FIGURE 4.
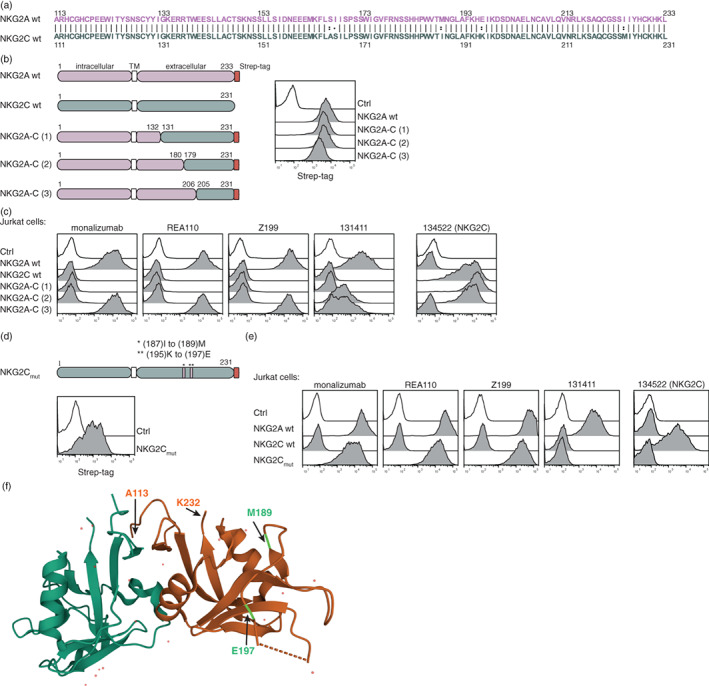
Identification of the epitopes of NKG2A antibodies. (a) Sequence alignment of NKG2A (A113 to L233) and NKG2C (A111 to L231). (b) Schematic representations of wild‐type NKG2A and NKG2C, as well as chimeric constructs of NKG2A‐C (#1, #2, #3), are depicted. Cell surface expression of the molecules was determined by using a Strep‐tag antibody. (c) Jurkat cells expressing the indicated molecules were incubated with the following NKG2A antibodies monalizumab, REA110, Z199, 131411, and a NKG2C antibody (134522), respectively (open histogram: the indicated antibodies on control cells). (d) Schematic representation of a mutated NKG2C construct (NKG2Cmut) and its cell surface expression detected with a Strep‐tag antibody. (e) Flow cytometric analysis of the depicted antibodies on cells expressing the NKG2Cmut molecule (open histogram: the indicated antibodies on control cells). (f) Crystal structure of NKG2A (orange) and CD94 (green) (PDB ID code 3BDW). Positions A113, M189 (light green), E197 (light green) and K232 are highlighted with arrows [35]. One representative experiment is shown (b–e).
