Abstract
Leishmaniasis is an infectious disease caused by protozoa of the genus Leishmania transmitted by insects of the genus Lutzomyia sp. or Phlebotomus sp. The main syndromes are cutaneous leishmaniasis, mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar) and post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis. This article reviews kidney involvement in cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis, highlighting the aspects of their pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, histopathological findings, outcome and treatment.
Keywords: Visceral leishmaniasis, American cutaneous leishmaniasis, Kala-azar, Kidney disease
Introduction
Leishmaniasis is an infectious disease caused by protozoa of the genus Leishmania transmitted by insects of the genus Lutzomyia sp. or Phlebotomus sp.1 There are more than 20 species of leishmanias causing clinical manifestations in humans, and the main syndromes are cutaneous leishmaniasis, mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar), and post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis.2 This article reviews kidney involvement in cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Kidney involvement in cutaneous leishmaniasis
There have been few studies showing renal dysfunction in American cutaneous leishmaniasis (ACL), which is, in some cases, associated with the use of specific treatment with pentavalent antimonial drugs.3, 4
In a recent study performed in our region, a total of 73 patients admitted with ACL were evaluated. Acute kidney injury (AKI) was observed in 17 cases (23.2%), and oliguria was seen in one case. Mean value of maximum serum creatinine (SCr) levels during hospital stay was 1.6 ± 0.6 mg/dL. Risk factors for AKI were advanced age, longer time between symptom onset and hospital admission and longer hospital stay. Complete renal function recovery was observed in 11 cases (64.7%) at the time of hospital discharge.5 This same study found urinary abnormalities, including proteinuria (4.1%), hematuria (4.1%) and leukocyturia (5.4%). Hypokalemia was found in 12.3% of cases.5 Proteinuria and AKI had been previously reported in other studies.6, 7
Decreased urinary concentrating ability, with no reduction of glomerular filtration rate (GFR), was demonstrated by Veiga et al.,8 who studied an animal model of leishmaniasis treated with high doses of meglumine antimoniate. This abnormality in urine concentration results from the action of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and also by a direct action of the drug in tubular cells.8 High doses of antimonial drugs also cause a reduction in GFR.
ACL is highly prevalent in the state of Ceará, Northeast of Brazil. Low treatment adherence favors the development of the mucocutaneous forms, which requires higher doses of antimonial drugs for longer periods, which, in turn, increases its toxicity even further. A recent study was performed in this region in order to investigate renal abnormalities in patients with ACL. Oliveira et al.9 studied 37 patients with confirmed diagnosis of ACL, performed urinary concentration and acidification tests and also investigated the expression of urinary exosomes in the urine of these patients.3 Urinary concentration deficit was found in 77% of cases. The expression of aquaporin was significantly reduced, while NKCC2 was increased, in comparison to that in a control group. Urinary acidification deficit was less frequent (40.5%). The expression of NHE3, H+-ATPase and pendrin was significantly higher among patients than in controls.3 In this same cohort, a urinary concentration deficit was shown in 27 cases (77%) before treatment with Glucantime®, while after treatment it was observed in 31 patients (88%) (p = 0.344). It is then possible that ACL can cause urinary concentration deficit and specific treatments do not decrease this defect, although it does not cause significant renal function impairment.
Combined defects (concentration and acidification) were seen in 12 patients. Comparing the patients with and without tubular dysfunction, there were no differences regarding age, gender, time of disease, and number of cutaneous lesions. There was no significant abnormality regarding excretion fraction of sodium, potassium, calcium and phosphate. There was a significant difference in serum magnesium concentrations between patients with and without acidification deficit (2.15 ± 0.06 vs. 2.33 ± 0.04, p = 0.02). No patient with urinary concentration or acidification deficit had albumin/creatinine ratio >30 mg/g3.
Other infectious diseases with predominant involvement of skin and nerves, such as leprosy, can also lead to glomerular dysfunction. Oliveira et al.,9 in a prospective study with 59 patients with leprosy, showed decreased GFR in 50% of cases when considering GFR < 80 mL/min/1.73 m2, and in 5% when considering GFR < 50 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Microalbuminuria is a known marker of glomerular dysfunction in diabetes mellitus10 and also in cardiovascular diseases.11, 12 Microalbuminuria higher than 30 mg/g creatinine was observed in 35% of patients with ACL followed in a health center in the state of Ceará, Brazil, before specific treatment, and in only 8% of patients after treatment,3 suggesting the presence of incipient glomerular lesion induced by ACL itself, without concomitant GFR decrease.
Urinary exosomes were also found to be altered in ACL.3 Some studies have shown that aquaporin-2 (AQP2) is excreted in urine in the form of vesicles. Its amount correlates with circulating levels, and is used in studies to investigate body water balance.13, 14 In the cohort of patients with ACL studied by Oliveira et al.,3 an increased percentage of patients with urine concentration deficit was observed and this was associated with lower expression of AQP2.3 The increase in the expression of NKCC2 can occur as a compensatory mechanism. Abnormalities in the transporters involved in acid–base regulation were also observed, including an increased expression of NHE3 (proximal tubule), H-ATPase and pendrin (distal tubule) in patients with ACL, which could explain the urinary acidification deficit.3
Pentavalent antimonial drugs are rapidly eliminated through the kidneys,15 so their use should be avoided in patients with renal dysfunction, due to cardiotoxicity and renal function worsening. Urinary concentrating defect has also been described and the heavy metal used in antimonial composition is the main factor responsible for the toxicity.16 AKI may be due to massive deposition of immune complexes formed after Leishmania destruction by antimonial drugs, a phenomenon similar to that of Herxheimer reaction.17 Sampaio et al.18 evaluated 11 patients with ACL who received a double dose of antimonials (40 mg Sbv/kg/day for 30 days), and observed that one patient developed AKI. Eight patients showed a decrease in GFR after 30 days of treatment. They also observed distal and proximal tubular dysfunction, evidenced as a decrease in urinary concentration ability and increased sodium excretion fraction.
Rarely, treatment with meglumine antimoniate can cause AKI due to interstitial nephritis.16 At low doses and for a short period, pentavalent antimonial shows low renal toxicity. In ACL treatment, however, it is many times necessary to use higher doses of pentavalent antimonial, which increases toxicity.
Visceral leishmaniasis
Visceral leishmaniasis is a chronic, lethal, parasitic disease, caused by the Leishmania parasite, an intracellular protozoan. A large spectrum of clinical manifestations accompanies the Leishmania attack on reticuloendothelial tissues – liver, spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and the digestive system. Symptoms range from irregular and recurrent fever to pancytopenia, hemorrhagic spells, and liver and spleen enlargement.19
Kidney involvement in chronic leishmaniasis is frequent and associated with increased mortality. It is endemic in southern Europe and in tropical and sub-tropical areas of the globe, with a worldwide incidence of approximately 0.5 million cases/year.20 When untreated, its mortality rate can reach 95%. Among the so-called tropical diseases, kala-azar is one of the WHO's priorities. Endemic in Brazil, its agent is Leishmania chagasi. Humans are infected through the vector insect, Lutzomyia longipalpis.21 Kala-azar diagnosis is confirmed by demonstrating the presence of the parasite in tissues using Giemsa stain, in addition to detection of parasite antigen K-39.19
Kidney involvement in visceral leishmaniasis
Patients presenting with chronic kala-azar can have mild proteinuria, microscopic hematuria and leukocyturia. Hypoalbuminemia, hypergammaglobulinemia and increased plasma levels of both IgG and b2-microglobulins were found in a group of 55 patients with visceral leishmaniasis.22 Increased albumin excretion has been observed in 44% of patients. Proteinuria consisted predominantly of low molecular weight protein fractions that migrated with alpha1, alpha2, beta, and especially gammaglobulins. Urinary b2-microglobulin excretion was elevated in all patients. Microalbuminuria was detected in more than 40% of patients with visceral leishmaniasis, even in those with normal creatinine levels.23 Interstitial nephritis with glomerular changes can be seen. A mesangial proliferative lesion is often found, yet a membranoproliferative lesion is not rare.19 Additionally, amyloid deposits can occur in chronic disease. Yet, renal involvement is usually mild and transitory. Loss of kidney function and urinary sediment changes have been reported in visceral leishmaniasis. Prospective studies with kala-azar patients have demonstrated hematuria, mild to moderate proteinuria, and increased urine leukocytes in over 50% of cases.24 A large, retrospective study demonstrated that more than 11% of patients with chronic Leishmania disease had decreased filtration rate at hospital admission – with anti-parasitic therapy, changes disappear. Table 1 depicts known kidney involvement in kala-azar. Interestingly, hypoalbuminemia, polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia and leukopenia usually occur in chronic leishmaniasis.19
Table 1.
Reports of kidney involvement in visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar).
| Reference | Number of cases | Age (years) | Sex | Immunosuppression | Kidney biopsy | Clinical presentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duarte et al. (1983)37 | 21 | No | Interstitial nephritis | |||
| Dutra et al. (1985)38 | 7 | No | Diffuse proliferative lesion | AKI Proteinuria |
||
| Caravaca et al. (1991)39 | 1 | 33 | M | No | Interstitial nephritis | AKI |
| Leblond et al. (1994)40 | 1 | 16 | F | No | Collapsing segmental and focal glomerular sclerosis | AKI Proteinuria |
| Chaigne et al. (2004)41 | 1 | 20 | M | No | Necrotizing segmental and focal glomerular sclerosis | AKI Nephrotic syndrome |
| Kumar et al. (2004)33 | 1 | 29 | F | No | Membranoproliferative lesion | Fever |
| Navarro et al. (2006)34 | 1 | 28 | M | HIV | AA amyloid glomerular deposits, no mesangial hyperplasia | Nephrotic syndrome AKI |
| Efstratiadis et al. (2006)42 | 1 | 65 | M | No | Chronic tubulo-interstitial nephritis, arteriolosclerosis | AKI |
| Lima Verde et al. (2007)32 | 50 | 18–55 | M (83%) | No | No | AKI (28%) Concentration defect (68%) Acidification defect (64%) |
| Alex et al. (2008)43 | 1 | 32 | F | HIV | Tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis, mononuclear infiltrate, mesangial hyperplasia, peritubular Leishmania-loaded histiocytes | Nephrotic syndrome |
| Daher et al. (2008)44 | 57 | 28 ± 18 | M (74%) | No | No | AKI (26%) |
| Dettwiler et al. (2010)45 | 1 | 69 | M | Kidney transplant l | Moderate to severe lymphocyte, histiocyte and plasma cell interstitial infiltrates; Leishmania-loaded macrophages | Acute interstitial nephritis AKI |
| Oliveira et al. (2010)29 | 224 | 15–84 | M (77%) | No | No | AKI (34%) |
| Suankratay et al. (2010)46 | 1 | 37 | M | HIV | Membranoproliferative lesion | Nephritic/nephrotic syndrome |
| Daher et al. (2011)26 | 14 | 18–64 | M (57%) | No | No | Concentration defect (21%) |
M, male; F, female; AKI, acute kidney injury; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
Other less frequent disorders have been described in visceral leishmaniasis, including hormone and electrolyte abnormalities. In a study by Limar Verde et al., of 72 patients with visceral leishmaniasis, plasma ACTH (corticotrophin) was found to be significantly higher among patients in comparison to normal subjects, as well as plasma renin activity. Primary adrenal insufficiency was observed in half of the patients: they showed low aldosterone/renin plasma ratio, low daily urinary aldosterone excretion and low transtubular potassium gradient. In the same study, all patients had normal plasma ADH concentrations, hyponatremia, and high urinary osmolality, and more than half of the patients had low plasma parathyroid hormone and hypomagnesemia. In another study from the same group, of 55 patients with visceral leishmaniasis and 20 normal individuals, hyponatremia and high urinary sodium were detected in all patients, suggesting persistent ADH secretion with no evidence of extracellular volume depletion. Normal plasma ADH levels were observed in kala-azar patients. The syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion could be responsible for these findings.25 Electrolyte disturbances found in patients with visceral leishmaniasis include hyponatremia (94.6%), hypokalemia (26%), hypochloremia (27.2%), hypocalcemia (32%), and hypomagnesemia (41.8%).22 Increased urinary excretion fraction of sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, inorganic phosphate and uric acid was found in one-third of the patients. Urinary excretion fraction of magnesium was high in all patients.22 Urinary concentration and acidification defects were also found in patients with visceral leishmaniasis.26
There are some differences between adults and children with visceral leishmaniasis. The time between symptom onset and beginning of treatment is usually longer in adults (89.5 vs. 48.5 days, p < 0.001). Treatment failure with glucantime is more common in adults (17.6% vs. 8.8%, p = 0.008). AKI associated with visceral leishmaniasis, which was observed in 37% of cases, is more severe in adults. Risk factors for AKI in adults were hypokalemia, leukopenia, chills and amphotericin B use. In children, secondary infections were found to increase the risk for AKI.27
AKI can be found in a significant proportion of patients with visceral leishmaniasis.28, 29 In a study of 146 children with visceral leishmaniasis, AKI was found in 45.9% of cases. Patients in the AKI group were significantly younger, and had jaundice and secondary infections more often than non-AKI patients. The AKI group had significantly lower serum sodium, potassium, and albumin levels, elevated serum globulins and a more prolonged prothrombin time. The risk factors for AKI were secondary infections (OR: 3.65, p = 0.007), serum albumin decrement (OR: 1.672, p = 0.019), and high serum globulin (OR: 1.35, p = 0.029).28 In a study of 224 adults with visceral leishmaniasis, AKI was observed in 33.9% of cases, and the risk factors for AKI were male gender (OR: 2.2; p = 0.03), advanced age (OR: 1.05; p < 0.001), and jaundice (OR: 2.9; p = 0.002).
Table 1 summarizes previous reports on kidney involvement in visceral leishmaniasis.
Pathophysiology
Most parasitic diseases evolve into chronic illness, with fluctuations in antigenemia and host response. There are several possible explanations, such as low natural immune response or the parasite's ability to evade the host immune system attack. It has been demonstrated that development of host resistance is usually dependent upon T-CD4+ cells producing interferon gamma (IFN) – a TH1-type cell. However, a mixed TH1 and TH2 response seems to be involved in extracellular parasite eradication.30 The Leishmania is able to manipulate the host immune system by inducing the production of growth factor b, a macrophage-inhibiting cytokine, and interleukin-10, besides interfering in IFN-gamma signaling, all of which affect cellular immune response and induce polyclonal B-cell activation, which has been associated with kala-azar glomerular disease.30 Antibodies produced in response to infection can be trapped in glomeruli by different mechanisms, such as immune complexes, in situ development of complexes (antibodies linked to previously implanted glomerular antigens), or directly attached to glomerular antigens. Yet, recent studies demonstrated that antibodies alone do not explain the occurrence of proteinuria.30, 31 Macrophages, granulocytes, and natural-killer lymphocytes are all part of host defenses, and participate in the genesis of glomerular lesions through an intricate chain of cytokines and inflammatory mediators, as demonstrated experimentally.30, 31 It is possible that reduced tubular concentration and acidification functions are caused by IgG overload of tubular cells, in patients presenting with major changes in plasma globulin levels.32 A distal tubule acidification defect can occur.
Histopathology
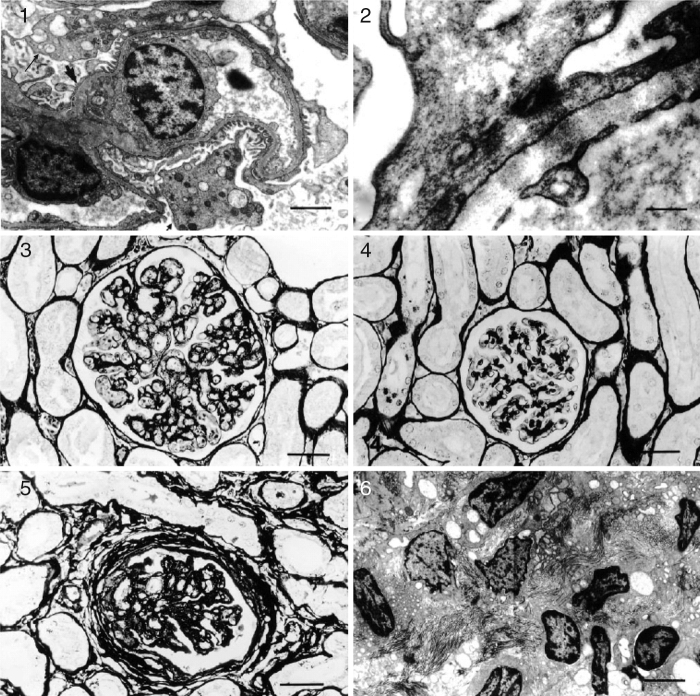
Mesangial proliferative, membranoproliferative, and collapsing FSGS seem to be the patterns that are most frequently seen in association with kala-azar nephropathy, the severity of which can vary from mononuclear interstitial infiltration to a severe, diffuse, inflammatory infiltrate consisting of macrophages, lymphocytes and plasma cells.33 On immunofluorescence microscopy, IgG, IgM, IGA and C3 deposits in the mesangial matrix can be found.33 Experimentally, tubular and interstitial lesions have been the most frequently seen kala-azar-associated kidney lesions. However, amyloid deposits and rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome have been reported in human leishmaniasis.34, 35 Experimental infection by L. donovani can result in amyloid deposition, following an initially diffuse proliferative glomerular lesion.36 The finding of the amastigote forms in the kidney is a rare event, yet it is possible to identify Leishmania antigens in inflammatory infiltrate.30 Fig. 1, Fig. 2 illustrate the pathological findings in visceral leishmaniasis.
Fig. 1.
Kidney: glomerulonephritis pattern in dogs with naturally acquired VL. Histopathology (light microscopy) and ultrastructure. (1) Minor glomerular abnormalities. Glomerular, visceral, and epithelial cell vacuolization and protein droplets in the cytoplasm of the podocytes (arrow). Foot process effacement (arrowhead) can be seen. EM. Bar = 500 μm; (2) focal, segmental glomerulosclerosis. Swelling and effacement of visceral and epithelial cell foot processes. Absence of electron-dense particles from the glomerular capillary basement membrane. EM. Bar = 2170 μm; (3) diffuse, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Segmental thickening and duplication of the peripheral glomerular capillary wall. PAMS. Bar = 25 μm; (4) diffuse, mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Normal glomerular capillary wall. PAMS. Bar = 25 μm; (5) crescentic glomerulonephritis. Fibrocellular or fibrous proliferation occupying part of the Bowman's space. PAMS. Bar = 25 μm; and (6) chronic glomerulonephritis. Intense activity of fibroblasts, collagen proliferation, and cell remnants in interstitial space. Bar = 350 μm.
Reprinted from Costa, et al., Veterinary Pathology 40(6):677–84. Copyright (2003) with permission from Veterinary Pathology.47
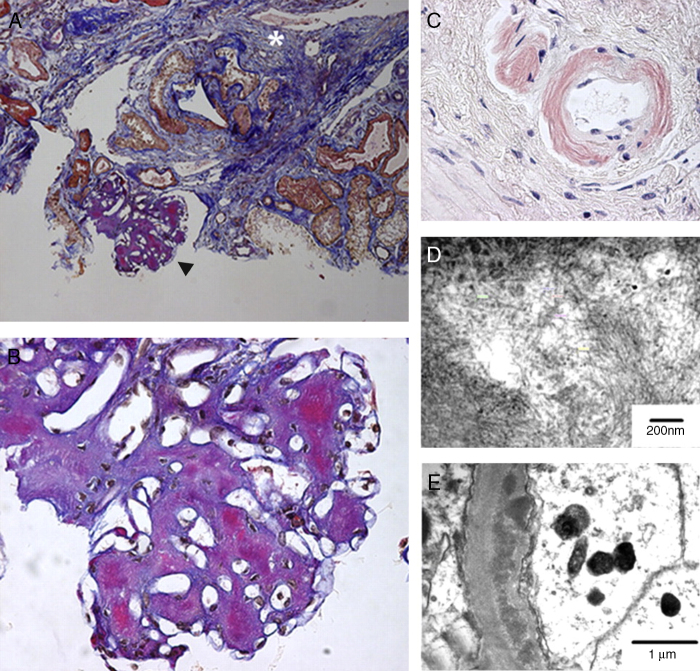
Fig. 2.
Renal amyloidosis in a patient with visceral leishmaniasis and HIV. (A) Abundant mesangial amyloid deposits (black arrowhead; enlarged in (B)) and interstitial fibrosis (white asterisk); FAOG stain; 100×, (B) almost complete obliteration of the glomerular architecture by mesangial amyloid deposits; FAOG stain; 600×, (C) amyloid deposits in arteriolar wall that are congophilic and produce apple-green birefringence; Congo red; 600×, (D) typical ultrastructural appearance of amyloid fibrils in the mesangium; transmission electron microscopy (uranyl acetate and lead citrate), and (E) amyloid fibrils are also seen in capillary membranes in a subendothelial location; transmission electron microscopy (uranyl acetate and lead citrate).
Reprinted from de Vallière, et al., The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 81(2):209–12. Copyright (2009) with permission from The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.35
Treatment
Pentavalent antimonial compounds are still the drugs of choice when treating visceral leishmaniasis. However, amphotericin B might be equally effective. Kidney alterations usually disappear soon after infection control.
Funding
Elzabeth De Francesco Daher received a grant (number: 300405/2012-0) from the Brazilian Research Council (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – CNPq; “Produtividade em Pesquisa”).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Contributor Information
Geraldo Bezerra da Silva Junior, Email: geraldobezerrajr@yahoo.com.br.
Elvino José Guardão Barros, Email: elvino.barros@gmail.com.
Elizabeth De Francesco Daher, Email: ef.daher@uol.com.br.
References
- 1.Magill A.J. In: Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. 7th ed. Mandell G.L., Bennett J.E., Dolin R., editors. Churchill Livingstone; London: 2009. Leishmania species: visceral (kala-azar), cutaneous, and mucosal leishmaniasis; pp. 3463–3480. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Clementi A., Battaglia G., Floris M., Castellino P., Ronco C., Cruz D.N. Renal involvement in leishmaniasis: a review of the literature. NDT Plus. 2011;4:147–152. doi: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfr008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Oliveira R.A., Diniz L.F., Teotônio L.O., et al. Renal dysfunction in patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Kidney Int. 2011;80:1099–1106. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Oliveira R.A., Lima C.G., Mota R.M., Martins A.M., Sanches T.R., Seguro A.C. Renal function evaluation in patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis after specific treatment with pentavalent antimonial. BMC Nephrol. 2012;13:44. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Daher E., Silva Junior G., Oliveira J., et al. Renal abnormalities in patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis [abstract MO226]. Abstracts from the world congress of nephrology; Vancouver, Canada; 2011. Available from http://www.abstracts2view.com/wcn [accessed April 2011] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Balsan M., Fenech F. Acute renal failure in visceral leishmaniasis treated with sodium stibogluconate. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1992;86:515–516. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(92)90091-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sampaio R.N.R., Veiga J.P.R., Limeira O.M., Vexenat A., Marsden P.D. Insuficiência renal aguda em leishmaniose tegumentar americana tratada com associação de glucantime® e alopurinol. An Bras Dermatol. 1991;66:133–134. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Veiga J.P.R., Khanan R., Rosa T.T., et al. Pentavalent antimonial nephrotoxicity in the rat. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo. 1990;32:304–309. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46651990000400012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Oliveira R.A., Silva Junior G.B., Souza C.J., et al. Evaluation of renal function in leprosy: a study of 59 consecutive patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:256–262. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Russo L.M., Bakris G.L., Comper W.D. Renal handling of albumin: a critical review of basics concepts and perspective. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39:899–919. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2002.32764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rose B.D., Bakris G.L. 2004. Microalbuminuria and cardiovascular disease. UpToDate 12.3. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wachtell K., Ibsen H., Olsen M.H., et al. Albuminuria and cardiovascular risk in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: the LIFE study. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:901–906. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-139-11-200312020-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wen H., Frokiaer J., Kwon T.H., Nielsen S. Urinary excretion of aquaporin-2 in rat is mediated by a vasopressin-dependent apical pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:1416–1429. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V1071416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Martin P.Y., Abraham W.T., Leiming X., et al. Selective V2-receptor vasopressin antagonism decreases urinary aquaporin-2 excretion in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:2165–2170. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V10102165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Melby P.C., Kreutzer R.D., McMahon-Pratt D., et al. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: review of 59 cases seem at the National Institute of Health. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;15:924–937. doi: 10.1093/clind/15.6.924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cucé L.C., Belda J., Dias W. Nephrotoxicyty to Glucantime® in the treatment of leishmaniasis. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo. 1990;32:249–251. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46651990000400003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rodrigues M.L.O., Costa R.S., Souza C.S., et al. Nephrotoxicity attributed to meglumine antimoniate (Glucantime) in the treatment of generalized cutaneous leishmaniasis. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo. 1999;41:33–37. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46651999000100007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sampaio R.N.R., Paula C.D.R., Sampaio J.H.D., et al. Avaliação da tolerância e nefrotoxicidade do antimonial pentavalente administrado na dose de 40 mg Sbv/kg/dia por 30 dias na forma cutânea-mucosa de leishmaniose. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1997;30:457–467. doi: 10.1590/s0037-86821997000600003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.7th ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; Philadelphia, PA: 2010. Mandell: Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dantas-Torres F., Brandão-Filho S.P. Visceral leishmaniasis in Brazil: revisiting paradigms of epidemiology and control. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo. 2006;48:151–156. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46652006000300007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Albuquerque P.L., Silva Junior G.B., Freire C.C., et al. Urbanization of visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar) in Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil. Rev Panam Salud Pública. 2009;26:330–333. doi: 10.1590/s1020-49892009001000007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lima Verde F.A.A., Lima Verde F.A., Daher E.F., Santos G.M., Saboia Neto A., Lima Verde E.M. Renal tubular dysfuncion in human visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar) Clin Neprhol. 2009;71:492–500. doi: 10.5414/cnp71492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Elnojomi N., Musa A.M., Younis B.M., et al. Surrogate markers of subtle renal injury in patients with visceral leishmaniasis. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2010;21:872–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Salgado Filho N., Ferreira T.M.A.F., Costa J.M.L. Envolvimento da função renal em pacientes com leishmaniose visceral (calazar) Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2003;36:217–221. doi: 10.1590/s0037-86822003000200004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lima Verde F.A., Lima Verde F.A., Neto A.S., Almeida P.C., Lima Verde E.M. Hormonal disturbances in visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar) Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011;84:668–673. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.09-0171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Daher E.F., Rocha N.A., Oliveira M.J., et al. Renal function improvement with pentavalent antimonial agents in patients with visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Nephrol. 2011;33:332–336. doi: 10.1159/000324914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rocha N.A., Oliveira M.J., Franco L.F., et al. Comparative analysis of pediatric and adult visceral leishmaniasis in Brazil. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182814eae. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Libório A.B., Rocha N.A., Oliveira M.J., et al. Acute kidney injury in children with visceral leishmaniasis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012;31:451–454. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318247f533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Oliveira M.J.C., Silva Junior G.B., Abreu K.L.S., et al. Risk factors for acute kidney injury in visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar) Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;82:449–453. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Costa F.A., Prianti M.G., Silva T.C., Silva S.M., Guerra J.L., Goto H. T cells, adhesion molecules and modulation of apoptosis in visceral leishmaniasis glomerulonephritis. BMC Infect Dis. 2010;10:112. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Prianti M.G., Yokoo M., Saldanha L.C.B., Costa F.A.L., Goto H. Leishmania (Leishmania) chagasi-infected mice as a model for the study of glomerular lesions in visceral leishmaniasis. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007;40:819–823. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2007000600011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lima Verde E.M., Lima Verde F.A.A., Lima Verde F.A., et al. Evaluation of renal function in human visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar): a prospective study on 50 patients from Brazil. J Nephrol. 2007;20:432–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kumar P.V., Daneshbod Y., Sadeghiporr A. Leishmania in the Glomerulus. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004;128:935–936. doi: 10.5858/2004-128-935-LITG. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Navarro M., Bonet J., Bonal J., et al. Amyloidosis secundaria por leishmaniasis visceral como causa de frecaso renal agudo irreversible en paciente con SIDA. Nefrología. 2006;26:745–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.De Vallière S., Mary C., Joneberg J.E., et al. AA-amyloidosis caused by visceral leishmaniasis in a human immunodeficiency virus-infected patient. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;81:209–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Oliveira A.V., Roque-Barreira M.C., Sartori A., et al. Mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis associated with progressive amyloid deposition in hamsters experimentally infected with leishmania donovani. Am J Pathol. 1985;120:256–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Duarte M.I., Silva M.R., Goto H., et al. Interstitial nephritis in human kala-azar. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77:531–537. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Dutra M., Martinelli R., de Carvalho E.M., et al. Renal involvement in visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1985;6:22–27. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(85)80034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Caravaca F., Muñoz A., Pizzaro J.L., et al. Acute renal failure in visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Nephrol. 1991;11:350–352. doi: 10.1159/000168337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Leblond V., Beaufils H., Ginsburg C., et al. Collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis associated with visceral leishmaniasis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1994;9:1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chaigne V., Knefati Y., Lafarge R., et al. Leishmaniose visceral autochtone avec insuffisance rénale aiguë par glomérulonéphrite infectieuse. Nephrologie. 2004;25:179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Efstratiadis G., Boura E., Giamalis P., et al. Renal involvement in a patient with visceral leishmaniasis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:235–236. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfi157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Alex S., Criado C., Fernandez-Guerrero M.L., et al. Nephrotic syndrome complicating chronic visceral leishmaniasis: re-emergence in patients with AIDS. Clin Nephrol. 2008;70:65–68. doi: 10.5414/cnp70065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Daher E.F., Evangelista L.F., Silva Junior G.B., et al. Clinical presentation and renal evaluation of human visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar): a retrospective study of 57 patients in Brazil. Braz J Infect Dis. 2008;12:329–332. doi: 10.1590/s1413-86702008000400015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dettwiler S., McKee T., Hadaya K., et al. Visceral leishmaniasis in a kidney transplant recipient: parasitic interstitial nephritis, a cause of renal dysfunction. Am J Transplant. 2010;10:1486–1489. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Suankratay C., Suwanpimolkul G., Wilde H., et al. Autochtonous visceral leishmaniasis in a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patient: the first in Thailand and review of the literature. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;82:4–8. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Costa F.A., Goto H., Saldanha L.C., et al. Histopathologic patterns of nephropathy in naturally acquired canine visceral leishmaniasis. Vet Pathol. 2003;40:677–684. doi: 10.1354/vp.40-6-677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]