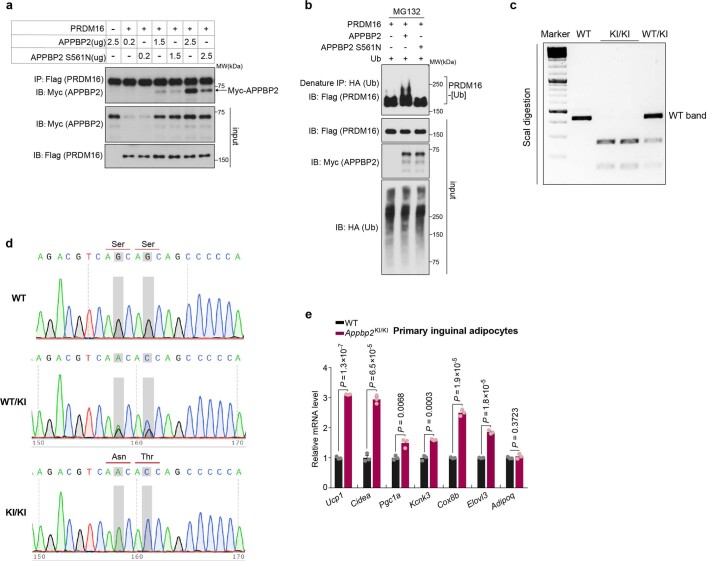
Extended Data Fig. 11. Functional characterization of the human APPBP2 S561N mutant.
a, Protein interaction between PRDM16 and the wild-type (WT) or S561N mutant form of APPBP2. b, PRDM16 polyubiquitination catalysed by the wild-type (WT) or S561N mutant form of APPBP2. c, Genotyping of S561N knock-in mice that carried the S561N mutation in mouse Appbp2 gene by PCR followed by enzymatic digestion with ScaI. d, Sanger sequencing of S561N knock-in mice. Note that the amino acid sequence of APPBP2 is well conserved between mice and humans in the C-terminus with the exception at T562 (S562 for mouse APPBP2, see Extended Data Fig. 10a). To recapitulate the human S561N variant of APPBP2 in mice, we introduced mutations at S561N and S562T of mouse APPBP2. e, Relative mRNA levels of indicated genes in primary inguinal WAT-derived adipocytes from S561N knock-in mice and control (WT) mice. Primary SVFs from the inguinal WAT were differentiated in culture. n = 3 per group, biologically independent samples. Data are mean ± s.e.m.; P-value was determined by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. Representative results in a, b, from two independent experiments. Gel source data are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1.