Abstract
Plant diseases cause significant decreases in yield and quality of crops and consequently pose a very substantial threat to food security. In the continuous search for environmentally friendly crop protection, exploitation of RNA interferance machinery is showing promising results. It is well established that small RNAs (sRNAs) including microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) are involved in the regulation of gene expression via both transcriptional and post-transcriptional RNA silencing. sRNAs from host plants can enter into pathogen cells during invasion and silence pathogen genes. This process has been exploited through Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS), in which plant transgenes that produce sRNAs are engineered to silence pest and pathogen genes. Similarly, exogenously applied sRNAs can enter pest and pathogen cells, either directly or via the hosts, and silence target genes. This process has been exploited in Spray-Induced Gene Silencing (SIGS). Here, we focus on the role of sRNAs and review how they have recently been used against various plant pathogens through HIGS or SIGS-based methods and discuss advantages and drawbacks of these approaches.
Keywords: HIGS, SIGS, sRNA, plant protection, pathogens
Introduction
All plant species are routinely challenged by pests and pathogenic microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, oomycetes, fungi, parasitic plants, or nematodes (Jones and Dangl, 2006;Bilir et al., 2019). Many plant diseases cause substantial damage to crop production, reducing crop quality and leading to substantial economic losses worldwide (Zhu et al., 2019). Concurrently, human population growth has created increasing demand for safe, nutritious and accessible foods produced in an environmentally sustainable manner. Eco-friendly plant protection strategies are an integral component of sustainable intensification to obtain increased crop yields (Liu et al., 2020).
One such strategy is to exploit plant RNA interference machinery (RNAi), which is an evolutionarily conserved regulatory mechanism to combat pathogens and control expression of endogenous genes (Hameed et al., 2017; Iqbal et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020).
In this review, we focus on two different approaches to exploit RNAi for disease control: Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS) and Spray Induced Gene Silencing (SIGS). HIGS is a transgenic technology, where double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) of a pathogen pathogen gene is expressed in the plant and the derivative small RNAs are taken up by the interacting pathogen, triggering silencing of the targeted gene (Sang and Kim, 2020). In contrast, SIGS relies on external application (e.g., spraying) of dsRNAs or small RNAs (sRNAs) that target pathogen genes (Bilir et al., 2019). Both approaches show promise for disease control. Here, we highlight recent advances and challenges.
Small RNA
Small RNAs have been recognized as key genetic and epigenetic regulators functioning in processes ranging from the modification of DNA methylation to the modulation of the abundance of coding or non-coding RNAs in various organisms (Qin et al., 2017). Regulatory sRNAs are involved in diverse biological programs, processes, and pathways in response to developmental signals, pathogen infection and pest attacks (Chen et al., 2014). In plants, sRNAs are versatile regulators of development, growth and response to biotic and abiotic stresses (Yang and Huang, 2014) and are comprised of two major classes – microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). miRNAs are derived from endogenous MIR genes that are transcribed by RNA polymerase II into primary miRNAs (pri-miRNA) having partially double-stranded (ds) stem–loop structures. Processed, mature miRNAs are 20–22 nucleotides in length. siRNAs are 21–24 nucleotides in length and are processed from long double-stranded RNA (Guleria et al., 2011). In contrast to miRNAs, siRNAs can be be produced from endogenous genes and exogenous sources such as viruses, transposons and transgenes (Guleria et al., 2011). Many sub-classes of siRNAs have been described in plants, including tasiRNAs, phasiRNAs, natsiRNAs, and hc−siRNAs (for detailed information seeHuang et al., 2016).
RNAi
RNA interference comprises potent, evolutionarily conserved genetic regulatory mechanisms to silence gene expression (Baulcombe, 2004). One of the major features of RNAi is the production of sRNAs of 21–30 nt in length that can regulate gene expression in a sequence-specific manner. siRNAs generated from dsRNA can guide transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene silencing (TGS and PTGS, respectively;De Felippes, 2019). The most extensively studied sRNA regulators control PTGS by base pairing with mRNA targets, thereby causing their degradation, inhibiting translation, or both (Vaucheret et al., 2001; Chen et al., 2014). Contrastingly, TGS is based on DNA methylation and histone modifications that form a heterochromatic environment around the target gene, restricting access to transcription factors and RNA polymerase (Vaucheret et al., 2001).
Plant immunity
Plants have a complex defense system against various invading pathogens and pests. Plant defense mechanisms against microbes is activated by receptor proteins that recognize two broad categories of pathogen-derived signals. One category, termed microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) is comprised of many classes of molecules, typically recognized by cell surface receptors, activating MAMP-trggered immunity (MTI). The second category is comprised of secreted pathogen virulence proteins called effectors, typically recognized inside plant cells, to activate effector-triggered immunity (ETI) (Jones and Dangl, 2006; Tör et al., 2009). Plant sRNAs have been demonstrated as critical regulators in the reprogramming of gene expression during both PTI and ETI downstream of recognition (Katiyar-Agarwal et al., 2007; Uddin et al., 2017). Moreover, pathogen effector proteins have been shown to target plant RNAi machinery as a means of disabling immunity (Xiong et al., 2014). Finally, recent studies demonstrated that sRNAs can themselves act as effectors by trans-kingdom RNAi (ckRNAi) by translocating from pathogen to host, wherein they silence host genes (Dunker et al., 2020). Altogether, sRNAs play pivotal roles in the link between hosts and their interacting pathogens (Koch et al., 2020). As such, sRNAs have received considerable attention as tools to enhance immunity and attenuate pathogen virulence.
Host-induced gene silencing
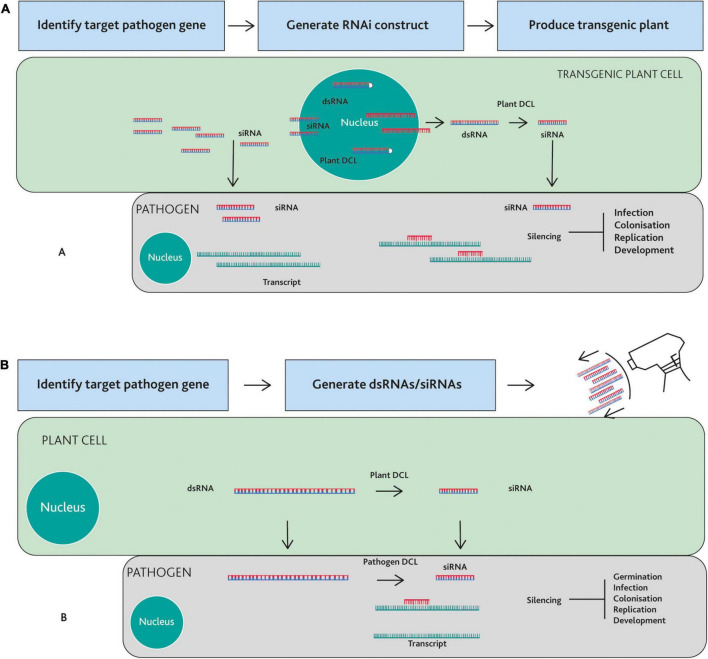
Host-induced gene silencing is a plant transgene-mediated technique, in which plants express an RNAi construct designed against a specific gene(s) endogenous to the pathogen (Santala and Valkonen, 2018). The transgenes typically produce dsRNA or a hairpin-structured dsRNA construct, with sequence identify to a specific pathogen gene. The transgenes can be stably transformed into the host plant; Alternatively, systems for transient transformation can be employed. The transgenic plant transcribes dsRNAs that are processed into siRNAs, which in turn are translocated into the plant pathogens (Figure 1A; Sang and Kim, 2020).
FIGURE 1.
Strategies to control plant pathogens using Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS) or Spray Induced Gene Silencing (SIGS). (A) HIGS: A target gene is identified in the pathogen and an RNAi construct is generated from the part of the target gene sequence. Plants are transformed with the construct and transgenic lines are selected. The transgenic plant cell produces double stranded RNA (dsRNA), which are subjected to the cleavage by the plant Dicer-like (DCL) proteins within the nucleus and/or cytoplasm, producing small interfering RNA (siRNAs) that translocate to the pathogen cell. siRNAs guide the RNA silencing machinery of the pathogen cell to silence mRNAs from the target gene. (B) SIGS: dsRNAs or siRNAs targeting a pathogen gene are synthesized and sprayed onto plants. Sprayed dsRNAs are directly taken up by fungal cells or are taken up by plant cells and then transferred into fungal cells. Plant or pathogen Dicer-like (DCL) proteins cleaves these dsRNAs into siRNAs. In this case, dsRNAs are likely cleaved in the cytoplasm although this process could also occur in the nucleus. Resultant siRNAs guide the RNA silencing machinery of the pathogen cell to silence targeted mRNA. Depending on the function of the target gene, HIGS- or SIGS-mediated gene silencing can lead to inhibition of spore germination, infection, colonization, replication, or development of the pathogen.
The crucial step for a successful HIGS strategy is the identification of suitable target genes in the pathogen (Koch and Kogel, 2014). This is often achieved by analyzing transcriptomic data or a genome database. Once the target genes are identified, an in vitro assay on pathogen cultures could be performed using artificially synthesized siRNAs/dsRNAs that solely target the gene under study. Subsequently, an expression vector is constructed, which, when expressed in plants, generates the dsRNA and siRNA population precisely targeting pathogen transcripts (Ghag, 2017). The other critical step in HIGS is to ensure that the dsRNA and corresponding siRNA species do not exert off-target effects (Koch and Kogel, 2014).
In principle, HIGS could provide a robust tool to down-regulate the expression of key fungal pathogen genes that are required for disease progression in the host (Majumdar et al., 2017). Moreover, HIGS might be used to control multiple diseases of a given crop because constructs can be designed that contain multiple (“stacked”) RNAi transgenes designed against different pathogens (Nowara et al., 2010). Another convenience is that the genes could be designed as “race-specific” or broad-spectrum based on the degree of sequence conservation within the targeted region. For example, Guo et al. (2019) used HIGS to target the MoAp1 in Magnaporthe oryzae (M. oryzae) and achieved improved resistance to 11 different strains of the pathogen with a single construct. Finally, such genes should not affect other plant traits as long a sufficient care is taken to avoid off-target effects. As such, this approach can provide a valuable complement to conventional breeding, or chemical controls, thereby supporting the goal of environmentally friendly and durable resistance in crops (Ghag, 2017; Zhu X. et al., 2017).
Spray-induced gene silencing
Although convenient in many contexts, transgenes are not necessary for ectopic activation of gene silencing in pathogens or pests. Highly effective gene silencing can also be achieved by exogenous application of sRNAs (Ghosh et al., 2018). When the exogenous dsRNAs are applied to plants, they move into pathogen cells and induce RNAi. The RNAs sprayed on the plant surfaces have at least two possible pathways to get into fungal or oomycete cells (Figure 1B; Koch et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2016). Once entering plant cells, dsRNAs are cleaved into sRNAs by plant Dicer-like proteins (DCLs). At the same time, some of these dsRNAs and sRNAs in the plant cells are also transferred into the cells of the fungal or oomycete pathogen. After this trans-kingdom spread, dsRNAs are processed into sRNAs mainly by the fungal DCLs. Alternatively, externally applied dsRNAs and sRNAs can be taken up directly by fungal or oomycete cells. Again, dsRNAs may be cleaved into sRNAs by fungal or oomycete DCLs (Figure 1B).
In practice, exogenous sRNA application has been carried out via surface treatments, such as spraying (Dalakouras et al., 2016) or soaking (San Miguel and Scott, 2016), and invasive methods, such as infiltration (Numata et al., 2014), injection, soil/root drench, or petiole absorption (Ghosh et al., 2017; Dalakouras et al., 2018). Foliar sprays, trunk injections, root drench, or delivery from clay granules can also be used for sustained release of dsRNA (Ghosh et al., 2018). Another promising approach, exemplified in some of the studies described below, is to use transgenic bacteria as a source of sRNA (Niño-Sánchez et al., 2021).
SIGS is an efficient, highly flexible, innovative strategy for crop protection against pathogen infection (Koch et al., 2019;Hu et al., 2020;Sang and Kim, 2020). The main difference and advantage relative to HIGS is that transgenic plants are not necessary, thereby saving the time and money of developing transgenic plants and avoiding the onerous, expensive deregulation as well as issues with acceptance of transgenic plant. However, there are still gaps in our knowledge of the mechanisms underlying SIGS and hurdles to implementation certainly exist (see discussion below andWerner et al., 2020).
sRNA-based antiviral defense
Plants recognize virus infection by an antiviral defense system called virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS,Santala and Valkonen, 2018). Manipulation of this process has become a weapon of choice against viruses in plants (Arif et al., 2012). For example, transgenes producing RNA that triggers RNAi have been at the forefront of resistance to viruses since the mid-1980s. One of the most successful applications of this technology are papaya in Hawaii with transgenes against the otherwise intractable papaya ringspot viruses (Gonsalves, 2006). Table 1 compiles a short list of the latest successful examples.
TABLE 1.
Summary of HIGS and SIGS applications for control of viral pathogens.
| Type of gene silencing | Pathogen | Host | RNA Type | Target Gene(s) | Main Effect(s) | References |
| HIGS | Wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV) | Wheat | hpRNA | NIa gene | Immunity to WSMV infection | Fahim et al., 2010 |
| Wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV) | Wheat | amiRNA-1 amiRNA-2 amiRNA-3 amiRNA-4 amiRNA-5 | 5′ UTR region, ORF pipo region of P3 cistron, P1 gene, P3 cistron, HCpro gene | Immunity to WSMV infection | Fahim et al., 2012 | |
| Rice tungro bacilliform virus (RTBV) | Rice | dsRNA | ORF IV | Decreased accumulation of RTBV in rice plants | Tyagi et al., 2008 | |
| Rice dwarf virus (RDV) | Rice | dsRNA |
Pns12 Psn4 |
Resistance to RDV | Shimizu et al., 2009 | |
| Rice stripe virus (RSV) | Rice | hpRNA |
CP SP CP/SP |
Enhanced resistance against RSV | Ma et al., 2011 | |
| Rice stripe virus (RSV) | Rice | hpRNA |
pC2 pC3 pC4 p4 |
Immunity to infection for pC2 and pC3, non-resistance for pC4 and p4 | Shimizu et al., 2011 | |
| Potato virus X (PVX) Potato virus Y (PVY) Potato leaf roll virus (PLRV) |
Potato | hpRNA |
ORF2 (PVX) HC-Pro (PVY) CP (PLRV) |
Broad-spectrum resistance to all three viruses | Arif et al., 2012 | |
| Potato virus X (PVX) Potato virus Y (PVY) Potato virus S (PVS) |
Potato | hpRNA | CP | Nearly 100% resistance against PVX, PVY, and PVS infection | Hameed et al., 2017 | |
| African cassava mosaic virus (ACMV) | Tobacco | dsRNA |
AC1 AC2 AC4 BC1 |
Resistance to bipartite geminivirus infection | Patil et al., 2016 | |
| Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) Bean yellow mosaic virus (BYMV) |
Tobacco | hpRNA | CP | Increased resistance of soybean to SMV and BYMV | Thu et al., 2016 | |
| Ugandan cassava brown streak virus (UCBSV) and Cassava brown streak virus (CBSV) | Tobacco | amiRNA |
P1 (CBSV and UCBSV) P3 (CBSV and UCBSV) CI (UCBSV) Nib (CBSV and UCBSV) |
Resistance against UCBSV and CBSV | Wagaba et al., 2016a | |
| Ugandan cassava brown streak virus (UCBSV) and Cassava brown streak virus (CBSV) | Tobacco | amiRNA | CP | High levels of resistance to both viruses | Wagaba et al., 2016b | |
| Tomato leaf curl Gujarat virus (ToLCGV) | Tobacco | siRNAs |
COP9 PPRP GPX-1 USP HSTF-B4 ARF18 WRKY-6 SDR |
Decreased expression of subunit-7 of CSN complex and WRKY6, increased expression of USPA-like protein | Prakash et al., 2020 | |
| Cucumber necrosis virus (CNV) | Tobacco | dsRNA | CP | Interfered with chloroplast-mediated plant defense | Alam et al., 2021 | |
| Pepper mottle virus (PepMoV) | Tobacco | dsRNA |
HC-Pro NIb |
Defended the host against viral infection instantly and inhibited viral growth effect | Yoon et al., 2021 | |
| Cowpea severe mosaic virus (CPSMV), Cowpea aphid-borne mosaic virus (CABMV) | Cowpea | hpRNA |
32K protein CP |
Resistance to CPSMV and CABMV | Cruz and Aragao, 2014 | |
| Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) | Soybean | hpRNA | HC-Pro | Strong viral resistance | Kim et al., 2016 | |
| Cassava brown streak virus (CBSV), Uganda cassava brown streak virus (UCBSV) | Cassava | hpRNA | CP | High levels of resistance to both viruses | Beyene et al., 2017 | |
| Co-inoculation-spraying | Sugarcane Mosaic Virus (SCMV) | Sugarcane | dsRNA with bacterial expression | CP | Inhibited SCMV infection | Gan et al., 2010 |
| SIGS (spraying) | Pea seed borne mosaic virus (PSbMV) | Pea | dsRNA | CP | Significant short-term reduction in the virus concentration, reduced viral titer | Safarova et al., 2014 |
| Bioclay- spraying | Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) and cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) | Tobacco Cowpea | dsRNA with bacterial expression | RP gene of PMMoV, 2b of CMV2b | Increased stability and protection period | Mitter et al., 2017 |
| Bioclay-spraying | Potyvirus bean common mosaic virus (BCMV) | Tobacco Cowpea |
dsRNAs with bacterial expression |
NIb CP |
Protected plants from aphid-transmission of BCMV | Worrall et al., 2019 |
hpRNA, hairpin RNA; amiRNA, artificial microRNA; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
Spray-induced gene silencing has been explored for protection of plants against viruses. Some studies have investigated the use of crude extracts of bacterially expressed dsRNA to protect plants against virus infections. Tenllado et al. (2003) tested a foliar spray of crude extracts of bacterially expressed dsRNA for protection of N. benthamiana against Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) or Plum pox virus (PPV). Following viral inoculation at 5 days after dsRNA application, the dsRNAs caused specific degradation of viral RNA and protection of the plants against viral infection. Notably, spraying plants with a crude bacterial preparation resulted in the dsRNA providing similar protection. In a similar experiment, Gan et al. (2010) sprayed maize with a crude extract of bacterially synthesized dsRNA derived from two fragments of the Sugarcane Mosaic Virus (SCMV) CP gene. Plants were inoculated with the virus 3 days after spraying with a half-strength extract and inhibition of viral infection was observed. In a different approach, Mitter et al. (2017) constructed a topical spray of layered double hydroxide (LDH) clay nanosheets loaded with dsRNA (BioClay) for protection of tobacco and cowpea against cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) or pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV). In contrast to naked dsRNA, which can be unstable, a single spray of bacterially expressed dsRNA loaded on BioClay could provide virus protection for at least 20 days, presumably due to sustained release of the dsRNA (Table 1).
sRNA-based protection of plants from bacterial invasion
Although bacteria do not have an RNAi machinery similar to eukaryotes, they do contain gene regulation mechanisms that employ RNA molecules. These include CRISPR RNAs that inhibit the uptake of foreign DNA and small RNA, which bind to proteins or base pair with target RNAs (Waters and Storz, 2009). Escobar et al. (2001) developed a HIGS-based strategy to improve resistance to Agrobacterium crown gall based on knowledge of the iaaM and ipt oncogenes, which are required for tumor formation. Arabidopsis thaliana and Lycopersicon esculentum plants were transformed with constructs to initiate RNAi against these two oncogenes. Following infection with A. tumefaciens, the transformed A. thaliana and L. esculentum plants displayed 0.0–1.5% tumorigenesis and 0.0 – 24.2% tumorigenesis, respectively, compared to nearly 100% in controls. Subsequent molecular investigation confirmed significant reduction in the accumulation of both iaaM and ipt transcripts in the transgenic line as compared with the wild type (Escobar et al., 2001). Similar work has also been carried out with walnut, and the silencing iaaM and ipt genes has been shown to decrease crown gall formation (Walawage et al., 2013).
Another approach to control bacterial pathogens using HIGS is the targeting of the host susceptibility genes. For example, the rice gene Os8N3 provides susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strain PXO99A (Yang et al., 2006). When Os8N3 was targeted with a HIGS system, transgenic plants became resistant to this strain of X. oryzae pv. oryzae.
Mahmoudi and Soleimani (2019) used HIGS and revealed that the expression of the aiiA gene in potato could reduce the N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum sensing signal and consequently enhance resistance to bacterial soft rot disease (Table 2). To our knowledge, there is no SIGS-based studies against bacterial plant pathogens.
TABLE 2.
Summary of HIGS applications for control of bacterial pathogens.
| Pathogen | Host | RNA type | Target gene(s) | Main effect(s) | References |
| A. tumefaciens | Arabidopsis Tobaco |
siRNA |
iaaM ags |
Inhibited infection | Dunoyer et al., 2006 |
| A. tumefaciens | Rice | hpRNA |
OsPDS OsSLR1 |
Triggered degradation of target transcripts in the adjacent tissues | Andrieu et al., 2012 |
| A. tumefaciens | Walnut | dsRNA |
iaaM ipt |
Decreased crown gall formation | Walawage et al., 2013 |
| A. tumefaciens | Plum Apricot |
hpRNA |
iaaM ipt |
Induces resistance to crown gall disease in plum but not in apricot | Alburquerque et al., 2017 |
| Pectobacterium carotovorum (Soft rot) | Potato | miRNA | aiiA | Induced resistance to the early stage of bacterial pathogenesis | Mahmoudi and Soleimani, 2019 |
hpRNA, hairpin RNA; dsRNA-Double-stranded RNA; siRNA, Small interfering RNA; miRNA, micro RNA.
Host-induced gene silencing-based protection of plants from fungal infection
Small RNAs strategies have been tested against plant pathogenic fungi and, to a lesser extent, oomycetes (Table 3). A large number of studies have focused on fungal pathogens of wheat and barley, using HIGS from transient viral expression vectors or from stably integrated transgenes. For example, Panwar et al. (2013) evaluated the efficiency of HIGS induced by transient transformation of wheat with a barley stripe mosaic virus (BSMV) construct targeting a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), a cyclophilin, and a calcineurin regulatory subunit in the wheat leaf rust fungus Puccinia triticina (Pt). They reported a reduction in endogenous transcript levels, suggesting the translocation of siRNA molecules from host to fungal cells. In addition, the subsequent disease suppression implicated the targeted fungal genes in pathogenicity. In another study from the same group, HIGS-based targeting of PtMAPK1 or PtCYC1 impaired fungal development and reduced disease severity in wheat (Panwar et al., 2018). Qi et al. (2017) used BSMV−mediated HIGS to silence the PsCPK1 gene of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst). They demonstrated that PsCPK1 is an important pathogenicity factor for Pst, and knockdown of PsCPK1 led to decreased virulence of Pst. Similarly, Zhu X. et al. (2017) demonstrated PsFUZ7 was a pathogenicity factor that regulated infection and development of Pst. They observed strong restriction of hyphal development and necrosis of plant cells (a possible defense response) within siRNA-producing host tissue. These examples demonstrate that transient transformation can be used to induce HIGS and test the functional importance of candidate fungal virulence genes. This approach can be used to quickly test candidate target genes for HIGS-based disease control before investing effort into creation of stable transgenic plants.
TABLE 3.
Summary of HIGS and SIGS applications for control of fungal and oomycete pathogens.
| Type of gene silencing | Pathogen | Host | RNA type | Target gene(s) | Main effect(s) | References |
| HIGS | Puccinia triticina/Wheat Leaf Rust | Wheat | siRNA | PtMAPK1 PtCYC1 PtCNB | Reduction in endogenous transcript levels | Panwar et al., 2013 |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium head blight and Fusarium seedling blight | Wheat | hpRNA | Chs3b | Durable resistance to Fusarium head blight and seedling blight in wheat | Cheng et al., 2015 | |
| Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici/Wheat Stripe Rust | Wheat | hpRNA | PsCPK1 | Decreased virulence of Pst | Qi et al., 2017 | |
| Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici/Wheat Stripe Rust | Wheat | dsRNA | PsFUZ7 | Strong restriction of hyphal development | Zhu X. et al., 2017 | |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Wheat | miRNA | FGSG_03101 | Suppressed invasion of F. graminearum | Jiao and Peng, 2018 | |
| Puccinia triticina/Wheat Leaf Rust | Wheat | hpRNA |
PtMAPK1 PtCYC1 |
Impaired fungal development and a reduction in disease severity and progression in wheat plants | Panwar et al., 2018 | |
| Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici/Wheat Powdery Mildew | Wheat | dsRNA | β2-tubulin, SvrPm3a1/f1 Bgt_Bcg-6 Bgt_Bcg-7 |
Impaired virulence of B. g. tritici at the haustorial stage | Schaefer et al., 2020 | |
| Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici/Wheat Stripe Rust | Wheat | TaCSN5 | Broad−spectrum resistance to wheat stripe rust | Bai et al., 2021 | ||
| Blumeria graminis/Powdery Mildew | Wheat Barley |
mRNA | Avra10 | Reduction in haustorium formation | Nowara et al., 2010 | |
| Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei/Barley Powdery Mildew | Barley | siRNA |
CSEP0062 CSEP0081 CSEP0145 CSEP0216 CSEP0222 CSEP0254 CSEP0398 |
Reduced rate of fungal penetration and haustoria formation | Ahmed et al., 2016 | |
| Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei/Barley Powdery Mildew | Barley | hpRNA | CSEP0139 CSEP0182 | Reduced haustorial formation and size of the lesions | Li et al., 2021 | |
| Rhizoctonia solani/Sheath Blight | Rice | hpRNA |
RPMK1-1 RPMK1-2 |
Reduced R. solani infection | Tiwari et al., 2017 | |
| Magnaporthe oryzae/Rice Blast Fungus | Rice | siRNA |
MoABC1 MoMAC1 MoPMK1 |
Inhibited disease development and reduced the transcription of the genes | Zhu L. et al., 2017 | |
| Magnaporthe oryzae/Rice Blast Fungus | Rice | asiR1245 asiR1362 asiR1115 |
MoAP1 | Inhibited disease development and reduced the transcription of targeted fungal genes | Guo et al., 2019 | |
| Aspergillus flavus/Aspergillus Ear Rot | Maize | siRNAs | aflR | Reduction to aflatoxin accumulation in transgenic maize | Masanga et al., 2015 | |
| Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus parasiticus | Maize | siRNAs | aflC | Reduced aflatoxin below the regulatory threshold | Thakare et al., 2017 | |
| Aspergillus flavus/Aspergillus Ear Rot | Maize | siRNA | aflM | Reduced aflatoxin contamination | Raruang et al., 2020 | |
| Phytophthora infestans/Potato Late Blight | Potato | hpRNA |
PiGPB1 PiCESA2 PiPEC PiGAPDH |
Enhanced resistance to the late blight disease | Jahan et al., 2015 | |
| Phytophthora infestans/Potato Late Blight | Potato | siRNA | Avr3a | Inhibition of target gene expression in P. infestans | Sanju et al., 2015 | |
| Sclerotinia sclerotiorum/White Mold | Tobacco | hpRNA | Chs | Reduction in the level of CHS endogenous transcripts | Andrade et al., 2016 | |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. cubense/Fusarium Wilt | Banana | ihpRNA |
VEL FTF1 |
Reduced growth and decreased pathogenesis | Ghag et al., 2014 | |
| Fusarium oxysporum/Fusarium Wilt | Banana | ihpRNA | Foc TR4 ERG6/11 | Inhibition of growth and development of Foc TR4 | Dou et al., 2020 | |
| Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici/Tomato Fusarium Wilt | Tomato | hpRNA |
FOW2 chsV |
Inhibited fungal growth and increased resistance to the pathogen | Bharti et al., 2017 | |
| Colletotrichum gloeosporioides/Anthracnose | Chilly Tomato | siRNA | CgCOM1 | Confers resistance against anthracnose disease in chilly and tomato | Mahto et al., 2020 | |
| Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici/Tomato Fusarium Wilt | Tomato | siRNA | ODC | Inhibited fungal growth and increased resistance to the pathogen | Singh et al., 2020 | |
| Verticillium dahliae/Verticillium Wilt | Tomato Arabidopsis | hpRNA |
Ave1 Sge1 NLP1 |
Reduced the disease | Song and Thomma, 2018 | |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Arabidopsis and Barley | dsRNA | CYP51 | Growth inhibition and alteration in fungal morphology | Koch et al., 2013 | |
| Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. conglutinans/Anthracnose | Arabidopsis | dsRNA |
FRP1 FOW2 OPR |
Enhanced disease resistance | Hu et al., 2015 | |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Arabidopsis | dsRNA |
FgCYP51A FgCYP51 FgCYP51C |
Reduction in infection | Höfle et al., 2020 | |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Arabidopsis | dsRNA |
CYP51A CYP51B CYP51C |
Inhibited growth of F. graminearum | Koch et al., 2020 | |
| Verticillium dahliae/Verticillium Wilt | Tobacco Arabidopsis |
sRNA | VdAK | Decreased mycelial growth and spore production during abiotic stress | Su et al., 2020 | |
| Phakopsora pachyrhizi/Asian Soybean Rust | Soybean | siRNA |
ATC UN_1 UN_2 UN_3 GCS_H PR_S16 CRP_6 PHR |
Reduced endogenous P. pachyrhizi transcript abundance, fungal biomass accumulation and the development of the disease symptoms; suppressed the expression of target genes | Hu et al., 2020 | |
| Fusarium oxysporum, Fusarium graminearum | Soybean | ihpRNA | CYP51B | Mild or no symptoms in leaves and root of three lines of six transgenic lines and better plant development | Perez et al., 2021 | |
| Bremia lactucae/Down Mildew Lettuce | Lettuce | siRNA |
HAM34 CES1 |
Reduced growth and inhibited sporulation of the pathogen | Govindarajulu et al., 2015 | |
| Rhizoctonia solani/Brown Patch | Tall Fescue | dsRNA |
RNApoly Imbs Coh UbiE3 |
Improved resistance against R. solani and reduced lesion size | Zhou et al., 2016 | |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Purple False Brom | dsRNA |
Fg00677 Fg08731 CYP51 |
Reduced pathogenicity of the fungus | He et al., 2019 | |
| Verticillium dahlia/Verticillium Wilt | Cotton |
VdILV2 VdILV6 |
A dramatic reduction in pathogenicity | Wei et al., 2020 | ||
| Rhizoctonia solani/Sheath Blight | Tomato | dsRNA | RS_CRZ1 | Significant reduction in disease symptoms and the depth of pathogen colonization | Ghosh et al., 2021 | |
| Cytospora chrysosperma/Cytospora Canker | Canadian poplar | Sge1 | Restricted vegetative growth, conidial reduction and lost pathogenicity | Han et al., 2021 | ||
| Arbuscular mycorrhizal | Medicago | RiNLE1 | Suppression of defense−related gene expression and enhanced colonization levels | Wang et al., 2021 | ||
| SIGS | Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Barley | dsRNA |
CYP51A CYP51B CYP51C |
Inhibited the growth of the necrotrophic fungus | Koch et al., 2016 |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Barley | dsRNA |
CYP51A CYP51B CYP51C |
Reduced F. graminearum infection areas | Koch et al., 2020 | |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Barley | dsRNA |
FgAGO1 FgAGO2 FgDCL1 FgDCL2 |
Reduced inhibition of fungal infection | Werner et al., 2020 | |
| Sclerotinia sclerotiorum/White Mold | Barley | dsRNA |
Ss-ThioR Ss-TIM44 Ss-CHC SS-AP2 Ss-Arf72A Ss-FCHO1 Ss-Amph Ss-VATPase Ss-eGFP |
Significantly reduced pathogen growth on plant | Wytinck et al., 2020 | |
| Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis (Hpa)/Downy Mildew | Arabidopsis | dsRNA | Hpa-CesA | Inhibited spore germination and infection | Bilir et al., 2019 | |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Arabidopsis | dsRNA |
FgCYP51A FgCYP51 FgCYP51C |
Increased disease resistance | Höfle et al., 2020 | |
| Botrytis cinerea/Gray Mold Rot | Tomato Strawberry Grape Lettuce Onion Rose Arabidopsis |
sRNAs dsRNA |
Bc-DCL1 Bc-DLC2 |
Inhibition of fungal growth, reduced symptoms of the disease and suppressed fungal DCL transcripts | Wang et al., 2016 | |
| Fusarium graminearum/Fusarium Head Blight | Wheat | dsRNA | Myosin 5 | Reduction in phenamacril-resistance | Song et al., 2018 | |
| F. asiaticum, B. cinerea, Magnaporthe oryzae, Colletotrichum truncatum | Cucumber Soya Barley Wheat |
dsRNA | Faβ2Tub-3 | Decreased resistance to carbendazim fungicide, inhibited fungal growth and lead to crooked and multiple-branching mycelium | Gu et al., 2019 | |
| Botrytis cinerea/Gray Mold Rot | Grapevine | dsRNA |
BcCYP51 Bcchs1 BcEF2 |
Significant reduction in pathogen development | Nerva et al., 2020 | |
| Phakopsora pachyrhizi/Soybean Rust | Soybean | dsRNA |
ATC GCS_H RP_S16 |
Reduction in fungal biomass and a lower number of pustules on leaves | Hu et al., 2020 | |
| Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Rhizoctonia solani, Aspergillus niger, Verticillium dahlia, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Trichoderma virens, Phytophthora infestans | Lettuce Tomato Rose Grape |
dsRNA |
VPS51 DCTN1 SAC1 |
Inhibited the virulence of B. cinerea, S. sclerotiorum, A. niger, R. solani, reduced disease symptoms by V. dahlia, no significant reduction in targeted mRNA expression levels at the P. infestans inoculated, no inhibition of infection of C. gloeosporioides | Qiao et al., 2021 | |
| Phytophthora infestans/Potato Late Blight | Potato | dsRNA |
SDH EF-1α GPI-HAM344 PLD-3 HSP-90 |
Enhanced disease resistance and less sporulation | Sundaresha et al., 2021 | |
| Plasmopara viticola/Grapevine downy mildew | Grapevine | dsRNA | PvDCL1/2 | Reduced disease progress rate | Haile et al., 2021 | |
| Phytophthora infestans/Potato late blight | Potato | dsRNA |
PiGPB1 PiHmp1 PiCut3 PiEndo3 |
Reduction in disease progression | Kalyandurg et al., 2021 |
hpRNA, hairpin RNA; ihpRNA, intron-containing hairpin RNA; miRNA, micro RNA; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; siRNA, small interfering RNA; asiRNA artificial siRNA.
Schaefer et al. (2020) created stable transgenic wheat lines for HIGS against the powdery mildew pathogen Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici. They targeted β2-tubulin, SvrPm3a1/f1, Bgt_Bcg-6 and Bgt_Bcg-7 genes of B.g. tritici. Their results suggested that silencing of these three target effectors impaired virulence of B.g. tritici at the haustorial stage indicating each gene contributes to the pathogen’s virulence. Similarly, HIGS targeting the effector gene Avra10 was used to protect wheat and barley against Blumeria graminis (Nowara et al., 2010). Ahmed et al. (2016) used HIGS in barley against 7 candidate secreted effector proteins of B. graminis f. sp. hordei (Bgh). They determined that only the silencing of CSEP0081 and CSEP0254 significantly reduced the rate of fungal penetration and haustoria formation, demonstrating their role as virulence factors (Table 2).
Jiao and Peng (2018) screened wheat sRNAs that could target the F. graminearum genome by silencing with BSMV. They found that a wheat microRNA (miR1023) could suppress the invasion of F. graminearum by silencing FGSG_03101, coding for an alpha/beta hydrolase in the fungus. Koch et al. (2013) evaluated the potential of HIGS targeting the fungal cytochrome P450 lanosterol C-14α-demethylase (CYP51) gene, which is important for ergosterol biosynthesis, to restrict infection of Arabidopsis and barley plants by Fusarium spp. They observed both growth inhibition and alteration in fungal morphology in axenic cultures of F. graminearum and restriction of mycelium formation on leaves expressing anti-CYP3 RNA. In another study, HIGS against cytochrome P450 sterol 14α-demethylase genes (CYP51A and CYP51B) in Arabidopsis inhibited the growth of F. graminearum (Koch et al., 2020). HIGS constructs targeting F. graminearum genes Fg00677 and Fg08731 in transgenic Brachypodium distachyon conferred resistance to this wheat pathogen, demonstrating that Brachypodium could be used as a facile test system for HIGS to enhance resistance in wheat (He et al., 2019).
Host-induced gene silencing also shows promise against Fusarium pathogens of dicot food crops. In banana, two F. oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) gene were targeted using HIGS, resulting in decreased pathogenesis (Ghag et al., 2014). Similarly, Dou et al. (2020) reported inhibition of Foc growth and development on transgenic bananas with HIGS constructs that targeted two ergosterol biosynthetic genes. HIGS technology was also used against the tomato wilt pathogen F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. In one study, FOW2 and chsV genes (Bharti et al., 2017), in another study, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) were targeted (Singh et al., 2020); both studies reported that silencing these genes inhibited fungal growth and increased resistance to the pathogen.
Mahto et al. (2020) HIGS against the Colletotrichum gloeosporioides COM1 (CgCOM1) gene, which is involved in fungal conidial and appressorium formation, inhibits the development of the appressorial/infection apparatus of the pathogenic fungi in chilly and tomato fruits and results in the prevention of manifestation of anthracnose disease in the plant.
Host-induced gene silencing also shows promise against the destructive rice blast disease caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Zhu L. et al. (2017) targeted MoABC1, MoMAC1, and MoPMK1 genes from M. oryzae to examine the effectiveness of transient, BMV-mediated HIGS in rice. They documented that mRNA abundance of the targeted genes was reduced and disease development was inhibited. In a SIGS-based approach against the same disease, Guo et al. (2019) showed silencing of M. oryzae MoAP1 by feeding artificial siRNAs (asiRNAs) to in vitro cultures of Magnaporthe oryzae, which resulted in the inhibition of disease development and reduced the transcription of targeted fungal genes.
In an example of how multiple pathogen genes can be simultaneously targeted from a single HIGS transgene, Tiwari et al. (2017) transformed rice with a hairpin RNAi construct containing a fusion of two Pathogenicity Map Kinase 1 (PKM1) genes, RPMK1-1 and RPMK1-2 of Rhizoctonia solani, which are essential for the formation of appressoria. The expression level of both RPMK1-1 and RPMK1-2 was significantly reduced in R. solani infecting transgenic rice lines. Zhou et al. (2016) transformed tall fescue with RNAi constructs of four “essential” genes from R. solani. They found that six of 19 transgenic plants showed improved resistance against R. solani and lesion size was decreased by as much as 90% indicating the value of multiple HIGS constructs for controlling the disease.
In a creative approach to reduce aflatoxin contamination of corn, Masanga et al. (2015) transformed plants with a hairpin construct targeting the aflatoxin biosynthesis transcription factor aflR of Aspergillus flavus and reported that aflR was downregulated and significantly lower levels of aflatoxins (14-fold) than those from wild type plants were observed. Thakare et al. (2017) determined that aflC gene encodes an enzyme in the A. flavus aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway and then transformed maize plants with an RNAi construct targeting the aflC gene. Following A. flavus infection, aflatoxin could not be detected in kernels from these RNAi transgenic maize plants, while non-transgenic control kernels showed high toxin loads. Recently, HIGS targeting A. flavus aflM gene encoding versicolorin dehydrogenase reduced aflatoxin contamination in transgenic maize under field conditions (Raruang et al., 2020). These results indicate that aflatoxin levels can be effectively reduced by targeting the mycotoxin biosynthetic pathway, without producing any overt off-target effects on the host crop plant.
The fungal pathogen Verticillium dahliae causes several destructive diseases. Hu et al. (2015) generated stable transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing RNAi constructs targeting three V. dahliae virulence genes. Verticillium wilt disease was suppressed by two of the three targets in transgenic Arabidopsis. Targeting the same three genes in tomato with transient viral expression resulted in disease suppression from only one of the three genes. In cotton, HIGS against two V. dahliae acetolactate synthase genes reduced pathogenicity dramatically, indicating that these genes are essential for pathogenicity of V. dahliae (Wei et al., 2020). Song and Thomma (2018) investigated whether HIGS can be utilized to suppress Verticillium wilt disease by silencing three previously identified virulence genes of V. dahliae (Ave1, Sge1, and NLP1) through the host plants tomato and Arabidopsis. In these hosts, V. dahliae infection studies showed reduced Verticillium wilt disease in HIGS experiments targeting two of the three genes. Su et al. (2020) generated transgenic N. benthamiana and A. thaliana harboring dsVdAK to silence VdAK gene of V. dahlia by HIGS. They reported that VdAK was crucial for energy metabolism and that silencing of this gene decreased mycelial growth and spore production during abiotic stress. This study illustrates the important point that the effectiveness of sRNA-based protection can be affected positively or negatively by environmental conditions.
Spray-induced gene silencing against fungal pathogens
In a pioneering study to test SIGS in multiple host plants against multiple fungal pathogens, Wang et al. (2016) applied Bc-sRNAs and dsRNAs onto the surface of fruits, vegetables and flowers; they determined that B. cinerea could take up both sRNAs and dsRNAs directly, and both could induce silencing of B. cinerea DCL1 and DCL2 genes. They found significant inhibition of fungal growth, decreased symptoms of gray mold disease and supressed fungal DCL transcripts. Also, Gu et al. (2019) determined that a β2-tubulin dsRNA derived from Fusarium asiaticum conferred plant resistance to multiple phytopathogens including F. asiaticum, F. graminearum, F. tricinctum, F. oxysporum, F. fujikuroi, B. cinerea, M. oryzae, and Colletotrichum truncatum and reduced resistance to carbendazim fungicide, inhibited fungal growth, and caused deformed and multiple-branching mycelium (Table 3). These studies indicate that SIGS is a broadly applicable tool for plant protection.
The SIGS method has recently been adopted against fungal wheat pathogens. For example, a spray application of a long non-coding dsRNA targeting the three fungal cytochrome P450 lanosterol C-14α-demethylases (CYP51A, CYP51B, CYP51C) inhibited the growth of F. graminearum in barley leaf tissue (Koch et al., 2016). Koch et al. (2020) sprayed whole barley plants with the 791-nt long F. graminearum CYP3-dsRNA. Hypocotyls of plants sprayed with CYP3-dsRNA developed fewer disease lesions compared to control plants, while CYP51-dsRNAs reduced F. graminearum infection areas by the factor of 80. In another study, Werner et al. (2020) sprayed dsRNAs targeting ARGONAUTE and DICER genes of F. graminearum, resulting in approximately 50% inhibition of fungal infection. In wheat, dsRNAs targeting the Myo5 gene of phenamacril-resistant F. asiaticum were applied on plants and high levels of host resistance were observed (Song et al., 2018). Höfle et al. (2020) tested HIGS and SIGS approaches with dsRNA precursors of increasing length ranging from 400 to 1,500 nt to assess the effect of lengthy on gene silencing efficiency of FgCYP51 genes. With HIGS-mediated disease control, they found no significant correlation between the length of the dsRNA precursor and the reduction of F. graminearum infection on Arabidopsis. Contrastingly, they observed that SIGS-mediated F. graminearum disease resistance negatively correlated with the length of the dsRNA construct that was sprayed, suggesting that increased size of the dsRNA interferes with uptake of dsRNAs by the fungus.
In soybean experiments, Hu et al. (2020) used both SIGS and HIGS to target genes of the rust pathogen Phakopsora pachyrhizi. First, eight genes involved in urediniospore germination or appressorium formation were targeted through a BPMV-based transient HIGS approach. HIGS against ATC, GCS_H and RP_S16 reduced fungal biomass accumulation by 58–80%, respectively, and significantly reduced the development of asian soybean rust symptoms in soybean leaves (Table 3). In a SIGS study, spraying soybean leaves with dsRNA of ATC, GCS_H, and RP_S16 achieved a reduction in the biomass of P. pachyrhizi of about 17.0, 20.9, and 25.1%, for each target gene, respectively (Hu et al., 2020). sRNA approaches could be particularly valuable for this pathogen, given the paucity of effective rust resistance genes in soybean germplasm Similarly, Nerva et al. (2020) applied dsRNA targeting Botrytis cinerea (Bc) genes BcCYP51, Bcchs1, and BcEF2 by high pressure spraying of grapevine leaves and postharvest spraying of grape bunches. Their results showed a significant reduction in pathogen development only when Bc dsRNAs were applied.
Host-induced gene silencing and spray-induced gene silencing against oomycetes
Compared to the extensive work on fungi, sRNA-based studies involving oomycetes are relatively scant. The first, by Sanju et al. (2015), targeted the Avr3a effector gene of the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Disease severity decreased and production of siRNA molecules in host cells resulted in the inhibition of target gene expression in P. infestans through HIGS. Jahan et al. (2015) concluded that the choice of target genes and precursor hairpin-RNA is crucial for obtaining successful results from HIGS against the late blight pathogen Phytophthora infestans. The authors found that transgenic potato lines carrying targeted hairpin-RNA constructs to Cellulose Synthase A2 (PiCESA2), Pectinesterase (PiPEC), and Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (PiGAPDH) demonstrated weaker resistance to the late blight disease than transgenic potato lines expressing hairpin-RNA constructs targeting P. infestans G proteinβ-subunit (PiGPB1). HIGS studies with lettuce targeting the Highly Abundant Message #34 (HAM34) or Cellulose Synthase (CES1) genes of the biotrophic downy mildew pathogen Bremia lactucae greatly reduced the growth and inhibited sporulation of the pathogen (Govindarajulu et al., 2015). Bilir et al. (2019) explored SIGS against an oomycete by targeting the Cellulose synthase A3 (CesA3) gene of Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis (Hpa), the downy mildew pathogen of Arabidopsis. They reported that antisense sRNAs targeting the Hpa-CesA3 gene in Emoy2 and Cala2 isolates inhibited spore germination and thus infection of Arabidopsis, while sense sRNAs had no obvious effect on Hpa pathogenicity. When Haile et al. (2021) used dsRNA targeting the DCL1 and DCL2 genes in grapevine downy mildew pathogen Plasmopara viticola, they observed reduction in the expression level of these genes as well as in the disease progress rate in the already established infection. Similar SIGS studies with dsRNA against the late blight pathogen P. infestans has been carried out by Kalyandurg et al. (2021). They have targeted several genes including PiGPB1, PiHmp1, PiCut3, and PiEndo3 and through careful evaluation, they have concluded that some of these genes inhibited the pathogen development significantly. To improve the the efficacy of SIGS against P. infestans, Kalyandurg et al. (2021) recommended a few parameters including the use of adjuvants with dsRNA in the experiments.
The encouraging results from these studies should inspire more investment in sRNA-based approaches against oomycetes.
sRNA-based protection of plants from nematodes
Host-induced gene silencing has successfully been used to control plant parasitic nematodes, including cyst nematodes (Alkharouf et al., 2007), root-knot nematodes (Huang et al., 2006), and recently, root lesion nematodes (Shivakumara et al., 2017; Chaudhary et al., 2019). For example, Huang et al. (2006) found that expression of dsRNAs in transgenic Arabidopsis that initiate siRNAs targeting the nematode parasitism gene 16D10 could reduce infestation by nematodes. Verma et al. (2018) demonstrated that the 30D08 effector protein is secreted from the nematode stylet into Arabidopsis cells and reported that plant-derived RNAi silencing of 30D08 decreased susceptibility to nematodes. Another study demonstrated that infection by root-knot nematodes is facilitated by the effector Mi-msp2. Arabidopsis lines expressing Mi-msp2 dsRNA exhibited a significant reduction in nematodes (Joshi et al., 2019). Iqbal et al. (2020) used HIGS to study the effects of 20 genes involved in the RNA interference (RNAi) pathways in Meloidogyne incognita. Expression of ego-1 and mes-2 could not be eliminated, and expression of xpo-1, pash-1, xpo-2, rha-1, ekl-4, and csr-1 was significantly elevated after RNAi treatment. However, there were significant decreases in expression of other genes indicating that genes can respond to RNAi differently, requiring an exhaustive assessment of target nematode genes by RNAi. Dinh et al. (2014) reported that HIGS-mediated downregulation of the putative effector gene Mc16D10L ensures a significant level of resistance against M. chitwoodi not only in Arabidopsis but also in stable transgenic lines of potato (Table 4).
TABLE 4.
Summary of HIGS application for control of nematodes.
| Pathogen | Host | RNA type | Target gene(s) | Main effect(s) | References |
| M. incognita, M. javanica, M. arenaria, M. hapla/Root-knot nematodes | Arabidopsis | dsRNA | 16D10 | Resistant to multiple root-knot nematode species | Huang et al., 2006 |
| Heterodera schachtii/Sugar beet cyst nematode | Arabidopsis | dsRNA | 30D08 | Less susceptible to nematode infection | Verma et al., 2018 |
|
M. hapla, M. arenaria M. graminicola/Root-knot nematode |
Arabidopsis | dsRNA | Mi-msp2 | Reduced parasitism | Joshi et al., 2019 |
| Meloidogyne incognita/Root-knot nematode | Arabidopsis | dsRNA |
rsd-3 xpo-1 xpo-2 drh-3 drsh-1 pash-1 vig-1 ego-1 smg-2 smg-6 eri-1 gfl-1 mut-7 mes-2 mes-6 rha-1 ekl-4 ppw-2 csr-1 2242 |
Significant reduction in nematode infectivity for drsh-1, mut-7, drh-3, rha-1, pash-1, and vig-1 genes | Iqbal et al., 2020 |
| Meloidogyne chitwoodi/Root-knot nematode | Arabidopsis Potato |
dsRNA | 16D10 | Enhanced resistance against Meloidogyne chitwoodi in two plants | Dinh et al., 2014 |
| Meloidogyne incognita/Root-knot nematode | Chardonnay grape | siRNA | 16D10 | Inhibition of the nematode infection | Yang et al., 2013 |
| Meloidogyne incognita/Southern root-knot nematode | Eggplant | dsRNA/ siRNA |
msp-18 msp-20 |
Improved resistance in eggplant | Shivakumara et al., 2017 |
| Meloidogyne incognita/Root-knot nematode | Adzuki bean Tobacco |
dsRNA | Mi-sbp-1 | Slower nematode development and reduced parasitism on plants | Shivakumara et al., 2019 |
| Meloidogyne incognita/Root-knot nematode | Eggplant | dsRNA/siRNA | Mi-msp-1 | Enhanced nematode resistance | Chaudhary et al., 2019 |
| Heterodera glycines/Soybean cyst nematode | Soybean | amiRNA |
J15 J20 J23 |
Significant suppression on SCN cyst and egg populations | Tian et al., 2016 |
| Heterodera glycines/Soybean cyst nematode | Soybean | hpRNA |
HgY25 HgPrp17 |
Significant reductions in numbers of SCN cysts and eggs | Tian et al., 2019 |
| Heterodera avenae/Cereal cyst nematode | Wheat | dsRNA | Galectin, cathepsin L, vap1, serpin, flp12, RanBPM chitinase | Reduced nematode penetration, development and reproduction | Dutta et al., 2020 |
| Meloidogyne graminicola/Root-knot nematode | Rice | hpRNA |
flp-1 flp-12 |
Reduction in gall formation, significant decrease in total number of endoparasites | Hada et al., 2020 |
|
Meloidogyne incognita/Root-knot nematode |
Tobacco | dsRNA | Chitin synthase, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, trehalase | Rreduced egg mass and egg number | Mani et al., 2020 |
| Meloidogyne incognita/Root-knot nematode | Arabidopsis | hpRNA | MiPDI1 | Reduced the amount of M. incognita infection | Zhao et al., 2020 |
hpRNA, hairpin RNA; amiRNA, artificial micro RNA; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
A conserved root-knot nematode effector gene, 16D10, was targeted by HIGS in transgenic grape hairy roots, showing successful inhibition of root-knot nematode infection (Yang et al., 2013). In addition, the HIGS suppression of msp-18 and msp-20 from M. incognita led to significant reduction in nematode multiplication (Shivakumara et al., 2017).
Tian et al. (2016) targeted three soybean cyst nematode genes (designated as J15, J20, and J23) by artificial microRNA (amiRNA), leading to downregulation of expression of these genes within soybean cyst nematode eggs in populations feeding on transgenic hairy roots. In addition, Tian et al. (2019) demonstrated that transgenic soybean lines expressing hairpin RNAi constructs targeting the HgY25 and HgPrp17 genes, related to reproduction and fitness of the nematodes, showed significant reductions (up to 73%) in eggs/g root in the T3 and T4 homozygous transgenic lines (Table 4). To date, SIGS has not been tested against nematodes.
Current challenges of host-induced gene silencing and spray-induced gene silencing
From the extensive literature on HIGS, it is clear the transgenic approach using HIGS has been successful in revealing gene functions in a variety of plant pathogens and in protecting plants against diverse diseases. HIGS offers several potential advantages over other plant disease control methods. In principle, HIGS-based resistance does not require input from the grower, and thereby provides an effective crop protection strategy to replace costly and environmentally unfriendly chemical protection. HIGS-based resistance can be durable and long-lasting compared to conventional R genes that are often overcome quickly by compensatory mutations in pathogen Avr genes. Moreover, HIGS can be used to control multiple diseases of a given crop. Finally, new HIGS genes can be designed easily to keep pace with co-evolving pathogens.
Despite these advantages, commercially available crop plants with HIGS transgenes have not penetrated the marketplace. This may be due to the fact that HIGS requires transgene technology (Santala and Valkonen, 2018) and this is not accepted readily by the public in many countries, who are concerned about genetically modified organisms. For example, the literature indicates that European researchers are leaders in developing RNAi technology. However, Europe’s strict legislation against deployment of genetically engineered crops presents a stumbling block for the adoption of HIGS-based crop improvement. Moreover, genetic transformation protocols may not be accessible for some crop plants. As HIGS technology relies on the successful movement of siRNAs from the host plant to the pathogen, some pathogens may not be amenable to manipulation using this method. Off-target effects are another negative factor to be considered. Moreover, if the target region is not selected properly, the resultant functional redundancy and/or incomplete silencing of mRNA may result in failure. In addition, pathogens may cause diseases in only particular parts of the plants such as roots and fruits, and specific targeting of these tissues with HIGS system may not be possible. Recent studies indicate exosome-like extracellular vesicles are involved in sRNA trafficking between organisms (Cai et al., 2018). However, there are still gaps in our knowledge in this area and it is not known whether all plant-microbe interactions rely on the same mechanisms. Additional research into the fundamental mechanisms of trans-kingdom RNA silencing will undoubtedly improve efforts to streamline HIGS and SIGS as disease control tools.
Because SIGS technology has been used successfully on both monocots and dicots, it seems to be a potentially useful plant protection strategy. In comparison to current disease control methods, SIGS could be sustainable and environmentally friendly and it offers a rapid method suitable for both pre- and post-harvest plant protection. As a non-transgenic approach SIGS is potentially more acceptable to consumers. In addition, as SIGS technology targets specific genes using bioinformatic tools any off-target effects are reduced, and the sprays can be tailored toward particular pests or pathogens to enhance specificity.
However, as for HIGS, SIGS-based disease control also faces challenges: The effect of SIGS on plants may last for only a few days because of RNA degradation, and the level of protective RNA in the plant could be limited by uptake such that regular re-application of sRNA may be needed or limited by the size of dsRNA (Höfle et al., 2020) requiring a size optimization. Furthermore, it should be noted that efficiency of dsRNA uptake by the eukaryotic microbes and cell types could vary across fungal or oomycete species (Qiao et al., 2021). In addition, some of the delivery methods such as high pressure spraying of dsRNA may not yield the expected gene silencing (Uslu et al., 2020). The cost associated with manufacturing could be high. To overcome this, new approaches in this area, such as using bacteria to produce sRNAs, are being developed (Goodfellow et al., 2019); however, it is too early to judge whether this approach is commercially scalable. Also, although SIGS may work efficiently under the laboratory conditions, there have been very few large-scale field trials and only few delivery methods, including nanoclay, have been tested. Large scale production may rely on formulations containing synergists or co-formulants that stabilize dsRNA in the environment or enhance transport into the target cells. However, any active substance or product placed on the market to protect plants will be subject to authorization from the participating countries. This may cause a delay in the wide acceptance of SIGS technology as it may take some time for new regulatory frameworks to be developed. As SIGS technology is a new RNAi-based innovation, consumer acceptance has yet to be assessed.
Conclusion and future prospects
In the near future, we should expect further developments in the commercial application of HIGS in regions where transgenic technology has been permitted. Similarly, an increasing number of studies have been carried out across the globe on a SIGS approach for disease control. However, several important aspects of SIGS, including risk assessment and legislation on the use of SIGS, need to be improved. As the genomic sequences of more plants and pathogens become increasingly available, designing HIGS and SIGS specific to the targets should get easier. Recent developments in clustered regularly interspaced short palindrome repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) editing technology (Wada et al., 2020) may be combined with HIGS and SIGS to give more durable disease resistance in crop plants.
Author contributions
ÖB, DG, YH, JM, and MT wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
Financial support from the Turkish Ministry of Agriculture to ÖB was gratefully acknowledged. DG was supported by BBSRC grant BB/V014609/1 to MT. This work was also supported in parts by grants from the Ministry of Science & Technology of China (Key International R&D Program 2017YFE0110900), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872636). JM received support from the Virginia Agricultural Experiment Station and the Hatch Program of the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture, project VA- 160106.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- Ahmed A. A., Pedersen C., Thordal-Christensen H. (2016). The barley powdery mildew effector candidates CSEP0081 and CSEP0254 promote fungal infection success. PLoS One 11:e0157586. 10.1371/journal.pone.0157586 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam S. B., Reade R., Maghodia A., Ghoshal B., Theilmann J., Rochon D. A. (2021). Targeting of cucumber necrosis virus coat protein to the chloroplast stroma attenuates host defense response. Virology 554 106–119. 10.1016/j.virol.2020.10.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alburquerque N., Faize L., Burgos L. (2017). Silencing of Agrobacterium tumefaciens oncogenes ipt and iaaM induces resistance to crown gall disease in plum but not in apricot. Pest. Manag. Sci. 73 2163–2173. 10.1002/ps.4600 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkharouf N. W., Klink V. P., Matthews B. F. (2007). Identification of Heterodera glycines (soybean cyst nematode [SCN]) cDNA sequences with high identity to those of Caenorhabditis elegans having lethal mutant or RNAi phenotypes. Exp. Parasitol. 115 247–258. 10.1016/j.exppara.2006.09.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade C. M., Tinoco M. L. P., Rieth A. F., Maia F. C. O., Aragao F. J. L. (2016). Host-induced gene silencing in the necrotrophic fungal pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Pathol. 65 626–632. 10.1111/ppa.12447 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Andrieu A., Breitler J. C., Sire C., Meynard D., Gantet P., Guiderdoni E. (2012). An in planta, Agrobacterium-mediated transient gene expression method for inducing gene silencing in rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaves. Rice 5:23. 10.1186/1939-8433-5-23 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arif M., Azhar U., Arshad M., Zafar Y., Mansoor S., Asad S. (2012). Engineering broad-spectrum resistance against RNA viruses in potato. Transgenic Res. 21 303–311. 10.1007/s11248-011-9533-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai X., Huang X., Tian S., Peng H., Zhan G., Goher F., et al. (2021). RNAi-mediated stable silencing of TaCSN5 confers broad-spectrum resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. Sp. Tritici. Mol. Plant Pathol. 22 410–421. 10.1111/mpp.13034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulcombe D. (2004). RNA silencing in plants. Nature 431 356–363. 10.1038/nature02874 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyene G., Chauhan R. D., Ilyas M., Wagaba H., Fauquet C. M., Miano D., et al. (2017). Virus-derived stacked RNAi construct confers robust resistance to cassava brown streak disease. Front. Plant Sci. 7:2052. 10.3389/fpls.2016.02052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharti P., Jyoti P., Kapoor P., Sharma V., Shanmugam V., Yadav S. K. (2017). Host-induced silencing of pathogenicity genes enhances resistance to Fusarium oxysporum wilt in tomato. Mol. Biotechnol. 59 343–352. 10.1007/s12033-017-0022-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilir Ö, Telli O., Norman C., Budak H., Hong Y., Tör M. (2019). Small RNA inhibits infection by downy mildew pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis. Mol. Plant Pathol. 20 1523–1534. 10.1111/mpp.12863 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai Q., Qiao L., Wang M., He B., Lin F. M., Palmquist J., et al. (2018). Plants send small RNAs in extracellular vesicles to fungal pathogen to silence virulence genes. Science 360 1126–1129. 10.1126/science.aar4142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary S., Dutta T. K., Tyagi N., Shivakumara T. N., Papolu P. K., Chobhe K. A., et al. (2019). Host-induced silencing of Mi-msp-1 confers resistance to root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita in eggplant. Transgenic Res. 28 327–340. 10.1007/s11248-019-00126-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I.-C., Griesenauer B., Yu Y.-T. N., Velicer G. J. (2014). A recent evolutionary origin of a bacterial small RNA that controls multicellular fruiting body development. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 73 1–9. 10.1016/j.ympev.2014.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng W., Song X.-S., Li H.-P., Cao L.-H., Sun K., Qiu X.-L., et al. (2015). Host-induced gene silencing of an essential chitin synthase gene confers durable resistance to Fusarium head blight and seedling blight in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 13 1335–1345. 10.1111/pbi.12352 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz A. R. R., Aragao F. J. L. (2014). RNAi-based enhanced resistance to Cowpea severe mosaic virus and Cowpea aphid-borne mosaic virus in transgenic cowpea. Plant Pathol. 63 831–837. 10.1111/ppa.12178 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakouras A., Jarausch W., Buchholz G., Bassler A., Braun M., Manthey T., et al. (2018). Delivery of hairpin RNAs and small RNAs into woody and herbaceous plants by trunk injection and petiole absorption. Front. Plant Sci. 9:1253. 10.3389/fpls.2018.01253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakouras A., Wassenegger M., McMillan J. N., Cardoza V., Maegele I., Dadami E., et al. (2016). Induction of silencing in plants by high-pressure spraying of in vitro-synthesized small RNAs. Front. Plant Sci. 7:1327. 10.3389/fpls.2016.01327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Felippes F. F. (2019). Gene Regulation Mediated by microRNA-Triggered Secondary Small RNAs in Plants. Plants 8:112. 10.3390/plants8050112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinh P. T. Y., Brown C. R., Elling A. A. (2014). RNA interference of effector gene Mc16D10L confers resistance against Meloidogyne chitwoodi in Arabidopsis and potato. Phytopathology 104 1098–1106. 10.1094/PHYTO-03-14-0063-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou T., Shao X., Hu C., Li S., Sheng O., Bi F., et al. (2020). Host-induced gene silencing of Foc TR4 ERG6/11 genes exhibits superior resistance to Fusarium wilt of banana. Plant Biotechnol. J. 18 11–13. 10.1111/pbi.13204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker F., Trutzenberg A., Rothenpieler J. S., Kuhn S., Pröls R., Schreiber T., et al. (2020). Oomycete small RNAs bind to the plant RNA-induced silencing complex for virulence. eLife 9:e56096. 10.7554/eLife.56096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunoyer P., Himber C., Voinnet O. (2006). Induction, suppression and requirement of RNA silencing pathways in virulent Agrobacterium tumefaciens infections. Nat. Genet. 38 258–263. 10.1038/ng1722 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta T. K., Papolu P. R., Singh D., Sreevathsa R., Rao U. (2020). Expression interference of a number of Heterodera avenae conserved genes perturbs nematode parasitic success in Triticum aestivum. Plant Sci. 301:110670. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar M. A., Civerolo E. L., Summerfelt K. R., Dandekar A. M. (2001). RNAi-mediated oncogene silencing confers resistance to crown gall tumorigenesis. PNAS 98 13437–13442. 10.1073/pnas.241276898 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahim M., Ayala-Navarrate L., Millar A. A., Larkin P. J. (2010). Hairpin RNA derived from viral Nia gene confers immunity to wheat streak mosaic virus infection in transgenic wheat plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 8 821–834. 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00513.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahim M., Millar A. A., Wood C. C., Larkin P. J. (2012). Resistance to wheat streak mosaic virus generated by expression of an artificial polycistronic microRNA in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 10 150–163. 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00647.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan D., Zhang J., Jiang H., Jiang T., Zhu S., Cheng B. (2010). Bacterially expressed dsRNA protects maize against SCMV infection. Plant Cell Rep. 29 1261–1268. 10.1007/s00299-010-0911-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghag S. B. (2017). Host induced gene silencing, an emerging science to engineer crop resistance against harmful plant pathogens. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 100 242–254. 10.1016/j.pmpp.2017.10.003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ghag S. B., Shekhawat U. K., Ganapathi T. R. (2014). Host-induced post-transcriptional hairpin RNA-mediated gene silencing of vital fungal genes confers efficient resistance against Fusarium wilt in banana. Plant Biotechnol. J. 12 541–553. 10.1111/pbi.12158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K. B., Hunter W. B., Park A. L., Gundersen-Rindal D. E. (2017). Double strand RNA delivery system for plant-sap-feeding insects. PLoS One 12:e0171861. 10.1371/journal.pone.0171861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K. B., Hunter W. B., Park A. L., Gundersen-Rindal D. E. (2018). Double-stranded RNA oral delivery methods to induce RNA interference in phloem and plant-sap-feeding hemipteran insects. J. Vis. Exp. 135:e57390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Kant R., Pradhan A., Jha G. (2021). RS_CRZ1, a C2H2-Type Transcription Factor Is Required for Pathogenesis of Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA in Tomato. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 34 26–38. 10.1094/mpmi-05-20-0121-r [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonsalves D. (2006). Transgenic papaya: Development, release, impact and challenges. Adv. Virus Res. 67 317–354. 10.1016/S0065-3527(06)67009-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow S., Zhang D., Wang M. B., Zhang R. (2019). Bacterium-Mediated RNA Interference: Potential Application in Plant Protection. Plants 8:572. 10.3390/plants8120572 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindarajulu M., Epstein L., Wroblewski T., Michelmore R. W. (2015). Host-induced gene silencing inhibits the biotrophic pathogen causing downy mildew of lettuce. Plant Biotechnol. J. 13 875–883. 10.1111/pbi.12307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu K. X., Song X. S., Xiao X. M., Duan X. X., Wang J. X., Duan Y. B., et al. (2019). A β2-tubulin dsRNA derived from Fusarium asiaticum confers plant resistance to multiple phytopathogens and reduces fungicide resistance. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 153 36–46. 10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.10.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guleria P., Mahajan M., Bhardwaj J., Yadav S. K. (2011). Plant small RNAs: Biogenesis, mode of action and their roles in abiotic stresses. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 9 183–199. 10.1016/S1672-0229(11)60022-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X. Y., Li Y., Fan J., Xiong H., Xu F. X., Shi J., et al. (2019). Host-induced gene silencing of MoAP1 confers broad-spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. Front. Plant Sci. 10:433. 10.3389/fpls.2019.00433 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hada A., Kumari C., Phani V., Singh D., Chinnusamy V., Rao U. (2020). Host-Induced Silencing of FMR Famide-Like Peptide Genes, flp-1 and flp-12, in Rice Impairs Reproductive Fitness of the Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne graminicola. Front. Plant Sci. 11:894. 10.3389/fpls.2020.00894 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haile Z. M., Gebremichael D. E., Capriotti L., Molesini B., Negrini F., Collina M., et al. (2021). Double-Stranded RNA Targeting Dicer-Like Genes Compromises the Pathogenicity of Plasmopara viticola on Grapevine. Front. Plant Sci. 12:667539. 10.3389/fpls.2021.667539 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hameed A., Tahir M. N., Asad S., Bilal R., Van Eck J., Jander G., et al. (2017). RNAi-mediated simultaneous resistance against three RNA viruses in potato. Mol. Biotechnol. 59 73–83. 10.1007/s12033-017-9995-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Z., Yu R., Xiong D., Tian C. (2021). A Sge1 homolog in Cytospora chrysosperma governs conidiation, virulence and the expression of putative effectors. Gene 778:145474. 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He F., Zhang R., Zhao J., Qi T., Kang Z., Guo J. (2019). Host-Induced Silencing of Fusarium graminearum genes enhances the resistance of Brachypodium distachyon to Fusarium Head Blight. Front. Plant Sci. 10:1362. 10.3389/fpls.2019.01362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfle L., Biedenkopf D., Werner B. T., Shrestha A., Jelonek L., Koch A. (2020). Study on the efficiency of dsRNAs with increasing length in RNA-based silencing of the Fusarium CYP51 genes. RNA Biol. 17 463–473. 10.1080/15476286.2019.1700033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu D., Chen Z.-Y., Zhang C., Ganiger M. (2020). Reduction of Phakopsora pachyrhizi infection on soybean through host- and spray-induced gene silencing. Mol. Plant Pathol. 21 794–807. 10.1111/mpp.12931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Z., Parekh U., Maruta N., Trusov Y., Botella J. R. (2015). Down-regulation of Fusarium oxysporum endogenous genes by host-delivered RNA interference enhances disease resistance. Front. Chem. 3:1. 10.3389/fchem.2015.00001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang G. Z., Allen R., Davis E. L., Baum T. J., Hussey R. S. (2006). Engineering broad root-knot resistance in transgenic plants by RNAi silencing of a conserved and essential root-knot nematode parasitism gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 103 14302–14306. 10.1073/pnas.0604698103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., Yang M., Lu L., Zhang X. (2016). Diverse functions of small RNAs in different plant–pathogen communications. Front. Microbiol. 7:1552. 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal S., Fosu-Nyarko J., Jones M. G. K. (2020). Attempt to silence genes of the RNAi pathways of the root-rnot rematode, Meloidogyne incognita results in diverse responses including increase and no change in expression of some genes. Front. Plant Sci. 11:328. 10.3389/fpls.2020.00328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahan S. N., Asman A. K., Corcoran P., Fogelqvist J., Vetukuri R. R., Dixelius C. (2015). Plant-mediated gene silencing restricts growth of the potato late blight pathogen Phytophthora infestans. J. Exp. Bot. 66 2785–2794. 10.1093/jxb/erv094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiao J., Peng D. (2018). Wheat MicroRNA1023 suppresses invasion of Fusarium graminearum via targeting and silencing FGSG_03101. J. Plant Interact. 13 514–521. 10.1080/17429145.2018.1528512 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. D. G., Dangl J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444 323–329. 10.1038/nature05286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi I., Kumar A., Singh A. K., Kohli D., Raman K. V., Sirohi A., et al. (2019). Development of nematode resistance in Arabidopsis by HD-RNAi-mediated silencing of the effector gene Mi-msp2. Sci. Rep. 9:17404. 10.1038/s41598-019-53485-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalyandurg P. B., Sundararajan P., Dubey M., Ghadamgahi F., Zahid M. A., Whisson S. C., et al. (2021). Spray-Induced Gene Silencing as a Potential Tool to Control Potato Late Blight Disease. Phytopathology 111 2168–2175. 10.1094/PHYTO-02-21-0054-SC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar-Agarwal S., Gao S., Vivian-Smith A., Jin H. (2007). A novel class of bacteria-induced small RNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 21 3123–3134. 10.1101/gad.1595107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. J., Kim M.-J., Pak J. H., Im H. H., Lee D. H., Kim K.-H., et al. (2016). RNAi-mediated Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) resistance of a Korean Soybean cultivar. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 10 257–267. 10.1007/s11816-016-0402-y [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A., Kogel K.-H. (2014). New wind in the sails: Improving the agronomic value of crop plants through RNAi-mediated gene silencing. Plant Biotechnol. J. 12 821–831. 10.1111/pbi.12226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A., Biedenkopf D., Furch A., Weber L., Rossbach O., Abdellatef E., et al. (2016). An RNAi-based control of Fusarium graminearum infections through spraying of long dsRNAs involves a plant passage and is controlled by the fungal silencing machinery. PLoS Pathog. 12:e1005901. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A., Höfle L., Werner B. T., Imani J., Schmidt A., Jelonek L., et al. (2019). SIGS vs HIGS: A study on the efficacy of two dsRNA delivery strategies to silence Fusarium FgCYP51 genes in infected host and non-host plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 20 1636–1644. 10.1111/mpp.12866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A., Kumar N., Weber L., Keller H., Imani J., Kogel K. H. (2013). Host-induced gene silencing of cytochrome P450 lanosterolC14alpha-demethylase-encoding genes confers strong resistance to Fusarium species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110 19324–19329. 10.1073/pnas.1306373110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A., Schlemmer T., Höfle L., Werner B. T., Preuber C., Hardt M., et al. (2020). Host-induced gene silencing involves transfer of dsRNA-derived siRNA via extracellular vesicles. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 10.1101/2020.02.12.945154 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Jin C., Yuan H., Huang W., Liu F., Fan R., et al. (2021). The barley powdery mildew effectors CSEP0139 and CSEP0182 suppress cell death and promote B. Graminis fungal virulence in plants. Phytopathol. Res. 3:7. 10.1186/s42483-021-00084-z [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S., Jaouannet M., Dempsey D. A., Imani J., Coustau C., Kogel K.-H. (2020). RNA-based technologies for insect control in plant production. Biotechnol. Adv. 39:107463. 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Song Y., Wu B., Jiang M., Li K., Zhu C., et al. (2011). Production of transgenic rice new germplasm with strong resistance against two isolations of Rice stripe virus by RNA interference. Transgenic Res. 20 1367–1377. 10.1007/s11248-011-9502-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi E., Soleimani R. (2019). Host-induced gene silencing of Pectobacterium carotovorum quorum sensing gene enhances soft rot disease resistance in potato plants. Arch. Phytopathol. Pflanzenschutz. 52 371–384. 10.1080/03235408.2019.1623503 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mahto B. K., Singh A., Pareek M., Rajam M. V., Dhar-Ray S., Reddy P. M. (2020). Host-induced silencing of the Colletotrichum gloeosporioides conidial morphology 1 gene (CgCOM1) confers resistance against anthracnose disease in chilli and tomato. Plant Mol. Biol. 104 381–395. 10.1007/s11103-020-01046-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar R., Rajasekaran K., Cary J. W. (2017). RNA Interference (RNAi) as a Potential Tool for Control of Mycotoxin Contamination in Crop Plants: Concepts and Considerations. Front. Plant Sci. 8:200. 10.3389/fpls.2017.00200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani V., Reddy C. S., Lee S.-K., Park S., Ko H.-R., Kim D.-G., et al. (2020). Chitin Biosynthesis Inhibition of Meloidogyne incognita by RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing Increases Resistance to Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:6626. 10.3390/ijms21186626 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masanga J. O., Matheka J. M., Omer R. A., Ommeh S. C., Monda E. O., Alakonya A. E. (2015). Downregulation of transcription factor aflR in Aspergillus flavus confers reduction to aflatoxin accumulation in transgenic maize with alteration of host plant architecture. Plant Cell Rep. 34 1379–1387. 10.1007/s00299-015-1794-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitter N., Worrall E. A., Robinson K. E., Li P., Jain R. G., Taochy C., et al. (2017). Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses. Nat. Plants 3:16207. 10.1038/nplants.2016.207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerva L., Sandrini M., Gambino G., Chitarra W. (2020). Double-Stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) as a Sustainable Tool against Gray Mold (Botrytis cinerea) in Grapevine: Effectiveness of Different Application Methods in an Open-Air Environment. Biomolecules 10:200. 10.3390/biom10020200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niño-Sánchez J., Chen L.-H., De Souza J. T., Mosquera S., Stergiopoulos I. (2021). Targeted Delivery of Gene Silencing in Fungi Using Genetically Engineered Bacteria. J. Fungi 7:125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowara D., Gay A., Lacomme C., Shaw J., Ridout C., Douchkov D., et al. (2010). HIGS: Host-Induced Gene Silencing in the Obligate Biotrophic Fungal Pathogen Blumeria graminis. Plant Cell. 22 3130–3141. 10.1105/tpc.110.077040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numata K., Ohtani M., Yoshizumi T., Demura T., Kodama Y. (2014). Local gene silencing in plants via synthetic dsRNA and carrier peptide. Plant Biotechnol. J. 12 1027–1034. 10.1111/pbi.12208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panwar V., Jordan M., McCallum B., Bakkeren G. (2018). Host-induced silencing of essential genes in Puccinia triticina through transgenic expression of RNAi sequences reduces severity of leaf rust infection in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 16 1013–1023. 10.1111/pbi.12845 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panwar V., McCallum B., Bakkeren G. (2013). Host-induced gene silencing of wheat leaf rust fungus Puccinia triticina pathogenicity genes mediated by the Barley stripe mosaic virus. Plant Mol. Biol. 81 595–608. 10.1007/s11103-013-0022-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil B. L., Bagewadi B., Yadav J. S., Fauquet C. M. (2016). Mapping and identification of cassava mosaic geminivirus DNA-A and DNA-B genome sequences for efcient siRNA expression and RNAi based virus resistance by transient agro-infiltration studies. Virus Res. 213 109–115. 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.11.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez C. E. B., Cabral G. B., Aragao F. J. L. (2021). Host-induced gene silencing for engineering resistance to Fusarium in soybean. Plant Pathol. 70 417–425. 10.1111/ppa.13299 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash V., Singh A., Singh A. K., Dalmay T., Chakraborty S. (2020). Tobacco RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 affects the expression of defence-related genes in Nicotiana benthamiana upon Tomato leaf curl Gujarat virus infection. Planta 252:11. 10.1007/s00425-020-03417-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi T., Zhu X., Tan C., Liu C., Guo J., Kang Z., et al. (2017). Host-induced gene silencing of an important pathogenicity factor PsCPK1 in Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici enhances resistance of wheat to stripe rust. Plant Biotechnol. J. 16 797–807. 10.1111/pbi.12829 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiao L., Lan C., Capriotti L., Ah-Fong A., Sanchez N., Hamby R., et al. (2021). Spray-induced gene silencing for disease control is dependent on the efficiency of pathogen RNA uptake. Plant Biotechnol. J. 19 1756–1768. 10.1111/pbi.13589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin C., Li B., Fan Y., Zhang X., Yu Z., Ryabov E., et al. (2017). Roles of Dicer-Like proteins 2 and 4 in Intra- and Intercellular Antiviral Silencing. Plant Physiol. 174 1067–1081. 10.1104/pp.17.00475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raruang Y., Omolehin O., Hu D., Wei Q., Han Z.-Q., Rajasekaran K., et al. (2020). Host Induced Gene Silencing Targeting Aspergillus flavus aflM Reduced Aflatoxin Contamination in Transgenic Maize Under Field Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 11:754. 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00754 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safarova D., Brazda P., Navratil M. (2014). Effect of Artificial dsRNA on Infection of Pea Plants by Pea seed-borne mosaic virus. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 50 105–108. 10.17221/120/2013-CJGPB [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- San Miguel K., Scott J. G. (2016). The next generation of insecticides: dsRNA is stable as a foliar-applied insecticide. Pest. Manag. Sci. 72 801–809. 10.1002/ps.4056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sang H., Kim J. (2020). Advanced strategies to control plant pathogenic fungi by host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) and spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS). Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 14 1–8. 10.1007/s11816-019-00588-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sanju S., Siddappa S., Thakur A., Shukla P. K., Srivastava N., Pattanayak D., et al. (2015). Host-mediated gene silencing of a single effector gene from the potato pathogen Phytophthora infestans imparts partial resistance to late blight disease. Funct. Integr. Genom. 15 697–706. 10.1007/s10142-015-0446-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santala J., Valkonen J. P. T. (2018). Sensitivity of Small RNA-Based Detection of Plant Viruses. Front. Microbiol. 9:939. 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00939 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer K. L., Parlange F., Buchmann G., Jung E., Wehrli A., Herren G., et al. (2020). Cross-Kingdom RNAi of Pathogen Effectors Leads to Quantitative Adult Plant Resistance in Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 11:253. 10.3389/fpls.2020.00253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Nakazono-Nagaoka E., Uehara-Ichiki T., Sasaya T., Omura T. (2011). Targeting specific genes for RNA interference is crucial to the development of strong resistance to Rice stripe virus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 9 503–512. 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00571.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Yoshii M., Wei T., Hirochika H., Omura T. (2009). Silencing by RNAi of the gene for Pns12, a viroplasm matrix protein of Rice dwarf virus, results in strong resistance of transgenic rice plants to the virus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 7 24–32. 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00366.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumara T. N., Chaudhary S., Kamaraju D., Dutta T. K., Papolu P. K., Banakar P., et al. (2017). Host-induced silencing of two pharyngeal gland genes conferred transcriptional alteration of cell wall-modifying enzymes of Meloidogyne incognita vis-a-vis perturbed nematode infectivity in eggplant. Front. Plant Sci. 8:473. 10.3389/fpls.2017.00473 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumara T. N., Somvanshi S. V., Phani V., Chaudhary S., Hada A., Budhwar R., et al. (2019). Meloidogyne incognita (Nematoda: Meloidogynidae) sterol-binding protein Mi-SBP-1 as a target for its management. Int. J. Parasitol. 49 13–14. 10.1016/j.ijpara.2019.09.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N., Mukherjee S. K., Rajam M. V. (2020). Silencing of the Ornithine Decarboxylase Gene of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici by Host-Induced RNAi Confers Resistance to Fusarium Wilt in Tomato. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 38 419–429. 10.1007/s11105-020-01205-2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Song X. S., Gu K. X., Duan X. X., Xiao X. M., Hou Y. P., Duan Y. B., et al. (2018). A myosin5 dsRNA that reduces the fungicide resistance and pathogenicity of Fusarium asiaticum. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 150 1–9. 10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.07.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Y., Thomma B. H. J. (2018). Host-induced gene silencing compromises Verticillium wilt in tomato and Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant Pathol. 19 77–89. 10.1111/mpp.12500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su X., Lu G., Li X., Rehman L., Liu W. (2020). Host-Induced Gene Silencing of an Adenylate Kinase Gene Involved in Fungal Energy Metabolism Improves Plant Resistance to Verticillium dahliae. Biomolecules 10:127. 10.3390/biom10010127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresha S., Sharma S., Bairwa A., Tomar M., Kumar R., Bhardwaj V., et al. (2021). Spraying of dsRNA Molecules Derived from Phytophthora Infestans, as a Plant Protection Strategies for the Management of Potato Late Blight. Life Sci. 2021:2021020280. 10.20944/preprints202102.0280.v1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenllado F., Martinez-Garcia B., Vargas M., Diaz-Ruiz J. R. (2003). Crude extracts of bacterially expressed dsRNA can be used to protect plants against virus infections. BMC Biotechnol. 3:3. 10.1186/1472-6750-3-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakare D., Zhang J., Wing R., Cotty P., Schmidt M. (2017). Aflatoxin-free transgenic maize using host-induced gene silencing. Sci. Adv. 3:e1602382. 10.1126/sciadv.1602382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thu L. T. M., Thuy V. T. X., Duc L. H., Son L. V., Ha C. H., Mau C. H. (2016). RNAi-mediated resistance to SMV and BYMV in transgenic tobacco. Crop. Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 16 213–218. 10.1590/1984-70332016v16n3a32 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tian B., Li J., Oakley T. R., Todd T. C., Trick H. N. (2016). Host-derived artificial microRNA as an alternative method to improve soybean resistance to soybean cyst nematode. Genes 7:122. 10.3390/genes7120122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian B., Li J., Vodkin L. O., Todd T. C., Finer J. J., Trick H. N. (2019). Host-derived gene silencing of parasite fitness genes improves resistance to soybean cyst nematodes in stable transgenic soybean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 132 2651–2662. 10.1007/s00122-019-03379-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari I. M., Jesuraj A., Kamboj R., Devanna B. N., Botella J. R., Sharma T. R. (2017). Host Delivered RNAi, an efficient approach to increase rice resistance to sheath blight pathogen (Rhizoctonia solani). Sci. Rep. 7:7521. 10.1038/s41598-017-07749-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tör M., Lotze M. T., Holton N. (2009). Receptor mediated signalling in plants: Molecular patterns and programmes. J. Exp. Bot. 60 3645–3654. 10.1093/jxb/erp233 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi H., Rajasubramaniam S., Rajam M. V., Dasgupta I. (2008). RNA-interference in rice against Rice tungro bacilliform virus results in its decreased accumulation in inoculated rice plants. Transgenic Res. 17 897–904. 10.1007/s11248-008-9174-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddin M. N., Akhter S., Chakraborty R., Baek J. H., Cha J.-Y., Park S. J., et al. (2017). SDE5, a putative RNA export protein, participates in plant innate immunity through a flagellin-dependent signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 7:9859. 10.1038/s41598-017-07918-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uslu V. V., Bassler A., Krczal G., Wassenegger M. (2020). High-Pressure-Sprayed Double Stranded RNA Does Not Induce RNA Interference of a Reporter Gene. Front. Plant Sci. 11:534391. 10.3389/fpls.2020.534391 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaucheret H., Beclin C., Fagard M. (2001). Post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants. J. Cell Sci. 114 3083–3091. 10.1242/jcs.114.17.3083 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A., Lee C., Morriss S., Odu F., Kenning C., Rizzo N., et al. (2018). The novel cyst nematode effector protein 30D08 targets host nuclear functions to alter gene expression in feeding sites. New Phytol. 219 697–713. 10.1111/nph.15179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada N., Ueta R., Osakabe Y., Osakabe K. (2020). Precision genome editing in plants: State-of-the-art in CRISPR/Cas9-based genome engineering. BMC Plant Biol. 20:234. 10.1186/s12870-020-02385-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagaba H., Patil B. L., Mukasa S., Alicai T., Fauquet C. M., Taylor N. J. (2016a). Artificial microRNA-derived resistance to Cassava brown streak disease. J. Virol. Methods 231 38–43. 10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.02.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagaba H., Beyen G., Aleu J., Odipio J., Okao-Okuja G., Chauhan R. D., et al. (2016b). Field Level RNAi-mediated resistance to Cassava Brown Streak Disease across multiple cropping cycles and diverse East African agro-ecological locations. Front. Plant Sci. 7:2060. 10.3389/fpls.2016.02060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walawage S. L., Britton M. T., Leslie C. A., Uratsu S. L., Li Y., Dandekar A. M. (2013). Stacking resistance to crown gall and nematodes in walnut rootstocks. BMC Genom. 4:668. 10.1186/1471-2164-14-668 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M., Weiberg A., Lin F. M., Thomma B. P. H. J., Huang H. D., Jin H. (2016). Bidirectional cross-kingdom RNAi and fungal uptake of external RNAs confer plant protection. Nat. Plants 2:16151. 10.1038/nplants.2016.151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P., Jiang H., Boeren S., Dings H., Kulikova O., Bisselling T., et al. (2021). A nuclear-targeted effector of Rhizophagus irregularis interferes with histone 2B mono-ubiquitination to promote arbuscular mycorrhisation. New Phytol. 230 1142–1155. 10.1111/nph.17236 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. S., Storz G. (2009). Regulatory RNAs in Bacteria. Cell 136 615–628. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C., Qin T., Li Y., Wang W., Dong T., Wang Q. (2020). Host-induced gene silencing of the acetolactate synthases VdILV2 and VdILV6 confers resistance to Verticillium wilt in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 524 392–397. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.01.126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner B. T., Gaffar F. Y., Schuemann D., Biedenkopf D., Koch A. M. (2020). RNA-spray-mediated silencing of Fusarium graminearum AGO and DCL genes improve barley disease resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 11:476. 10.3389/fpls.2020.00476 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrall E. A., Bravo-Cazar A., Nilon A. T., Fletcher S. J., Robinson K. E., Carr J. P., et al. (2019). Exogenous application of RNAi-inducing double-stranded RNA inhibits aphid-mediated tansmission of a plant virus. Front. Plant Sci. 10:265. 10.338/fpls.2019.00265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wytinck N., Sullivan D. S., Biggar K. T., Crisostomo L., Pelka P., Belmonte M., et al. (2020). Clathrin mediated endocytosis is involved in the uptake of exogenous double-stranded RNA in the white mold phytopathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Sci. Rep. 10:12773. 10.1038/s41598-020-69771-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Q., Ye W., Choi D., Wong J., Qiao Y., Tao K., et al. (2014). Phytophthora suppressor of RNA silencing 2 is a conserved RXLR effector that promotes infection in soybean and Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 27 1379–1389. 10.1094/MPMI-06-14-0190-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang B., Sugio A., White F. F. (2006). Os8N3 is a host disease-susceptibility gene for bacterial blight of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 10503–10508. 10.1073/pnas.0604088103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Huang H. (2014). Roles of small RNAs in plant disease resistance. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 56 962–970. 10.1111/jipb.12200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. Z., Jittayasothorn Y., Chronis D., Wang X., Cousins P., Zhong G. Y. (2013). Molecular characteristics and efficacy of 16D10 siRNAs in inhibiting root-knot nematode infection in transgenic grape hairy roots. PLoS One 8:e69463. 10.1371/journal.pone.0069463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J., Fang M., Lee D., Park M., Kim K.-H., Shin C. (2021). Double-stranded RNA confers resistance to pepper mottle virus in Nicotiana benthamiana. Appl. Biol. Chem. 64:1. 10.1186/s13765-020-00581-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J., Mejias J., Quentin M., Chen Y., de Almeida-Engler J., Mao Z., et al. (2020). The root-knot nematode effector MiPDI1 targets a stress-associated protein (SAP) to establish disease in Solanaceae and Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 228 1417–1430. 10.1111/nph.16745 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou B., Bailey A., Niblett C. L., Qu R. (2016). Control of brown patch (Rhizoctonia solani) in tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.) by host-induced gene silencing. Plant Cell Rep. 35 791–802. 10.1007/s00299-015-1921-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu C., Liu T., Chang Y.-N., Duan C.-G. (2019). Small RNA Functions as a Trafficking Effector in Plant Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:E2816. 10.3390/ijms20112816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., Zhu J., Liu Z., Wang Z., Zhou C., Wang H. (2017). Host-Induced Gene Silencing of Rice Blast Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae Pathogenicity Genes Mediated by the Brome Mosaic Virus. Genes 8:241. 10.3390/genes8100241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X., Qi T., He F., Tan C., Ma W., Voegele R. F., et al. (2017). Host-Induced Gene Silencing of the MAPKK Gene PsFUZ7 Confers Stable Resistance to Wheat Stripe Rust. Plant Physiol. 175 1853–1863. 10.1104/pp.17.01223 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]