INTRODUCTION
Humans beings can be identified through a series of methods, being fingerprints the most widely adopted when soft tissue is preserved. However, when the cadaver is carbonized or in skeletal form, forensic dental and anthropologic analysis may become necessary to identify the individual1. Medical documentation (mainly x-ray images) may substantially improve the chances of identifying corpses initially deemed unrecognizable. This paper describes a forensic case in which human remains could be positively correlated to the identity of a missing person through analysis of images of the subject’s frontal sinus in skull posterior-anterior x-ray images.
CASE PRESENTATION
Parts of a human skeleton were found in a patch of woodlands in December of 2006. Many of the remaining bones - ulna, ribs, vertebrae etc - were fractured. The skull had sings of trauma and carbonization. Only the cranial vault was relatively preserved, while face bones were fractured and detached from their joints. Preliminary anthropologic analysis revealed the corpse had characteristic traits of an adult woman.
Police investigation indicated that the tentative victim was a Caucasian woman of 30 years of age missing since May of 2006. She had a head injury when she was 8, and was clinically followed up until she was 25.
The forensics team was given a series of images to try and determine whether the remains belonged to the missing person. Among them were two skull posteroanterior x-ray images from 1989 and 1993 (Fig. 1A and 1B). X-ray images of the skull remains were then taken to support anthropologic comparison (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1.
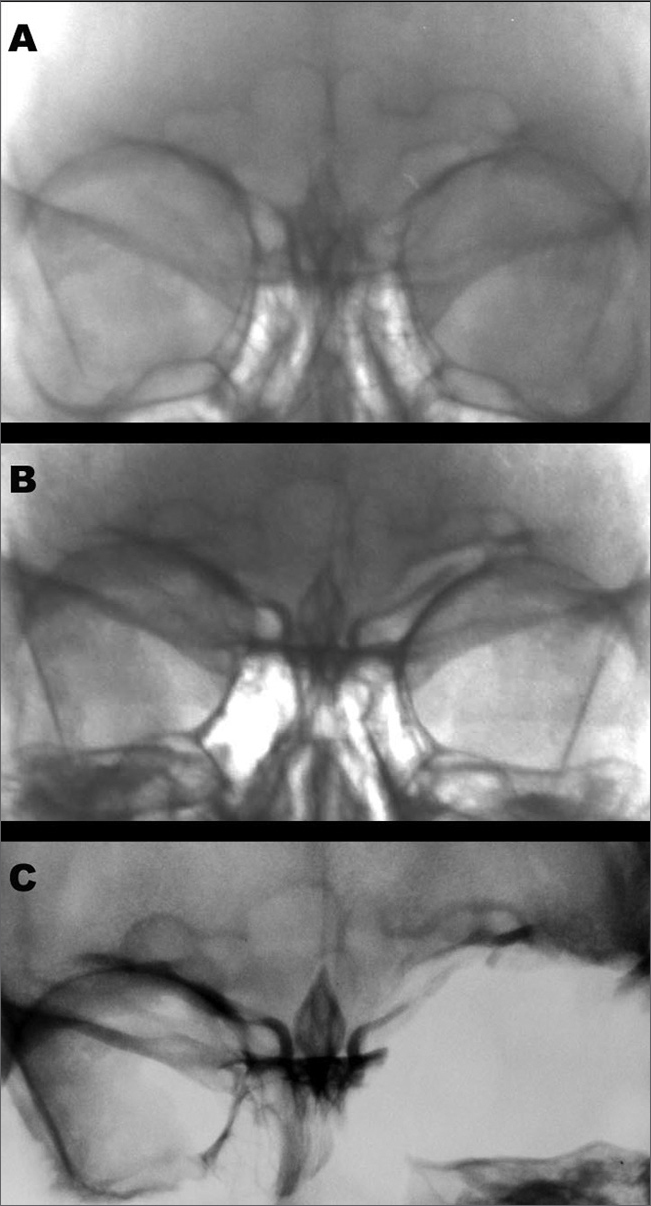
Images of the victim’s frontal sinus in 1989(A), 1993(B), and post-mortem in 2006(C).
DISCUSSION
The frontal sinuses are pneumatic cavities lined with mucosa situated between and internal and external laminae of the frontal bone2. They become radiologically evident at age 5–6, and are fully developed at age 10–123.
The frontal sinus is absent in only 4% of the population and presents distinctive variations in shape, area, and symmetry, thus becoming an important parameter to determine gender dimorphism4 and allow subject identification5. Posteroanterior x-ray images taken under proper processing standards and obtained through adequate technique are essential for good forensic practices6.
CLOSING REMARKS
The identity of the mortal remains was found to be that of a missing woman were identified as the x-ray images produced while she was alive were properly taken, thus enabling frontal sinus morphological analysis. The x-ray images were digitized and adjusted for brightness and contrast to allow improved contour visualization. The results from the comparison between the x-ray images taken before and after the subject’s death indicated the existence of converging traits in both sides of the face, although the left orbit was fractured (Fig. 1C). Aside from their use in the medical practice in identifying frontal sinus trauma and disease, posteroanterior x-ray images allow the visualization of the morphology of the area thus supporting forensic identification efforts.
Footnotes
This paper was submitted to the RBORL-SGP (Publishing Manager System) on 24 December 2006. code 3568.
REFERENCES
- 1.Silva RF, Cruz BVM, Daruge Júnior E, Daruge E, Francesquini Júnior L. La importância de la documentación odontológica en la identificación humana. Acta Odontol Venez. 2005;43(2):67–74. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schwartz JH. In: Skeleton keys: an introduction to human skeletal morphology, development and analysis. Schwartz JH, editor. Oxford University Press; New York: 1995. The Skull; pp. 23–78. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Montovani JC, Nogueira EA, Ferreira FD, Lima Neto AC, Nakajima V. Cirurgia das fraturas do seio frontal: estudo epidemiológico e análise de técnicas. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. 2006;72(2):204–209. doi: 10.1016/S1808-8694(15)30056-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Camargo JR. Estimativa do sexo, através das características radiográficas dos seios frontais [dissertação] Universidade Estadual de Campinas; Piracicaba (SP): 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Riepert T, Ulmcke D, Scheweden F, Nafe B. Identification of unknown dead bodies by X-ray image comparison of the skull using the X-ray simulation program FoXSIS. Forensic Sci Int. 2001 Mar;117(1–2):89–98. doi: 10.1016/s0379-0738(00)00452-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wood RE. Forensic aspects of maxillofacial radiology. Forensic Sci Int. 2006 May;159(Suppl 1):S47–S55. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2006.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


