treatment efficacy and safety for NP and VAP patients.
Methods
Eligibility criteria
To be eligible a study would have to be designed as a RCT that directly compared efficacy or safety of doripenem with any other active antimicrobial agents for treating bacterial infections.
Retrospective studies were excluded, as well as those focused on in vitro susceptibility testing, experimental animal studies or pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic evaluations.
Outcome measures
The primary outcome measure was clinical treatment efficacy on clinical evaluable (CE) population and clinical modified intent-to-treatment (c-mITT) population. The secondary outcomes were microbiological treatment success rates on microbiology evaluable (ME) population and microbiological modified intent-to-treatment (m-mITT) population. At last, AEs and all-cause mortality on modified intent-to-treatment (m-ITT) population were assessed.
The details and definitions for study populations were demonstrated as followed: (i) mITT: patients who received at least one dose of study drugs; (ii) c-mITT: patients who met minimum disease criteria on mITT population; (iii) CE: patients who did not receive confounding doses of prior or concomitant study drugs, received sufficient therapeutic doses, and had a test-of-cure (TOC) efficacy assessment per protocol on c-mITT population. (iv) m-mITT: patients who had at least one baseline isolate on c-mITT population; and (vi) ME: patients who had at least one baseline isolate susceptible to each regimen and had a microbiologic response assigned on CE population.
Information sources and literature search
Publications at PubMed and Embase data sets up to July 31, 2014 were reviewed with the search strategies “doripenem” or “Doribax” and “efficacy”, “safety”, “infection” or “randomized controlled trials”.
Study selection and data extraction
Two reviewers (Qu and Hu) searched and examined the publications independently. The included studies were examined separately according to the eligibility criteria described above. Evaluation of the methodological quality of the RCTs was performed by two reviewers independently according to the Jadad scoring system.7 The high quality trials were awarded three or more points with a maximum of five points. When disagreement occurred, a third author (Zhou) resolved the problem in time. The following data were extracted from every included study: year of publication, type of infection, patient population, drug information, clinical and microbiological outcomes of treatment, incidence of AEs, and all-cause mortality.
Statistical analysis
The software Review Manager, version 5.2 was used to conduct the statistical analyses. Heterogeneity was evaluated with Q statistic generated from the χ2 test and inconsistency with I2 measure.8 Heterogeneity was considered significant when p-value was less than 0.10 or I2 more than 50%. A Mantel–Haenszel fixed-effect model (FEM) with pooled odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) was used for outcome analyses when heterogeneity was not significant. When heterogeneity was obvious DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model (REM) was used for outcome analysis.
Results
Study selection outcomes
The flow diagram in Fig. 1 shows the details of the study selection process. The studies were selected with the search programs and inclusion criteria previously determined. In total, six trials,3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 which fulfilled all inclusion criteria, were included in this meta-analysis.
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram for selection of the RCTs reviewed.
Study characteristics
Table 1 shows the following characteristics of the included RCTs: study design, type of infection, number of patients (mITT), mean age, drug information, and Jadad score. The meta-analysis was composed of six RCTs for cIAI, cUTI, acute biliary tract infection (aBTI) and NP, including VAP. All included studies were RCTs conducted between 2008 and 2014. Five of six trials were multinational studies. The total sample of the included trials was 2542 subjects and all trials were conducted exclusively in adults. The meta-analysis included comparisons of doripenem with imipenem–cilastatin, meropenem, levofloxacin, and piperacillin/tazobactam. Subjects in doripenem group received doripenem at doses of 1 g or 0.5 g every 8 h. The mean Jadad score of the six publication RCTs was 3.5 (rang 2–5). The higher the Jadad score the better the quality of the meta-analysis.
Table 1.
The main characteristic of included trials.
| Study ID | Study design | Type of infection | Number of patients |
Age(years),mean(SD) |
Drug information |
Study quality | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expe | Comp | Expe | Comp | Expe | Expe | ||||
| Chastre2008 | Multicentre, randomized, open label, phase 3 | VAP | 262 | 263 | 50.7 (19.6) | 50.3 (19.0) | Doripenem 0.5 g q8 h via a 4-h IV | Imipenem 0.5 g q6 h via a 30 min IV or 1 g q8 h via a 60-min IV | 2 |
| Kollef2012 | Multicentre, randomized, double blind, phase 3 | VAP | 115 | 112 | 57.5(16.5) | 54.6 (18.5) | Doripenem 1 g q8 h via a 4-h IV | Imipenem/cilastatin 1 g q8 h via a 1-h IV | 5 |
| Lucasti2008 | Multicentre, randomized, double blind, phase 3 | cIAI | 235 | 236 | 46.9 (18.1) | 46.4 (17.5) | Doripenem 0.5 g q8 h IV over 1 h | Meropenem 1 g q8 h via 20-mL IV bolus over 3–5 min | 5 |
| Naber2009 | Multicentre, randomized, double blind, phase 3 | cUTI | 377 | 376 | 51.2 (21.1) | 51.1 (21.0) | Doripenem 0.5 g, q8 h, i.v.gtt | Levofloxacin 0.25 g, qd, i.v.gtt | 5 |
| Neto2008 | Multicentre, randomized, open label, phase 3 | NP | 223 | 221 | 57.5 (19.2) | 59.3(18.9) | Doripenem 0.5 g, q8 h, i.v.gtt over 1 h | Piperacillin/tazobactam 4.5 g, q6 h via a 30 min IV | 2 |
| Tazuma2014 | Randomized, open label | aBTI | 58 | 64 | 74 (11.5) | 73 (12.8) | Doripenem 0.5 g, q8 h, i.v.gtt over 30 min or 1 h | Imipenem/cilastatin 0.5 g, q8 h, i.v.gtt over 30 min or 1 h | 2 |
Expe, experimental group; Comp, comparator group; VAP, ventilator-associated pneumonia; cIAI, complicated intra-abdominal infection; cUTI, complicated urinary tract infection; NP, nosocomial pneumonia; aBTI, acute biliary tract infection; IV, intravenous injection; i.v.gtt, intravenous drip; q8 h, every 8 h.
Clinical and microbiological treatment success
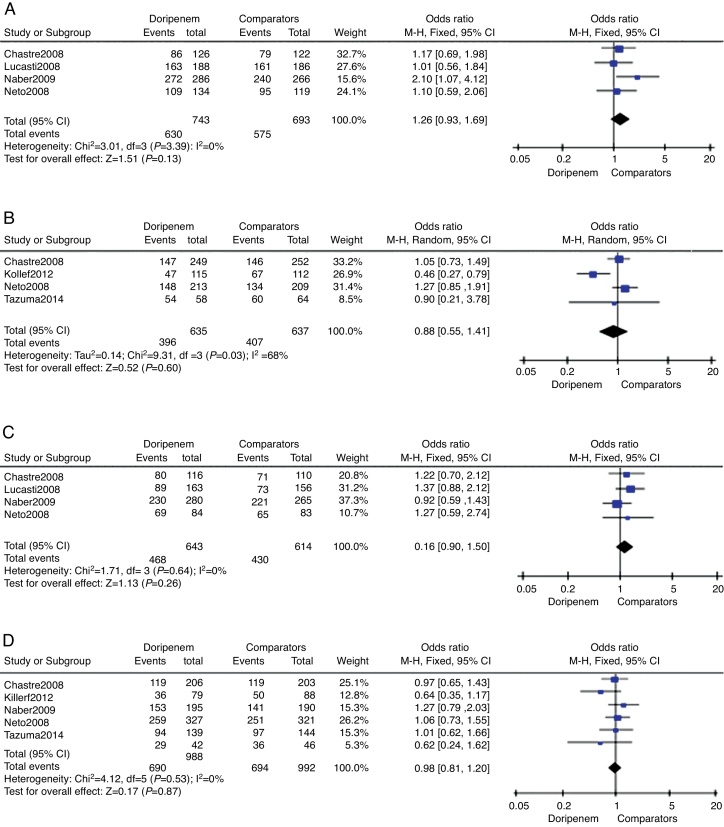
Clinical treatment success rate on the CE sample was provided in four trials totaling 1427 subjects. The doripenem group was associated with higher rate of clinical treatment success, but the difference was not significant (OR = 1.26, 95% CI 0.93–1.69, p = 0.13, Fig. 2A). Data on c-mITT population were also provided in four trials with 1272 subjects. In contrary, the clinical treatment success rate of doripenem group was lower than comparator group (OR = 0.88, 95% CI 0.55–1.41, p = 0.60, Fig. 2B), but again the difference was not significant. The overall meta-analysis of clinical treatment success suggested that doripenem was as effective as comparators for treating bacterial infections.
Fig. 2.
The meta-analysis of doripenem and comparator groups on treatment efficacy.
Four of the six trials reported microbiological treatment success on ME sample, and all trials provided data on c-mITT sample. There were 1257 subjects and 1980 subjects on ME and c-mITT samples, respectively. In both comparisons, doripenem was as effective as comparators (for ME population, OR = 1.16, 95% CI 0.90–1.50, p = 0.26, Fig. 2C; for m-mITT population, OR = 0.98, 95% CI 0.81–1.20, p = 0.87, Fig. 2D).
Outcomes of treatment safety
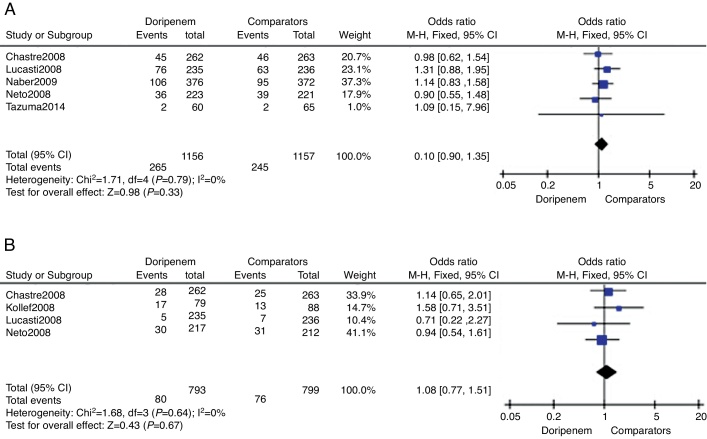
Treatment safety was assessed by meta-analysis in terms of AEs incidence and all-cause mortality risk. Five trials provided relevant AEs outcomes. According to the data of meta-analysis, doripenem was numerically higher than comparators on incidence of AEs, but the difference was not significant (3313 subjects, OR = 1.10, 95% CI 0.90–1.35, p = 0.33, Fig. 3A). All-cause mortality during the study period was available in four of the included trials. Although numerically higher mortality in the doripenem groups could be seen, there was no significant difference between doripenem and comparator group (1592 subjects, OR = 1.08, 95% CI 0.77–1.51, p = 0.67, Fig. 3B).
Fig. 3.
The meta-analysis of doripenem and comparator groups on treatment safety.
Evaluation of efficacy and safety for NP and VAP treatment
There were three trials 3, 10, 13 comparing doripenem with comparators for pneumonia treatment, two trials for VAP and one for NP. The comparator drugs were piperacillin/tazobactam and imipenem–cilastatin. The meta-analysis of outcomes shown in Table 2 demonstrates that the doripenem group was associated with higher rates of treatment success on CE and ME sample. In contrast, doripenem group was associated with lower rates on c-mITT and m-mITT samples. However, the differences of clinical and microbiological treatment successes were not significant.
Table 2.
The outcomes of meta-analysis for pneumonia treatment.
| Population | No. patients | OR | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE | 353 | 1.1 | 0.59–2.06 | 0.76 |
| c-mITT | 1150 | 0.88 | 0.52–1.49 | 0.63 |
| ME | 393 | 1.24 | 0.79–1.94 | 0.35 |
| m-ITT | 859 | 0.9 | 0.68–1.18 | 0.45 |
| AEs | 969 | 0.94 | 0.67–1.31 | 0.72 |
| All-cause mortality | 1121 | 1.12 | 0.79–1.59 | 0.53 |
Regarding safety, although numerically higher mortality in the doripenem group was observed, there was no significant difference between the doripenem and comparator groups. Drug-related AEs in the doripenem group were numerically lower than in the comparator groups without significance. The outcomes of meta-analysis for pneumonia treatment showed that doripenem was as effective as comparator drugs, with non-significant higher occurrence of AEs and all-cause mortality.
Discussion
As far as we know, in contrast to the earlier doripenem meta-analysis which only assessed patients infected by Pseudomonas, this is the first meta-analysis assessing the efficacy and safety of doripenem treatment for overall bacterial infections.6 Furthermore, we focused on the efficacy and safety of doripenem on NP treatment to confirm the FDA statement. The results of this current meta-analysis demonstrate that doripenem is as effective as comparators for bacterial infections, including cIAI, cUTI, aBTI and NP. In terms of safety, although the incidence of AEs and all-cause mortality with doripenem was slight higher than comparators, the difference was not significant. Regarding NP and VAP, although doripenem has not yet been approved by the FDA, the outcomes of this meta-analysis show that doripenem is non-inferior to other antibacterial agents in terms of efficacy and safety. In addition, a recent study has demonstrated a significantly shorter length of hospital stay and time on mechanical ventilation of patients with VAP treated with doripenem compared to imipenem. This study suggests that doripenem use may be beneficial both economically and clinically to patients.14
The current meta-analysis suggests that there is no significant difference between doripenem and comparator drugs on treatment efficacy and safety, but doripenem remains a valuable alternative as it has several advantages. First, a total daily dose of 1.5 g of doripenem is equivalent to 3 g of meropenem or 2–3 g of imipenem in terms of clinical and microbiological cure rates. Doripenem does not require the addition of cilastatin, and has a lower seizure potential compared to imipenem. Furthermore, the plasma maximum concentration of doripenem is higher than that achieved by imipenem and similar to that of meropenem.15 Second, in vitro studies have shown that doripenem has great activity against Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas and has lower potential to select for decreased drug susceptibility compared with imipenem–cilastatin. Doripenem and meropenem were the most active compounds against these isolates, both better than imipenem.16 Our findings support the excellent sensitivity to Gram-negative bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae. Doripenem therapy is associated with favorable microbiological treatment success in great majority of subjects with baseline isolates. Third, concerning treatment safety, in general, doripenem is well tolerated. The most common adverse reactions reported in RCTs are nausea, diarrhea, headache, rash, and phlebitis. Previous carbapenems have been considered to induce seizures primarily via inhibition of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding. By contrast, doripenem has low affinity to the GABA receptor, resulting in low potential for seizure induction.17
The finding of our meta-analysis has several limitations: first, we had no access to unpublished data. Although we have included conference papers and clinical trial information, the meta-analysis still lacks unpublished data. Second, the small number of subjects becomes a limitation of this meta-analysis. Third, there was heterogeneity in RCTs such as patients, comparator drugs, and subjective diversity of clinicians.
In conclusion, doripenem is a valuable and well-tolerated drug that is as effective as empirical antimicrobial agents for treating cIAI, cUTI, aBTI, and NP. It can play an important role for patients with serious nosocomial bacterial infections in the setting of multidrug resistant pathogens, such as Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas. However, to obtain more definite conclusions, further investigation on doripenem treatment is warranted.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
Qu had the original idea for the research, drafted the research strategy, wrote the manuscript, and performed all statistical analyses. Hu searched the research articles and made all the figures and tables. Zhou advised and commented on the statistical analysis and reviewed the results.
All authors have revised the final manuscript.
References
- 1.Kaniga K., Flamm R., Tong S.Y., Lee M., Friedland I., Redman R. Worldwide experience with the use of doripenem against extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing and ciprofloxacin-resistant Enterobacteriacea: analysis of six phase 3 clinical studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:2119–2124. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01450-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rice D.A., Kaniga K., Lee M., Redman R. Activity of doripenem versus comparators in subjects with baseline bacteraemia in six pooled phase 3 clinical trials. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013;41:388–392. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kollef M.H., Chastre J., Clavel M., et al. A randomized trial of 7-day doripenem versus 10-day imipenem–cilastatin for ventilator-associated pneumonia. Crit Care. 2012;16:R218. doi: 10.1186/cc11862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Statement on recently terminated clinical trial with Doribax (doripenem) (January 5, 2012). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm285883.htm.
- 5.US Food and Drug Administration. FDA drug safety communication: FDA approves label changes for antibacterial Dorbax (doripenem) describing increased risk of death for ventilator patients with pneumonia (March 6, 2014). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm387971.htm.
- 6.Jenkins S.G., Fisher A.C., Peterson J.A., Nicholson S.C., Kaniga K. Meta-analysis of doripenem vs comparators in patients with pseudomonas infections enrolled in four phase III efficacy and safety clinical trials. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25:3029–3036. doi: 10.1185/03007990903396790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jadad A.R., Moore R.A., Carroll D., et al. Assessing the quality of report of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary. Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(95)00134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Higgins J.P., Thompson S.G., Deeks J.J., Altman D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tazuma S., Igarashi Y., Inui K., Ohara H., Tsuyuguchi T., Ryozawa S. Clinical efficacy of intravenous doripenem in patients with acute biliary tract infection: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial with imipenem/cilastatin as comparator. J Gastroenterol. 2014 doi: 10.1007/s00535-014-0960-0. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rea-Neto A., Niederman M., Lobo S.M., et al. Efficacy and safety of doripenem versus piperacillin/tazobactam in nosocomial pneumonia: a randomized, open-label, multicenter study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24:2113–2126. doi: 10.1185/03007990802179255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lucasti C., Jasovich A., Umeh O., Jiang J., Kaniga K., Friediand I. Efficacy and tolerability of IV doripenem versus meropenem in adults with complicated intra-abdominal infection: a phase III, prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, noninferiority study. Clin Ther. 2008;30:868–883. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Naber K.G., Llorens L., Kaniga K., Kotey P., Hedrich D., Redman R. Intravenous doripenem at 500 milligrams versus levofloxacin at 250 milligrams, with an option to switch to oral therapy, for treatment of complicated lower urinary tract infection and pyelonephritis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:3782–3792. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00837-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chastre J., Wunderink R., Prokocimer P., Lee M., Kaniga K., Friedland I. Efficacy and safety of intravenous infusion of doripenem versus imipenem in ventilator-associated pneumonia: a multicenter, randomized study. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:1089–1096. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181691b99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lo T.S., Borchardt S.M., Welch J.M., Rohrich M.A., Alonto A.M., Alonto A.V. Doripenem in hospital infections: a focus on nosocomial pneumonia, complicated intra-abdominal infections, and complicated urinary tract infections. Infect Drug Resist. 2009;2:41–49. doi: 10.2147/idr.s4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Walsh F. Doripenem: a new carbapenem antibiotic a review of comparative antimicrobial and bactericidal activities. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007;3:789–794. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mendes R.E., Rhomberg P.R., Bell J.M., Turnidge J.D., Sader H.S. Doripenem activity tested against a global collection of Enterobacteriaceae, including isolates resistant to other extended-spectrum agents. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009;63:415–425. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Horiuchi M., Kimura M., Tokumura M., Hasebe N., Arai T., Abe K. Absence of convulsive liability of doripenem, a new carbapenem antibiotic, in comparison with beta-lactam antibiotics. Toxicology. 2006;222:114–124. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]