Abstract
In recent years, the incidence rate of breast cancer has increased year by year, and it has become a major threat to the health of women globally. Among all breast cancer subtypes, the hormone receptor (HR)+/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)− luminal subtype breast cancer is the most common form of breast cancer. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors, the hotspots in the field of targeted therapy for breast cancer, have proved to exhibit a good effect on patients with HR+/HER2− breast cancer in a number of clinical trials, but the problem of drug resistance is inevitable. At present, three specific CDK4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, ribociclib and abemaciclib) have been approved by the USA Food and Drug Administration for the first-line treatment of HR+/HER2− breast cancer. The drug resistance mechanisms of CDK4/6 inhibitors can be divided into cell cycle-specific resistance and cell cycle non-specific resistance. With the discovery of the drug resistance mechanism of CDK4/6 inhibitors, various targeted strategies have been proposed. The present review mainly discusses the mechanism of CDK4/6 inhibitors, drug resistance mechanisms and treatment strategies after resistance.
Keywords: CDK4/6, breast cancer, drug resistance, mechanisms, strategies
1. Introduction
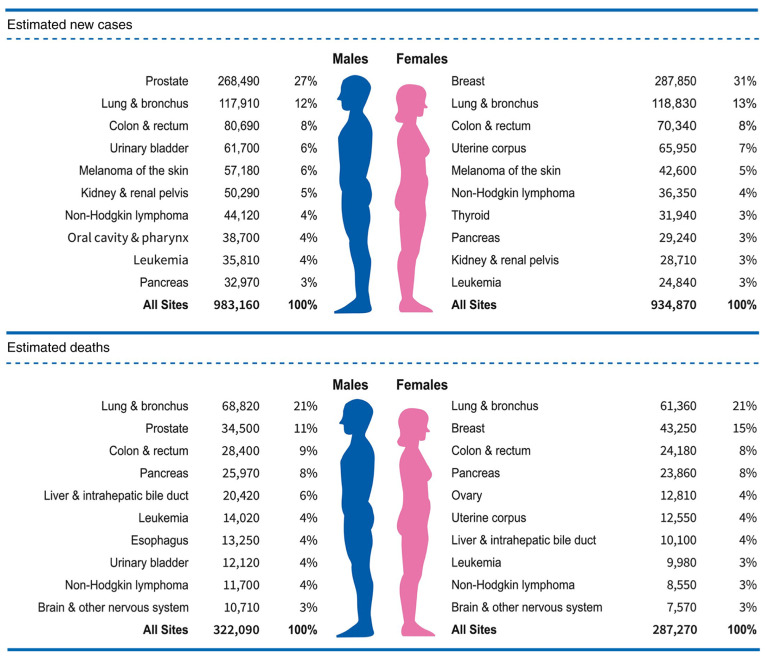
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer (31% of the total cancer incidence) and the second highest cause of cancer-associated death (15% of the total cancer-associated mortality) in women worldwide (Fig. 1) (1). Among all breast cancer subtypes, hormone receptor (HR)+ luminal subtype breast cancer is the most common form of breast cancer, accounting for 75% of the total breast cancer cases and 70% of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) cases (2). Endocrine therapy is the main treatment for HR+ luminal subtype breast cancer, but its effectiveness is restricted by drug resistance, which is almost inevitable in patients with advanced breast cancer (ABC) (3-6). In recent years, the use of targeted therapy combined with endocrine therapy to overcome the endocrine therapy resistance of specific populations has provided a new therapeutic prospect for patients with HR+ breast cancer (7). One of the most basic biological characteristics of malignant tumors is the malignant transformation and uncontrolled proliferation of tumor cells caused by the disorder of cell cycle regulation. CDK4/6 inhibitors restore the cell cycle by selectively inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6), and block cell proliferation in a variety of tumor cells, including those of breast cancer. CDK4/6 inhibitors can effectively improve the prognosis of patients with HR+/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)− breast cancer, but different individuals have different sensitivities to CDK4/6 inhibitors. The present review aims to discuss the mechanism of CDK4/6 inhibitors, drug resistance mechanisms and treatment strategies after resistance.
Figure 1.
Top 10 cancer types with regard to estimated new cases and cancer-associated deaths in the United States in 2022.
2. Mechanism of CDK4/6 inhibitors
To ensure that each cell cycle is completed accurately, complex regulatory mechanisms exist in the normal cell cycle. CDK4/6 is a key regulator of the cell cycle, acting by forming a complex with cyclin D (8). This complex can directly phosphorylate retinoblastoma gene (RB), then release transcription factor E2F and promote the transcription of cell cycle-related genes, promoting the cell cycle from the G1 mitosis phase to the S phase, leading to DNA replication (Fig. 2) (9). In estrogen receptor (ER)+ breast cancer, estrogen induces the activation of the ER signaling pathway, which leads to the upregulation of the expression of cyclin D and CDK4/6, and further leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation (10,11). CDK4/6 is activated in ER+ breast cancer; therefore, CDK4/6 inhibitors can significantly inhibit the progression of ER+ breast cancer.
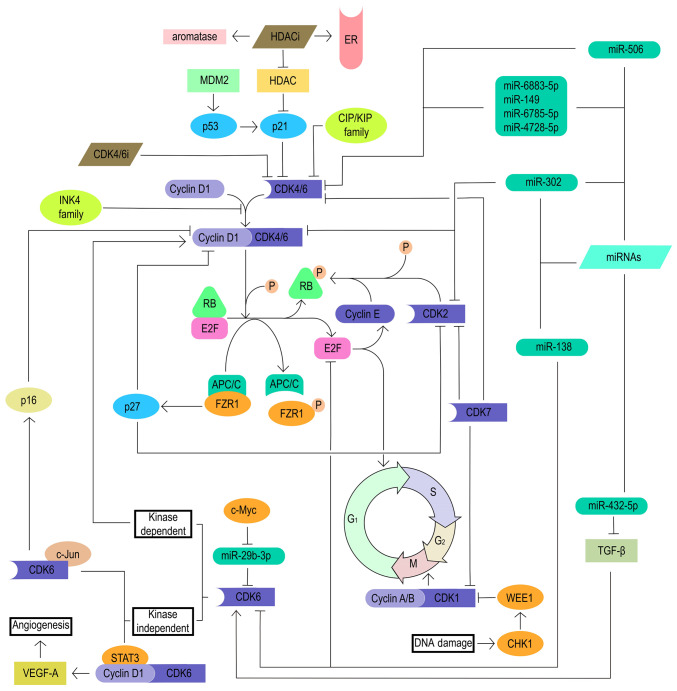
Figure 2.
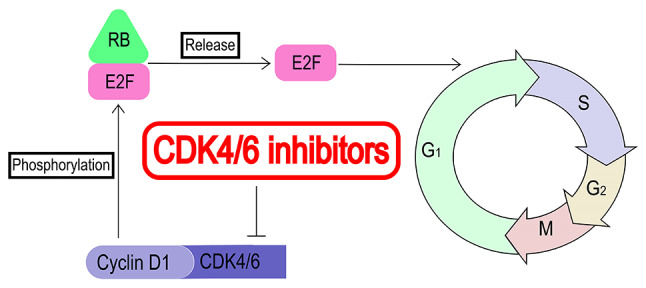
Mechanism of CDK4/6 inhibitors. CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; RB, retinoblastoma protein.
3. Key clinical trials of CDK4/6 inhibitors
Based on the data from three series of clinical trials, namely PALOMA, MONALEESA and MONARCH, three CDK4/6 inhibitors have been approved by the USA Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency for the treatment of patients with HR+/HER2− ABC: Palbociclib (Ibrance®; Pfizer, Inc.), ribociclib (Kisqali®; Novartis International AG) and abemaciclib (Verzenio®; Eli Lilly and Company) (12-17). In addition, a new CDK4/6 inhibitor, dalpiciclib, was reported in the 2021 ASCO meeting (18). The DAWNA-1 study showed that the dalpiciclib + fulvestrant group exhibited a significantly improved median progression-free survival time (15.7 vs. 7.2 months; hazard ratio, 0.42; P<0.0001) compared with the placebo + fulvestrant group in patients with HR+/HER2− ABC whose condition had relapsed or advanced after endocrine therapy (Table I) (19). In addition, the safety of dalpiciclib (SHR6390) was confirmed in clinical trial NCT03481998 (20).
Table I.
Key clinical trials on CDK4/6 inhibitors in patients with hormone receptor+/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2− advanced breast cancer/metastatic breast cancer.
| NCT | Study name | Phase | Intervention | LOT | Menopausal status | mPFS time, months | mOS time, months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00721409 | PALOMA-1 | II | Let ± Pal | 1st | Post | 20.2 vs. 10.2 | 37.5 vs. 34.5 |
| NCT01740427 | PALOMA-2 | III | Let ± Pal | 1st | Post | 24.8 vs. 14.5 | 53.9 vs. 51.2 |
| NCT01942135 | PALOMA-3 | III | Ful ± Pal | 1st + 2nd + later | Pre/post | 9.2 vs. 3.8 | 34.9 vs. 28.0 |
| NCT02297438 | PALOMA-4 | III | Let ± Pal | 1st (Asian) | Post | 21.5 vs. 13.9 | 51.7 vs. 51.5 |
| NCT01958021 | MONALEESA-2 | III | Let ± Ribo | 1st | Post | 25.3 vs. 16.0 | 63.9 vs. 51.4 |
| NCT02422615 | MONALEESA-3 | III | Ful ± Ribo | 1st + 2nd | Post | 20.5 vs. 12.8 | 53.7 vs. 41.5 |
| NCT02278120 | MONALEESA-7 | III | TAM/NSAI ± Ribo | 1st + 2nd | Pre | 23.8 vs. 13.0 | NR vs. 40.9 |
| NCT02102490 | MONARCH-1 | II | Abema | 2nd | Pre/post | 6.0 | 22.32 |
| NCT02107703 | MONARCH-2 | III | Ful ± Abema | 1st + 2nd | Pre/post | 16.4 vs. 9.3 | 46.7 vs. 37.3 |
| NCT02246621 | MONARCH-3 | III | NSAI ± Abema | 1st | Post | 28.18 vs. 14.76 | - |
| NCT02763566 | MONARCH plus | III | Cohort A: NSAI ± Abema; cohort B: Ful ± Abema | ≥1st (Chinese) | Post | A: NR vs. 14.73; B: 11.47 vs. 5.59 | - |
| NCT03927456 | DAWNA-1 | III | Ful ± Dal | 2nd | Pre/post | 15.7 vs. 7.2 | - |
NCT, National ClinicalTrials.gov identifier; LOT, line of therapy; mPFS, median progression-free survival; mOS, median overall survival; Pal, palbociclib; Ribo, ribociclib; Abema, abemaciclib; Let, letrozole; NSAI, non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor; Ful, fulvestrant; TAM, tamoxifen; Dal, dalpiciclib; Pre, premenopausal; Post, postmenopausal; NR, not reached.
4. Resistance mechanisms of CDK4/6 inhibitors
Cell cycle-specific mechanisms Loss of RB
As a tumor suppressor, RB is the main target of the cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex and controls the CDK4/6-RB1 pathway and the cell cycle. Loss of RB is one of the most important reasons for the development of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors (9). The main reason for the loss of RB is the inactivion of the RB1 gene by a mutation. Despite the loss of RB, the constitutive progression of the cell cycle continues through the activation of other cell cycle mechanisms, including the E2F and cyclin E-CDK2 axes, indicating that the progression of the cell cycle from G1 to S phase has lost its dependence on CDK4/6 (21). This indicates that the combination of cyclin E-CDK2 axis inhibitors and CDK4/6 inhibitors may reverse the resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors in patients with loss of RB (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Cell cycle-specific mechanisms for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; RB, retinoblastoma protein; CHK1, checkpoint kinase 1; HDAC, histone deacetylases; HDACi, histone deacetylases inhibitor; INK4, inhibitor of CDK4; WEE1, WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase; FZR1, fizzy and cell division cycle 20-related 1; VEGF-A, vascular endothelial growth factor A; MDM2, mouse double minute 2 homolog; ER, estrogen receptor; CIP/KIP, CDK interaction protein/kinase inhibitor protein; P, phosphate; CDK4/6i, CDK4/6 inhibitor; miR/miRNA, microRNA; APC/C, anaphase-promoting complex.
E2F amplification
The RB-E2F complex plays an important role in regulating the cell cycle from G1 to S phase. As aforementioned, the hyperphosphorylation of RB by the cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex reduces the association between RB and E2F. In turn, the RB-E2F complex separates and releases the transcription factor E2F, which promotes the cell cycle from the G1 mitosis phase to the S phase, leading to DNA replication. At the same time, cyclin E transcription is activated by the E2F transcription factor, which activates CDK2 and other proteins to form the cyclin E-CDK2 complex. The cyclin E-CDK2 complex further phosphorylates RB, which forms a positive feedback loop, leading to synthesis of protein and DNA eventually (22). Therefore, E2F amplification and the formation of the cyclin E-CDK2 complex are also associated with the resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 3).
Overexpression of the inhibitor of CDK4 (INK4) family
The INK4 family is a set of intrinsic tumor suppressor factors, including p16INK4A (coded by CDKN2A), p15INK4B (coded by CDKN2B), p18INK4C (coded by CDKN2C) and p19INK4D (coded by CDKN2D). The INK4 family members can inhibit the formation of the cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex by competitively binding CDK4/6, and further inhibit the transition of cells from the G1 phase to the S phase (23). The expression of CDKN2 in tumor cells is often silenced, resulting in the continuous activation of CDK4/6 and the drug resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors. However, when these inhibitors are overexpressed, due to the inhibition of the cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex, tumor cell cycle progression may partly depend on other signaling pathways besides CDK4/6 signaling, resulting in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. The study by Green et al (24) also reported that the p16 protein family can inhibit the binding of small molecule inhibitors, including palbociclib, to CDK4. However, the PALOMA-1 trial did not reveal a significant difference in terms of PFS for the cohort with p16/CCND1 amplification loss compared with the unselected cohort (25). Similar results were gathered by biomarker analysis in the PALOMA-2 and PALOMA-3 trials (26,27). Therefore, the use of p16INK4 amplification as a biomarker is controversial (Fig. 3).
CDK amplification
As aforementioned, CDK4/6 plays a vital role in the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S phase. Various mechanisms such as gene amplification, mutation and epigenetic changes can upregulate CDK4/6, thereby activating the cyclin D-CDK4/6-RB pathway, which leads to a decreased blocking effect of CDK4/6 inhibitors on cell cycle progression (28-30). In addition to kinase-dependent functions, CDK6 also has some non-kinase-dependent functions. CDK6 upregulates the transcription of p16 in the presence of STAT3 and cyclin D (31). In addition, CDK6 and c-Jun synergistically upregulate VEGF-A, induce tumor angiogenesis, and usually promote cancer progression and drug resistance (32,33). A previous study found that the oncogene c-Myc could reduce the inhibitory effect of microRNA (miRNA/miR)-29b-3p on CDK6 by downregulating miR-29b-3p, and that activated CDK6 further induced breast cancer resistance to palbociclib (34).
Cyclin E-CDK2 also plays an important role in the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S phase. A previous study emphasized that after CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cells lost their dependence on cyclin D-CDK4/6 signaling, the inhibition of a variety of alternative signal pathways, including the cyclin E-CDK2 pathway, could significantly inhibit cell growth. CDK2 inhibitors effectively reduced the growth of cells overexpressing cyclin E1 (35).
Moreover, CDK7 is a cell cycle regulator. CDK7 plays the role of CDK-activating kinase (CAK) and participates in the G1 and G2 phases by maintaining the activity of CDK1/2/4/6 (36). It has been reported that the increase in CDK7 expression confers resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 3) (37). At the 2021 SABCS meeting, a study reported the confirmed efficacy and safety of the first oral selective CDK7 inhibitor samuraciclib (CT7001) + fulvestrant in patients with HR+/HER2− ABC (38).
Loss of CDK interaction protein/kinase inhibitor protein (CIP/KIP) family expression
The CIP/KIP family includes p21CIP1 (coded by CDKN1A), p27KIP1 (coded by CDKN1B) and p57KIP2 (coded by CDKN1C). This protein family has both CDK inhibitors and stable cyclin-CDK complexes, and a study has concluded that p21 and p27 are involved in cell G1/S phase regulation (39). Therefore, the activation of the cyclin-CDK-Rb pathway signal caused by the deletion of the CIP/KIP family is associated with the resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors (40).
In addition, a study has found that histone deacetylases (HDACs) have an inhibitory effect on the intrinsic CDK inhibitor p21CIP1, and HDAC inhibitors can upregulate the expression of p21CIP1. Whether in vitro or in vivo, HDAC inhibitors can increase the expression of ER and aromatase, and restore the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to hormone blockade (41). Adding entinostat or tucidinostat to exemestane can improve the mPFS time (entinostat: 4.3 vs. 2.3 months; P=0.055; tucidinostat: 7.4 vs. 3.8 months; P=0.033), and significant improvement has been observed in patients with non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) resistance (42,43). This supports the hypothesis that HDAC inhibition may enhance the activity of CDK4/6 inhibitors through the CIP/KIP family, suggesting that the combination of HDAC inhibitors and CDK4/6 inhibitors may be beneficial to patients with CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance (Fig. 3).
Overexpression of WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase (WEE1)
WEE1 belongs to the serine/threonine protein kinase family, which plays a key role in ensuring accurate DNA replication, maintaining chromosome integrity, blocking abnormal cell DNA replication and G2/M phase transition during the cell cycle (44). WEE1 and CDK1 synergistically inhibit DNA-damaged cells from entering mitosis, whereas WEE1 inhibition promotes mitosis and propagates genomic instability by forcing the cell through successive replication cycles, ultimately resulting in apoptosis from mitotic catastrophe. It was found that WEE1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy could synergistically strengthen the DNA damage to tumor cells and block cell cycle transition (44). At the same time, a study has shown that overexpression of WEE1 can induce tumor resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Therefore, inhibiting WEE1 can increase the sensitivity of CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cells to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 3) (45).
Loss of fizzy and cell division cycle 20-related 1 (FZR1)
FZR1 forms the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C)-FZR1 complex by activating the ubiquitin ligase APC/C. The APC/C-FZR1 complex interacts with RB during the G1 phase of the cell cycle (46). In addition, the APC/C-FZR1 complex further upregulates the natural CDK inhibitor p27 by degrading S-phase kinase-associated protein 2, leading to the decrease in the expression of CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 (47). Therefore, the loss of FZR1 leads to resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, the mechanism of which needs further exploration (Fig. 3).
Mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) overexpression
MDM2 is a protein that negatively regulates p53 activity. MDM2 inhibitors can activate p53 by disrupting the MDM2-p53 complex (48). p53 can activate the natural CDK4 inhibitor p21CIP1, leading to cell cycle arrest (49). NVP-CGM097 is one of the first new-generation inhibitors and has entered phase I clinical trials (NCT01760525) (9). Although the mechanism of action of MDM2 inhibitors still needs further research and exploration, MDM2 inhibition may be a new therapeutic target for the treatment of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 3).
miRNAs
Numerous preclinical studies have discovered the role of miRNAs in the progression of various tumors, including glioblastoma, ovarian cancer and colon cancer. miR-302 induces cell cycle G1/S arrest by inhibiting the cyclin D-CDK4/6 and cyclin E-CDK2 pathways (50). miR-138 induces cell cycle G1/S arrest by directly targeting cell cycle genes such as CDK6, E2F2 and E2F3 (51). miR-506 directly targets CDK4 and CDK6, and further inhibits CDK4/6-forkhead box M1 signaling to inhibit cell proliferation (52). A family of miRNAs containing miR-6883-5p, miR-149, miR-6785-5p and miR-4728-5p inhibit cell proliferation by directly targeting the untranslated regions of CDK4/6 mRNAs (53). miR-432-5p induces the overexpression of CDK6 in ER+ breast cancer cells by inhibiting the TGF-β pathway, further antagonizing the effect of CDK4/6 inhibitors (54). Therefore, targeted regulation of associated miRNAs provides a therapeutic direction for patients with breast cancer who are resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 3).
Cell cycle non-specific mechanisms
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) signaling pathway
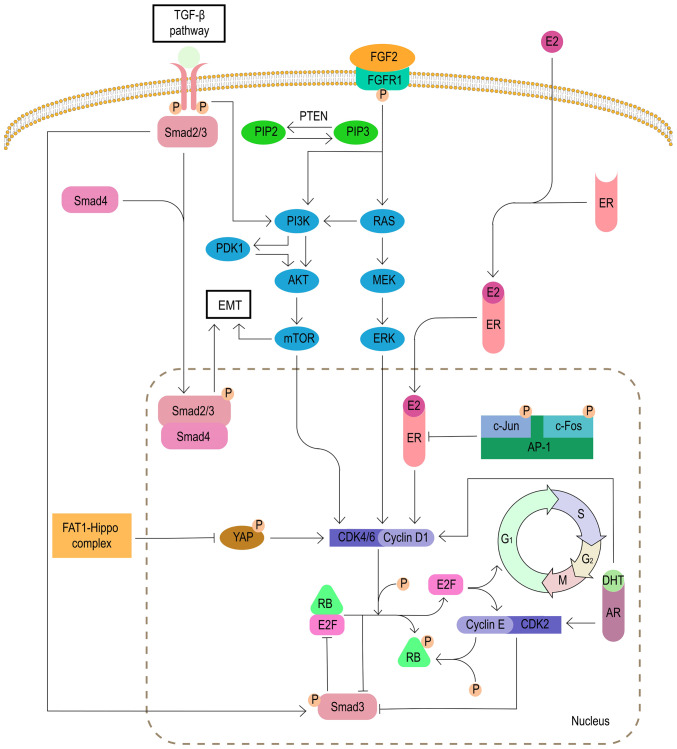
The FGFR1 signaling pathway is related to pivotal biological processes, including proliferation, differentiation and cell survival (55). FGFR1 plays an important role in cancer progression. In endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells, the expansion of FGFR1 activates the PI3K/AKT and RAS/MEK/ERK signaling pathways, which is associated with CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance (56). In the MONALEESA-2 trial, combined treatment with FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor lucitanib eliminated the resistance to ribociclib, a specific CDK4/6 inhibitor (57). Therefore, inhibition of FGFR1 pathway may be a viable option to overcome resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 4).
Figure 4.
Cell cycle non-specific mechanisms for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. FGF2, fibroblast growth factor 2; FGFR1, fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; ER, estrogen receptor; AR, androgen receptor; PDK1, 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1; DHT, 5-α-dihydrotestosterone; AP-1, activator protein 1; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; RB, retinoblastoma protein; P, phosphate; FAT1, FAT atypical cadherin 1; YAP, yes-associated protein; PIP, prolactin-induced protein; Smad, drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic protein.
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
It has been reported that the PIK3/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is associated with resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. A study has shown that direct inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway can reduce the expression of cyclin D and cause cell cycle arrest, which may be the potential mechanism of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors (58).
In addition, as a negative regulator of the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, PTEN deletion causes tumor cells to develop resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors by activating AKT (59). It has also been found that the deletion of PTEN induces the downregulation of the nuclear CDK inhibitor protein p27 (coded by CDKN1B), which also leads to resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 4) (60).
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway
The MAPK signaling pathway is one of the signaling pathways downstream of FGFR1. The MAPK pathway is also known as the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway based on the composition of its key kinases. Therefore, MEK/ERK is a key target for the treatment of patients with resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. A study has found that the MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib combined with fulvestrant and palbociclib can effectively inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 4) (57).
Loss of ER/progesterone receptor (PR) expression and higher transcriptional activity of activator protein 1 (AP-1)
The activity of breast cancer cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex depends on the activation of ER/PR induced by estrogen and progesterone hormones (61). A study has indicated that the resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors is associated with changes in ER/PR levels (30). Therefore, for patients with CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance due to the loss of ER/PR expression, HR− breast cancer subtype relative treatments may be a good choice.
As a transcription factor that regulates cyclin D1, the AP-1 family consists of homodimers and heterodimers of the Jun, Fos, activation transcription factor and transcription factor MAF sub-families (62). A study has found that 20-40% of human patients with breast cancer have high levels of c-Jun activation, which inhibits the activity of ER and activates the transcription of cyclin D1 to induce CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance (63). Currently, various AP-1 inhibitors are under active development, and a selective c-Fos/AP-1 inhibitor (T-5224) has entered the second phase of clinical trials (64). The efficacy of AP-1 inhibitors for patients with breast cancer resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors needs further exploration, but the results are worth looking forward to (Fig. 4).
Overexpression of androgen receptor (AR)
It has been reported that the acquired resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors is associated with the activation of AR, which is expressed in >70% of breast cancer cases (65). A study has found ER signal loss and AR signal activation in the palbociclib-resistant breast cancer cell line MCF-7pR. The non-aromatizable androgen 5-α-dihydrotestosterone-activated AR promotes G1/S transition by activating cyclin D1, cyclin E1 and CDK2, thereby inducing resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. As a new type of selective AR inhibitor, the combination therapy of enzalutamide and palbociclib can resensitize breast cancer cells to palbociclib and reverse the resistance to the drug (66). Therefore, AR inhibitors may be one of the treatment options for patients with breast cancer who are resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 4).
Hippo pathway
The tumor suppressor FAT atypical cadherin 1 (FAT1) belongs to the cadherin superfamily and interacts with the Hippo and β-catenin signaling pathways (25). In a genome analysis of 348 cases of ER+ breast cancer after CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment, loss of function mutations of FAT1 were detected in CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant patients. Loss of FAT1 led to the inhibition of the Hippo pathway and induced the nuclear localization of Yes-related protein/tafazzin to induce CDK6 expression. At the same time, the inactivation of neurofibrin 2, a component of the hippocampus pathway, also increased the expression of CDK6. The two approaches synergistically reduced the sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibitors (Fig. 4) (67).
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathway and Smad3 suppression
EMT refers to the transformation of cells from epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells. The process plays an important role in embryonic development and tissue reconstruction, but EMT also confers the ability to invade and metastasize to cancer cells. The inhibition of CDK4/6 can induce EMT by activating the TGF-β-Smad and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways (68-70). Phosphorylated TGF-β activates Smad2 and Smad3, and then forms a complex with Smad4, resulting in EMT by activation of the EMT transcription factor (70). However, it has been found that the inhibition of Smad3 can also induce resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors (71). Inhibition of Smad3 induces the recovery of cell cycle arrest by releasing its blockage of E2F from the Rb-E2F complex (72). In addition, the inhibition of Smad3 is associated with the activation of the cyclin E-CDK2 axis (73). As aforementioned, miR-432-5p antagonizes the effects of CDK4/6 inhibitors by inhibiting the TGF-β pathway. Therefore, the TGF-β pathway has a very complicated association with CDK4/6 inhibitors, and more research is needed (Fig. 4).
5. Treatment strategies after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance
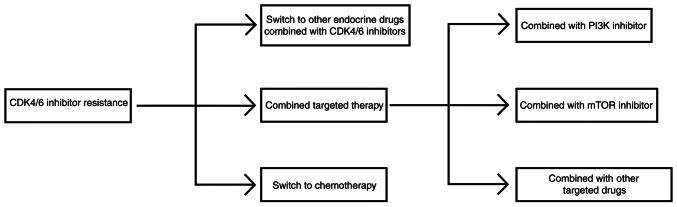
Treatment with endocrine therapy drugs combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors has become the international recommended treatment plan for HR+ ABC without visceral crisis, and the level I recommended treatment plan of the 2020 CSCO guidelines also agrees with this (74). However, CDK4/6 inhibitors can significantly delay but not prevent the emergence of acquired resistance of endocrine therapy. At present, there is no uniform recommended treatment option for patients who have progressed after treatment with endocrine therapy drugs combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors. Generally, the various treatment options can be divided into three categories: Switching to other endocrine therapy + CDK4/6i, combining targeted therapy and switching to chemotherapy (Fig. 5).
Figure 5.
Treatment strategies after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance. CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase.
Switch to other endocrine drugs combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors
The MonarchE and nextMONARCH studies have confirmed the effectiveness of abemaciclib combined with endocrine therapy (75,76). Another study from Harvard Medical School suggested that for patients who had previously received the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib or ribociclib, switching to abemaciclib monotherapy or a combination with endocrine therapy after the disease progressed resulted in a mPFS time of 5.4 months (77). As reported at the 2022 ASCO meeting, a phase II clinical study (MAINTAIN study) compared the effect of receiving switch endocrine therapy ± ribociclib after the progression on CDK4/6 inhibitors (78). The PFS time of the combination group was prolonged by 2.5 months (5.29 vs. 2.76 months; P=0.006) compared with the monotherapy group (Table II). A phase II clinical study (PACE study) compared the post-progression effect of receiving fulvestrant ± palbociclib on aromatase inhibitors (AIs) combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors and is currently ongoing (79). The results of the EMERALD phase 3 study presented at the 2021 SABCS meeting showed that elacestrant (an oral selective ER administration) was more effective than AI in patients with ER+/HER2− MBC who had advanced following prior endocrine therapy in combination with CDK4/6 inhibitors (80,81). Therefore, switching to other endocrine drugs combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors is one of the options after drug resistance.
Table II.
Key clinical trials on treatments after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in patients with hormone receptor+/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2− advanced breast cancer/metastatic breast cancer.
| NCT | Study name | Phase | Intervention | LOT | Menopausal status | mPFS time, months | mOS time, months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02632045 | MAINTAIN | II | Ful ± Ribo | 2nd | Pre/post | 5.29 vs. 2.76 | - |
| NCT02437318 | SOLAR-1 | III | Ful ± Alp | 2nd | Post | 11 vs. 5.7 | 39.3 vs. 31.4 |
| NCT03056755 | BYLieve | II | Cohort A: Ful ± Alp Cohort B: Let ± Alp | 2nd | Pre/post | A: 7.3; B: 5.7 | - |
| NCT00863655 | BOLERO-2 | III | Exe ± Eve | 2nd | Post | 6.93 vs. 2.83 | 31.0 vs. 26.6 |
| NCT02482753 | ACE | III | Exe ± Chi | 2nd | Post | 7.4 vs. 3.8 | - |
| NCT03584009 | Veronica | II | Ful ± Ven | 2nd | Pre/post | 2.69 vs. 1.94 | - |
NCT, National ClinicalTrials.gov identifier; LOT, line of therapy; mPFS, median progression-free survival; mOS, median overall survival; Ful, fulvestrant; Ribo, ribociclib; Alp, alpelisib; Exe, exemestane; Eve, everolimus; Chi, chidamide; Ven, venetoclax; Pre, premenopausal; Post, postmenopausal.
Combined targeted therapy
Combined with phosphatidylinositol- 4, 5-bisphos-phate 3-kinase catalytic subunit α (PI3K) inhibitor
PIK3CA is one of the most commonly mutated genes in breast cancer. Approximately 40% of patients with HR+ and HER2− ABC have PIK3CA mutations. PIK3CA mutations can promote endocrine resistance through the activation of the PI3K pathway, which is associated with a poor prognosis (82).
As an α-selective PI3K inhibitor, alpelisib demonstrated its efficacy for the first time in the SOLAR-1 study (74). In the SOLAR-1 study, alpelisib + fulvestrant was compared with placebo + fulvestrant for patients with HR+/HER2− ABC with PIK3CA mutations who progressed during or after treatment with AI. The PFS time was prolonged by 5.3 months (11 vs. 5.7 months; P=0.00065) (Table II). The 2020 ESMO meeting reported the final results of this study. Compared with that of the placebo + fulvestrant group, the median overall survival (mOS) time of alpelisib + fulvestrant group was prolonged by 7.9 months (39.3 vs. 31.4 months) [https://dailyreporter.esmo.org/esmo-congress-2020/articles/solar-1-trial-reports-overallsurvival-benefits-in-breast-cancer-patients-with-limited-options-of-treatment] (83). Alpelisib has also been approved by the FDA for marketing due to these study results. However, <10% of the patients enrolled in the SOLAR-1 study received CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment. The BYLieve study reported at the 2020 ASCO meeting addresses the question of whether alpelisib plays the same role in patients who progress after treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitors (84). Patients with PIK3CA mutations who progressed after first-line treatment with AIs combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors were enrolled in cohort A and received alpelisib combined with fulvestrant as the second-line treatment. At the 2020 ASCO meeting, the mPFS time was reported as 7.3 months, and the 6-month PFS rate was 50.4% (85). This time was 11.0 months in the SOLAR-1 study, suggesting that the first-line CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment may not affect the efficacy of the follow-up PI3K inhibitor (alpelisib) treatment (86). In addition, patients with PIK3CA mutations who progressed after fulvestrant combined with CDK4/6 inhibitor first-line treatment were enrolled in cohort B in the BYLieve study and received alpelisib combined with letrozole as the second-line treatment. At the 2020 SABCS meeting, the mPFS time was reported as 5.7 months, and the 6-month PFS rate was 46.1% (Table II) (87). Therefore, for patients with PIK3CA mutations who have progressed after endocrine therapy combined with CDK4/6 inhibitor first-line treatment, the treatment of endocrine therapy combined with PI3K inhibitors can be a choice for patients.
Combined with mTOR inhibitor
The mTOR pathway is an important signaling pathway downstream of PI3K, so mTOR inhibitors have received as much attention as PI3K inhibitors. Everolimus is a representative of the mTOR inhibitors, and its effect has been confirmed in the BOLERO-2 study. In the BOLERO-2 study, for patients who progressed after NSAI treatment, the everolimus plus exemestane (SAI) group had significantly longer mPFS and mOS times than the placebo plus exemestane group (mPFS: 6.93 vs. 2.83 months; HR, 0.43; P<0.0001; mOS: 31.0 vs. 26.6 months; HR, 0.89; P=0.14) (Table II). In patients who progressed after treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitors, the study also showed a good therapeutic effect of everolimus (88). The TRINITI clinical study reported at the 2019 ASCO meeting enrolled patients who progressed after treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitors (89). After receiving exemestane, everolimus and ribociclib combination therapy, the clinical benefit rate at 24 weeks reached 41%, which exceeds the pre-defined primary endpoint threshold (>10%). The mPFS time of the overall population reached 5.7 months (90). Therefore, mTOR inhibitors seem to be a good option for patients who are resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors.
Combine with other targeted drugs
Resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors is a complex process involving multiple different mechanisms, including CDK2 and CDK7 activation, and FGFR1 mutations, among others. Therefore, a series of corresponding clinical studies are currently underway to explore whether the addition of these new targeted drugs can overcome the resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors.
AKT acts as a bridge connecting the PI3K and mTOR signaling pathways. The TAKTIC study evaluated the efficacy of AKT-1 inhibitor ipatasertib + endocrine therapy ± CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in the treatment of patients with HR+/HER2− ABC. The interim analysis of group C (ipatasertib + fulvestrant + palbociclib) was reported at the 2020 ASCO meeting (91). The results showed that for patients who had failed previous CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment, AKT inhibitor + CDK4/6 inhibitor + endocrine therapy achieved good clinical effects in some patients (8/12) and was well tolerated. The follow-up results of the TAKTIC study remain to be seen. Therefore, AKT inhibitors may become one of the treatment choices after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance.
HDAC inhibitors are another of the targeted drugs most focused upon. The ACE study showed that the mPFS time of the chidamide combined with exemestane group was longer than that of the placebo combined with exemestane group (7.4 vs. 3.8 months; P=0.033) (Table II) (43). At the 2021 SABCS meeting, another HADC inhibitor, entinostat, was shown to improve PFS time in patients with HR+/HER2− ABC with AI resistance. Therefore, HDAC inhibitors also provide new options for patients who are resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors.
B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL2) is an estrogen-responsive gene and anti-apoptotic protein overexpressed in ~80% of patients with HR+ breast cancer (92). Venetoclax combined with tamoxifen had a tolerable safety profile and significant activity in patients with ER+/HER2− ABC that overexpresses BCL2 in a phase I clinical trial (93). In addition, an ongoing phase I clinical trial, PALVEN (NCT03900884), is evaluating the safety and efficacy of AI + CDK4/6 inhibitor + venetoclax triple therapy as first-line treatment for patients with ER+/HER2− ABC with BCL2 overexpression. Another ongoing phase II clinical trial, Veronica (NCT03584009), is evaluating venetoclax + fulvestrant vs. fulvestrant in patients who have progressed after CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy. There was no significant difference in PFS time between the combination and monotherapy groups in the preliminary results of the Veronica trial presented at the ASCO 2021 meeting (2.69 vs. 1.94 months; P=0.7853) (Table II) (94,95). However, with the support of results from further clinical studies, BCL2 inhibitors are still expected to be a second-line option after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance.
CDK4/6 inhibitors can effectively inhibit the proliferation of regulatory T cells and enhance the function of effector T cells in the tumor microenvironment, which provides a theoretical basis for the combination of CDK4/6 inhibitors with immune checkpoint inhibitors (96). An ongoing phase IB clinical trial, JPCE (NCT02779751), is evaluating the efficacy and safety of abemaciclib in combination with pembrolizumab (PD-1 inhibitor) in the treatment of HR+/HER2− MBC. Another ongoing phase II clinical trial, PACE (NCT03147287), is evaluating the efficacy of fulvestrant, palbociclib and avelumab (PD-L1 inhibitor) in patients with ER+/HER2− breast cancer who are resistant to palbociclib.
Switch to chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is also a good option for patients with HR+/HER2− ABC who are resistant to endocrine therapy + CDK4/6i (97). In clinical practice, chemotherapy is usually chosen as the follow-up treatment plan. In the PALOMA-3 clinical study, most of the patients who received fulvestrant combined with palbociclib treatment exhibited disease progression, and most of the researchers recommended that the patients should receive chemotherapy after leaving the group (98). A real-world study from the United States showed that out of 525 patients who progressed after receiving CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment, more than one-third of the patients received subsequent chemotherapy, and the chemotherapy drugs used were capecitabine and taxanes (99). There are three ongoing clinical trials (NCT04251169, NCT03901339 and NCT04134884) evaluating the efficacy of chemotherapy after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in patients with ER+/HER2− breast cancer. In addition, eribulin, a tubulin polymerization inhibitor, was reported at the 2021 ASCO meeting as a monotherapy for patients with HR+/HER2− MBC after CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment (100). Therefore, following resistance to endocrine therapy + CDK4/6i for patients with HR+/HER2− ABC, chemotherapy still remains a usual choice of treatment.
6. Conclusions
Optimizing the treatment of those patients with HR+/HER2− ABC with the highest proportion of ABC will have great significance for improving the prognosis of ABC. Drug resistance is an unavoidable problem. In fact, the molecular mechanism of the resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors is very complicated, so clarifying its resistance mechanism is crucial to the choice of the next treatment plan. According to the different resistance mechanisms, the targeted drugs that can be selected after resistance should also be different. Firstly, abnormalities in the key molecules of the cyclin D-CDK4/6-RB regulatory axis itself can lead to drug resistance. Secondly, abnormal upstream regulators of the cell cycle pathway are also common causes of drug resistance. Thirdly, in addition to cyclin D-CDK4/6, cyclin E-CDK2 also participates in promoting cell G1/S transition through phosphorylation of Rb. Lastly, tumor cells may also trigger drug resistance through other non-specific cell growth signaling pathways that activate the cell cycle. Dual-target or even multi-target combinations can be used to simultaneously inhibit cell cycle pathways and abnormally activated growth bypasses, thereby delaying CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance.
At present, treatment options after resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors are still limited and full of controversy. There is no clear and systematic treatment strategy internationally. The treatment options after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance can be basically divided into three categories: The first is to switch to other endocrine drugs combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors, the second is to used combined targeted therapy and the third is to switch to cytotoxic drugs for chemotherapy. However, the choice of treatment after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance is mainly based on the number of lines of endocrine therapy combined with CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment used in previous treatment, the combination of drugs, the length of treatment time, the current metastatic site, the size of the metastatic load, whether there is a target for mutation in the circulating tumor DNA and the economic situation of the patient. After comprehensive consideration, patients should be provided with an individualized treatment plan.
The treatment solution after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance is still the focus of research by scientists. At present, delaying resistance is more important for patients who use CDK4/6 inhibitors. For example, attempts should be made to use CDK4/6 inhibitors as the second line treatment as much as possible. In this way, the early occurrence of acquired drug resistance can be avoided. Combined targeted therapy is also a common combination method in clinical practice, which also helps delay the occurrence of drug resistance. However, it also depends on the status of the disease. If the disease progresses rapidly, it may be necessary to speed up the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors to control the condition. Therefore, in order to more accurately determine the resistance mechanism of CDK4/6 inhibitors and find new targets to overcome the resistance of CDK4/6 inhibitors, further exploratory research and clinical verification are needed.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 82172917).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
JH investigated and wrote the original draft of the manuscript. ZS and LZ reviewed and edited the manuscript. JL proposed the theme of the review and helped in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Data authentication is not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dai X, Li T, Bai Z, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhan J, Shi B. Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical use and future trends. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:2929–2943. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cardoso F, Costa A, Senkus E, Aapro M, André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Bhattacharyya G, Biganzoli L, Cardoso MJ, et al. 3rd ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 3) Ann Oncol. 2017;28:3111. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Milani A, Geuna E, Mittica G, Valabrega G. Overcoming endocrine resistance in metastatic breast cancer: Current evidence and future directions. World J Clin Oncol. 2014;5:990–1001. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Clarke R, Tyson JJ, Dixon JM. Endocrine resistance in breast cancer-an overview and update. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;418:220–234. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.09.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brufsky AM, Dickler MN. Estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: Exploiting signaling pathways implicated in endocrine resistance. Oncologist. 2018;23:528–539. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhu W, Xu B. Overcoming resistance to endocrine therapy in hormone receptor-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HR+/HER2−) advanced breast cancer: A meta-analysis and systemic review of randomized clinical trials. Front Med. 2021;15:208–220. doi: 10.1007/s11684-020-0795-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nair BC, Vadlamudi RK. Regulation of hormonal therapy resistance by cell cycle machinery. Gene Ther Mol Biol. 2008;12:395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Spring LM, Wander SA, Andre F, Moy B, Turner NC, Bardia A. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: Past, present, and future. Lancet. 2020;395:817–827. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Altucci L, Addeo R, Cicatiello L, Germano D, Pacilio C, Battista T, Cancemi M, Petrizzi VB, Bresciani F, Weisz A. Estrogen induces early and timed activation of cyclin-dependent kinases 4, 5, and 6 and increases cyclin messenger ribonucleic acid expression in rat uterus. Endocrinology. 1997;138:978–984. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.3.5002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Geum D, Sun W, Paik SK, Lee CC, Kim K. Estrogen-induced cyclin D1 and D3 gene expressions during mouse uterine cell proliferation in vivo: Differential induction mechanism of cyclin D1 and D3. Mol Reprod Dev. 1997;46:450–458. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199704)46:4<450::AID-MRD2>3.0.CO;2-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I, Boer K, Bondarenko IM, Kulyk SO, Ettl J, Patel R, Pinter T, Schmidt M, et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): A randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:25–35. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Finn RS, Boer K, Bondarenko I, Patel R, Pinter T, Schmidt M, Shparyk YV, Thummala A, Voitko N, Bananis E, et al. Overall survival results from the randomized phase 2 study of palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone for first-line treatment of ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1, TRIO-18) Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020;183:419–428. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05755-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Turner NC, Slamon DJ, Ro J, Bondarenko I, Im SA, Masuda N, Colleoni M, DeMichele A, Loi S, Verma S, et al. Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1926–1936. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1810527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, Campone M, Petrakova K, Blackwell KL, Winer EP, et al. Updated results from MONALEESA-2, a phase III trial of first-line ribociclib plus letrozole versus placebo plus letrozole in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:1842. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Jerusalem G, De Laurentiis M, Im S, Petrakova K, Valeria Bianchi G, Martín M, Nusch A, et al. Ribociclib plus fulvestrant for postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer in the phase III randomized MONALEESA-3 trial: Updated overall survival. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:1015–1024. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sledge GW, Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J, Inoue K, Pivot X, Burdaeva O, Okera M, Masuda N, Kaufman PA, et al. The effect of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant on overall survival in hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer that progressed on endocrine therapy-MONARCH 2: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:116–124. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xu B, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Hu X, Li W, Tong Z, Sun T, Teng Y, Wu X, Ouyang Q, et al. Dalpiciclib versus placebo plus fulvestrant in HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer that relapsed or progressed on previous endocrine therapy (DAWNA-1): A multi-center, randomized, phase 3 study. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15 Suppl):S1002–S1002. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.1002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Xu B, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Hu X, Li W, Tong Z, Sun T, Teng Y, Wu X, Ouyang Q, et al. Dalpiciclib or placebo plus fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive and HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: A randomized, phase 3 trial. Nat Med. 2021;27:1904–1909. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang P, Xu B, Gui L, Wang W, Xiu M, Zhang X, Sun G, Zhu X, Zou J. A phase 1 study of dalpiciclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor in Chinese patients with advanced breast cancer. Biomark Res. 2021;9:24. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00271-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Malumbres M, Sotillo R, Santamaria D, Galán J, Cerezo A, Ortega S, Dubus P, Barbacid M. Mammalian cells cycle without the D-type cyclin-dependent kinases Cdk4 and Cdk6. Cell. 2004;118:493–504. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Guarducci C, Bonechi M, Boccalini G, Benelli M, Risi E, Di Leo A, Malorni L, Migliaccio I. Mechanisms of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer and potential biomarkers of response. Breast Care (Basel) 2017;12:304–308. doi: 10.1159/000484167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Siebert R, Willers CP, Opalka B. Role of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor gene family p15, p16, p18 and p19 in leukemia and lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 1996;23:505–520. doi: 10.3109/10428199609054859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Green JL, Okerberg ES, Sejd J, Palafox M, Monserrat L, Alemayehu S, Wu J, Sykes M, Aban A, Serra V, Nomanbhoy T. Direct CDKN2 modulation of CDK4 alters target engagement of CDK4 inhibitor drugs. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019;18:771–779. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Finn RS, Crown JP, Ettl J, Schmidt M, Bondarenko IM, Lang I, Pinter T, Boer K, Patel R, Randolph S, et al. Efficacy and safety of palbociclib in combination with letrozole as first-line treatment of ER-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer: Expanded analyses of subgroups from the randomized pivotal trial PALOMA-1/TRIO-18. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18:67. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0721-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Turner NC, Liu Y, Zhu Z, Loi S, Colleoni M, Loibl S, DeMichele A, Harbeck N, André F, Bayar MA, et al. Cyclin E1 expression and palbociclib efficacy in previously treated hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:1169–1178. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Finn RS, Liu Y, Zhu Z, Martin M, Rugo HS, Diéras V, Im SA, Gelmon KA, Harbeck N, Lu DR, et al. Biomarker analyses of response to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition and endocrine therapy in women with treatment-Naïve metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:110–121. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu A, Wu B, Guo J, Luo W, Wu D, Yang H, Zhen Y, Yu X, Wang H, Zhou Y, et al. Elevated expression of CDK4 in lung cancer. J Transl Med. 2011;9:38. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Olanich ME, Sun W, Hewitt SM, Abdullaev Z, Pack SD, Barr FG. CDK4 amplification reduces sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibition in fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:4947–4959. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yang C, Li Z, Bhatt T, Dickler M, Giri D, Scaltriti M, Baselga J, Rosen N, Chandarlapaty S. Acquired CDK6 amplification promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and loss of ER signaling and dependence. Oncogene. 2017;36:2255–2264. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tigan AS, Bellutti F, Kollmann K, Tebb G, Sexl V. CDK6-a review of the past and a glimpse into the future: From cell-cycle control to transcriptional regulation. Oncogene. 2016;35:3083–3091. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kollmann K, Heller G, Schneckenleithner C, Warsch W, Scheicher R, Ott RG, Schäfer M, Fajmann S, Schlederer M, Schiefer AI, et al. A kinase-independent function of CDK6 links the cell cycle to tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:359–360. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gacche RN, Assaraf YG. Redundant angiogenic signaling and tumor drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2018;36:47–76. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2018.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ji W, Zhang W, Wang X, Shi Y, Yang F, Xie H, Zhou W, Wang S, Guan X. c-myc regulates the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to palbociclib via c-myc/miR-29b-3p/CDK6 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:760. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02980-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Etemadmoghadam D, Au-Yeung G, Wall M, Mitchell C, Kansara M, Loehrer E, Batzios C, George J, Ftouni S, Weir BA, et al. Resistance to CDK2 inhibitors is associated with selection of polyploid cells in CCNE1-amplified ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:5960–5971. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schachter MM, Merrick KA, Larochelle S, Hirschi A, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Rubin SM, Fisher RP. A Cdk7-Cdk4 T-loop phosphorylation cascade promotes G1 progression. Mol Cell. 2013;50:250–260. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Martin LA, Pancholi S, Ribas R, Gao Q, Simigdala N, Nikitorowicz-Buniak J, Johnston SR, Dowsett M. Abstract P3-03-09: Resistance to palbociclib depends on multiple targetable mechanisms highlighting the potential of drug holidays and drug switching to improve therapeutic outcome. Cancer Res. 2017;77(4 Suppl):P3-03-09. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.SABCS16-P3-03-09. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Howell SJ, Krebs MG, Lord S, Kenny L, Bahl A, Clack G, Ainscow E, Arkenau HT, Mansi JL, Palmieri C, et al. 265P Study of samuraciclib (CT7001), a first-in-class, oral, selective inhibitor of CDK7, in combination with fulvestrant in patients with advanced hormone receptor positive HER2 negative breast cancer (HR+BC) Ann Oncol. 2021;32(Suppl 5):S477–S478. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.08.548. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Orlando S, Gallastegui E, Besson A, Abril G, Aligué R, Pujol MJ, Bachs O. p27Kip1 and p21Cip1 collaborate in the regulation of transcription by recruiting cyclin-Cdk complexes on the promoters of target genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:6860–6873. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Álvarez-Fernández M, Malumbres M. Mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition. Cancer Cell. 2020;37:514–529. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sabnis GJ, Goloubeva O, Chumsri S, Nguyen N, Sukumar S, Brodie AM. Functional activation of the estrogen receptor-α and aromatase by the HDAC inhibitor entinostat sensitizes ER-negative tumors to letrozole. Cancer Res. 2011;71:1893–1903. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yardley DA, Ismail-Khan RR, Melichar B, Lichinitser M, Munster PN, Klein PM, Cruickshank S, Miller KD, Lee MJ, Trepel JB. Randomized phase II, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of exemestane with or without entinostat in postmenopausal women with locally recurrent or metastatic estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer progressing on treatment with a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2128–2135. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.43.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jiang Z, Li W, Hu X, Zhang Q, Sun T, Cui S, Wang S, Ouyang Q, Yin Y, Geng C, et al. Tucidinostat plus exemestane for postmenopausal patients with advanced, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (ACE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:806–815. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30164-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Matheson CJ, Backos DS, Reigan P. Targeting WEE1 kinase in cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016;37:872–881. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2016.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pandey K, An HJ, Kim SK, Lee SA, Kim S, Lim SM, Kim GM, Sohn J, Moon YW. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: A review. Int J Cancer. 2019;145:1179–1188. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ramanujan A, Tiwari S. APC/C and retinoblastoma interaction: Cross-talk of retinoblastoma protein with the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. Biosci Rep. 2016;36:e00377. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fujita T, Liu W, Doihara H, Wan Y. Regulation of Skp2-p27 axis by the Cdh1/anaphase-promoting complex pathway in colorectal tumorigenesis. Am J Pathol. 2008;173:217–228. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Laroche-Clary A, Chaire V, Algeo MP, Derieppe MA, Loarer FL, Italiano A. Combined targeting of MDM2 and CDK4 is synergistic in dedifferentiated liposarcomas. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:123. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0482-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cox LS. Multiple pathways control cell growth and transformation: Overlapping and independent activities of p53 and p21Cip1/WAF1/Sdi1. J Pathol. 1997;183:134–140. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199710)183:2<134::AID-PATH960>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lin SL, Chang DC, Ying SY, Leu D, Wu DT. MicroRNA miR-302 inhibits the tumorigenecity of human pluripotent stem cells by coordinate suppression of the CDK2 and CDK4/6 cell cycle pathways. Cancer Res. 2010;70:9473–9482. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Qiu S, Huang D, Yin D, Li F, Li X, Kung HF, Peng Y. Suppression of tumorigenicity by microRNA-138 through inhibition of EZH2-CDK4/6-pRb-E2F1 signal loop in glioblastoma multiforme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1832:1697–1707. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Liu G, Sun Y, Ji P, Li X, Cogdell D, Yang D, Parker Kerrigan BC, Shmulevich I, Chen K, Sood AK, et al. MiR-506 suppresses proliferation and induces senescence by directly targeting the CDK4/6-FOXM1 axis in ovarian cancer. J Pathol. 2014;233:308–318. doi: 10.1002/path.4348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lulla AR, Slifker MJ, Zhou Y, Lev A, Einarson MB, Dicker DT, El-Deiry WS. miR-6883 family miRNAs target CDK4/6 to induce G1 phase cell-cycle arrest in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2017;77:6902–6913. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Cornell L, Wander SA, Visal T, Wagle N, Shapiro GI. MicroRNA-mediated suppression of the TGF-β pathway confers transmissible and reversible CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance. Cell Rep. 2019;26:2667–2680.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Turner N, Grose R. Fibroblast growth factor signalling: From development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:116–129. doi: 10.1038/nrc2780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Turner N, Pearson A, Sharpe R, Lambros M, Geyer F, Lopez-Garcia MA, Natrajan R, Marchio C, Iorns E, Mackay A, et al. FGFR1 amplification drives endocrine therapy resistance and is a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:2085–2094. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Formisano L, Lu Y, Servetto A, Hanker AB, Jansen VM, Bauer JA, Sudhan DR, Guerrero-Zotano AL, Croessmann S, Guo Y, et al. Aberrant FGFR signaling mediates resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1373. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09068-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kilker RL, Planas-Silva MD. Cyclin D1 is necessary for tamoxifen-induced cell cycle progression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11478–11484. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Costa C, Wang Y, Ly A, Hosono Y, Murchie E, Walmsley CS, Huynh T, Healy C, Peterson R, Yanase S, et al. PTEN loss mediates clinical cross-resistance to CDK4/6 and PI3Kα inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:72–85. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bencivenga D, Caldarelli I, Stampone E, Mancini FP, Balestrieri ML, Della Ragione F, Borriello A. p27Kip1 and human cancers: A reappraisal of a still enigmatic protein. Cancer Lett. 2017;403:354–365. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Finn RS, Aleshin A, Slamon DJ. Targeting the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 4/6 in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18:17. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0661-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Shaulian E, Karin M. AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene. 2001;20:2390–2400. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Shen Q, Uray IP, Li Y, Zhang Y, Hill J, Xu XC, Young MR, Gunther EJ, Hilsenbeck SG, Colburn NH, et al. Targeting the activator protein 1 transcription factor for the prevention of estrogen receptor-negative mammary tumors. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2008;1:45–55. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Tewari D, Nabavi SF, Nabavi SM, Sureda A, Farooqi AA, Atanasov AG, Vacca RA, Sethi G, Bishayee A. Targeting activator protein 1 signaling pathway by bioactive natural agents: Possible therapeutic strategy for cancer prevention and intervention. Pharmacol Res. 2018;128:366–375. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.McNamara KM, Yoda T, Takagi K, Miki Y, Suzuki T, Sasano H. Androgen receptor in triple negative breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;133:66–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ji W, Shi Y, Wang X, He W, Tang L, Tian S, Jiang H, Shu Y, Guan X. Combined androgen receptor blockade overcomes the resistance of breast cancer cells to palbociclib. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15:522–532. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.30572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Li Z, Razavi P, Li Q, Toy W, Liu B, Ping C, Hsieh W, Sanchez-Vega F, Brown DN, Da Cruz Paula AF, et al. Loss of the FAT1 tumor suppressor promotes resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors via the Hippo pathway. Cancer Cell. 2018;34:893–905.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Liu F, Korc M. Cdk4/6 inhibition induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances invasiveness in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11:2138–2148. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Moustakas A, Heldin CH. Non-Smad TGF-beta signals. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:3573–3584. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:178–196. doi: 10.1038/nrm3758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Zelivianski S, Cooley A, Kall R, Jeruss JS. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4-mediated phosphorylation inhibits Smad3 activity in cyclin D-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:1375–1387. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Yang J, Song K, Krebs TL, Jackson MW, Danielpour D. Rb/E2F4 and Smad2/3 link survivin to TGF-beta-induced apoptosis and tumor progression. Oncogene. 2008;27:5326–5338. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Decker JT, Wan L, Shea LD, Jeruss JS. Abstract P4-03-16: Cyclin E affects Smad3 pathway in trastuzumab resistant HER2+ breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2018;78(4 Suppl):P4-03-16. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.SABCS17-P4-03-16. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Jiang Z, Song E, Wang X, Wang H, Wang X, Wu J, Yin Y, Zhang Q, Chen J, Che W, et al. Guidelines of Chinese society of clinical oncology (CSCO) on diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer (2020 version). 2020. Transl Breast Cancer Res. 2020;1:27. doi: 10.21037/tbcr-2020-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Johnston SRD, Harbeck N, Hegg R, Toi M, Martin M, Shao ZM, Zhang QY, Martinez Rodriguez JL, Campone M, Hamilton E, et al. Abemaciclib combined with endocrine therapy for the adjuvant treatment of HR+, HER2-, node-positive, high-risk, early breast cancer (monarchE) J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:3987–3998. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Hamilton E, Cortes J, Ozyilkan O, Chen SC, Petrakova K, Manikhas A, Jerusalem G, Hegg R, Huober J, Chapman SC, et al. nextMONARCH: Abemaciclib monotherapy or combined with tamoxifen for metastatic breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 2021;21:181–190.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Wander SA, Zangardi M, Niemierko A, Kambadakone A, Kim LSL, Xi J, Pandey AK, Spring L, Stein C, Juric D, et al. A multicenter analysis of abemaciclib after progression on palbociclib in patients (pts) with hormone receptor-positive (HR+)/HER2-metastatic breast cancer (MBC) J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(15 Suppl):S1057. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.1057. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kalinsky K, Accordino MK, Chiuzan C, Mundi PS, Trivedi MS, Novik Y, Tiersten A, Raptis G, Baer LN, Oh SY, et al. A randomized, phase II trial of fulvestrant or exemestane with or without ribociclib after progression on anti-estrogen therapy plus cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition (CDK 4/6i) in patients (pts) with unresectable or hormone receptor-positive (HR+), HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC): MAINTAIN trial. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(17 Suppl):LBA1004–LBA1004. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.17_suppl.LBA1004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Mayer EL, Wander SA, Regan MM, DeMichele A, Forero-Torres A, Rimawi MF, Ma CX, Cristofanilli M, Anders CK, Bartlett CH, et al. Palbociclib after CDK and endocrine therapy (PACE): A randomized phase II study of fulvestrant, palbociclib, and avelumab for endocrine pre-treated ER+/HER2-metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15 Suppl):TPS1104. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.TPS1104. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Bardia A, Aftimos P, Bihani T, Anderson-Villaluz AT, Jung J, Conlan MG, Kaklamani VG. EMERALD: Phase III trial of elacestrant (RAD1901) vs endocrine therapy for previously treated ER+ advanced breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2019;15:3209–3218. doi: 10.2217/fon-2019-0370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Bidard FC, Kaklamani VG, Neven P, Streich G, Montero AJ, Forget F, Mouret-Reynier MA, Sohn JH, Taylor D, Harnden KK, et al. Elacestrant (oral selective estrogen receptor degrader) versus standard endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: Results from the randomized phase III EMERALD trial. J Clin Oncol. 2022:JCO2200338. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.00338. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Mosele F, Stefanovska B, Lusque A, Tran Dien A, Garberis I, Droin N, Le Tourneau C, Sablin MP, Lacroix L, Enrico D, et al. Outcome and molecular landscape of patients with PIK3CA-mutated metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:377–386. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2019.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.André F, Ciruelos EM, Juric D, Loibl S, Campone M, Mayer IA, Rubovszky G, Yamashita T, Kaufman B, Lu YS, et al. Alpelisib plus fulvestrant for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: Final overall survival results from SOLAR-1. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:208–217. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Rugo HS, Lerebours F, Ciruelos E, Drullinsky P, Borrego MR, Neven P, Park YH, Prat A, Bachelot T, Juric D, et al. Alpelisib (ALP) + fulvestrant (FUL) in patients (pts) with PIK3CA-mutated (mut) hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer (ABC) previously treated with cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor (CDKi) + aromatase inhibitor (AI): BYLieve study results. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(15 Suppl):S1006. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.1006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Bartsch R. ASCO 2020: Highlights in breast cancer. Memo. 2021;14:58–61. doi: 10.1007/s12254-021-00674-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.André F, Ciruelos E, Rubovszky G, Campone M, Loibl S, Rugo HS, Iwata H, Conte P, Mayer IA, Kaufman B, et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1929–1940. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1813904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Suppan C. Post San Antonio update-my top three abstracts! Memo-Mag Eur Med Oncol. 2021;14:244–246. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Piccart M, Hortobagyi GN, Campone M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F, Ito Y, Noguchi S, Perez A, Rugo HS, Deleu I, et al. Everolimus plus exemestane for hormone-receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: Overall survival results from BOLERO-2†. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:2357–2362. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Bardia A, Hurvitz SA, DeMichele A, Clark AS, Zelnak AB, Yardley DA, Karuturi MS, Sanft TB, Blau S, Hart LL, et al. Triplet therapy (continuous ribociclib, everolimus, exemestane) in HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer postprogression on a CDK4/6 inhibitor (TRINITI-1): Efficacy, safety, and biomarker results. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(15 Suppl):S1016. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.1016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Bardia A, Hurvitz SA, DeMichele A, Clark AS, Zelnak A, Yardley DA, Karuturi M, Sanft T, Blau S, Hart L, et al. Phase I/II trial of exemestane, ribociclib, and everolimus in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer after progression on CDK4/6 inhibitors (TRINITI-1) Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27:4177–4185. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Wander SA, Juric D, Supko JG, Micalizzi DS, Spring L, Vidula N, Beeler M, Habin KR, Viscosi E, Fitzgerald DM, et al. Phase Ib trial to evaluate safety and anti-tumor activity of the AKT inhibitor, ipatasertib, in combination with endocrine therapy and a CDK4/6 inhibitor for patients with hormone receptor positive (HR+)/HER2 negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC) (TAKTIC) J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(15 Suppl):S1066. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.1066. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Martin LA, Dowsett M. BCL-2: A new therapeutic target in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer? Cancer Cell. 2013;24:7–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lok SW, Whittle JR, Vaillant F, The CE, Lo LL, Policheni AN, Bergin ART, Desai J, Ftouni S, Gandolfo LC, et al. A phase Ib dose-escalation and expansion study of the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax combined with tamoxifen in ER and BCL2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:354–369. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.A phase II study comparing the efficacy of venetoclax + fulvestrant vs fulvestrant in women with estrogen receptor-positive, Her2-negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who experienced disease recurrence or progression during or after CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy (Veronica) [Google Scholar]
- 95.Lindeman GJ, Bowen R, Jerzak KJ, Song X, Decker T, Boyle FM, McCune SL, Armstrong A, Shannon CM, Bertelli G, et al. Results from VERONICA: A randomized, phase II study of second-/third-line venetoclax (VEN) + fulvestrant (F) versus F alone in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, HER2-negative, locally advanced, or metastatic breast cancer (LA/MBC) J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15 Suppl):S1004. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.1004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Goel S, DeCristo MJ, Watt AC, BrinJones H, Sceneay J, Li BB, Khan N, Ubellacker JM, Xie S, Metzger-Filho O, et al. CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity. Nature. 2017;548:471–475. doi: 10.1038/nature23465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Ogata R, Kishino E, Saitoh W, Koike Y, Kurebayashi J. Resistance to cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors confers cross-resistance to other CDK inhibitors but not to chemotherapeutic agents in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer. 2021;28:206–215. doi: 10.1007/s12282-020-01150-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Rugo HS, Cristofanilli M, Loibl S, Harbeck N, DeMichele A, Iwata H, Park YH, Brufsky A, Theall KP, Huang X, et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: Analyses from PALOMA-3. Oncologist. 2021;26:e1339–e1346. doi: 10.1002/onco.13833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Princic N, Aizer A, Tang DH, Smith DM, Johnson W, Bardia A. Predictors of systemic therapy sequences following a CDK 4/6 inhibitor-based regimen in post-menopausal women with hormone receptor positive, HEGFR-2 negative metastatic breast cancer. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019;35:73–80. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2018.1519500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kolyadina IV, Bolotina L, Zhukova L, Vladimirova LU, Sultanbaev A, Karabina E, Ganshina I, Ovchinnikova E, Kolyadina IV, Antonova G, et al. The effectiveness and safety of eribulin therapy in HR-positive HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer post-CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy in Russian clinical practice. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15 Suppl):e13035. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.e13035. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.