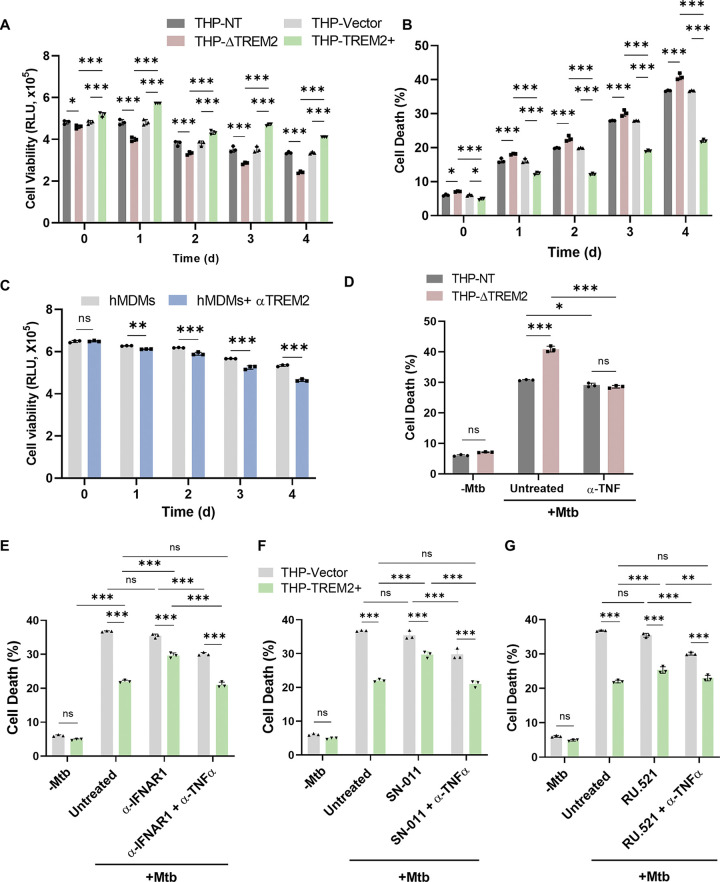
FIG 4.
TREM2 regulates cell death through a mechanism dependent on type I IFN-mediated inhibition of TNF-α production. (A) THP-NT, THP-ΔTREM2, THP-Vector, and THP-TREM2+ macrophages were infected with M. tuberculosis, and cell viability was assessed using CellTiter-Glo (measured as relative luminescence units [RLU]). (B) THP-NT, THP-ΔTREM2, THP-Vector, and THP-TREM2+ macrophages were infected with M. tuberculosis, stained with FVS780 at the indicated time points, and analyzed using flow cytometry to measure the levels of cell death. (C) hMDMs mock treated or pretreated with anti-TREM2 antibody were infected with M. tuberculosis and assessed for cell viability using CellTiter-Glo. (D) THP-NT and THP-ΔTREM2 macrophages were mock treated or pretreated with 100 ng/mL anti-TNF-α antibody for 2 h. Cells were then infected with M. tuberculosis, and cell viability was quantified at day 4 postinfection by flow cytometry using FVS780 stain (12). THP-Vector, and THP-TREM2+ macrophages were mock treated or pretreated with (E) anti-IFNAR1 (2.5 μg/mL), (F) SN-011 (STING inhibitor; 1 μM), or (G) RU.521 (cGAS inhibitor; 10 μg/mL) for 2 h and 6 h (in the case of SN-011). Cells were then mock treated or pretreated with anti-TNF-α (100 ng/mL) for 2 h, followed by M. tuberculosis infection. The percentage of macrophage death was assessed at day 4 postinfection by staining with FVS780. An MOI of 10 was used for all infections in this figure. Error bars in this figure represent the mean ± SD from three independent biological replicates.