Figure 1.
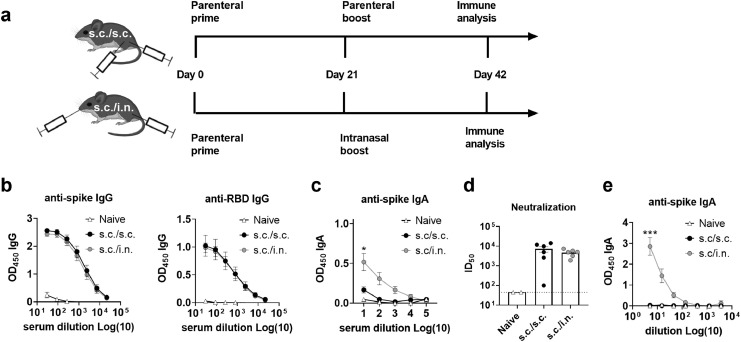
Mucosal boosting elicits serum neutralizing antibody responses comparable to parenteral immunization and additionally boosts IgA responses. Mice were immunized with two doses of spike trimer protein formulated in cationic liposomes (CAF®01). The trimer protein was either the S-2P version (a-e) or the HexaPro variant. (f) The vaccine was administered as a conventional subcutaneous two dose regimen (s.c./s.c.) or as subcutaneous priming followed by intranasal boosting (s.c./i.n.) Serum was sampled at 21 days after the 2nd immunization. a) Experimental setup. b) IgG antibody responses against spike protein (left panel) and the receptor binding domain (RBD) (right panel). c) Serum IgA antibody responses against spike protein. d) Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a pseudovirus neutralization assay. The stippled line indicates neutralization below the limit of detection and is plotted as ID50=45. e) Spike-specific IgA antibody responses in nasal washes. Mean ± SEM is displayed. Statistically significant differences are indicated by * or *** (one-way ANOVA, comparing the mean of each column with each other column, p<0.05 or 0.001, respectively). There was no statistically significance among groups if not otherwise indicated. Figures represent n= two (naïve controls) to six (vaccinated) mice per group. Created with BioRender.com.