Abstract
Angionvasive mucormycosis is an emerging fungal disease known to affect mainly diabetics or subjects with profound neutropenia. Infection usually occurs through the inhalation route, but cutaneous inoculation may occur after trauma or burns. However, mucormycosis remains unusual in HIV infection. We report a fatal case of cutaneous mucormycosis due to Rhizopus arrhizus involving the scalp following herpes zoster infection. The patient was a 42-year-old man with advanced AIDS failing on salvage antiretroviral therapy. The fungus was diagnosed on the basis of histopathology and culture. Our case emphasizes the need to consider mucormycosis in the differential diagnosis of necrotic cutaneous lesions in patients with late-stage HIV disease.
Keywords: HIV, Mucormycosis, Rhizopus, AIDS
Introduction
Invasive fungal infections represent a major cause of morbimortality in AIDS patients.1 Pneumocystosis, cryptococcosis, and histoplasmosis are typically seen in HIV-infected patients with profound immune suppression (e.g. CD4+<200 cells). The rapid expansion of antiretroviral therapy has contributed to a reduction in the incidence of these fungal infections. However, mucormycosis remains infrequently seen in patients whose only risk factor is HIV infection, and few cases have been reported in the literature describing this rare association.2, 3 In a recent systematic review of 929 reported cases of mucormycosis, HIV infection was the attributed risk factor in just 2% but was associated with a higher mortality rate.4 Similarly, in a study of 1630 autopsies conducted in AIDS patients from 1984 to 2002, mucormycosis was detected in only two cases.5 Herein, we report a fatal case of cutaneous mucormycosis due to Rhizopus arrhizus in an AIDS patient failing salvage combination antiretroviral therapy.
Case report
A 42-year-old male was admitted to our center with complaints of a severe headache for a month, accompanied by scalp redness and difficulty in making facial movements. His past medical history included chronic HIV infection, with poor adherence to antiretroviral drugs. He was diagnosed with HIV infection in 2008, had been on several antiretroviral drugs and his latest regimen was a combination of 3TC, DRV/r, RAL, and MVQ. The most recent immunovirology panel showed CD4+ T-cell count of 2 cells/mm3 and HIV viral load of 57.147 copies/mL. One month prior to presentation, he was seen in the walk-in outpatient clinic for acute sinusitis and facial herpes zoster; levofloxacin, prednisone, and valacyclovir were prescribed. The condition deteriorated with the development of bilateral facial palsy, diffuse facial edema and multiple fistulas with purulent discharges over the scalp. Upon admission, a computed tomography (CT) scan of the brain showed air fluid levels and mucosal thickening in the left maxillary and sphenoid sinuses, obliteration of the posterior right ethmoid cells, and a diffuse increase of the facial subcutaneous tissue with an organized collection in the left temporal region. No brain parenchyma lesions were noted.
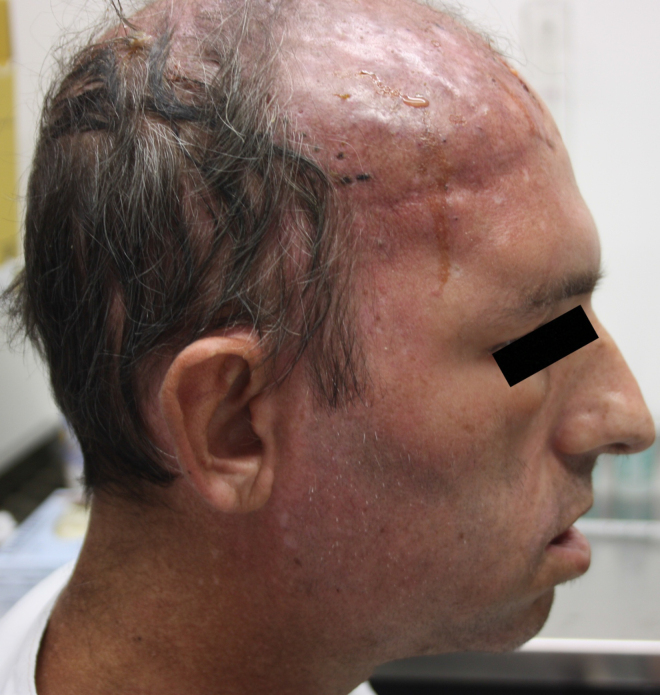
Broad-spectrum antibiotics were started and blood cultures for mycobacteria, fungi and bacteria were drawn. On examination, he was underweight (BMI: 15.9 kg/m2) and anemic, but vital signs were normal. Neurological examination showed bilateral seventh cranial nerve palsy. An area of infiltrative edema and cellulitis in the scalp and forehead region was visible coupled with multiple back eschars lesions, some of them draining serupurulent discharge (Fig. 1). Aspirates of scalp lesions and a scalp biopsy were performed and samples were cultured in Sabouraud dextrose Agar 2% (Biolog, Brazil) and Mycobiotic Agar (Becton, Dickinson and Company, USA). Cultures were kept at 25 °C. Fungal identification was performed by morphophysiological tests, such as macroscopic and microscopy analysis, and thermo-tolerance. Microscopic fungal aspects were evaluated under a Zeiss Primo Starlight microscope. After four days, gray colonies with cotton-like dense growth were observed. Microscopic aspects of the fungus included broad-hyphae with a few septa; rhizoids produced under unbranched sporangiopores that terminated with dark round sporangia (60–200 μm diameter) producing brown to black sporangiospores (around 6 μm length) (Fig. 2). Histopathology showed a chronic necrotizing and suppurative granulomatous dermatitis with numerous coenocytic (aseptate) hyphae (Fig. 3). The fungus was able to grow at 30 °C and 37 °C, but not at 45 °C. The fungus was then identified as R. arrhizus. Blood cultures taken at hospital admission were negative.
Fig. 1.
Features on admission: infiltrative lesions and cellulitis concentrated in forehead and scalp region; multiple ulcers covered with black eschar, draining seropurulent secretion; seventh nerve palsy.
Fig. 2.
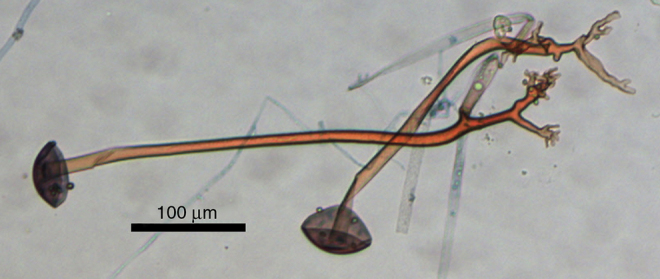
Microscopic examination of Rhizopus arrhizus: unbranched sporangiospores with collapsed columella and rhizoids. Bar: 100 μm.
Fig. 3.
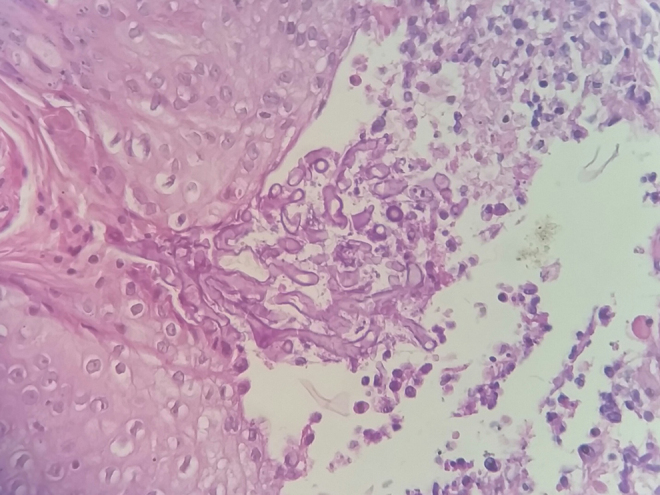
Histopathology (hematoxylin–eosin) of scalp biopsy: chronic necrotizing and suppurative granulomatous dermatitis with numerous coenocytic (aseptate) hyphae.
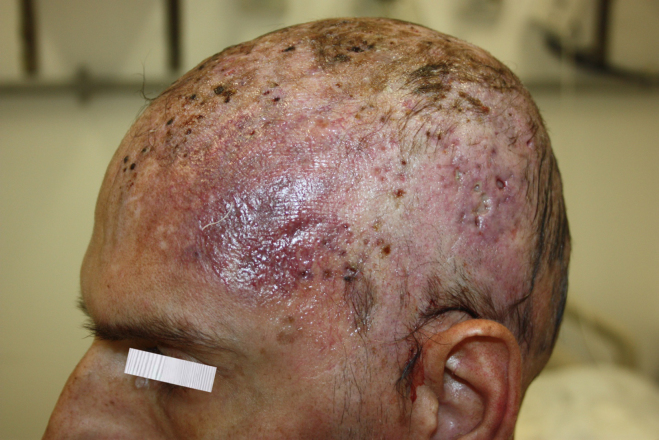
Initial treatment was intravenous oxacillin and ceftazidime resulted in partially improvement of the subcutaneous edema and erythema. Treatment with intravenous deoxycolate amphotericin B (1 mg/kg/d) was then started on day 7 of admission. Despite some improvement after amphotericin B administration, the facial palsy and scalp purulent drainage remained (Fig. 4). During hospitalization, recurrent episodes of severe neutropenia were observed and improved by the addition of granulocyte colony-stimulant factor. In parallel, the patient developed several episodes of catheter-associated sepsis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. A repeat CT scan after 6-weeks of antibiotic and antifungal therapy still showed mucosal thickening and a small fluid level in the left maxillary sinus, extensive opacification of sphenoidal sinus and a small bone discontinuity of the intersphenoidal sinus. The patient was unsuitable for sinus biopsy due to the ongoing bloodstream infections. After eight weeks of follow-up, the patient had received a cumulative dose of 2 g of amphotericin B. The patient died on the 49th day of hospital admission and the 41st day of antifungal therapy.
Fig. 4.
Day 10 after admission: persistence of erythematous lesions dispersed over the scalp region. Note the tiny ulcers covered by black eschars.
Discussion
Mucormycosis is an emergent fungal infection which affects a substantial proportion of immunosuppressed hosts, especially diabetics, those with hematological malignancy and recipients of bone marrow transplants. Fungi are comprised of two main subphyla – Mucormycotina and Entomophthoromycotina.6 Disease caused by members of the Mucormycotina play an increasing role in the clinical settings especially in immunocompromised patients. The usual sites of infection reflect portals of entry and include sinuses, lungs and skin.
Cutaneous involvement occurs in almost 20% of cases involving patients without underlying immunosuppression.4 The three main forms are superficial, nodular, and gangrenous. The mechanism of acquisition is thought to be from inoculation of spores into injured skin. Moreover, hospital-related procedures such as catheter insertion, injection sites, adhesion tapes, wooden tongue depressors, ostomy bags, and contaminated cotton clothes are some of the risk factors previously described.7 Cases of post-traumatic, such as road traffic accidents, scorpion and spider bites, and burns in otherwise healthy individuals have also been reported in the literature.8, 9, 10, 11, 12 The clinical presentation consists of a single, painful area of cellulitis, which often progress into ecthyma. Necrosis may develop rapidly and subsequent dissemination to adjacent tissue may follow. These features are hallmarks of mucormycosis attributable mainly to angioinvasion and subsequent tissue thrombosis.
Here, we described an AIDS patient with cutaneous mucormycosis due to R. arrhizus, diagnosed based on a positive skin histopathology and confirmed by culture. In addition, we hypothesized that dissemination of the infection to subcutaneous tissue and then to the sinuses (the latter suggested by the temporal relation and the radiological features in the absence of the other common causes of sinusitis) did occur.
Even though we could not perform an endoscopic evaluation of the sinuses to make a precise diagnosis, it is likely that the sinusitis was also due to mucormycosis. In addition, we argue that the herpetic lesions led to tissue ischemia and acted as a possible portal of entry and a contributing factor to the cutaneous mucormycosis superinfection.
HIV-associated mucormycosis does occur predominantly in relatively young males, with lower CD4+ cell counts but without the traditional risk factors linked to mucormycosis.13 In some cases, there are underlying predisposing factors such as transient episodes of neutropenia and intravenous injections drug abuse. Mucormycosis has been the initial presentation of HIV infection and, in some cases, unusual manifestations have been described.14 Co-infection with other opportunistic diseases such as cytomegalovirus vasculitis, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, and Kaposi's sarcoma resulted in complicated cases as their presence contributes to increased virulence in the disease process.15 Multi-organ dissemination does occur.16 Due to the difficulty in distinguishing mucormycosis from other angioinvasive diseases (e.g. diseases caused by Aspergillus, Fusarium, Pseudallescheria), clinicians should always consider mucormycosis in the differential diagnosis in patients with advanced AIDS. Collectively, those facts draw attention to the importance of mucormycosis as an emergent severe opportunistic pathogen in the late-stage of HIV infection.
Mortality rates for mucormycosis vary between 38 and 66%; however, there is large variation depending on the underlying condition, site of infection, species involved, and regimen of antifungals administered.4, 17, 18 For instance, infection due to Cunninghamella species, disseminated disease, active malignancy, and monocytopenia were independent predictors of poor outcome, whereas salvage posaconazole-based therapy and neutrophil count recovery were predictive of a favorable outcome.4, 17
A combination of surgical debridement coupled with fungicidal therapy improve patient outcomes.6 Amphotericin B remains the drug of choice. Posaconazole has been used as a salvage therapy in extensive and refractory cases.6 Recently, an open-label phase 3 study of isavuconazole – a new broad-spectrum triazole – for treatment of mucormycosis, showed that isavuconazole improves treatment success in up to 36% of patients with primary or refractory disease.19 The main advantages of isavuconazole over other antifungal agents include the availability of a water-soluble intravenous formulation, excellent oral bioavailability, predictable pharmacokinetics, and fewer side effects.20 Besides administration of antifungal therapy, it is vital to promptly reverse the underlying risk factors that triggered mucormycosis (e.g. neutropenia, diabetes mellitus, corticosteroids). In our case, treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor was introduced to reverse neutropenia.
The lipid-based formulations of amphotericin B have become the antifungals of choice for the treatment of invasive fungal infections due to less renal toxicity, fewer infusion-related reactions and provision of higher doses over a shorter period of time compared to conventional amphotericin B. We were unable to provide those formulations in our case because of restricted drug availability due to high drug prices. However, we believe that our report represents a real life situation and mirrors the current challenges facing Brazilian medical institutions. Provision of the most effective and safe amphotericin B formulations in the treatment of mucormycosis, especially in the developing world, needs to be urgently addressed.
Our patient presented severe immunosuppression and transient episodes of neutropenia occurred prior to and during hospitalization, possibly contributing to mucormycosis. The patient also received high-dose steroid therapy for two weeks, when herpes zoster and sinusitis were treated before admission. Despite the extensive sinusitis showed on repeat CT scans, we were unable to perform sinus drainage and debridement because the patient was critically-ill and severely undernourished, which contraindicated surgery. Prompt sinus and skin debridement might have allowed a better outcome in this case.
In conclusion, our case highlights the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion for mucormycosis in the impaired host, especially those at late stage AIDS, presenting with necrotic cutaneous lesions.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge the support of the medical and nursing staff at Instituto Nacional de Infectologia Evandro Chagas for the dedicated care of this patient. Moreover, we thank Fabio Santos for his help in fungus identification.
José Moreira is supported by a scholarship from Programa de Estudantes-Convênio de Pós-graduação (PEC-PG, CAPES/CNPQ).
References
- 1.de Oliveira R.B., Atobe J.H., Souza S.A., de Castro Lima Santos D.W. Epidemiology of invasive fungal infections in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome at a reference hospital for infectious diseases in Brazil. Mycopathologia. 2014;178:71–78. doi: 10.1007/s11046-014-9755-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kutlu M., Ergin C., Bir F., et al. Pulmonary mucormycosis due to Lichtheimia ramosa in a patient with HIV infection. Mycopathologia. 2014;178:111–115. doi: 10.1007/s11046-014-9761-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Patel A., Bishburg E., Nagarakanti S. Mucormycosis in an HIV-infected renal transplant patient: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Case Rep. 2014;15:74–78. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.890026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roden M.M., Zaoutis T.E., Buchanan W.L., et al. Epidemiology and outcome of zygomycosis: a review of 929 reported cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:634–653. doi: 10.1086/432579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Antinori S., Nebuloni M., Magni C., et al. Trends in the postmortem diagnosis of opportunistic invasive fungal infections in patients with AIDS: a retrospective study of 1,630 autopsies performed between 1984 and 2002. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;132:221–227. doi: 10.1309/AJCPRAAE8LZ7DTNE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Douglas A.P., Chen S.C., Slavin M.A. Emerging infections caused by non-Aspergillus filamentous fungi. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rammaert B., Lanternier F., Zahar J.R., et al. Healthcare-associated mucormycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(Suppl. 1):S44–S54. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Katz T., Wasiak J., Cleland H., Padiglione A. Incidence of non-candidal fungal infections in severe burn injury: an Australian perspective. Burns. 2014;40:881–886. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2013.11.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rabie N.B., Althaqafi A.O. Rhizopus-associated soft tissue infection in an immunocompetent air-conditioning technician after a road traffic accident: a case report and review of the literature. J Infect Public Health. 2012;5:109–111. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2011.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lechevalier P., Hermoso D.G., Carol A., et al. Molecular diagnosis of Saksenaea vasiformis cutaneous infection after scorpion sting in an immunocompetent adolescent. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:3169–3172. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00052-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Saravia-Flores M., Guaran D.M., Argueta V. Invasive cutaneous infection caused by Apophysomyces elegans associated with a spider bite. Mycoses. 2010;53:259–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2009.01698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.de Oliveira-Neto M.P., Da Silva M., Fialho Monteiro P.C., et al. Cutaneous mucormycosis in a young, immunocompetent girl. Med Mycol. 2006;44:567–570. doi: 10.1080/13693780600622411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Van den Saffele J.K., Boelaert J.R. Zygomycosis in HIV-positive patients: a review of the literature. Mycoses. 1996;39:77–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1996.tb00106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Moraru R.A., Grossman M.E. Palatal necrosis in an AIDS patient: a case of mucormycosis. Cutis. 2000;66:15–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Samant J.S., Namgoong S.H., Parveen T., Katner H.P. Cytomegalovirus vasculitis and mucormycosis coinfection in late-stage HIV/AIDS. Am J Med Sci. 2007;333:122–124. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200702000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mugambi M.S., Theron A., Cox S., Pillay K., Millar A.J.W., Numanoglu A. Disseminated mucormycosis and necrotizing fasciitis in immune-compromised patients: two case reports. Ann Pediatr Surg. 2015;11:35–39. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chamilos G., Lewis R.E., Kontoyiannis D.P. Delaying amphotericin B-based frontline therapy significantly increases mortality among patients with hematologic malignancy who have zygomycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:503–509. doi: 10.1086/590004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kontoyiannis D.P., Azie N., Franks B., Horn D.L. Prospective antifungal therapy (PATH) alliance(®): focus on mucormycosis. Mycoses. 2014;57:240–246. doi: 10.1111/myc.12149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marty F.M., Perfect J.R., Cornely O.A., et al. An open-label phase 3 study of isavuconazole (VITAL): focus on mucormycosis. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2014;1:S235–S236. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Miceli M.H., Kauffman C.A. Isavuconazole: a new broad-spectrum triazole antifungal agent. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:1558–1565. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]