The cup-shaped conformation of the title molecule is largely determined by an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond. In the crystal, double layers of molecules are formed by O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bond, indole, arylacetamide, Hirshfeld surface
Abstract
The cup-shaped conformation of the title molecule, C21H22N2O4, is largely determined by an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond. In the crystal, double layers of molecules are formed by O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. A Hirshfeld surface analysis was performed, which confirms the regions that are active for intermolecular interactions.
1. Chemical context
1H-Indole-2,3-dione, also known as isatin, represents a synthetically useful substrate that can be used to prepare a broad range of heterocyclic compounds, including examples of pharmacological significance (Bekircan & Bektas, 2008 ▸). Its derivates are biologically active and have significant importance in medicinal chemistry (Feng et al., 2010 ▸). They show potent anticonvulsant activity at low concentrations (Mathur & Nain, 2014 ▸), as well as antibacterial (Hu et al., 2017 ▸), anticancer (Ding et al., 2020 ▸) and antitubercular (Nath et al., 2020 ▸) activities. Arylacetamide-based compounds have attracted increasing attention because of their important pharmacological activities (Beccalli et al., 2007 ▸; Valeur & Bradley, 2009 ▸; Allen & Williams, 2011 ▸; Missioui et al., 2021 ▸, 2022a
▸,b
▸,c
▸). As part of our interest in the identification of bioactive compounds, we report herein on the synthesis, crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis of the title arylacetamide-based derivative containing an isatin moiety, namely N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-[3-hydroxy-2-oxo-3-(2-oxopropyl)indolin-1-yl]acetamide (Fig. 1 ▸)
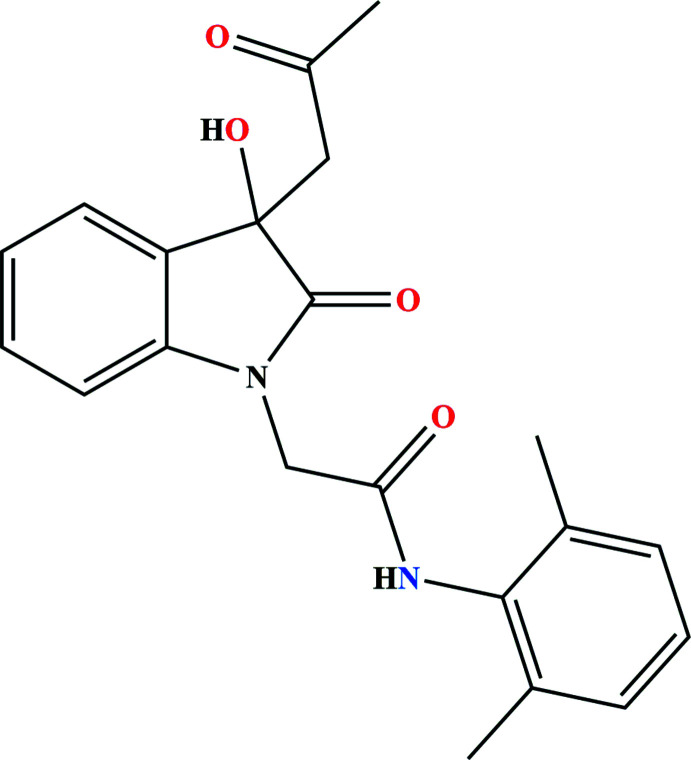
Figure 1.
The title molecule with labeling scheme and 50% probability ellipsoids. The intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond and C=O⋯ring interaction are depicted, respectively by violet and light-blue dashed lines.
2. Structural commentary
The molecule adopts a cup-shaped conformation (Fig. 1 ▸), which is largely determined by the intramolecular N2—H2A⋯O3 hydrogen bond (Table 1 ▸). As this places O3 directly over the five-membered ring [O3⋯centroid = 2.7062 (8) Å, C10⋯centroid = 2.9956 (9) Å, C10=O3⋯centroid = 99.56 (9)°], there is the possibility of an added C=O⋯π interaction reinforcing the observed conformation. The indole moiety is slightly non-planar as seen from the 1.89 (3)° dihedral angle between the mean planes of its constituent rings. The dihedral angle between the mean plane of the C1/C6/C7/C8/N1 ring and that of the C12/C13/N2/O4 unit is 82.83 (5)° while that between the latter plane and the mean plane of the C14–C19 ring is 72.24 (4)°. All bond distances and bond angles appear as expected for the given formulation.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯O2i | 0.864 (15) | 1.942 (15) | 2.7829 (9) | 164.1 (14) |
| N2—H2A⋯O3 | 0.874 (15) | 2.154 (15) | 3.0193 (10) | 170.3 (13) |
| C3—H3⋯O4ii | 0.95 | 2.44 | 3.3280 (12) | 155 |
| C9—H9A⋯O4iii | 0.99 | 2.33 | 3.2537 (11) | 154 |
| C11—H11B⋯O4iii | 0.98 | 2.59 | 3.2988 (12) | 129 |
| C12—H12A⋯O1iv | 0.99 | 2.60 | 3.5835 (11) | 173 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 ; (iv)
; (iv)
 .
.
3. Supramolecular features
In the crystal, centrosymmetric dimers are formed by self-complementary O1—H1⋯O2 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) and these units are assembled into corrugated layers parallel to the bc plane by C3—H3⋯O4 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸). Although these layers clearly contain large pores, they are combined in pairs across centers of symmetry by C9—H9A⋯O4, C11—H11B⋯O4 and C12—H12A⋯O1 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) so that the pores in one layer are capped by molecules in the second and the resulting double layer has no significant pores (Fig. 3 ▸).
Figure 2.
A plan view of a portion of one layer viewed along the a-axis direction. O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are depicted, respectively, by red and black dashed lines while intramolecular interactions and non-interacting hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity.
Figure 3.
Packing viewed along the b-axis direction with O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds depicted, respectively, by red and black dashed lines. Intramolecular interactions and non-interacting hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity.
4. Database survey
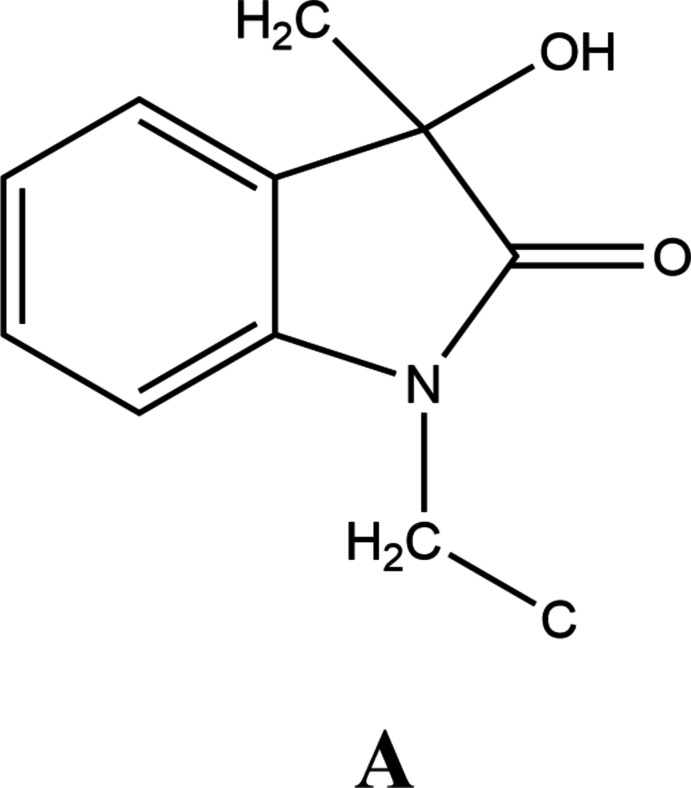
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD version 5.43 updated to March 2022; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) with the fragment A provided 28 hits, most of which contained a benzyl group attached to the ring nitrogen atom. Of these, seven [DEVVUY (Liu et al., 2018 ▸), DIDVAO (Makaev et al., 2006 ▸), ODUWIV (Duan et al., 2013 ▸), PUZBAQ (Becerra et al., 2020 ▸), PUZBEU (Becerra et al., 2020 ▸), PUZBIY (Becerra et al., 2020 ▸) and PUZBOE (Becerra et al., 2020 ▸)] are most similar to the title molecule having a β-carbonyl group in the substituent attached to the saturated carbon of the five-membered ring. As in the title compound, all of these form dimers through complementary O— H⋯O hydrogen bonds between the hydroxy and keto groups and these units are also further assembled into chains and/or layers by hydrogen-bonding interactions.
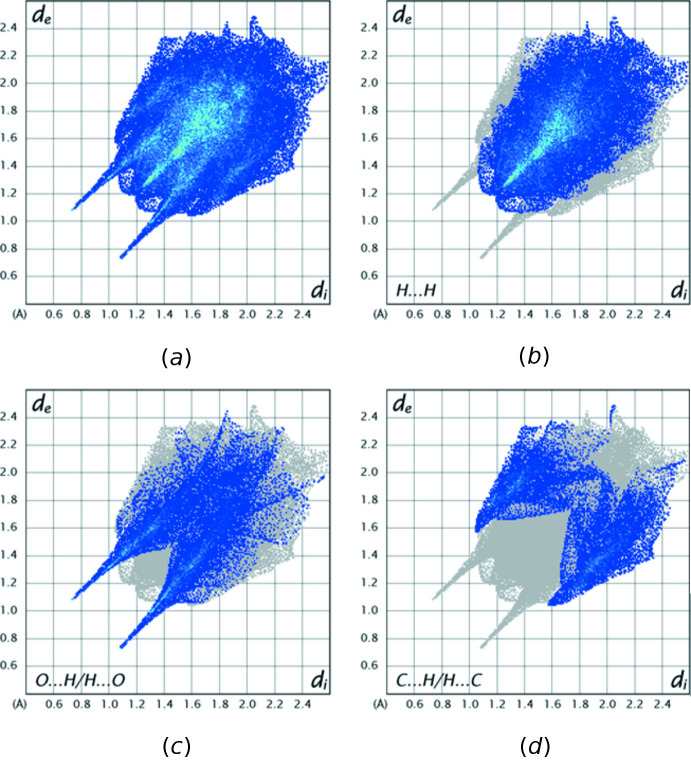
5. Hirshfeld surface analysis
The analysis was performed with CrystalExplorer 21.5 (Spackman et al., 2021 ▸) with the details of the pictorial output described in a recent publication (Tan et al., 2019 ▸). Fig. 4 ▸ shows the d norm surface for the asymmetric unit plotted over the limits −0.6060 to 1.5193 a.u. together with three adjacent molecules that are hydrogen-bonded to it. The one on the lower left, adjacent to the pair of intense red spots, is the second half of one inversion dimer with these red spots indicating the strong O1—H1⋯O2 hydrogen bonds (cf. Fig. 2 ▸). The molecules above and below the surface are members of two adjacent layers of molecules (cf. Fig. 3 ▸), which are linked by the C9—H9A⋯O4 hydrogen bonds (lighter red spots). Fig. 5 ▸ a presents a fingerprint plot of all intermolecular interactions while Fig. 5 ▸ b shows the 55.2% of these attributable to H⋯H interactions. Fig. 5 ▸ c and 5d delineate the O⋯H/H⋯O (24.1%) and C⋯H/H⋯C (17.8%) interactions, respectively.
Figure 4.
The Hirshfeld surface for the title molecule with three close neighbors added.
Figure 5.
Fingerprint plots for the title molecule: (a) all contacts, (b) H⋯H contacts, (c) O⋯H/H⋯O contacts and (d) C⋯H/H⋯C contacts.
6. Synthesis and crystallization
Indoline-2,3-dione (0.1g, 0.0679 mmol) was taken up in 10 mL of acetone under stirring. Solid potassium carbonate (0.11 g, 0.815 mmol) was added in one portion. Then, the dark-colored suspension was raised to room temperature and stirred for a further 1 h. The appropriate 2-chloro-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide (0.119 g, 0.0679 mmol) and potassium iodide (0.05 g, 0.301 mmol) were added. Then, the reaction mixture was stirred at 353.15–373 K for 2 h until the reaction was complete, which was confirmed using TLC (ethyl acetate:hexane, 40:60). The resulting solid was filtered and recrystallized from ethanol to give title compound as colorless crystals. Yield: 64%; m.p. 527.15–529.15 K. FT–IR (ATR, υ, cm−1) 3292 υ (N—H amide), 1021 υ (N—C amide), 1675 υ (C=O amide), 1708 υ (C=O lactam), 1615 υ (C=O ketone), 3073 υ(C—Harom), 1175 υ(C—N), 2952 υ(C—H, CH3), 3348 (O—H). 1H NMR (DMSO–d 6) δ ppm: 9.086 (s, 1H, NH); 7.011–7.338 (m, 7H, Harom); 6.134 (s, 1H, OH); 3.16-4.52 (2d, 2H, CH2); 2.03 (s, 6H, 2 CH3) 1.97 (s, 3H, CH3). 13C NMR (DMSO–d 6) δ ppm: 207.448 (C=O), 177.126 (C=Olactam), 166.770 (C=Oamide), 143.329; 135.794; 134.718; 131.196; 129.746; 128.268; 127.327; 124.150; 123.094; 109.196 (12CHarom), 72.740 (Cq), 51.075 (CH2—N), 40.200 (CH2—COCH3), 31.024 (CH3), 18.498 (2 CH3). Its mass spectrum showed a molecular ion peak (MH+, m/z = 367.15799 and MNa+, m/z = 389.13943) that conforms to its molecular formula C21H22N2O4
7. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. Hydrogen atoms attached to carbon were included as riding contributions in idealized positions (C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å) with isotropic displacement parameters tied to those of the attached atoms [U iso(H) = 1.2–1.5U eq(C)]. Those attached to nitrogen and to oxygen were placed in locations derived from a difference map and refined with DFIX 0.91 0.01 and DFIX 0.84 0.01 instructions, respectively.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C21H22N2O4 |
| M r | 366.40 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 150 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 13.8608 (5), 8.8352 (3), 15.5411 (6) |
| β (°) | 98.468 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1882.46 (12) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.46 × 0.37 × 0.26 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 QUEST PHOTON 3 |
| Absorption correction | Numerical (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.95, 0.98 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 101980, 6815, 5846 |
| R int | 0.035 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.759 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.045, 0.129, 1.07 |
| No. of reflections | 6815 |
| No. of parameters | 254 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.42, −0.31 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022007848/zn2021sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022007848/zn2021Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022007848/zn2021Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2194736
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Author contributions are as follows. Conceptualization, YR and AA; methodology, YR; investigation, IN; theoretical calculations, JTM; writing (original draft), JMT and YR; writing (review and editing of the manuscript), YR; formal analysis, AA and YR; supervision, YR; crystal-structure determination and validation, JTM.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C21H22N2O4 | F(000) = 776 |
| Mr = 366.40 | Dx = 1.293 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 13.8608 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 9714 reflections |
| b = 8.8352 (3) Å | θ = 3.0–32.6° |
| c = 15.5411 (6) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 98.468 (1)° | T = 150 K |
| V = 1882.46 (12) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.46 × 0.37 × 0.26 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 QUEST PHOTON 3 diffractometer | 6815 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5846 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.035 |
| Detector resolution: 7.3910 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 32.6°, θmin = 3.0° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −21→21 |
| Absorption correction: numerical (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | k = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.95, Tmax = 0.98 | l = −23→23 |
| 101980 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.129 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0697P)2 + 0.4122P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6815 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 254 parameters | Δρmax = 0.42 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The diffraction data were obtained from 9 sets of frames, each of width 0.5° in ω or φ, collected with scan parameters determined by the "strategy" routine in APEX3. The scan time was 5 sec/frame. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. H-atoms attached to carbon were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 - 0.99 Å) and were included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 - 1.5 times those of the attached atoms. Those attached to nitrogen and to oxygen were placed in locations derived from a difference map and refined with DFIX 0.91 0.01 and DFIX 0.84 0.01 instructions, respectively. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | −0.01619 (5) | 0.15240 (7) | 0.58519 (4) | 0.02331 (13) | |
| H1 | −0.0211 (11) | 0.0551 (17) | 0.5810 (10) | 0.035* | |
| O2 | 0.06628 (5) | 0.15275 (7) | 0.41710 (4) | 0.02433 (13) | |
| O3 | 0.27892 (5) | 0.18850 (8) | 0.55047 (5) | 0.03248 (16) | |
| O4 | 0.20771 (5) | 0.56774 (9) | 0.30204 (4) | 0.02884 (15) | |
| N1 | 0.10667 (5) | 0.38567 (7) | 0.47826 (4) | 0.01780 (13) | |
| N2 | 0.28454 (5) | 0.43751 (9) | 0.41823 (5) | 0.02231 (14) | |
| H2A | 0.2780 (10) | 0.3724 (17) | 0.4593 (10) | 0.035 (3)* | |
| C1 | 0.12285 (6) | 0.44754 (8) | 0.56329 (5) | 0.01798 (14) | |
| C2 | 0.14520 (7) | 0.59580 (9) | 0.58717 (6) | 0.02279 (16) | |
| H2 | 0.154105 | 0.670797 | 0.545243 | 0.027* | |
| C3 | 0.15409 (7) | 0.63026 (10) | 0.67608 (6) | 0.02693 (17) | |
| H3 | 0.169109 | 0.730952 | 0.694915 | 0.032* | |
| C4 | 0.14134 (7) | 0.51983 (11) | 0.73723 (6) | 0.02757 (18) | |
| H4 | 0.147813 | 0.545934 | 0.797102 | 0.033* | |
| C5 | 0.11902 (7) | 0.37041 (10) | 0.71126 (5) | 0.02376 (16) | |
| H5 | 0.110095 | 0.294882 | 0.752878 | 0.029* | |
| C6 | 0.11028 (6) | 0.33536 (9) | 0.62380 (5) | 0.01846 (14) | |
| C7 | 0.08199 (6) | 0.18914 (8) | 0.57660 (5) | 0.01790 (14) | |
| C8 | 0.08473 (6) | 0.23521 (9) | 0.48075 (5) | 0.01807 (14) | |
| C9 | 0.15003 (6) | 0.05606 (9) | 0.60396 (5) | 0.02081 (15) | |
| H9A | 0.147274 | 0.032787 | 0.665866 | 0.025* | |
| H9B | 0.125732 | −0.033851 | 0.569376 | 0.025* | |
| C10 | 0.25502 (6) | 0.08274 (10) | 0.59283 (6) | 0.02231 (15) | |
| C11 | 0.32861 (7) | −0.02778 (12) | 0.63580 (7) | 0.0316 (2) | |
| H11A | 0.307193 | −0.131044 | 0.619844 | 0.047* | |
| H11B | 0.335063 | −0.015875 | 0.699085 | 0.047* | |
| H11C | 0.391777 | −0.008787 | 0.616620 | 0.047* | |
| C12 | 0.10666 (6) | 0.47028 (9) | 0.39869 (5) | 0.01999 (14) | |
| H12A | 0.077300 | 0.570684 | 0.406183 | 0.024* | |
| H12B | 0.063673 | 0.417265 | 0.351674 | 0.024* | |
| C13 | 0.20497 (6) | 0.49478 (9) | 0.36878 (5) | 0.01973 (14) | |
| C14 | 0.37969 (6) | 0.45788 (11) | 0.39438 (6) | 0.02663 (18) | |
| C15 | 0.42552 (8) | 0.33352 (14) | 0.36257 (7) | 0.0365 (2) | |
| C16 | 0.51776 (9) | 0.3568 (2) | 0.33836 (10) | 0.0557 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.550264 | 0.275060 | 0.315182 | 0.067* | |
| C17 | 0.56220 (9) | 0.4971 (2) | 0.34769 (11) | 0.0664 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.625396 | 0.510315 | 0.332070 | 0.080* | |
| C18 | 0.51564 (10) | 0.6172 (2) | 0.37936 (10) | 0.0579 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.547197 | 0.712839 | 0.385442 | 0.069* | |
| C19 | 0.42263 (8) | 0.60162 (14) | 0.40288 (7) | 0.0381 (2) | |
| C20 | 0.37803 (12) | 0.18097 (16) | 0.35535 (11) | 0.0515 (3) | |
| H20A | 0.315758 | 0.187197 | 0.316412 | 0.077* | |
| H20B | 0.366401 | 0.147447 | 0.413048 | 0.077* | |
| H20C | 0.420847 | 0.108401 | 0.331858 | 0.077* | |
| C21 | 0.37171 (12) | 0.73438 (15) | 0.43604 (10) | 0.0528 (3) | |
| H21A | 0.322214 | 0.772932 | 0.389673 | 0.079* | |
| H21B | 0.419331 | 0.814269 | 0.454501 | 0.079* | |
| H21C | 0.340299 | 0.702735 | 0.485625 | 0.079* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0214 (3) | 0.0181 (3) | 0.0320 (3) | −0.0025 (2) | 0.0089 (2) | 0.0019 (2) |
| O2 | 0.0324 (3) | 0.0196 (3) | 0.0212 (3) | −0.0036 (2) | 0.0045 (2) | −0.0041 (2) |
| O3 | 0.0261 (3) | 0.0303 (3) | 0.0419 (4) | −0.0001 (3) | 0.0079 (3) | 0.0139 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0303 (3) | 0.0361 (4) | 0.0206 (3) | 0.0004 (3) | 0.0053 (2) | 0.0107 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0230 (3) | 0.0147 (3) | 0.0162 (3) | −0.0012 (2) | 0.0045 (2) | 0.0007 (2) |
| N2 | 0.0221 (3) | 0.0242 (3) | 0.0213 (3) | 0.0006 (2) | 0.0051 (2) | 0.0069 (2) |
| C1 | 0.0214 (3) | 0.0153 (3) | 0.0178 (3) | −0.0010 (2) | 0.0045 (2) | −0.0007 (2) |
| C2 | 0.0296 (4) | 0.0157 (3) | 0.0237 (3) | −0.0032 (3) | 0.0062 (3) | −0.0013 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0348 (4) | 0.0198 (4) | 0.0266 (4) | −0.0037 (3) | 0.0057 (3) | −0.0062 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0356 (5) | 0.0269 (4) | 0.0203 (3) | −0.0020 (3) | 0.0044 (3) | −0.0053 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0311 (4) | 0.0226 (4) | 0.0179 (3) | −0.0012 (3) | 0.0049 (3) | 0.0008 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0226 (3) | 0.0153 (3) | 0.0179 (3) | −0.0010 (2) | 0.0044 (2) | −0.0002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.0206 (3) | 0.0145 (3) | 0.0193 (3) | −0.0019 (2) | 0.0050 (2) | 0.0012 (2) |
| C8 | 0.0196 (3) | 0.0155 (3) | 0.0193 (3) | −0.0005 (2) | 0.0037 (2) | −0.0005 (2) |
| C9 | 0.0235 (3) | 0.0157 (3) | 0.0236 (3) | 0.0004 (3) | 0.0045 (3) | 0.0029 (3) |
| C10 | 0.0236 (3) | 0.0200 (3) | 0.0236 (3) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0044 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0271 (4) | 0.0310 (4) | 0.0374 (5) | 0.0081 (3) | 0.0072 (3) | 0.0093 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0228 (3) | 0.0196 (3) | 0.0180 (3) | 0.0010 (3) | 0.0043 (3) | 0.0041 (2) |
| C13 | 0.0237 (3) | 0.0186 (3) | 0.0173 (3) | −0.0003 (3) | 0.0044 (3) | 0.0011 (2) |
| C14 | 0.0215 (3) | 0.0354 (5) | 0.0230 (4) | −0.0008 (3) | 0.0034 (3) | 0.0095 (3) |
| C15 | 0.0299 (4) | 0.0478 (6) | 0.0334 (5) | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0102 (4) | 0.0136 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0342 (5) | 0.0853 (11) | 0.0517 (7) | 0.0270 (6) | 0.0199 (5) | 0.0313 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0237 (5) | 0.1103 (14) | 0.0668 (9) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0503 (10) |
| C18 | 0.0323 (5) | 0.0797 (10) | 0.0591 (8) | −0.0212 (6) | −0.0020 (5) | 0.0332 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0328 (5) | 0.0454 (6) | 0.0342 (5) | −0.0131 (4) | −0.0010 (4) | 0.0135 (4) |
| C20 | 0.0586 (8) | 0.0398 (6) | 0.0598 (8) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0215 (7) | −0.0014 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0691 (9) | 0.0350 (6) | 0.0522 (7) | −0.0196 (6) | 0.0019 (6) | −0.0015 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.4242 (10) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| O1—H1 | 0.864 (15) | C10—C11 | 1.4965 (13) |
| O2—C8 | 1.2248 (9) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| O3—C10 | 1.2167 (11) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| O4—C13 | 1.2266 (10) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C8 | 1.3655 (10) | C12—C13 | 1.5187 (11) |
| N1—C1 | 1.4170 (10) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C12 | 1.4450 (10) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| N2—C13 | 1.3467 (11) | C14—C15 | 1.3956 (15) |
| N2—C14 | 1.4329 (11) | C14—C19 | 1.4005 (15) |
| N2—H2A | 0.874 (15) | C15—C16 | 1.4002 (16) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3840 (11) | C15—C20 | 1.497 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.3948 (11) | C16—C17 | 1.382 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.4026 (12) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C17—C18 | 1.370 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3913 (13) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C18—C19 | 1.3976 (17) |
| C4—C5 | 1.4017 (13) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C19—C21 | 1.499 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3818 (11) | C20—H20A | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C20—H20B | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.5087 (11) | C20—H20C | 0.9800 |
| C7—C9 | 1.5279 (11) | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.5501 (11) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C9—C10 | 1.5091 (12) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9900 | ||
| C7—O1—H1 | 106.6 (10) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—C1 | 110.76 (6) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—C12 | 123.77 (7) | C10—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C12 | 125.35 (6) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C13—N2—C14 | 120.85 (7) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C13—N2—H2A | 120.0 (9) | N1—C12—C13 | 116.66 (7) |
| C14—N2—H2A | 118.0 (9) | N1—C12—H12A | 108.1 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 122.48 (7) | C13—C12—H12A | 108.1 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 127.85 (7) | N1—C12—H12B | 108.1 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 109.65 (6) | C13—C12—H12B | 108.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 116.96 (8) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.3 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.5 | O4—C13—N2 | 123.73 (8) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 121.5 | O4—C13—C12 | 118.34 (7) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.27 (8) | N2—C13—C12 | 117.91 (7) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C15—C14—C19 | 122.55 (10) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C15—C14—N2 | 118.49 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.58 (8) | C19—C14—N2 | 118.96 (9) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C14—C15—C16 | 117.43 (13) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C14—C15—C20 | 121.16 (10) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.55 (8) | C16—C15—C20 | 121.41 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.7 | C17—C16—C15 | 120.95 (14) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.7 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.16 (7) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 130.47 (7) | C18—C17—C16 | 120.38 (11) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 109.27 (7) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 109.46 (6) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| O1—C7—C9 | 110.96 (6) | C17—C18—C19 | 121.27 (14) |
| C6—C7—C9 | 114.71 (7) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.4 |
| O1—C7—C8 | 107.99 (6) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.4 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 101.59 (6) | C18—C19—C14 | 117.39 (13) |
| C9—C7—C8 | 111.59 (6) | C18—C19—C21 | 120.81 (13) |
| O2—C8—N1 | 125.24 (7) | C14—C19—C21 | 121.80 (10) |
| O2—C8—C7 | 126.03 (7) | C15—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—C7 | 108.66 (6) | C15—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C7 | 114.46 (6) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 108.6 | C15—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C7—C9—H9A | 108.6 | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9B | 108.6 | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C7—C9—H9B | 108.6 | C19—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 107.6 | C19—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| O3—C10—C11 | 121.37 (8) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| O3—C10—C9 | 121.73 (8) | C19—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 116.90 (7) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—C1—C2 | −178.96 (8) | C6—C7—C8—N1 | −2.55 (8) |
| C12—N1—C1—C2 | −2.79 (13) | C9—C7—C8—N1 | −125.24 (7) |
| C8—N1—C1—C6 | −0.65 (9) | O1—C7—C9—C10 | 177.23 (7) |
| C12—N1—C1—C6 | 175.53 (7) | C6—C7—C9—C10 | −58.09 (9) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.55 (13) | C8—C7—C9—C10 | 56.75 (9) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 177.57 (8) | C7—C9—C10—O3 | −13.37 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.25 (14) | C7—C9—C10—C11 | 167.08 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.08 (15) | C8—N1—C12—C13 | −98.64 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.18 (14) | C1—N1—C12—C13 | 85.66 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.47 (13) | C14—N2—C13—O4 | −0.69 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −176.29 (8) | C14—N2—C13—C12 | −179.30 (8) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.68 (13) | N1—C12—C13—O4 | −179.12 (8) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −177.74 (7) | N1—C12—C13—N2 | −0.44 (11) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 177.32 (7) | C13—N2—C14—C15 | −107.45 (10) |
| N1—C1—C6—C7 | −1.11 (9) | C13—N2—C14—C19 | 71.84 (12) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | 64.33 (11) | C19—C14—C15—C16 | −0.29 (15) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | −111.85 (7) | N2—C14—C15—C16 | 178.98 (9) |
| C5—C6—C7—C9 | −61.13 (12) | C19—C14—C15—C20 | 179.24 (11) |
| C1—C6—C7—C9 | 122.69 (7) | N2—C14—C15—C20 | −1.49 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 178.34 (9) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 1.46 (18) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | 2.16 (8) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | −178.06 (13) |
| C1—N1—C8—O2 | 179.22 (8) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −1.3 (2) |
| C12—N1—C8—O2 | 2.97 (12) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −0.1 (2) |
| C1—N1—C8—C7 | 2.07 (9) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | 1.18 (18) |
| C12—N1—C8—C7 | −174.18 (7) | C17—C18—C19—C21 | −178.97 (13) |
| O1—C7—C8—O2 | −64.57 (10) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | −1.01 (15) |
| C6—C7—C8—O2 | −179.67 (8) | N2—C14—C19—C18 | 179.73 (10) |
| C9—C7—C8—O2 | 57.64 (10) | C15—C14—C19—C21 | 179.15 (11) |
| O1—C7—C8—N1 | 112.55 (7) | N2—C14—C19—C21 | −0.12 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O2i | 0.864 (15) | 1.942 (15) | 2.7829 (9) | 164.1 (14) |
| N2—H2A···O3 | 0.874 (15) | 2.154 (15) | 3.0193 (10) | 170.3 (13) |
| C3—H3···O4ii | 0.95 | 2.44 | 3.3280 (12) | 155 |
| C9—H9A···O4iii | 0.99 | 2.33 | 3.2537 (11) | 154 |
| C11—H11B···O4iii | 0.98 | 2.59 | 3.2988 (12) | 129 |
| C12—H12A···O1iv | 0.99 | 2.60 | 3.5835 (11) | 173 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+1; (ii) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iv) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
JTM thanks Tulane University for support of the Tulane Crystallography Laboratory.
References
- Allen, C. L. & Williams, J. M. J. (2011). Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 3405–3415. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Beccalli, E. M., Broggini, G., Martinelli, M. & Sottocornola, S. (2007). Chem. Rev. 107, 5318–5365. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Becerra, D., Castillo, J., Insuasty, B., Cobo, J. & Glidewell, C. (2020). Acta Cryst. C76, 433–445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bekircan, O. & Bektas, H. (2008). Molecules, 13, 2126–2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2012). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2021). APEX4 and SAINT. Bruker AXS LLC, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ding, Z., Zhou, M. & Zeng, C. (2020). Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 353, 1900367–380.
- Duan, Z., Han, J., Qian, P., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y. & Pan, Y. (2013). Org. Biomol. Chem. 11, 6456–6459. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Feng, L. S., Liu, M. L., Wang, B., Chai, Y., Hao, X. Q., Meng, S. & Guo, H. Y. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 3407–3412. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y. Q., Zhang, S., Xu, Z., Lv, Z. S., Liu, M. L. & Feng, L. S. (2017). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 141, 335–345. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-W., Yang, J., Wang, G.-L., Gong, Y., Feng, T.-T., Liu, X.-L., Cao, Y., Zhou, Y. & Yuan, W.-C. (2018). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 55, 351–359.
- Makaev, F. Z., Radul, O. M., Gdaniec, M., Malinovsky, S. T. & Gudima, A. P. (2006). Zh. Strukt. Khim. 47, 803.
- Mathur, G. & Nain, S. (2014). Med. Chem. 4, 417–427.
- Missioui, M., Lgaz, H., Guerrab, W., Lee, H., Warad, I., Mague, J. T., Ali, I. H., Essassi, E. M. & Ramli, Y. (2022a). J. Mol. Struct. 1253, 132132–143.
- Missioui, M., Mortada, S., Guerrab, W., Serdaroğlu, G., Kaya, S., Mague, J. T., Essassi, E. M., Faouzi, M. E. A. & Ramli, Y. (2021). J. Mol. Struct. 1239, 130484–494.
- Missioui, M., Said, M. A., Demirtaş, G., Mague, J. T., Al-Sulami, A., Al-Kaff, N. S. & Ramli, Y. (2022b). Arab. J. Chem. 15, 103595–103613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Missioui, M., Said, M. A., Demirtaş, G., Mague, J. T. & Ramli, Y. (2022c). J. Mol. Struct. 1247, 131420–433.
- Nath, R., Pathania, S., Grover, G. & Akhtar, M. J. (2020). J. Mol. Struct. 1222, 128900–993.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, P. R., Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2021). J. Appl. Cryst. 54, 1006–1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tan, S. L., Jotani, M. M. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 308–318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Valeur, E. & Bradley, M. (2009). Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 606–631. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022007848/zn2021sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022007848/zn2021Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022007848/zn2021Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2194736
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report