The asymmetric unit contains two independent molecules having opposite conformations and each forming self-dimers through complementary O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. These dimers are linked by weak C—H⋯π interactions involving the phenyl ring and the olefinic double bond into zigzag chains extending along the c-axis direction. The chains are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form the full three-dimensional structure in which one can discern layers parallel to the bc plane.
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bond, carboxylic acid, Hirshfeld surface
Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title molecule, C12H12O3, contains two independent molecules having opposite conformations and each forming self-dimers through complementary O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. These dimers are linked by weak C—H⋯π interactions and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into a three-dimensional structure in which one can discern layers parallel to the bc plane. A Hirshfeld surface analysis of the intermolecular interactions is included.
1. Chemical context
Levulinic acid has various derivatives, some of which have a wide range of pharmacological activities. Photodynamic therapy in gastroenterology (Mordon et al., 2005 ▸) and cancer treatment for the detection of tumor tissue (Manzo, 2012 ▸) are some of the pharmacological applications. These derivatives are also the main compounds used in the synthesis of some pyridazinone derivatives (Boukharsa et al., 2016a
▸,b
▸; Zaoui et al., 2019 ▸, 2021 ▸). In our research, great attention has been given to the development of diversely functionalized heterocycles (Guerrab et al., 2020 ▸, 2021 ▸; Abad et al. 2021 ▸; Missioui et al., 2021 ▸, 2022a
▸,b
▸). Given the wide range of therapeutic applications for such compounds, and in continuation of our research efforts, we report the synthesis, molecular and crystal structure and a Hirshfeld surface analysis of the title compound (see Scheme).
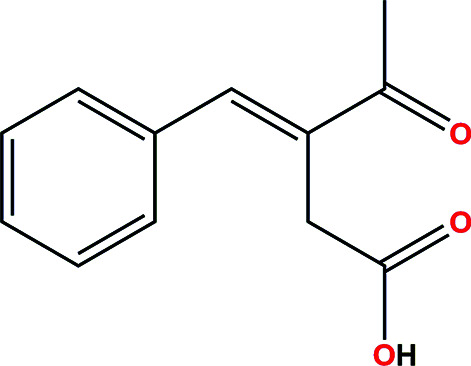
2. Structural commentary
The asymmetric unit consists of two independent molecules (Fig. 1 ▸) having opposite configurations, as shown in Fig. 2 ▸, where inverting the molecule containing atom O4 allows almost complete overlap between the two independent portions of the asymmetric unit [r.m.s. deviations = 1.204 (no inversion) and 0.163 Å (inversion)]. They also differ in the dihedral angle between their planar parts. Thus, the C2—C1—C7—C8 torsion angle is −143.15 (14)°, while the C14—C13—C19—C20 torsion angle is 139.55 (15)°. The dihedral angle between the mean plane of the C1–C6 phenyl ring and that defined by atoms C7–C9/C11 is 36.54 (5)° in one molecule, while that between the C13–C18 ring and the plane defined by atoms C19–C21/C23 in the other molecule is 41.67 (6)°. In the first molecule, the dihedral angle between the best planes through C7–C9/C11 and C9/C10/O1/O2 is 81.96 (5)°, while that between the C19–C21/C23 and C21/C22/O4/O5 planes in the second molecule is 75.53 (6)°. Finally, the dihedral angle between the mean C8/C11/C12/O3 and C7–C9/C11 planes in the first molecule is 2.88 (12)°, while that between the mean C20/C23/C24/O6 and C19–C21/C23 planes in the second molecule is 5.22 (3)°. All bond lengths and angles are as expected.
Figure 1.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids. The C—H⋯π interaction is depicted by a dashed line.
Figure 2.
Overlay of the two independent molecules as found (left) and with the second one inverted (right).
3. Supramolecular features
In the crystal, each independent molecule forms a centrosymmetric self-dimer with the dimers connected by a C—H⋯π interaction between C21—H21A and the C7=C8 olefinic bond [H21A⋯Cg = 2.60 Å, C21⋯Cg = 3.547 (2) Å and C21—H21A⋯Cg = 161°; Cg is the centroid of C7=C8; see Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 3 ▸]. The unit shown in Fig. 3 ▸ is linked to others through weak C19—H19⋯O6 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) to form a three-dimensional network structure. Although these intermolecular interactions propagate in three dimensions, one can discern layers constructed by the hydrogen-bond interactions which are connected by the C—H⋯π interactions. These layers are parallel to the bc plane (Fig. 4 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2A⋯O1i | 0.84 (1) | 1.78 (1) | 2.6226 (13) | 178 (2) |
| O5—H5A⋯O4ii | 0.86 (1) | 1.74 (1) | 2.6000 (13) | 176 (2) |
| C19—H19⋯O6iii | 0.95 | 2.60 | 3.447 (1) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 .
.
Figure 3.

Detail of the interactions between hydrogen-bonded dimers viewed along the b-axis direction. The O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and the C—H⋯π interactions are depicted, respectively, by red and green dashed lines. Non-interacting H atoms have been omitted for clarity. [Symmetry codes: (i) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1; (ii) x + 1, y, z + 1; (iii) −x, −y + 1, −z.]
Figure 4.
Packing viewed along the c-axis direction with O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds depicted, respectively, by red and black dashed lines. The C—H⋯π interactions are depicted by green dashed lines and non-interacting H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
4. Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database updated to November 2021 (Groom et al., 2016 ▸) with a search fragment consisting of the title molecule with H2A and H7, as well as all H atoms on the phenyl ring deleted, found mainly bicyclic molecules not closely related to the title molecule. Using the above search fragment but with H7 now present, one hit, namely, 3-(4-methylbenzylidene)-4-oxopentanoic acid (CSD refcode UCOXOC; Boukharsa et al., 2016a ▸,b ▸) was obtained (also found in the previous search). This structure also contains two independent molecules (A and B) which form A–A and B–B hydrogen-bonded inversion dimers, as seen in the present structure. The packing in UCOXOC appears to generate also a layer structure, but no mention is made of additional intermolecular interactions.
5. Hirshfeld surface analysis
The Hirshfeld surface analysis was performed with CrystalExplorer (Version 21.5; Spackman et al., 2021 ▸); the details of the pictorial output are described in a recent publication (Tan et al., 2019 ▸). Fig. 5 ▸ shows two views of the d norm surfaces for the two components of the asymmetric unit plotted over the limits from −0.1211 to 1.4747 a.u. The O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds with which each molecule forms its self-dimer are indicated by the bright red spots in Figs. 5 ▸(a) and 5(b), respectively. The weak intermolecular C—H⋯π interaction with the olefinic double bond appears in Fig. 5 ▸(c) as the lighter red spot in the centre of the left side of the drawing, showing the acceptor site, and in a similar location in Fig. 5 ▸(d), showing the donor site. Fig. 6 ▸ presents the two-dimensional fingerprint plots involving all intermolecular interactions [Fig. 6 ▸(a)] and delineated into O⋯H/H⋯O [Fig. 6 ▸(b)] and C⋯H/H⋯C [Fig. 6 ▸(c)] interactions. Figs. 6 ▸(d) and 6(e) show the fractions of the overall surface corresponding, respectively, to the two above interactions (28.8% for the fomer and 18.2% for the latter). For completeness, the H⋯H interactions constitute 48.4% of the surface.
Figure 5.
The Hirshfeld surface plots for the title molecule: (a) d norm for the O1-containing molecule (front side); (b) d norm for the O4-containing molecule (front side); (c) d norm for the O1-containing molecule (back side); (d) d norm for the O4-containing molecule (back side).
Figure 6.
Fingerprint plots for the title molecule: (a) all interactions; (b) O⋯H/H⋯O; (c) C⋯H/H⋯C; (d) fragment of the surface involved in O⋯H/H⋯O interactions; (e) fragment of the surface involved in C⋯H/H⋯C interactions.
6. Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of benzaldehyde (0.01 mol) and levulinic acid (0.02 mol) in a solution of acetic acid (50 ml) was saturated with dry hydrogen chloride gas for 2 h. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The resulting product was extracted and washed with chloroform. The crude compound was crystallized from acetone to give small colourless crystals (yield: 59%; m.p 398–400 K). IR (KBr, ν (cm−1)): 1692 (C=O ketone), 1755 (C=O acid); 1H NMR [300 MHz DMSO-d 6, δ(ppm)]: δ 2.42 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.74 (s, 2H, CH2), 7.27–7.75 (m, 5H, phenyl), 7.98 (s, 1H, CH=C), 12.21 (s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR [300 MHz DMSO-d 6, δ(ppm)]: δ 26.10, 32.83, 128.01, 131,09, 131.52, 133.79, 137.32, 137.43, 171.78, 192.72; MS (ESI+): m/z = 205.88 [M + H]+
7. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms attached to carbon were placed in idealized positions and included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2–1.5 times those of the attached atoms. H atoms attached to oxygen were placed in locations derived from a difference map and refined with a DFIX 0.84 0.01 instruction.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C12H12O3 |
| M r | 204.22 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 125 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 15.5987 (3), 13.0782 (3), 11.0396 (2) |
| β (°) | 109.063 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 2128.60 (8) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.75 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 × 0.18 × 0.07 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON 3 CPAD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.85, 0.95 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 36991, 3894, 3477 |
| R int | 0.042 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.603 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.037, 0.098, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 3894 |
| No. of parameters | 281 |
| No. of restraints | 2 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.26, −0.16 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022004789/vm2263sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022004789/vm2263Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2170436
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The support of an NSF–MRI grant for the purchase of the diffractometer and Tulane University for support of the Tulane Crystallography Laboratory are gratefully acknowledged. Authors’ contributions are as follows. Conceptualization, HA; methodology, HA and YZ; investigation, SEG and IAEH; theoretical calculations, JTM; writing (original draft), JMT and YR; writing (review and editing of the manuscript), YR; formal analysis, MA and YR; supervision, MA and JT; crystal-structure determination and validation, JTM.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C12H12O3 | F(000) = 864 |
| Mr = 204.22 | Dx = 1.274 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 15.5987 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 9897 reflections |
| b = 13.0782 (3) Å | θ = 3.0–68.3° |
| c = 11.0396 (2) Å | µ = 0.75 mm−1 |
| β = 109.063 (1)° | T = 125 K |
| V = 2128.60 (8) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.35 × 0.18 × 0.07 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON 3 CPAD diffractometer | 3894 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: INCOATEC IµS micro-focus source | 3477 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.042 |
| Detector resolution: 7.3910 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 68.3°, θmin = 3.0° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −18→18 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | k = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.85, Tmax = 0.95 | l = −13→13 |
| 36991 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.098 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0449P)2 + 0.7261P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3894 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 281 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The diffraction data were obtained from 13 sets of frames, each of width 0.5° in ω or φ, collected with scan parameters determined by the "strategy" routine in APEX3. The scan time varied between 4 and 10 sec/frame, increasing with increasing θ. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. H-atoms attached to carbon were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 - 0.99 Å) and included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 - 1.5 times those of the attached atoms. Those attached to oxygen were placed in locations derived from a difference map and refined with a DFIX 0.84 0.01 instruction. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.01466 (6) | 0.43636 (7) | 0.13158 (8) | 0.0335 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.11775 (6) | 0.53207 (7) | 0.08370 (9) | 0.0330 (2) | |
| H2A | 0.0747 (10) | 0.5405 (15) | 0.0145 (12) | 0.059 (6)* | |
| O3 | 0.15617 (8) | 0.23912 (8) | 0.24312 (9) | 0.0428 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.11190 (8) | 0.51281 (10) | 0.51675 (12) | 0.0287 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.13778 (9) | 0.52531 (10) | 0.64944 (13) | 0.0319 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.149625 | 0.466767 | 0.703342 | 0.038* | |
| C3 | 0.14645 (10) | 0.62214 (11) | 0.70370 (14) | 0.0381 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.165783 | 0.629690 | 0.794220 | 0.046* | |
| C4 | 0.12690 (10) | 0.70747 (11) | 0.62572 (16) | 0.0425 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.134096 | 0.773842 | 0.662664 | 0.051* | |
| C5 | 0.09682 (11) | 0.69635 (11) | 0.49382 (16) | 0.0425 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.081391 | 0.755016 | 0.440322 | 0.051* | |
| C6 | 0.08917 (9) | 0.59974 (11) | 0.43962 (14) | 0.0352 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.068235 | 0.592658 | 0.349008 | 0.042* | |
| C7 | 0.11215 (9) | 0.40800 (10) | 0.46866 (12) | 0.0283 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.093428 | 0.356028 | 0.514695 | 0.034* | |
| C8 | 0.13551 (8) | 0.37633 (10) | 0.36773 (11) | 0.0277 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.16595 (9) | 0.44565 (10) | 0.28089 (12) | 0.0296 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.189225 | 0.510133 | 0.326857 | 0.036* | |
| H9B | 0.216439 | 0.412547 | 0.259955 | 0.036* | |
| C10 | 0.09137 (9) | 0.47015 (9) | 0.15870 (11) | 0.0263 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.13621 (9) | 0.26565 (10) | 0.33666 (12) | 0.0308 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.11327 (11) | 0.18699 (11) | 0.42061 (14) | 0.0390 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.051375 | 0.198520 | 0.421374 | 0.059* | |
| H12B | 0.155908 | 0.192707 | 0.508058 | 0.059* | |
| H12C | 0.117594 | 0.118474 | 0.387117 | 0.059* | |
| O4 | 0.49089 (6) | 0.43991 (8) | 0.62632 (9) | 0.0363 (2) | |
| O5 | 0.38438 (7) | 0.52938 (8) | 0.47860 (9) | 0.0362 (2) | |
| H5A | 0.4271 (11) | 0.5378 (16) | 0.4462 (19) | 0.068 (6)* | |
| O6 | 0.35094 (8) | 0.24526 (8) | 0.60897 (9) | 0.0465 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.37323 (9) | 0.51643 (11) | 0.91953 (12) | 0.0321 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.33171 (10) | 0.52973 (12) | 1.01313 (14) | 0.0390 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.312493 | 0.471674 | 1.049168 | 0.047* | |
| C15 | 0.31836 (11) | 0.62700 (13) | 1.05381 (16) | 0.0465 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.289284 | 0.635179 | 1.116582 | 0.056* | |
| C16 | 0.34705 (11) | 0.71187 (12) | 1.00363 (16) | 0.0484 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.336386 | 0.778415 | 1.030129 | 0.058* | |
| C17 | 0.39153 (11) | 0.69983 (12) | 0.91436 (15) | 0.0446 (4) | |
| H17 | 0.412634 | 0.758112 | 0.881168 | 0.053* | |
| C18 | 0.40518 (10) | 0.60291 (11) | 0.87360 (14) | 0.0376 (3) | |
| H18 | 0.436686 | 0.595157 | 0.813635 | 0.045* | |
| C19 | 0.38059 (9) | 0.41173 (10) | 0.87494 (13) | 0.0313 (3) | |
| H19 | 0.395855 | 0.359823 | 0.938630 | 0.038* | |
| C20 | 0.36805 (9) | 0.38144 (10) | 0.75365 (12) | 0.0302 (3) | |
| C21 | 0.34049 (9) | 0.45106 (11) | 0.63929 (12) | 0.0314 (3) | |
| H21A | 0.288072 | 0.420238 | 0.572571 | 0.038* | |
| H21B | 0.320109 | 0.516898 | 0.664775 | 0.038* | |
| C22 | 0.41342 (9) | 0.47210 (10) | 0.58225 (12) | 0.0287 (3) | |
| C23 | 0.37236 (9) | 0.27147 (11) | 0.72132 (13) | 0.0339 (3) | |
| C24 | 0.40272 (11) | 0.19335 (11) | 0.82582 (15) | 0.0418 (3) | |
| H24A | 0.399988 | 0.125163 | 0.787939 | 0.063* | |
| H24B | 0.362870 | 0.195663 | 0.878428 | 0.063* | |
| H24C | 0.465178 | 0.208109 | 0.879500 | 0.063* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0347 (5) | 0.0383 (5) | 0.0257 (5) | −0.0049 (4) | 0.0075 (4) | 0.0069 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0388 (5) | 0.0329 (5) | 0.0257 (5) | −0.0063 (4) | 0.0082 (4) | 0.0062 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0669 (7) | 0.0353 (5) | 0.0304 (5) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0219 (5) | −0.0038 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0276 (6) | 0.0284 (7) | 0.0310 (6) | 0.0001 (5) | 0.0108 (5) | 0.0006 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0347 (7) | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0319 (7) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0011 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0397 (8) | 0.0382 (8) | 0.0382 (7) | 0.0013 (6) | 0.0154 (6) | −0.0083 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0470 (8) | 0.0284 (7) | 0.0564 (9) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0229 (7) | −0.0088 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0514 (9) | 0.0283 (7) | 0.0521 (9) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0065 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0395 (7) | 0.0314 (7) | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0039 (6) | 0.0123 (6) | 0.0036 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0311 (6) | 0.0269 (6) | 0.0253 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0070 (5) | 0.0034 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0299 (6) | 0.0280 (6) | 0.0220 (6) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0031 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0328 (7) | 0.0298 (7) | 0.0257 (6) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0088 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0359 (7) | 0.0216 (6) | 0.0231 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0120 (5) | −0.0004 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0375 (7) | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0224 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0067 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0595 (9) | 0.0266 (7) | 0.0334 (7) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0185 (7) | −0.0001 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0337 (5) | 0.0428 (6) | 0.0339 (5) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0084 (4) |
| O5 | 0.0373 (5) | 0.0402 (6) | 0.0340 (5) | 0.0066 (4) | 0.0155 (4) | 0.0103 (4) |
| O6 | 0.0692 (7) | 0.0404 (6) | 0.0334 (5) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0218 (5) | −0.0070 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0336 (7) | 0.0330 (7) | 0.0278 (6) | −0.0023 (5) | 0.0074 (5) | −0.0018 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0483 (8) | 0.0373 (8) | 0.0347 (7) | −0.0060 (6) | 0.0183 (6) | −0.0047 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0520 (9) | 0.0456 (9) | 0.0470 (9) | −0.0059 (7) | 0.0232 (7) | −0.0146 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0508 (9) | 0.0358 (8) | 0.0566 (10) | −0.0040 (7) | 0.0149 (8) | −0.0151 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0501 (9) | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0489 (9) | −0.0104 (6) | 0.0133 (7) | −0.0038 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0409 (8) | 0.0372 (8) | 0.0359 (7) | −0.0069 (6) | 0.0141 (6) | −0.0040 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0346 (7) | 0.0309 (7) | 0.0301 (7) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0128 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0310 (7) | 0.0312 (7) | −0.0024 (5) | 0.0141 (5) | 0.0003 (5) |
| C21 | 0.0320 (7) | 0.0342 (7) | 0.0285 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0104 (5) | −0.0010 (5) |
| C22 | 0.0363 (7) | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0248 (6) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0098 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C23 | 0.0377 (7) | 0.0345 (7) | 0.0334 (7) | −0.0033 (6) | 0.0168 (6) | −0.0026 (6) |
| C24 | 0.0533 (9) | 0.0314 (7) | 0.0414 (8) | −0.0001 (6) | 0.0164 (7) | 0.0000 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C10 | 1.2177 (15) | O4—C22 | 1.2207 (16) |
| O2—C10 | 1.3165 (15) | O5—C22 | 1.3180 (16) |
| O2—H2A | 0.843 (9) | O5—H5A | 0.860 (9) |
| O3—C11 | 1.2221 (16) | O6—C23 | 1.2234 (17) |
| C1—C6 | 1.3950 (19) | C13—C18 | 1.396 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3961 (18) | C13—C14 | 1.3981 (19) |
| C1—C7 | 1.4704 (18) | C13—C19 | 1.4722 (19) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3885 (19) | C14—C15 | 1.387 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.381 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.379 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.387 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.386 (2) | C17—C18 | 1.385 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.3458 (18) | C19—C20 | 1.3479 (18) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C8—C11 | 1.4885 (18) | C20—C23 | 1.4887 (19) |
| C8—C9 | 1.5046 (17) | C20—C21 | 1.5011 (18) |
| C9—C10 | 1.5002 (17) | C21—C22 | 1.4949 (18) |
| C9—H9A | 0.9900 | C21—H21A | 0.9900 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9900 | C21—H21B | 0.9900 |
| C11—C12 | 1.5040 (18) | C23—C24 | 1.497 (2) |
| C12—H12A | 0.9800 | C24—H24A | 0.9800 |
| C12—H12B | 0.9800 | C24—H24B | 0.9800 |
| C12—H12C | 0.9800 | C24—H24C | 0.9800 |
| C10—O2—H2A | 109.3 (13) | C22—O5—H5A | 109.9 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.28 (12) | C18—C13—C14 | 118.30 (13) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 124.71 (12) | C18—C13—C19 | 123.78 (12) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 117.00 (11) | C14—C13—C19 | 117.92 (12) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.89 (13) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.54 (14) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.6 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.6 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.83 (13) | C16—C15—C14 | 120.35 (14) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.1 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.1 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.05 (13) | C15—C16—C17 | 119.83 (14) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C17—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.11 (14) | C18—C17—C16 | 120.04 (14) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C18—C17—H17 | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C16—C17—H17 | 120.0 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.69 (13) | C17—C18—C13 | 120.83 (13) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.7 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.7 | C13—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| C8—C7—C1 | 128.26 (12) | C20—C19—C13 | 127.13 (13) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 115.9 | C20—C19—H19 | 116.4 |
| C1—C7—H7 | 115.9 | C13—C19—H19 | 116.4 |
| C7—C8—C11 | 120.96 (12) | C19—C20—C23 | 121.25 (12) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 124.70 (12) | C19—C20—C21 | 124.47 (12) |
| C11—C8—C9 | 114.30 (11) | C23—C20—C21 | 114.03 (11) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 112.85 (10) | C22—C21—C20 | 114.69 (11) |
| C10—C9—H9A | 109.0 | C22—C21—H21A | 108.6 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.0 | C20—C21—H21A | 108.6 |
| C10—C9—H9B | 109.0 | C22—C21—H21B | 108.6 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.0 | C20—C21—H21B | 108.6 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 107.8 | H21A—C21—H21B | 107.6 |
| O1—C10—O2 | 123.54 (11) | O4—C22—O5 | 123.84 (12) |
| O1—C10—C9 | 123.69 (11) | O4—C22—C21 | 124.00 (12) |
| O2—C10—C9 | 112.77 (11) | O5—C22—C21 | 112.16 (11) |
| O3—C11—C8 | 119.59 (12) | O6—C23—C20 | 119.67 (13) |
| O3—C11—C12 | 120.27 (12) | O6—C23—C24 | 120.19 (13) |
| C8—C11—C12 | 120.14 (11) | C20—C23—C24 | 120.14 (12) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C23—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C23—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C23—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −4.16 (19) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 3.5 (2) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 174.86 (12) | C19—C13—C14—C15 | −176.45 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.8 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.9 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.4 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −1.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −2.2 (2) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 1.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.3 (2) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | 1.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 3.4 (2) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | −3.6 (2) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | −175.55 (13) | C19—C13—C18—C17 | 176.32 (14) |
| C6—C1—C7—C8 | 35.8 (2) | C18—C13—C19—C20 | −40.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C7—C8 | −143.15 (14) | C14—C13—C19—C20 | 139.55 (15) |
| C1—C7—C8—C11 | 176.80 (12) | C13—C19—C20—C23 | −176.30 (12) |
| C1—C7—C8—C9 | −0.8 (2) | C13—C19—C20—C21 | −2.2 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −98.93 (15) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 109.04 (15) |
| C11—C8—C9—C10 | 83.34 (14) | C23—C20—C21—C22 | −76.51 (14) |
| C8—C9—C10—O1 | −1.06 (18) | C20—C21—C22—O4 | −3.04 (19) |
| C8—C9—C10—O2 | 179.02 (11) | C20—C21—C22—O5 | 176.86 (11) |
| C7—C8—C11—O3 | 178.72 (13) | C19—C20—C23—O6 | 171.99 (13) |
| C9—C8—C11—O3 | −3.45 (18) | C21—C20—C23—O6 | −2.65 (18) |
| C7—C8—C11—C12 | −1.81 (19) | C19—C20—C23—C24 | −8.0 (2) |
| C9—C8—C11—C12 | 176.02 (12) | C21—C20—C23—C24 | 177.38 (12) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2A···O1i | 0.84 (1) | 1.78 (1) | 2.6226 (13) | 178 (2) |
| O5—H5A···O4ii | 0.86 (1) | 1.74 (1) | 2.6000 (13) | 176 (2) |
| C19—H19···O6iii | 0.95 | 2.60 | 3.447 (1) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: National Science Foundation, Major Research Instrumentation Program (grant No. 1228232).
References
- Abad, N., Sallam, H. H., Al-Ostoot, F. H., Khamees, H. A., Al-horaibi, S. A., Khanum, S. A., Madegowda, M., Hafi, M. E., Mague, J. T., Essassi, E. M. & Ramli, Y. (2021). J. Mol. Struct. 1232, 130004.
- Boukharsa, Y., Meddah, B., Tiendrebeogo, R. T., Ibrahimi, A., Taoufik, J., Cherrah, Y., Benomar, A., Faouzi, M. E. A. & Ansar, M. (2016a). Med. Chem. Res. 25, 494–500.
- Boukharsa, Y., Touré, H. A., Taoufik, J., Benzeid, H. & Ansar, M. (2016b). IUCRData, 1, x162003.
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2012). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2021). APEX3, SAINT and SHELXTL, Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Guerrab, W., El Jemli, M., Akachar, J., Demirtaş, G., Mague, J. T., Taoufik, J., Ibrahimi, A., Ansar, M., Alaoui, K. & Ramli, Y. (2021). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. pp. 1–18. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Guerrab, W., Lgaz, H., Kansiz, S., Mague, J. T., Dege, N., Ansar, M., Marzouki, R., Taoufik, J., Ali, I. H., Chung, I. & Ramli, Y. (2020). J. Mol. Struct. 1205, 127630.
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Manzo, N. (2012). Neurochirurgie, 58, 435.
- Missioui, M., Mortada, S., Guerrab, W., Serdaroğlu, G., Kaya, S., Mague, J. T., Essassi, E. M., Faouzi, M. E. A. & Ramli, Y. (2021). J. Mol. Struct. 1239, 130484.
- Missioui, M., Said, M. A., Demirtaş, G., Mague, J. T., Al-Sulami, A., Al-Kaff, N. S. & Ramli, Y. (2022a). Arab. J. Chem. 15, 103595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Missioui, M., Said, M. A., Demirtaş, G., Mague, J. T. & Ramli, Y. (2022b). J. Mol. Struct. 1247, 131420.
- Mordon, S., Maunoury, V., Bulois, P., Ducrotté, P., Rochon, P. & Boyer, J. (2005). Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 29, 949–954. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, P. R., Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2021). J. Appl. Cryst. 54, 1006–1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tan, S. L., Jotani, M. M. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 308–318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zaoui, Y., Ramli, Y., Tan, S. L., Tiekink, E. R. T., Chemlal, L., Mague, J. T., Taoufik, J., Faouzi, M. E. A. & Ansar, M. (2021). J. Mol. Struct. 1234, 130177.
- Zaoui, Y., Ramli, Y., Taoufik, J., Mague, J. T., Jotani, M. M., Tiekink, E. R. T. & Ansar, M. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 392–396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022004789/vm2263sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022004789/vm2263Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2170436
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report







