Abstract
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are plasma membrane proteins associated with an array of functions. Mutations in these receptors lead to a number of genetic diseases, including diseases involving the endocrine system. A particular subset of loss-of-function mutant GPCRs are misfolded receptors unable to traffic to their site of function (i.e. the cell surface plasma membrane). Endocrine disorders in humans caused by GPCR misfolding include, among others, hypo- and hyper-gonadotropic hypogonadism, morbid obesity, familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia and neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism, X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, congenital hypothyroidism, and familial glucocorticoid resistance. Several in vitro and in vivo experimental approaches have been employed to restore function of some misfolded GPCRs linked to endocrine disfunction. The most promising approach is by employing pharmacological chaperones or pharmacoperones, which assist abnormally and incompletely folded proteins to refold correctly and adopt a more stable configuration to pass the scrutiny of the cell’s quality control system, thereby correcting misrouting. This review covers the most important aspects that regulate folding and traffic of newly synthesized proteins, as well as the experimental approaches targeted to overcome protein misfolding, with special focus on GPCRs involved in endocrine diseases.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptors, GPCRs, intracellular trafficking, quality control system, molecular chaperones, pharmacological chaperones, pharmacoperones
Introduction
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) and their associated signaling modules represent one of the major systems employed by the cells to communicate with each other and transmit information across long and short distances within the body. Sensory receptors for light, taste, and smell also belong to the GPCRs superfamily (1–3). GPCRs constitute the largest family of membrane receptors in many animal species, including humans. In fact, 4-5% of the human genome codes for these important plasma membrane proteins (1, 3). The importance of GPCRs and GPCR ligands in human disease is supported by the fact that both still continue to be the focus for new drug discovery (currently in the form of small molecules and peptides), despite being known as druggable targets for a long time. Indeed, it is estimated that approximately 30-40% of approved drugs target this family of membrane receptors (4–6).
Although GPCRs widely vary in molecular size (7–9), they share a common structure conformed by a single, serpentine-like, polypeptide chain that crosses the plasma membrane (PM) seven times forming transmembrane domains (TMD), which are hydrophobic, α-helix structures connected by extracellular (EL) and intracellular (IL) loops, with an ectodomain (ECD) and an intracellular carboxyl-terminal (COOH) domain also called C-tail (7, 9). These cell surface plasma membrane-embedded receptors exist in complex with one or several heterotrimeric G proteins and also associate with membrane-linked intracellular proteins that activate upon ligand binding and that regulate activation of a number of G protein-dependent and -independent signaling cascades (7, 9, 10). Upon activation, GPCRs are desensitized and internalized through the formation of endosomes, where a second wave of signaling may occur or terminate, and the destiny of the internalized receptor is defined (11–13). Therefore, the net amount of a particular GPCR expressed at the PM that is exposed to extracellular messengers, including the cognate ligand, will depend on its dynamics of intracellular trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where it is synthesized, to the its final destination at the PM, the fate of the receptor following agonist-stimulated internalization (degradation vs. recycling), and the normal membrane turnover (13). Since GPCRs participate in an array of functions, it is not surprising that they are activated by a number of structurally diverse ligands that include photons, ions, odorants, lipids, peptide and non-peptide hormones, and several neurotransmitters that vary in size (7–9). Approximately 50% of GPCRs bind endogenous ligands, whereas the remaining receptors sense the chemical environment (1, 14). Therefore, in complex organisms, GPCRs are intermediate stations that communicate the internal and external environments of cells.
Mutations in GPCR genes may alter receptor synthesis or function in a number of genetically- determined disorders (15). Loss-of-function GPCR mutations may affect the amino acid sequence of the protein and lead to alterations in domains critical for recognition and binding of agonist, receptor activation and/or coupling to G proteins, or internalization. They also may cause errors in the three dimensional configuration of the receptor protein (i.e. misfolding) due to non-native interactions that may impact in a significant manner not only the overall architecture of the protein but also its physicochemical characteristics, leading to its intracellular retention (13, 16–20). Protein misfolding can also occur as the result from protein overexpression, thermal or oxidative stress, and activation of pathways involved in the regulation of protein folding, maturation, and quality control (16). Although some non-specific, non-native interactions with other intracellular peptide or proteins may occur during the normal dynamics of folding (to mask aggregating-prone regions), abnormally folded proteins may accumulate as toxic aggregates and form extracellularly deposited amyloids (21–23).
Recent studies on how the folding process occurs have provided important information for the design of pharmacological interventions that may correct misfolding of defective proteins that cause disease. The finding that some alterations in the amino acid sequence of a protein leading to misfolding do not involve domains essential for its function has further open the way for discovering new therapeutic avenues, including pharmacologic strategies to correct abnormal folding and routing to the PM of mutant misfolded ion channels (e.g. the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein -CFTR-) and GPCRs (see below) (20, 24–33).
The present review focuses on GPCR trafficking, misfolding, and misrouting as a cause of endocrine disorders and how different genetic, physical and pharmacological strategies may rescue, partially or completely, function of GPCRs with folding defects. To better understand these aspects, let’s briefly review how the cell quality control system works to preserve a stable and functional proteostasis within the cell, with particular focus on GPCRs.
The quality control system (QCS)of the cell and the role of molecular chaperones
The QCS of the cell is a complex molecular machinery that continuously surveys and monitors newly synthesized proteins at the ER, Golgi and the PM (34–36). The molecular chaperones and companion factors (e.g. co-chaperones, modification enzymes, and targeting factors) are key elements of this QCS that play an essential role in maintaining the integrity of the proteostasis network (35, 37–39). Molecular chaperones are an essential driving force in the highly dynamic and complex folding process of the nascent proteins occurring within a crowded and viscous environment of proteins accumulated in the ER. Molecular chaperones are resident proteins involved in the co- and posttranslational regulation of several processes occurring during protein synthesis, including folding, assembling, and degradation of defective proteins; they also regulate ER exit and prevent toxic accumulation and aggregation of misfolded intermediates (37, 40–42). When proteins fail to achieve proper folding and an appropriate minimal-energy configuration, the QCS will promote the export of the conformationally defective protein to the degradation pathway, mainly the ubiquitin-proteasome system (43–45). Contrariwise, achievement of a conformation compatible with ER export will lead to translocation of the protein to the Golgi apparatus to complete processing and maturation (Figure 1A). Surveillance of the QCS relies more on its capacity to detect misfolding of the nascent proteins based on non-native structural determinants including exposure of hydrophobic shapes, unpaired cysteines or immature glycans, and specific amino acid sequences or motifs involved in the regulation of protein trafficking within the cell (37).
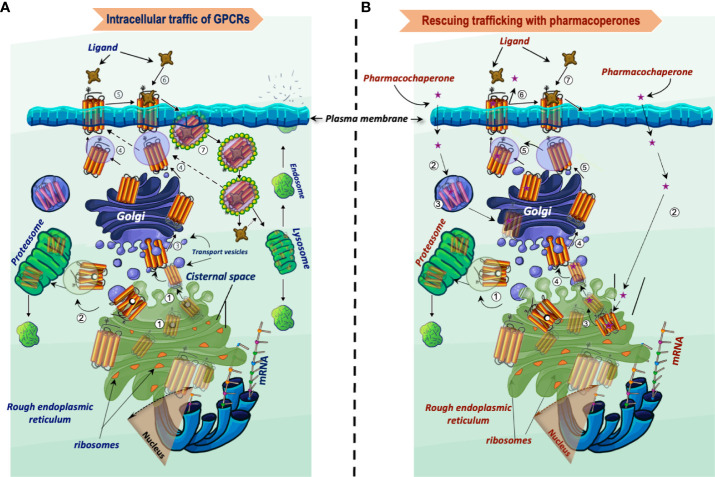
Figure 1.
Intracellular trafficking of GPCRs belonging to the rhodopsin-like family of receptors. (A) Newly synthesized proteins fold in the endoplasmic reticulum (step 1), where misfolded proteins interact with molecular chaperones and co-chaperones (oval black and white structures, respectively), which attempt to correct folding and stabilize the protein in a conformation adequate for endoplasmic reticulum export. When correction of misfolding fails, the abnormal protein is dislocated into the cytoplasm for proteasomal degradation (step 2). Folded GPCRs are translocated to the Golgi apparatus to complete their maturation process including glycosylation (arbor-like structure within the magnifier). Mature receptors then traffic to the plasma membrane where they bind their cognate ligands (steps 4 to 6). Following activation of the receptor by agonists, phosphorylation and recruitment of β-arrestins occur, which provoke endocytosis and internalization of the receptor–ligand complex (step 7). The internalized complex is embedded in clathrin-coated vesicles, which may be either targeted to lysosomes for degradation or dissociate with subsequent sorting of the receptor to the recycling pathway (step 4). (B) Rescue of misfolded receptors by pharmacoperones. Misfolded/misrouted receptors that could not be stabilized by molecular chaperones are submitted to degradation (step 1). The pharmacoperone drug crosses the cell surface plasma membrane, penetrates into the cell (step 2) and specifically binds the misfolded GPCR (step 3). Receptors stabilized by the pharmacoperone are then exported to the Golgi apparatus for further processing (step 4), and finally to the plasma membrane (step 5); here, the pharmacoperone (in the case of antagonists or agonists of the receptor) must dissociate from the rescued receptor for allowing the agonist to recognize and bind the rescued receptor promoting its activation (steps 6 and 7). Interaction of pharmacoperones with intracellularly trapped receptors also may occur in compartments other than the ER before degradation (step 3, left) (46).
Major molecular chaperones represent a key machinery for quality control [e.g. the heat shock proteins of 70 kDa and 90 kDa (HSP70 and HSP90, respectively)]; these chaperones assist proteins in folding and remodeling (47–49). HSP70 ATP-dependent molecular chaperones are highly conserved and the best studied heat shock proteins (49). Nascent polypeptides are recognized by HSP70 chaperones, which promote their folding, stabilization, translocation, and degradation when necessary (48–52). One of the most important folding factors is BiP/Grp78 which is a member of the HSP70 family of proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum (47, 53–55) and a key folding factor of the ER. Several GPCRs interact with BiP; these include the luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor (LHCGR), the angiotensin II AT1 receptor, rhodopsin, and the thyroid-stimulating hormone (or thyrotropin) receptor (TSHR) (56–59). This chaperone is assisted by the DnaJ family members of cofactors (HSP40) to recognize hydrophobic regions during the protein folding process, aiding to keep proteins in a conformation permissive for continuing folding and oligomerization (55). Among the roles of nucleotide-bound BiP is on the protective unfolded protein response (UPR), which is an important stress reaction that decreases unfolded protein load to maintain proteostasis, cell viability, and function during cellular stress (60, 61).
Calnexin/calreticulin and protein disulfide isomerases also belong to the major chaperone family. Calnexin/calreticulin works on N-linked carbohydrates and unfolded regions in the protein, assisting in folding through the so-called calnexin/calreticulin cycle (62–66). Meanwhile, the protein disulfide isomerases (PDI), such as the oxidoreductase PDI, decreases the thermodynamic stability of the protein by introducing disulfide bridges, thereby promoting reorganization of folding intermediates (67–70). Several GPCRs, associate with calnexin and calreticulin; in this vein, mutations that impair protein glycosylation may result in misfolding, which when detected by the ER-QCS, limits the anterograde traffic of the misfolded conformer to the PM (71). PDI works as a co-chaperone with calnexin and calreticulin during their association with glycoproteins (72). Their study have allowed to recognize differences in folding between species of particular mutant proteins such the inactivating Ala593Pro and Ser616Tyr mutants of the LHCGR, which lead to male pseudohermaphroditism; patients with this disorder exhibit severely impaired response to LH and hCG due to misfolding and intracellular trapping of the mutant receptors [reviewed in (73)]. Similar to the wild-type (WT) LHCGR, the Ala593Pro and Ser616Tyr LHCGR mutants were detected associated with calnexin, whereas the WT receptor interacted with PDI. Although both of this receptor mutants appeared to interact with BiP/Grp78, only Ala593Pro was found to associate with Grp94 (74). Their distinct association with molecular chaperones (57) suggests that these mutant receptors differ in conformation.
Other chaperones (called non-classic private chaperones) and interacting proteins also associate with GPCRs during their upward trafficking. As these interacting proteins regulate protein folding and trafficking in different ways, they may be considered as molecular chaperones with a specific function on particular GPCRs [reviewed in (75)]. Among these non-classic chaperones are: a. ANKRD13 (ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 13C); GPCRs that interact with this chaperone include the prostaglandin D2 receptor, the thromboxane A2 receptor, the chemoattractant receptors, and the β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR) (76); b. Ribophorin I, a chaperone that interacts with the μ-opioid receptor (77); c. ATBP50 (angiotensin II receptor-binding protein of 50 kDa), which associates with the C-tail of the angiotensin II AT2 receptor (78); d. Golgin-160 (which localizes in the Golgi) and gC1q-R (receptor for globular heads of C1q), which promote upward trafficking of the β1AR and α1BAR, respectively (79); e. Receptor activity modifying proteins (RAMPs) interact with a number of GPCRs from different classes, including the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor, the corticotropin-releasing factor 1 receptor, and the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR), promoting their translocation to the PM as well as desensitization and recycling of particular GPCRs (80); f. RanBP2, which binds red/green opsin molecules (81); g. The molecular chaperone ODR4, facilitates folding, exit from the endoplasmic reticulum, and PM targeting of a subset of olfactory GPCRs, such as such as ODR10 in C. elegans and rat U131 in undifferentiated olfactory-derived odorant receptor activatable (odora) cells and Chinese hamster ovary cells (82–84). Its homolog in humans, C1orf27, interacts with the α2A-AR to regulate its anterograde traffic (85); h. Melanocortin-2 receptor (MC2R) accessory protein (MRAP), which enhances MC2R traffic (86, 87); i. RTP1 and RTP2, which interact with odorant receptors, and enhance responses to odorants (88); and j. DRiP78, the ER-membrane protein, dopamine receptor interacting protein of 78 kDa, which associates to the F(x)3F(x)3F hydrophobic motif at the proximal COOH-terminus of α-helix8 of several GPCRs (89, 90)
Molecular chaperones and the chaperone network at the ER and the Golgi as well as the peripheral quality control checkpoints [see for review (91)], are attractive therapeutic targets for exogenously regulating protein trafficking and secretion (92–94).
Structural determinants and GPCR-dependent factors that regulate anterograde trafficking from the ER to the plasma membrane
Several sequences present in GPCRs have been identified associated with components of coat complex protein II transport machinery and Ras-related small GTPases necessary to allow the protein to exit the ER and enter the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (90, 95–98). These motifs are particularly localized in the C-tails and less frequently in the loops and ectodomain of GPCRs, and include the above mentioned F(x)3F(x)3F motif identified in helix-8 of the angiotensin II AT1 receptor, the dopamine D1 receptor, and the M2-muscarinic receptor (99), and the E(x)3LL and FN(x)2LL(x)3L leucine motifs in the human vasopressin 2 (V2R) and vasopressin 3 (V3R) receptors, respectively (100–103). Alterations in these motifs lead to trapping of the protein and hence markedly impact receptor export to the PM. Some GPCRs employ these motifs for anterograde trafficking from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface PM through association with the small GTPase Rab8 (97). The export sequence F(x) 6LL motif identified in the proximal NH2-terminal end of the C-tail of several GPCRs (104, 105), including the gonadotropin receptors, the angiotensin AT1 receptor, and the α2B-, α1B-, and β2-ARs, is an important motif that controls the upward trafficking of GPCRs. The location of this latter motif is important given the known interaction of DRiP78 with the overlapping conserved (hydrophobic) sequence F(x)3F(x)3F present in several GPCRs; alteration in this motif leads to intracellular retention of the receptor (89). Modifications in retention motifs that limit GPCR ER exit for further processing may improve trafficking of the cargo protein. Some of these motifs are: a. the RSRR sequence in the GABA-B1 receptor (106); b. the 5R (penta-arginine) sequence in the α2CAR (107); and c. the conserved ALAAALAAAAA hydrophobic sequence in the extracellular NH2-terminal region of the α2-AR (108). These retention signals probably act by limiting intracellular traffic of receptors that do not hide retention motifs as a consequence of misfolding or that fail to heterodimerize (109). Therefore, export and retention signals are mechanisms that regulate that only adequately folded and assembled receptor complexes are exported to the PM.
Two highly conserved motifs present in GPCRs belonging to the rhodopsin/β-adrenergic-like receptors are important, the E/DRY motif at the boundary of the α-helix3 and the IL2 and the N/DPxxY motif at α-helix7, near its cytoplasmic face of the PM. Alterations in these sequences may lead to misrouting, depending on the particular GPCR [e.g. alteration on both motifs in the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR) and the V2R, and on the N/DPxxY motif in the endothelin-B receptor, melanocortin-4 rreceptor (MC4R), and the CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) (110, 111)]. Another important structural feature of GPCRs belonging to rhodopsin/β-adrenergic-like family of GPCRs is a disulfide bond between the EL1 and EL2, which seems necessary for stabilization of the TMD structure. Alterations in or around this disulfide bridge severely alter the 3-dimensional structure of the receptor, and lead to intracellular retention and degradation of the receptor protein. In fact, mutations at this particular location make the human GnRHR difficult to stabilize with pharmacological chaperones (see below) (111).
Few export motifs in the loops and ectodomain of GPCRs have been identified. A distinct YS motif in the NH2-terminus of both the α2A- and α2B-AR has been identified as an export motif from the Golgi apparatus (112). A single and highly conserved leucine residue at the center of the IL1 seems to play an important role in ER export of several adrenergic receptors and the angiotensin II AT1 receptor (113), and lastly, a triple arginine (3R) motif in the IL3 mediates interaction of the α2BAR with protein transport Sec24C/D isoforms (95).
Glycosylation and palmitoylation are frequent posttranslational modifications that in some GPCRs regulate anterograde GPCR traffic. N-linked glycosylation at the consensus sequence N-x-S/T is a frequent modification that helps folding by increasing the solubility of the protein and enhancing its conformational stability (63, 114). When N-linked glycosylation or early glycan processing is altered, misfolded glycoproteins are identified by the QCS blocking further anterograde trafficking to the PM (71). Mutations at or close to glycosylation sites in GPCRs (in which glycosylation in their ectodomain is required for anterograde export), may lead to reduced PM expression (115, 116). Nevertheless, it is important to note that that alterations in the structure of the receptor ectodomain bearing particular glycosylation sites may also hamper folding and thereby lead to limited PM expression. Meanwhile, the reversible addition of fatty acids to the cysteine residues in the C-tail of several GPCRs is another frequent posttranslational modification (117). This modification anchors the receptor to the PM forming a fourth intracellular loop (117), and also regulates several functions of the receptor, including upward trafficking, coupling to G proteins, β-arrestin recruitment, and the fate of the internalized receptor (118–121).
It has been shown that a number of GPCRs associate in multi-unit complexes during their biosynthesis or processing in the Golgi (122). Oligomerization as an effective quality control of protein folding before export to the PM has been demonstrated in a number of GPCRs (122–132). A typical example is the association between the GABA-B receptor-1 and GABA-B receptor-2, which is apparently an obligatory requisite for cell surface PM expression of a functional receptor; in this particular GPCR, association between the C-tails of these GABA-B receptors hides a retention motif (e.g. the RxR ER retention signal in the GABA-B1 receptor C-tail), thereby promoting export of the heterodimer to the PM (133). In this vein, mutations in GPCRs may provoke dominant negative effects via protein-protein association, thereby interfering with WT and/or mutant receptor upward trafficking and PM expression (131). This effect of mutant receptors on upward trafficking occurs in several GPCRs (134–139) and might have a physiopathogenic role in the phenotypic expression of disease in individuals carrying simple heterozygous mutations.
In ensemble, upward trafficking of GPCRs through the secretory pathway relies on several factors, including: a. The molecular chaperones of the QCS of the cell; b. Retention and export motifs present within the nascent GPCR protein; c. The well-organized association and interaction between GPCRs; and d. Particular posttranslational modifications involved in export of the GPCR from the ER to the Golgi and from the latter to the PM, as well as on the post-endocytic fate of the receptor after agonist-stimulated internalization.
Misfolding of GPCRs as a cause of endocrine disorders
A wide variety of genetic diseases in humans occurs as a result of mutations in GPCR genes, some of which lead to defects in receptor folding and intracellular trapping of the receptor protein. Examples of endocrine diseases caused by GPCR misfolding and misrouting are shown in Table 1. These include a significant number of Class II loss-of-function mutants [which lead to intracellular retention of receptors due to misfolding of the protein (20, 162)] causing familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia and neonatal hyperparathyrodism provoked by mutations in the CaSR (calcium-sensing receptor), hypogonadotropic hypogonadism [mutations in the GnRHR and the prokineticin receptor 2 (PROKR2) genes], X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (mutations in the V2R gene), congenital hypothyroidism (mutations in the TSHR gene), morbid obesity caused by mutations in the MC4R gene, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) insensitivity with adrenal insufficiency (mutations in the MC2R gene), and reproductive disorders [LHCGR and follicle-stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR) gene mutations], among others (73, 75, 140, 149, 157, 163, 166–168) (Table 1). Diseases caused by mutations that lead to GPCR misrouting are of particular interest because they may be specifically treated with drugs that correct trafficking and rescue function of the mutant receptors, whenever critical domains involved in essential functions (i.e. binding to agonist, activation of the receptor and/or coupling to effectors) are not compromised by the mutation. Some examples of drugs whose development is based on targeting trafficking of misfolded, mutant GPCRs in endocrine diseases include small molecules designed for rescuing function of the V2R, MC4R, GnRHR, and more recently gonadotropin receptors (169–171). The discovery of this pharmacological approach suggests that by screening drugs for treating variant GPCRs may efficiently detect novel therapeutic approaches (172). Probably one of the most notable examples of pharmacological rescue of misfolded membrane proteins is the case of the ΔF508 defective cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator -CFTR- for which several pharmacoperones have succeeded in restoring membrane expression and function of the mutant Cl- channel in individuals with cystic fibrosis (25, 28–33).
Table 1.
Endocrine diseases caused by misfolded, trafficking defective GPCRs.
| Disease | GPCR involved | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus | Vasopressin 2 receptor (V2R) | (140–148) |
| Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR), prokineticin receptor 2 (PROKR2) | (73, 140, 149–152) |
| Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia | Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) | (153–156) |
| Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism | Luteinizing hormone receptor and follicle-stimulating hormone receptor (LHCGR and FSHR, respectively) | (73) |
| Congenital hypothyroidism | Thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) | (157–159) |
| Adrenal insufficiency | Melanocortin-2 receptor (MC2R) | (160, 161) |
| Obesity | Melanocortin-3 and -4 receptors (MC3R and MC4R) | (75, 162–165) |
Experimental strategies to rescue misfolded GPCRs
Among the experimental strategies that may promote rescue of misfolded GPCRs in vitro and/or in vivo are genetic, physical, chemical, and pharmacological approaches. Genetic strategies for increasing PM expression of misfolded proteins are intended to introduce or delete particular sequences into the mutated protein (173–175). By using this approach, the defective receptor may be overexpressed or conformationally stabilized without global changes in the ER secretory activity. This may be achieved, for example, by adding residues or motifs for glycosylation at the NH2-terminal domain of the receptor protein or COOH-terminal sequences to expression-deficient GPCRs, thereby markedly enhancing ER export to the PM. In some cases, the genetic modification increase PM expression of the misfolded receptor (Figure 2A), but also may affect receptor activation because of the conformational modification in the domain involved in this particular function (174) (Figure 2B). In others, such as the P320L human GnRHR mutant, the abnormal protein is unrescuable by genetic approaches because proline´s peptide backbone is constrained in a ring structure; the presence of proline is associated with an imposed turn in the sequence of the α-helix in TMD7, whose structure is severely disturbed when replaced. One example of efficient genetic rescue is the mammalian GnRHR; this particular receptor lacks the intracellular C-tail extension and by adding this domain from the catfish GnRHR or by deleting de arginine residue at position K191 [whose presence limits PM expression of the primate receptor (177)], significantly increased cell surface PM expression (175) of the mutant GnRHR protein (Figure 2A). Genetic approaches, albeit effective, are somehow impractical for in vivo application because the mutation could be directly corrected by modifying the corresponding DNA gene sequence (178).
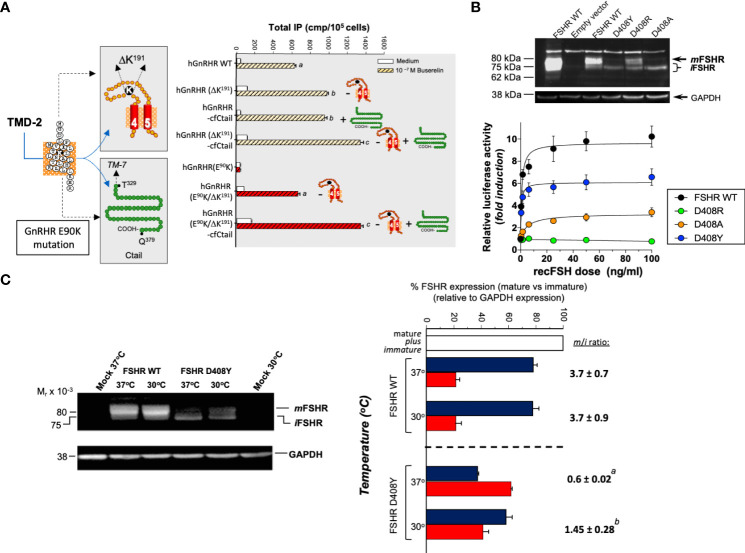
Figure 2.
The effects of genetic (A, B) and physical (C) maneuvers on the expression and function of misfolded mutant human (h) GnRHR and hFSHR in vitro. (A) Left image: The E90K mutation at the TMD2 of the hGnRHR leads to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and provokes misfolding and intracellular trapping of the receptor protein (169). Two genetic modifications rescued membrane expression and function of the receptor: (a) Deletion of a lysine residue at position 191 in the EL2, which connects TMDs 4 and 5 (K191 is absent in the rat GnRH receptor, which exhibits a high membrane expression of the corresponding receptor); and (b). Addition of the C-tail of the catfish GnRHR (the C-tail is absent in the hGnRHR) (left image). In the right graphic of A, it can be observed how deletion of K191 (-) in both the WT and mutant E90K GnRHR and/or addition (+) of the C-tail from the catfish GnRHR increased total inositol phosphates production upon stimulation with the GnRH analog Buserelin. Different letters above bars indicate statistically significant differences among inositol phosphate values. Data taken from ref (169).(B) This figure shows the effect of different amino acid replacements on the hFSHR at position D408 (D408Y, D408R, and D408A) in the TMD2, on the plasma membrane expression of the receptor (top) and activation of the cAMP-sensitive pSOMLuc reporter plasmid (bottom). Top : Western blot of hFSHR WT and mutants (D408Y, D408R, and D408A, respectively) hFSHRs. The blot shows the migration of hFSHRs from protein extracts of HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the WT (lane 3) or mutant hFSHR (lanes 4-6) cDNAs inserted in the pSG5 vector. The first lane from left to right shows the migration of the WT hFSHR from HEK293 cells stably expressing the receptor. The immunoblot shows that the naturally occurring mutant D408Y is mainly detected as an intracellular, immature (i) form of the receptor [≤ 75 kDa], whereas in the case of the D408R, laboratory-manufactured mutant, the replacement leads to an FSHR molecule that is present as both mature [plasma membrane expressed, ~80 kDa; (m)] and immature forms, albeit the expression of the mature form is lower compared with that of the WT hFSHR (lane 3). In the case of the D408A mutant, the expression of the mature form is marginal and that of the immature form predominates. Bottom: Recombinant FSH-stimulated intracellular signaling of the WT and the D408Y, D408R, and D408A hFSHR mutants, as assessed by a reporter gene assay, in HEK293 cells transiently cotransfected with the WT or mutant hFSHRs and the cAMP-sensitive pSOMLuc reporter plasmid. The results showed that the WT hFSHR induced a robust dose-dependent response in luciferase activity, whereas the D408Y and D408A mutants showed markedly reduced responses to FSH stimulation, and the D408R mutant showed virtually absent response to agonist. Thus, replacement of aspartate with arginine at position 408 rescued membrane expression but not function of the receptor, whereas replacement with alanine was ineffective in restoring PM expression and marginally effective in rescuing function of the mutant hFSHR (from ref (174). (C) The effect of reducing the incubation temperature of HEK293 cells transiently expressing the WT and mutant D408Y hFSHR, on the plasma membrane expression of the FSHRs and the trafficking defective D408Y mutant. Incubation at a reduced temperature (30°C) enhanced PM expression of the mutant D408Y receptor (left immunoblot), with the corresponding increase in the mature (m) to immature ratio (i) (m/i ratio) (right graph). From ref (176).
Physical approaches to rescue misfolded proteins include incubating the cells at lower (e.g. 28-32 °C) than the physiological temperature. Lower incubation temperatures has resulted in enhanced PM expression of several conformationally defective vasopressin 2, GnRH, and FSH receptors with distinct point mutations (16, 176) (Figure 2C). It seems that for some misfolded receptors that are temperature-sensitive, the mechanism of this rescuing effect (75, 141, 179–182) is by preventing association and/or aggregation of the conformationally abnormal receptor with inhibitory chaperones (e.g. HSP90) (19, 183, 184), allowing the misfolded protein to be exposed to those mechanisms that favor processing and anterograde trafficking through the secretory pathway (185).
Chemical rescue is a general mechanism through which cell surface PM expression of misfolded proteins may be achieved (186) Chemical chaperones (e.g. non-specific stabilizing agents like polyols and sugars) are low molecular weight compounds that do not interact with the misfolded proteins or interefere with their function, and that correct folding by stabilizing their conformation. Osmolytes stabilize misfolded proteins by reducing their free movement and increasing their hydration (186), thereby preventing aggregation of immature conformers. They modify the free-energy difference between partially folded and more compact native structures. Since high concentrations of chemical chaperones are required to be effective in promoting folding of mutant proteins they are too toxic as an in vivo therapeutic strategy. Since chemical chaperones unspecifically rescue misfolded proteins, the risk exists of increasing retention in different cellular compartments or enhancing secretion of proteins unrelated to the mutant one, thereby leading to inappropriate changes in their local levels and/or secretion that may compromise cell function (187). As an exception, TMAO (trimethylamine-N-oxide), glycerol, and 4-phenylbutyric acid, may increase the secretion efficiency of misfolded α1-antitrypsin in a selective manner, without an impact on levels of other proteins or proteasomal degradation (188).
Rescue of intracellularly trapped GPCRs can also be achieved through the manipulation of the ER and/or post-ER regulatory mechanisms involved in protein export. For example, in the P23H mutation in the rhodopsin gene, which leads to autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa due to rhodopsin misfolding, overexpression of BiP/Grp78 may reduce photoreceptor apoptosis and retinal degeneration, thereby allowing recovery of retinal function in rats (189). Another strategy to manipulate the QCS to correct misrouting is by using cell-penetrating peptides, which modify cytosolic Ca2+ stores and, consequently, impact on Ca2+-regulated chaperones that regulate post-ER quality control (93). However, similar to chemical chaperones, a major problem with these approaches is their poor specificity for the target protein.
Molecular chaperoning has been a tremendously useful paradigm to develop pharmacoperones (or pharmacochaperones), which may regulate with high specificity folding and intracellular trafficking of WT and mutant, misfolded proteins ( Figure 1B ). In contrast with the poor specificity of chemical chaperones (190) (which is similar to that exhibited by a number of molecular chaperones), small molecule pharmacoperones have several advantages: a. they exhibit highly selective binding to the conformationally abnormal protein; and b. they do not interfere with the degradation of other misfolded proteins that are normally cleared by the QCS (191, 192). Pharmacoperones serve as a molecular template to help misfolded proteins to properly fold and become more stable, minimal free-energy conformers that may pass the scrutiny of the QCS (193). Of course, the efficiency of pharmacoperones to stabilize the target protein and restore its PM expression and function relays on several factors, including their specific structure and mode of action (either as agonist, antagonist of the natural ligand or allosteric modulator of the receptor, which in turn determine the selectivity towards the target receptor), the degree of the folding defect, and the specific location of the mutation which should not involve motifs essential for receptor function (see above) (194).
For instance, human V2R mutants (which cause X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus) displaying amino acid exchanges at the TMD2 and TMD4 interface (H80R, W164R, and S167L mutants), are recalcitrant to pharmacoperones, probably because the replaced residues provoke a severe folding defect (195). This is also the case of the human GnRHR S168R and S217R mutants at the TMDs 4 and 5, which cause congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism; replacement of any of these serine residues (at the lipid membrane-contact phase of those TMDs) with arginine (which is a highly hydrophilic amino acid) provokes a thermodynamically unfavorable exchange that causes rotation of the TMDs 4 and 5, thereby changing the orientation of the EL2, making extremely difficult the formation of the C14-C200 disulfide bridge, which in this particular receptor is essential for receptor trafficking and function (17, 111). Mutational defects that interfere with agonist binding would also display limited functional recovery of the misfolded receptor in response to pharmacoperones, despite the successfully increased cell surface PM expression of the mutant receptor.
Pharmacoperones and functional rescue of misfolded GPCRs
Pharmacological chaperones are molecules that correct folding of misfolded proteins preventing their aggregation and/or degradation, thereby facilitating escape of the abnormal protein from the QCS to correct misrouting. Characteristics of pharmacoperones for in vivo administration should include at least the following features (193):
To easily reach physiologically effective concentrations with minimal side effects when administered in vivo.
To easily cross the cell surface PM and bind with high specificity the misfolded protein, primarily in the ER, but also in other intracellular compartments ( Figure 1B ).
To localize and act where the misfolded protein is intracellularly retained.
To exhibit high specificity and enough residence time in the ER or other post-ER compartment so that mutants can be effectively rescued, and
To bind the target protein in a reversible manner, facilitating its dissociation after routing the stabilized receptor to its functional location, to prevent any competition with the endogenous ligand, particularly in the case of agonist and antagonist pharmacoperones.
Antagonist pharmacoperones aid the misfolded GPCR mutant to reach its minimal energy, and stabilize its native conformation allowing trafficking of the protein to the PM. Nevertheless, pharmacoperone antagonists should be removed after promoting receptor trafficking and PM expression so that it may be recognized by and bind its cognate ligand (194). Interestingly, in vivo studies administering the antagonist IN3 to male mice harboring the E90K mutation did not require an additional maneuver to rescue function of the misfolded receptor other than administration of the pharmacoperone in a pulsatile manner, so that during the inter-pulse intervals the antagonist can be “washed” from the rescued receptor (196, 197). Ideally, antagonist pharmacoperones should be effective at the lowest concentration, so that it may easily dissociate from the rescued receptor (198).
Unlike antagonists, agonist pharmacoperones do not need to dissociate from the receptor protein after rescue, albeit the potential problem of promoting receptor desensitization and internalization should be considered since this may provoke decreased response to the endogenous ligand. Interestingly, some particular pharmacoperones with agonist acitivity may promote rescue and PM expression of misfolded human V2R mutants and enhance arginine vasopressin-stimulated cAMP signaling without promoting β-arrestin recruitment, ligand/receptor internalization, and β-arrestin-mediated mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation, similar to the effects of biased agonists (199), which may have some therapeutic implications because of their selective effect on a particular function. Finally, allosteric ligand pharmacoperones (see below) are compounds that specifically bind the receptor protein at a site different from the orthosteric binding site of the receptor, and thus do not interfere with binding of the natural ligand, albeit positive allosteric modulators may also lead to increased desensitization/internalization of the rescued receptor.
The efficacy of pharmacoperones to prevent abnormal intracellular accumulation and rescue misfolded GPCRs has been demonstrated for a number of receptors, including those associated with endocrine disease (Table 1). Some of these misfolded GPCR mutants leading to endocrine disorders have shown functional rescue in response to different pharmacoperone molecules in vitro and in vivo. Some examples follow.
In patients with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI), concentration of urine by the kidney is not possible due to defects in the V2R, which is localized in the basolateral membrane of principal cells in the renal collecting duct (142, 200). Occupancy of the V2R by its ligand, arginine-vasopressin (AVP), stimulates translocation and exocytic insertion to the luminal membrane of the water channel protein aquaporin-2, leading to water reabsorption in the kidney (201). Mutations in the V2R are associated with the development of NDI, a disease in infants that has an unfavorable prognosis if untreated early in life (142, 202–204). Given that a number of mutant V2Rs can be included in Class II GPCR mutants (18, 75), they can be rescued either by genetic or pharmacologic means. In this regard, it has been shown that a number of PM permeable antagonists may specifically bind and rescue function of several misfolded, trafficking-defective V2R mutants in in vitro conditions (110). V2R non-peptide antagonists include SR49059 (relcovaptan, which is a V1A receptor antagonist exhibiting moderate affinity for the V2R), OPC31260, OPC41061 (tolvaptan), and SR121463B (satavaptan). These pharmacoperones have been shown to promote maturation and basolateral membrane localization of some V2R mutants stably transfected in MDCK cells (143). In a proof-of-concept in vivo study, the effects of the V1AR/V2R antagonist SR49059 to rescue function of three V2R mutants (R137H, W164S, and des185-193 V2R mutants) expressed by young patients with NDI were studied (110). Urine production and water intake decreased, and concomitantly urine osmolarity was significantly enhanced in response to this compound. More clinically safe than SR49059 (which is hepatotoxic) for rescuing misfolded V2Rs at feasible concentrations in vivo are the pharmacoperones OPC31260 and OPC41061, which represent promising candidates to specifically treat NDI (143).
Contrary to pharmacoperone antagonists, pharmacoperone agonists activate the cAMP/PKA signaling cascade after binding to V2R mutants. It has been shown that the non-peptide agonists MCF14, MCF18, and MCF57 may selectively rescue cell surface plasma membrane expression and restore the response to AVP of several V2R mutants, including L44P, A294P, and R337X misfolded V2Rs, without stimulating receptor internalization and MAPK activation (199, 205). On the contrary, the cell membrane-permeable agonists VA999088, VA999089, and OPC51803 only stimulated intracellular signaling but not PM expression (144). Analogously to the S168R and S217R human GnRHR mutants, the V2Rs with amino acid exchanges at the TMD2 and TMD4 interface (H80R, W164R, and S167L mutants) also showed recalcitrance to pharmacoperone treatment, most probably due to the severity of the folding defect as a consequence of the nature of the amino acid replacement (111, 195). These data underline the importance of the location of the amino acid substitution, the physicochemical properties of the replacing residue, and the nature of the pharmacoperone drug administered on the response of misfolded V2R mutants (and also of other GPCRs). Finally, it has been shown that the aminoglycoside antibiotic (G418) can rescue X-linked NDI caused by a V2R mutant bearing a premature truncation (206). Cultured kidney collecting duct cells expressing the V2R E242X mutant and exposed to this particular antibiotic exhibited enhanced AVP-stimulated cAMP responses. In addition, G418 suppressed the premature stop codon present in mice bearing the E242X replacement; in this model, mRNA translation proceeded effectively to the normal end of the gene, improving urine concentration. In addition, it has also been shown that stop codons can be suppressed by aminoglycosides in vitro and in vivo (207).
MC3R and MC4R are GPCRs mainly expressed in the central nervous system and involved in energy homeostasis, regulating food intake and energy expenditure (75, 163, 208); mutations in their corresponding genes lead to early-onset severe obesity. A large number of mutant MC3 and MC4 receptors correspond to Class II loss-of-function mutants. Several MC4R Class II loss-of-function mutants may be rescued by pharmacological chaperones in vitro and in vivo. For example, the small molecule ML00253764, which is a MC4R antagonist and partial inverse agonist permeable to the blood-brain barrier, enhanced cell surface PM expression and ligand-stimulated cAMP response of mutant MC4Rs in vitro (163, 209). Nonetheless, this molecule has a relatively high EC50 rescue dose (∼10 μM), which is not practical for in vivo rescue. In contrast, Ipsen 5i and Ipsen 17 are more potent pharmacoperones for MC4R mutants (EC50 dose approximates 10 nM) (210); in fact, the former has been shown to correct misrouting and signaling of intracellularly trapped MC4R mutants (75, 162). More recently, in vivo studies in humanized mouse models bearing the R165W human MC4R mutant showed that UM013086 rescued PM expression and function of this obesity-causing mutant MC4R in mice; treated animals restored the anorexigenic response to the MC4R agonist melanotan II (211). This study represents a proof-of-principle for pharmacoperone application as a therapeutic strategy for severe obesity associated with mutations in the MC4R.
The CaSR is a GPCR essential to maintain blood Ca2+ homeostasis by sensing fluctuations of extracellular Ca2+, modulating parathyroid hormone secretion by parathyroid cells and Ca2+ reabsorption by the kidney (153, 154). Loss-of-function of the CaSR caused by heterozygous mutations in this receptor gene leads to familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia, whereas homozygous mutations cause severe neonatal hyperparathyroidism (155). A number of CaSR loss-of-function mutations (e.g. R66C, R185Q, R680C, R795W, and V817I, which affect proper trafficking of the CaSR through the secretory pathway), can be partially or completely rescued in vitro by the membrane-permeant allosteric agonist NPS R-568 or MG132 (which prevents proteasomal degradation) (156, 212). The finding that the location and function of inactivating CaSR misfolded mutants can be rescued by pharmacoperones, opens the possibility for novel therapeutic approaches for diseases caused by structural alterations leading to misrouting of this important receptor.
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH) in humans may originate at different levels along the hypothalamic pituitary unit (73, 213). Kallmann syndrome is an X-linked recessive inherited disease whose phenotype includes delayed puberty and anosmia or hyposmia due to failure of GnRH producing neurons to migrate from the olfactory placode to the basal hypothalamus and to the presence of insufficient projections from the lateral olfactory placode to the forebrain, resulting in aplasia or hypoplasia of the olfactory bulbs. Mutations in the PROKR2, some of which provoke misfolding and misrouting of the receptor, may be associated with this syndrome (150, 214). In this particular receptor, the small molecule PROKR2 antagonist A457 has been shown to rescue PM expression and signaling of the misrouted P290S PROKR2 mutant (150).
Other mutations causing hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, without affecting olfaction, include mutations in the GnRHR (73, 149, 215, 216). This receptor binds GnRH, a hypothalamic decapeptide released into the median eminence at the base of the hypothalamus, which serves as an interface between the neural and the endocrine system governed by the anterior pituitary (217). Here, several hypothalamic hormones, including GnRH, are released into the portal capillary bed to be transported to the anterior pituitary. GnRH binds to the GnRHR to promote the synthesis and secretion of the pituitary gonadotropins, which are essential for gonadal function. The molecular mechanisms through which small molecules rescue misfolded human GnRHRs has been dilucidated with some detail (46, 191, 198). Using a number of methods including site-directed mutagenesis, confocal microscopy, computational modeling, and pharmacoperone docking, it has been possible to elucidate the mechanism whereby distinct pharmacoperones (e.g. the indole IN3) stabilize misfolded GnRHRs (191). In the E90K mutant (and probably in other GnRHR mutants as well), whose PM expression and functional rescue in vitro is complete when pharmacological approaches are applied (see above) (173), this effect occurs through the association of residues D98 and K121 (at the extracellular face of the TMD1 and at the TMD3, respectively) via formation a surrogate bond for the highly conserved, naturally occurring E90-K121 salt bridge; the pharmacoperone IN3 leads to stabilization of the TMD2-TMD3 configuration which has been severely altered by the E90K substitution (191). Notably, all GnRHR pharmacoperones tested, including indoles, the quinolone Q89, and two erythromycin macrolides, A177775 and TAK-013, which were originally developed as GnRH peptidomimetic antagonist molecules, rescued function of the majority of the human GnRHR mutants studied in vitro, including the T32I, E90K, C200Y, C279Y, and L266R GnRHR mutants identified in patients with HH (198, 218), despite their different distribution accross the receptor protein. This finding indicates that the orientation between the TMD2 and 3 is a critical structural feature monitored by the QCS of the cell (17, 191, 198). Even more importantly, employing a HH murine model expressing the E90K GnRHR mutation (178), it was demonstrated that pulsatile administration of IN3 was able to induce changes in several biomarkers, of hypogonadism, including restoration of spermatogenesis, providing evidence on the efficacy of pharmacoperone treatment on this mutant receptor (196).
Loss-of-function mutations in the LHCGR and the FSHR may lead to hypergonadotropic hypogonadism in humans (73, 219, 220), whenever both alleles are affected by the mutation. Loss-of-function mutations in the LHCGR gene lead to different phenotypes in male patients, from severe genital ambiguity to cryptorchidism and micropenis, whereas women with inactivating mutations in this receptor frequently exhibit primary or secondary amenorrhea and infertility (73). In men, loss-of-function mutations in the FSHR gene, may cause decrease in the quality of spermatogenesis but with normal testosterone production; this latter feature probably contributes to the preservation of fertility exhibited by some patients bearing these mutations (221). In women, inactivating mutations in the FSHR lead to more severe phenotypes, mainly varying forms of premature ovarian failure (222–224). Approximately fifty percent of loss-of-function mutations in the LHCGR and ∼30% in the FSHR are misfolded, trafficking defective proteins which fail to be recruited to the secretory pathway (185). Exposure of cells expressing the A593P and S616Y misfolded LHCGR mutants (which cause in men varying degrees of genital ambiguity due to hypoplasia of testicular interticial cells; Table 1) to the cell-permeant, small molecule agonist Org 42599 rescued PM expression and function of these LHCGR misfolded mutants (225),whereas in misfolded FSHR mutants, in vitro exposure to the thienopyr(im)idine Org41841 (226) or to the FSHR allosteric agonist CAN1404 (a dihydrobenzoindazole analogue) resulted in increased PM expression and function of some misfolded mutants [e.g. the A189V mutant (at the receptor ectodomain) by Org41841, and the D408Y, A419T, A575V, P587H, P519T, and F591S FSHR mutants (at the serpentine region of the receptor) by CAN1404] (170, 171).
Conclusions
Current challenges in the area of targeting trafficking of misfolded proteins as a pharmacological approach include identification of novel small molecules that may effectively exert its therapeutic effect in vivo to cure conformational diseases, including those due to GPCR misfolding. It is also important to discover molecules that may increase PM expression of WT receptors and provoke conformational bias with positive effects on GPCR-signalosome assembly and signaling upon exposure to agonist (227). Assays to identify pharmacological chaperones lacking antagonistic activity are currently available (172, 228–234), but nevertheless, new assays are still needed to bypass the complex pharmacological interactions occurring when both antagonist and conformational biased activities are present.
An example of pharmacoperones as a feasible therapeutic approach to ameliorate the effect of misrouting is the case of the misfolded ΔF508 CFTR chloride channel leading to cystic fibrosis (235, 236). This CFTR mutant is retained by the chaperone HSP70 and its co-chaperone CHIP in the ER and retro-translocated into the cytosol for degradation by the ubiquiting-proteasome machinery (237–239). Nevertheless, in the presence of small molecule correctors, the ΔF508 CFTR mutant may route to the PM and exert function. An additional problem is that the peripheral QCS of the cell may recognize this particular mutant when is present at the PM and accelerate its internalization, thereby enhancing its lysosomal degradation, which may reduce the net amount of functional CFTR molecules at the PM. To overcome this problem, combination of modulators (correctors and potentiators) of this channel, which may be considered as pharmacoperone drugs, have been succesfully administered to patients with cystic fibrosis bearing the ΔF508 CFTR mutation (25, 27, 30, 240–246), resulting in a significant improvement on some primary and secondary end points (30, 242). Small molecule modulators of CFTR are thus highly promising therapeutic interventions for patients with cystic fibrosis, particularly those expressing the ΔF508 mutation.
It is currently possible to obtain valuable information on the mechanism of action of different chemical classes of small molecule pharmacoperone drugs and how they interact with the misfolded GPCRs, applying high-throughput screening assays coupled with virtual computed, artificial intelligence-aided structural approaches (172, 247–253). This might provide new medicines to cure endocrine diseases caused by mutations leading to misfolding and misrouting of GPCRs.
Author contributions
AU-A: Write the manuscript. TZ: Write the manuscript and provided data. RG-S: Write the manuscript. Y-XT: checked the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
Research in the authors’ laboratories are supported by grants from the National University of Mexico (UNAM-CIC) (to AU-A).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- 1. Fredriksson R, Lagerstrom MC, Lundin LG, Schioth HB. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol (2003) 63(6):1256–72. doi: 10.1124/mol.63.6.1256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Gershengorn MC, Osman R. Minireview: Insights into G protein-coupled receptor function using molecular models. Endocrinology (2001) 142(1):2–10. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.1.7919 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Lagerstrom MC, Schioth HB. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov (2008) 7(4):339–57. doi: 10.1038/nrd2518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Insel PA, Sriram K, Wiley SZ, Wilderman A, Katakia T, McCann T, et al. GPCRomics: GPCR expression in cancer cells and tumors identifies new, potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Front Pharmacol (2018) 9:431. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Sriram K, Insel PA. G Protein-coupled receptors as targets for approved drugs: How many targets and how many drugs? Mol Pharmacol (2018) 93(4):251–8. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.111062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Hauser AS, Attwood MM, Rask-Andersen M, Schioth HB, Gloriam DE. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: new agents, targets and indications. Nat Rev Drug Discov (2017) 16(12):829–42. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Conn PM. G Protein-coupled receptors and the G protein family. In: Conn PM, editor. Handbook of physiology. section 7: The endocrine system. 1: Cellular endocrinology. New York: Oxford University Press; (1998). p. 87–124. [Google Scholar]
- 8. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Stanislaus D, Janovick JA, Conn PM. Structure-activity relationships of G protein-coupled receptors. Arch Med Res (1999) 30(6):420–35. doi: 10.1016/S0188-0128(99)00041-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Zarinan T, Castillo-Badillo J, Maravillas-Montero JL. Membrane signaling in health and disease. In: Reference module in neuroscience and biobehavioral psychology, Amsterdam, Netherlands:Elsevier; (2018). p. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Syrovatkina V, Alegre KO, Dey R, Huang XY. Regulation, signaling, and physiological functions of G-proteins. J Mol Biol (2016) 428(19):3850–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.08.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Sposini S, Hanyaloglu AC. Evolving view of membrane trafficking and signaling systems for G protein-coupled receptors. Prog Mol Subcell Biol (2018) 57:273–99. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-96704-2_10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Hanyaloglu AC, Zarinan T, Janovick JA, AL. Protein homeostasis and regulation of intreacellular trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors. In: Pey, editor. Protein homeostasis deseases. Academic Press, London, UK:Elsevier Inc; (2020). p. 247–77. [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Janovick JA, Zariñán T, Hanyaloglu AC. Intracellular trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors to the cell surface plasma membrane in health and disease. In: Ulloa-Aguirre A, Tao Y-X, editors. Cellular endocrinology in health and disease. Academic Press, London UK:Elsevier Inc; (2021). p. 375–412. [Google Scholar]
- 14. Kato A, Touhara K. Mammalian olfactory receptors: pharmacology, G protein coupling and desensitization. Cell Mol Life Sci (2009) 66(23):3743–53. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0111-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Schoneberg T, Schulz A, Biebermann H, Hermsdorf T, Rompler H, Sangkuhl K. Mutant G-protein-coupled receptors as a cause of human diseases. Pharmacol Ther (2004) 104(3):173–206. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.08.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Janovick JA, Brothers SP, Conn PM. Pharmacologic rescue of conformationally-defective proteins: implications for the treatment of human disease. Traffic (2004) 5(11):821–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00232.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Janovick JA, Miranda AL, Conn PM. G-Protein-coupled receptor trafficking: understanding the chemical basis of health and disease. ACS Chem Biol (2006) 1(10):631–8. doi: 10.1021/cb600360h [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Morello JP, Petaja-Repo UE, Bichet DG, Bouvier M. Pharmacological chaperones: a new twist on receptor folding. Trends Pharmacol Sci (2000) 21(12):466–9. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01575-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Conn PM. Targeting of G protein-coupled receptors to the plasma membrane in health and disease. Front Biosci (2009) 14:973–94. doi: 10.2741/3290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Hou ZS, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Tao YX. Pharmacoperone drugs: targeting misfolded proteins causing lysosomal storage-, ion channels-, and G protein-coupled receptors-associated conformational disorders. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol (2018) 11(6):611–24. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2018.1480367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Dobson CM. Principles of protein folding, misfolding and aggregation. Semin Cell Dev Biol (2004) 15(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.12.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Horwich A. Protein aggregation in disease: a role for folding intermediates forming specific multimeric interactions. J Clin Invest (2002) 110(9):1221–32. doi: 10.1172/JCI0216781 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Shastry BS. Neurodegenerative disorders of protein aggregation. Neurochem Int (2003) 43(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/S0197-0186(02)00196-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Bernier V, Lagace M, Bichet DG, Bouvier M. Pharmacological chaperones: potential treatment for conformational diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab (2004) 15(5):222–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2004.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Davies JC, Moskowitz SM, Brown C, Horsley A, Mall MA, McKone EF, et al. VX-659-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis and one or two Phe508del alleles. N Engl J Med (2018) 379(17):1599–611. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1807119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Cheung JC, Deber CM. Misfolding of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and disease. Biochemistry (2008) 47(6):1465–73. doi: 10.1021/bi702209s [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Cholon DM, Quinney NL, Fulcher ML, Esther CR, Jr, Das J, Dokholyan NV, et al. Potentiator ivacaftor abrogates pharmacological correction of DeltaF508 CFTR in cystic fibrosis. Sci Transl Med (2014) 6(246):246ra96. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008680 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Kim Chiaw P, Eckford PD, Bear CE. Insights into the mechanisms underlying CFTR channel activity, the molecular basis for cystic fibrosis and strategies for therapy. Essays Biochem (2011) 50(1):233–48. doi: 10.1042/bse0500233 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Lim M, Zeitlin PL. Therapeutic strategies to correct malfunction of CFTR. Paediatr Respir Rev (2001) 2(2):159–64. doi: 10.1053/prrv.2000.0124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Ramsey BW, Davies J, McElvaney NG, Tullis E, Bell SC, Drevinek P, et al. A CFTR potentiator in patients with cystic fibrosis and the G551D mutation. N Engl J Med (2011) 365(18):1663–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1105185 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Wellhauser L, Kim Chiaw P, Pasyk S, Li C, Ramjeesingh M, Bear CE. A small-molecule modulator interacts directly with deltaPhe508-CFTR to modify its ATPase activity and conformational stability. Mol Pharmacol (2009) 75(6):1430–8. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.055608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Zhang Z, Baksh MM, Finn MG, Heidary DK, Richards CI. Direct measurement of trafficking of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator to the cell surface and binding to a chemical chaperone. Biochemistry. (2017) 56(1):240–9. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00853 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Middleton PG, Mall MA, Drevinek P, Lands LC, McKone EF, Polineni D, et al. Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor for cystic fibrosis with a single Phe508del allele. N Engl J Med (2019) 381(19):1809–19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908639 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Hammond C, Helenius A. Quality control in the secretory pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol (1995) 7(4):523–9. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80009-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Helenius A. Quality control in the secretory assembly line. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci (2001) 356(1406):147–50. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0759 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Houry WA. Chaperone-assisted protein folding in the cell cytoplasm. Curr Protein Pept Sci (2001) 2(3):227–44. doi: 10.2174/1389203013381134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Hartl FU, Bracher A, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature. (2011) 475(7356):324–32. doi: 10.1038/nature10317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in the cytosol: from nascent chain to folded protein. Science. (2002) 295(5561):1852–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1068408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Macario AJ, Conway de Macario E. Molecular chaperones: multiple functions, pathologies, and potential applications. Front Biosci (2007) 12:2588–600. doi: 10.2741/2257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Glover JR, Lindquist S. Hsp104, Hsp70, and Hsp40: a novel chaperone system that rescues previously aggregated proteins. Cell. (1998) 94(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81223-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Duennwald ML, Echeverria A, Shorter J. Small heat shock proteins potentiate amyloid dissolution by protein disaggregases from yeast and humans. PloS Biol (2012) 10(6):e1001346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001346 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Gething MJ, Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. (1992) 355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Hiller MM, Finger A, Schweiger M, Wolf DH. ER degradation of a misfolded luminal protein by the cytosolic ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Science. (1996) 273(5282):1725–8. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5282.1725 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Ravid T, Hochstrasser M. Diversity of degradation signals in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2008) 9(9):679–90. doi: 10.1038/nrm2468 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Schubert U, Anton LC, Gibbs J, Norbury CC, Yewdell JW, Bennink JR. Rapid degradation of a large fraction of newly synthesized proteins by proteasomes. Nature (2000) 404(6779):770–4. doi: 10.1038/35008096 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Conn PM, Ulloa-Aguirre A. Pharmacological chaperones for misfolded gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors. Adv Pharmacol (2011) 62:109–41. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385952-5.00008-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Otero JH, Lizak B, Hendershot LM. Life and death of a BiP substrate. Semin Cell Dev Biol (2010) 21(5):472–8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.12.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Genest O, Wickner S, Doyle SM. Hsp90 and Hsp70 chaperones: Collaborators in protein remodeling. J Biol Chem (2019) 294(6):2109–20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV118.002806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Mayer MP, Gierasch LM. Recent advances in the structural and mechanistic aspects of Hsp70 molecular chaperones. J Biol Chem (2019) 294(6):2085–97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV118.002810 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Frydman J, Nimmesgern E, Ohtsuka K, Hartl FU. Folding of nascent polypeptide chains in a high molecular mass assembly with molecular chaperones. Nature (1994) 370(6485):111–7. doi: 10.1038/370111a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Langer T, Lu C, Echols H, Flanagan J, Hayer MK, Hartl FU. Successive action of DnaK, DnaJ and GroEL along the pathway of chaperone-mediated protein folding. Nature (1992) 356(6371):683–9. doi: 10.1038/356683a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Luheshi LM, Dobson CM. Bridging the gap: from protein misfolding to protein misfolding diseases. FEBS Lett (2009) 583(16):2581–6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.06.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Lievremont JP, Rizzuto R, Hendershot L, Meldolesi J. BiP, a major chaperone protein of the endoplasmic reticulum lumen, plays a direct and important role in the storage of the rapidly exchanging pool of Ca2+. J Biol Chem (1997) 272(49):30873–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.49.30873 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Yang Y, Turner RS, Gaut JR. The chaperone BiP/GRP78 binds to amyloid precursor protein and decreases Abeta40 and Abeta42 secretion. J Biol Chem (1998) 273(40):25552–5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.40.25552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Pobre KFR, Poet GJ, Hendershot LM. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone BiP is a master regulator of ER functions: Getting by with a little help from ERdj friends. J Biol Chem (2019) 294(6):2098–108. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV118.002804 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Lanctot PM, Leclerc PC, Escher E, Guillemette G, Leduc R. Role of n-glycan-dependent quality control in the cell-surface expression of the AT1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (2006) 340(2):395–402. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Mizrachi D, Segaloff DL. Intracellularly located misfolded glycoprotein hormone receptors associate with different chaperone proteins than their cognate wild-type receptors. Mol Endocrinol (2004) 18(7):1768–77. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Anukanth A, Khorana HG. Structure and function in rhodopsin. requirements of a specific structure for the intradiscal domain. J Biol Chem (1994) 269(31):19738–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Siffroi-Fernandez S, Giraud A, Lanet J, Franc JL. Association of the thyrotropin receptor with calnexin, calreticulin and BiP. efects on the maturation of the receptor. Eur J Biochem (2002) 269(20):4930–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03192.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Remondelli P, Renna M. The endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response in neurodegenerative disorders and its potential therapeutic significance. Front Mol Neurosci (2017) 10:187. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Schroder M, Kaufman RJ. The mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem (2005) 74:739–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.074134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Williams DB. Beyond lectins: the calnexin/calreticulin chaperone system of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci (2006) 119(Pt 4):615–23. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02856 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Caramelo JJ, Parodi AJ. Getting in and out from calnexin/calreticulin cycles. J Biol Chem (2008) 283(16):10221–5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R700048200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Rosenbaum EE, Hardie RC, Colley NJ. Calnexin is essential for rhodopsin maturation, Ca2+ regulation, and photoreceptor cell survival. Neuron (2006) 49(2):229–41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.12.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Schrag JD, Procopio DO, Cygler M, Thomas DY, Bergeron JJ. Lectin control of protein folding and sorting in the secretory pathway. Trends Biochem Sci (2003) 28(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0004(02)00004-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Ware FE, Vassilakos A, Peterson PA, Jackson MR, Lehrman MA, Williams DB. The molecular chaperone calnexin binds Glc1Man9GlcNAc2 oligosaccharide as an initial step in recognizing unfolded glycoproteins. J Biol Chem (1995) 270(9):4697–704. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4697 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Ferrari DM, Soling HD. The protein disulphide-isomerase family: unravelling a string of folds. Biochem J (1999) 339(Pt 1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj3390001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Forster ML, Sivick K, Park YN, Arvan P, Lencer WI, Tsai B. Protein disulfide isomerase-like proteins play opposing roles during retrotranslocation. J Cell Biol (2006) 173(6):853–9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200602046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Robinson PJ, Pringle MA, Woolhead CA, Bulleid NJ. Folding of a single domain protein entering the endoplasmic reticulum precedes disulfide formation. J Biol Chem (2017) 292(17):6978–86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.780742 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Turano C, Coppari S, Altieri F, Ferraro A. Proteins of the PDI family: unpredicted non-ER locations and functions. J Cell Physiol (2002) 193(2):154–63. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Morello JP, Salahpour A, Petaja-Repo UE, Laperriere A, Lonergan M, Arthus MF, et al. Association of calnexin with wild type and mutant AVPR2 that causes nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Biochemistry (2001) 40(23):6766–75. doi: 10.1021/bi002699r [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Kozlov G, Gehring K. Calnexin cycle - structural features of the ER chaperone system. FEBS J (2020) 287(20):4322–40. doi: 10.1111/febs.15330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Zarinan T, Dias JA, Conn PM. Mutations in G protein-coupled receptors that impact receptor trafficking and reproductive function. Mol Cell Endocrinol (2014) 382(1):411–23. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.06.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Pearl LH, Prodromou C. Structure and mechanism of the Hsp90 molecular chaperone machinery. Annu Rev Biochem (2006) 75:271–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142738 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Tao YX, Conn PM. Chaperoning G protein-coupled receptors: from cell biology to therapeutics. Endocr Rev (2014) 35(4):602–47. doi: 10.1210/er.2013-1121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Parent A, Roy SJ, Iorio-Morin C, Lepine MC, Labrecque P, Gallant MA, et al. ANKRD13C acts as a molecular chaperone for G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem (2010) 285(52):40838–51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Ge X, Loh HH, Law PY. Mu-opioid receptor cell surface expression is regulated by its direct interaction with ribophorin I. Mol Pharmacol (2009) 75(6):1307–16. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.054064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Rodrigues-Ferreira S, Nahmias C. An ATIPical family of angiotensin II AT2 receptor-interacting proteins. Trends Endocrinol Metab (2010) 21(11):684–90. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2010.08.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Hicks SW, Horn TA, McCaffery JM, Zuckerman DM, Machamer CE. Golgin-160 promotes cell surface expression of the beta-1 adrenergic receptor. Traffic (2006) 7(12):1666–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2006.00504.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Christopoulos A, Christopoulos G, Morfis M, Udawela M, Laburthe M, Couvineau A, et al. Novel receptor partners and function of receptor activity-modifying proteins. J Biol Chem (2003) 278(5):3293–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200629200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Ferreira PA, Nakayama TA, Pak WL, Travis GH. Cyclophilin-related protein RanBP2 acts as chaperone for red/green opsin. Nature. (1996) 383(6601):637–40. doi: 10.1038/383637a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Dwyer ND, Troemel ER, Sengupta P, Bargmann CI. Odorant receptor localization to olfactory cilia is mediated by ODR-4, a novel membrane-associated protein. Cell. (1998) 93(3):455–66. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81173-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Gimelbrant AA, Haley SL, McClintock TS. Olfactory receptor trafficking involves conserved regulatory steps. J Biol Chem (2001) 276(10):7285–90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005433200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Chen C, Itakura E, Weber KP, Hegde RS, de Bono M. An ER complex of ODR-4 and ODR-8/Ufm1 specific protease 2 promotes GPCR maturation by a Ufm1-independent mechanism. PloS Genet (2014) 10(3):e1004082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Xu X, Wu G. Human C1orf27 protein interacts with alpha2A-adrenergic receptor and regulates its anterograde transport. J Biol Chem (2022) 298(6):102021. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Metherell LA, Chapple JP, Cooray S, David A, Becker C, Ruschendorf F, et al. Mutations in MRAP, encoding a new interacting partner of the ACTH receptor, cause familial glucocorticoid deficiency type 2. Nat Genet (2005) 37(2):166–70. doi: 10.1038/ng1501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Sebag JA, Hinkle PM. Melanocortin-2 receptor accessory protein MRAP forms antiparallel homodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2007) 104(51):20244–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708916105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Saito H, Kubota M, Roberts RW, Chi Q, Matsunami H. RTP family members induce functional expression of mammalian odorant receptors. Cell. (2004) 119(5):679–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Bermak JC, Li M, Bullock C, Zhou QY. Regulation of transport of the dopamine D1 receptor by a new membrane-associated ER protein. Nat Cell Biol (2001) 3(5):492–8. doi: 10.1038/35074561 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Zhang M, Wu G. Mechanisms of the anterograde trafficking of GPCRs: Regulation of AT1R transport by interacting proteins and motifs. Traffic (2019) 20(2):110–20. doi: 10.1111/tra.12624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Okiyoneda T, Apaja PM, Lukacs GL. Protein quality control at the plasma membrane. Curr Opin Cell Biol (2011) 23(4):483–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.04.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Dorner AJ, Krane MG, Kaufman RJ. Reduction of endogenous GRP78 levels improves secretion of a heterologous protein in CHO cells. Mol Cell Biol (1988) 8(10):4063–70. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4063-4070.1988 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Oueslati M, Hermosilla R, Schonenberger E, Oorschot V, Beyermann M, Wiesner B, et al. Rescue of a nephrogenic diabetes insipidus-causing vasopressin V2 receptor mutant by cell-penetrating peptides. J Biol Chem (2007) 282(28):20676–85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611530200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Wei Z, Zhang M, Li C, Huang W, Fan Y, Guo J, et al. Specific TBC domain-containing proteins control the ER-golgi-plasma membrane trafficking of GPCRs. Cell Rep (2019) 28(2):554–66.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Dong C, Nichols CD, Guo J, Huang W, Lambert NA, Wu G. A triple arg motif mediates alpha(2B)-adrenergic receptor interaction with Sec24C/D and export. Traffic (2012) 13(6):857–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2012.01351.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Dong C, Zhou F, Fugetta EK, Filipeanu CM, Wu G. Endoplasmic reticulum export of adrenergic and angiotensin II receptors is differentially regulated by Sar1 GTPase. Cell Signal (2008) 20(6):1035–43. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.01.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Wang G, Wu G. Small GTPase regulation of GPCR anterograde trafficking. Trends Pharmacol Sci (2012) 33(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.09.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Li C, Wei Z, Fan Y, Huang W, Su Y, Li H, et al. The GTPase Rab43 controls the anterograde ER-golgi trafficking and sorting of GPCRs. Cell Rep (2017) 21(4):1089–101. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Leclerc PC, Auger-Messier M, Lanctot PM, Escher E, Leduc R, Guillemette G. A polyaromatic caveolin-binding-like motif in the cytoplasmic tail of the type 1 receptor for angiotensin II plays an important role in receptor trafficking and signaling. Endocrinology. (2002) 143(12):4702–10. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220679 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Robert J, Auzan C, Ventura MA, Clauser E. Mechanisms of cell-surface rerouting of an endoplasmic reticulum-retained mutant of the vasopressin V1b/V3 receptor by a pharmacological chaperone. J Biol Chem (2005) 280(51):42198–206. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510180200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Robert J, Clauser E, Petit PX, Ventura MA. A novel c-terminal motif is necessary for the export of the vasopressin V1b/V3 receptor to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem (2005) 280(3):2300–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410655200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Robert J, Clauser ER. [Vasopressin receptors: structure/function relationships and signal transduction in target cells]. J Soc Biol (2005) 199(4):351–9. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2005037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Thielen A, Oueslati M, Hermosilla R, Krause G, Oksche A, Rosenthal W, et al. The hydrophobic amino acid residues in the membrane-proximal c tail of the G protein-coupled vasopressin V2 receptor are necessary for transport-competent receptor folding. FEBS Lett (2005) 579(23):5227–35. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.08.043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Duvernay MT, Dong C, Zhang X, Zhou F, Nichols CD, Wu G. Anterograde trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors: function of the c-terminal F(X)6LL motif in export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Pharmacol (2009) 75(4):751–61. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.051623 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Duvernay MT, Zhou F, Wu G. A conserved motif for the transport of G protein-coupled receptors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. J Biol Chem (2004) 279(29):30741–50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313881200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Pagano A, Rovelli G, Mosbacher J, Lohmann T, Duthey B, Stauffer D, et al. C-terminal interaction is essential for surface trafficking but not for heteromeric assembly of GABA(b) receptors. J Neurosci (2001) 21(4):1189–202. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-04-01189.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Ma D, Zerangue N, Lin YF, Collins A, Yu M, Jan YN, et al. Role of ER export signals in controlling surface potassium channel numbers. Science. (2001) 291(5502):316–9. doi: 10.1126/science.291.5502.316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Angelotti T, Daunt D, Shcherbakova OG, Kobilka B, Hurt CM. Regulation of G-protein coupled receptor traffic by an evolutionary conserved hydrophobic signal. Traffic. (2010) 11(4):560–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01033.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Benke D, Zemoura K, Maier PJ. Modulation of cell surface GABA(B) receptors by desensitization, trafficking and regulated degradation. World J Biol Chem (2012) 3(4):61–72. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i4.61 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Bernier V, Morello JP, Zarruk A, Debrand N, Salahpour A, Lonergan M, et al. Pharmacologic chaperones as a potential treatment for X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. J Am Soc Nephrol (2006) 17(1):232–43. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005080854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Leanos-Miranda A, Janovick JA, Conn PM. Receptor-misrouting: an unexpectedly prevalent and rescuable etiology in gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor-mediated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2002) 87(10):4825–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-020961 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Dong C, Wu G. Regulation of anterograde transport of alpha2-adrenergic receptors by the n termini at multiple intracellular compartments. J Biol Chem (2006) 281(50):38543–54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605734200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Duvernay MT, Dong C, Zhang X, Robitaille M, Hebert TE, Wu G. A single conserved leucine residue on the first intracellular loop regulates ER export of G protein-coupled receptors. Traffic (2009) 10(5):552–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00890.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Helenius A, Aebi M. Roles of n-linked glycans in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem (2004) 73:1019–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073752 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Lanctot PM, Leclerc PC, Clement M, Auger-Messier M, Escher E, Leduc R, et al. Importance of n-glycosylation positioning for cell-surface expression, targeting, affinity and quality control of the human AT1 receptor. Biochem J (2005) 390(Pt 1):367–76. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Rannikko A, Pakarinen P, Manna PR, Beau I, Misrahi M, Aittomaki K, et al. Functional characterization of the human FSH receptor with an inactivating Ala189Val mutation. Mol Hum Reprod (2002) 8(4):311–7. doi: 10.1093/molehr/8.4.311 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Chini B, Parenti M. G-Protein-coupled receptors, cholesterol and palmitoylation: facts about fats. J Mol Endocrinol (2009) 42(5):371–9. doi: 10.1677/JME-08-0114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Melo-Nava B, Casas-Gonzalez P, Perez-Solis MA, Castillo-Badillo J, Maravillas-Montero JL, Jardon-Valadez E, et al. Role of cysteine residues in the carboxyl-terminus of the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor in intracellular traffic and postendocytic processing. Front Cell Dev Biol (2016) 4:76. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Munshi UM, Clouser CL, Peegel H, Menon KM. Evidence that palmitoylation of carboxyl terminus cysteine residues of the human luteinizing hormone receptor regulates postendocytic processing. Mol Endocrinol (2005) 19(3):749–58. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0335 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Qanbar R, Bouvier M. Role of palmitoylation/depalmitoylation reactions in G-protein-coupled receptor function. Pharmacol Ther (2003) 97(1):1–33. doi: 10.1016/S0163-7258(02)00300-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Resh MD. Palmitoylation of ligands, receptors, and intracellular signaling molecules. Sci STKE (2006) 2006(359):re14. doi: 10.1126/stke.3592006re14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Milligan G. G protein-coupled receptor dimerisation: molecular basis and relevance to function. Biochim Biophys Acta (2007) 1768(4):825–35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.09.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Angers S, Salahpour A, Bouvier M. Dimerization: an emerging concept for G protein-coupled receptor ontogeny and function. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol (2002) 42:409–35. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.42.091701.082314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Ayoub MA, Couturier C, Lucas-Meunier E, Angers S, Fossier P, Bouvier M, et al. Monitoring of ligand-independent dimerization and ligand-induced conformational changes of melatonin receptors in living cells by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. J Biol Chem (2002) 277(24):21522–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200729200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Guan R, Wu X, Feng X, Zhang M, Hebert TE, Segaloff DL. Structural determinants underlying constitutive dimerization of unoccupied human follitropin receptors. Cell Signal (2010) 22(2):247–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.09.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Guo W, Shi L, Javitch JA. The fourth transmembrane segment forms the interface of the dopamine D2 receptor homodimer. J Biol Chem (2003) 278(7):4385–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200679200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Herrick-Davis K, Grinde E, Mazurkiewicz JE. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of serotonin 5-HT2C receptor homodimers on the plasma membrane of living cells. Biochemistry (2004) 43(44):13963–71. doi: 10.1021/bi048398p [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128. Mazurkiewicz JE, Herrick-Davis K, Barroso M, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Lindau-Shepard B, Thomas RM, et al. Single-molecule analyses of fully functional fluorescent protein-tagged follitropin receptor reveal homodimerization and specific heterodimerization with lutropin receptor. Biol Reprod (2015) 92(4):100. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.114.125781 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129. McVey M, Ramsay D, Kellett E, Rees S, Wilson S, Pope AJ, et al. Monitoring receptor oligomerization using time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. the human delta -opioid receptor displays constitutive oligomerization at the cell surface, which is not regulated by receptor occupancy. J Biol Chem (2001) 276(17):14092–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008902200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Mercier JF, Salahpour A, Angers S, Breit A, Bouvier M. Quantitative assessment of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor homo- and heterodimerization by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. J Biol Chem (2002) 277(47):44925–31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205767200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Salahpour A, Angers S, Mercier JF, Lagace M, Marullo S, Bouvier M. Homodimerization of the beta2-adrenergic receptor as a prerequisite for cell surface targeting. J Biol Chem (2004) 279(32):33390–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403363200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Terrillon S, Bouvier M. Roles of G-protein-coupled receptor dimerization. EMBO Rep (2004) 5(1):30–4. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Margeta-Mitrovic M, Jan YN, Jan LY. A trafficking checkpoint controls GABA(B) receptor heterodimerization. Neuron. (2000) 27(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00012-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Benkirane M, Jin DY, Chun RF, Koup RA, Jeang KT. Mechanism of transdominant inhibition of CCR5-mediated HIV-1 infection by ccr5delta32. J Biol Chem (1997) 272(49):30603–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.49.30603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Karpa KD, Lin R, Kabbani N, Levenson R. The dopamine D3 receptor interacts with itself and the truncated D3 splice variant d3nf: D3-D3nf interaction causes mislocalization of D3 receptors. Mol Pharmacol (2000) 58(4):677–83. doi: 10.1124/mol.58.4.677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Leanos-Miranda A, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Ji TH, Janovick JA, Conn PM. Dominant-negative action of disease-causing gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR) mutants: a trait that potentially coevolved with decreased plasma membrane expression of GnRHR in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2003) 88(7):3360–7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Lee SP, O'Dowd BF, Ng GY, Varghese G, Akil H, Mansour A, et al. Inhibition of cell surface expression by mutant receptors demonstrates that D2 dopamine receptors exist as oligomers in the cell. Mol Pharmacol (2000) 58(1):120–8. doi: 10.1124/mol.58.1.120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Zarinan T, Perez-Solis MA, Maya-Nunez G, Casas-Gonzalez P, Conn PM, Dias JA, et al. Dominant negative effects of human follicle-stimulating hormone receptor expression-deficient mutants on wild-type receptor cell surface expression. rescue of oligomerization-dependent defective receptor expression by using cognate decoys. Mol Cell Endocrinol (2010) 321(2):112–22. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.02.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Zhu X, Wess J. Truncated V2 vasopressin receptors as negative regulators of wild-type V2 receptor function. Biochemistry. (1998) 37(45):15773–84. doi: 10.1021/bi981162z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Conn PM, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Ito J, Janovick JA. G Protein-coupled receptor trafficking in health and disease: lessons learned to prepare for therapeutic mutant rescue in vivo . Pharmacol Rev (2007) 59(3):225–50. doi: 10.1124/pr.59.3.2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. Cheong HI, Cho HY, Park HW, Ha IS, Choi Y. Molecular genetic study of congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and rescue of mutant vasopressin V2 receptor by chemical chaperones. Nephrol (Carlton) (2007) 12(2):113–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2006.00759.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Morello JP, Bichet DG. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Annu Rev Physiol (2001) 63:607–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.607 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Robben JH, Deen PM. Pharmacological chaperones in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: possibilities for clinical application. BioDrugs. (2007) 21(3):157–66. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200721030-00003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Robben JH, Kortenoeven ML, Sze M, Yae C, Milligan G, Oorschot VM, et al. Intracellular activation of vasopressin V2 receptor mutants in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus by nonpeptide agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2009) 106(29):12195–200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900130106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Bichet DG, Birnbaumer M, Lonergan M, Arthus MF, Rosenthal W, Goodyer P, et al. Nature and recurrence of AVPR2 mutations in X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Am J Hum Genet (1994) 55(2):278–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. Fujiwara TM, Bichet DG. Molecular biology of hereditary diabetes insipidus. J Am Soc Nephrol (2005) 16(10):2836–46. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005040371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Knoers NV, Deen PM. Molecular and cellular defects in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Pediatr Nephrol (2001) 16(12):1146–52. doi: 10.1007/s004670100051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Morello JP, Salahpour A, Laperriere A, Bernier V, Arthus MF, Lonergan M, et al. Pharmacological chaperones rescue cell-surface expression and function of misfolded V2 vasopressin receptor mutants. J Clin Invest (2000) 105(7):887–95. doi: 10.1172/JCI8688 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Conn PM, Ulloa-Aguirre A. Trafficking of G-protein-coupled receptors to the plasma membrane: insights for pharmacoperone drugs. Trends Endocrinol Metab (2010) 21(3):190–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.11.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150. Chen DN, Ma YT, Liu H, Zhou QY, Li JD. Functional rescue of kallmann syndrome-associated prokineticin receptor 2 (PKR2) mutants deficient in trafficking. J Biol Chem (2014) 289(22):15518–26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.556381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Leanos-Miranda A, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Janovick JA, Conn PM. In vitro coexpression and pharmacological rescue of mutant gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors causing hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in humans expressing compound heterozygous alleles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2005) 90(5):3001–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-2071 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152. Maya-Nunez G, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Janovick JA, Conn PM. Pharmacological chaperones correct misfolded GPCRs and rescue function: protein trafficking as a therapeutic target. Subcell Biochem (2012) 63:263–89. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4765-4_14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153. Brown EM. Clinical lessons from the calcium-sensing receptor. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab (2007) 3(2):122–33. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet0388 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154. Chen X, Wang L, Cui Q, Ding Z, Han L, Kou Y, et al. Structural insights into the activation of human calcium-sensing receptor. Elife (2021) 10:e68578. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68578 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155. Egbuna OI, Brown EM. Hypercalcaemic and hypocalcaemic conditions due to calcium-sensing receptor mutations. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol (2008) 22(1):129–48. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2007.11.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156. White E, McKenna J, Cavanaugh A, Breitwieser GE. Pharmacochaperone-mediated rescue of calcium-sensing receptor loss-of-function mutants. Mol Endocrinol (2009) 23(7):1115–23. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157. Biebermann H, Schoneberg T, Krude H, Schultz G, Gudermann T, Gruters A. Mutations of the human thyrotropin receptor gene causing thyroid hypoplasia and persistent congenital hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (1997) 82(10):3471–80. doi: 10.1210/jc.82.10.3471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158. Calebiro D, de Filippis T, Lucchi S, Covino C, Panigone S, Beck-Peccoz P, et al. Intracellular entrapment of wild-type TSH receptor by oligomerization with mutants linked to dominant TSH resistance. Hum Mol Genet (2005) 14(20):2991–3002. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi329 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159. Tonacchera M, Agretti P, Pinchera A, Rosellini V, Perri A, Collecchi P, et al. Congenital hypothyroidism with impaired thyroid response to thyrotropin (TSH) and absent circulating thyroglobulin: Evidence for a new inactivating mutation of the TSH receptor gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2000) 85(3):1001–8. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.3.6460 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160. Lin L, Hindmarsh PC, Metherell LA, Alzyoud M, Al-Ali M, Brain CE, et al. Severe loss-of-function mutations in the adrenocorticotropin receptor (ACTHR, MC2R) can be found in patients diagnosed with salt-losing adrenal hypoplasia. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) (2007) 66(2):205–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02709.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161. Clark AJ, Metherell LA, Cheetham ME, Huebner A. Inherited ACTH insensitivity illuminates the mechanisms of ACTH action. Trends Endocrinol Metab (2005) 16(10):451–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2005.10.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162. Tao YX, Conn PM. Pharmacoperones as novel therapeutics for diverse protein conformational diseases. Physiol Rev (2018) 98(2):697–725. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00029.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163. Tao YX. The melanocortin-4 receptor: physiology, pharmacology, and pathophysiology. Endocr Rev (2010) 31(4):506–43. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164. Huang H, Tao YX. Functions of the DRY motif and intracellular loop 2 of human melanocortin 3 receptor. J Mol Endocrinol (2014) 53(3):319–30. doi: 10.1530/JME-14-0184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165. Tao YX, Segaloff DL. Functional characterization of melanocortin-4 receptor mutations associated with childhood obesity. Endocrinology (2003) 144(10):4544–51. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0524 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166. Colley NJ, Cassill JA, Baker EK, Zuker CS. Defective intracellular transport is the molecular basis of rhodopsin-dependent dominant retinal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (1995) 92(7):3070–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.3070 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167. D'Souza-Li L, Yang B, Canaff L, Bai M, Hanley DA, Bastepe M, et al. Identification and functional characterization of novel calcium-sensing receptor mutations in familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia and autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2002) 87(3):1309–18. doi: 10.1210/jc.87.3.1309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168. Fuchs S, Amiel J, Claudel S, Lyonnet S, Corvol P, Pinet F. Functional characterization of three mutations of the endothelin b receptor gene in patients with hirschsprung's disease: evidence for selective loss of gi coupling. Mol Med (2001) 7(2):115–24. doi: 10.1007/BF03401945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169. Hanyroup S, Anderson RC, Nataraja S, Yu HN, Millar RP, Newton CL. Rescue of cell surface expression and signalling of mutant follicle-stimulating hormone receptors. Endocrinology (2021) 162(12):1–18. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170. Newton CL, Anderson RC, Kreuchwig A, Krause G, Katz AA, Millar RP. Rescue of function of mutant luteinising hormone receptors with deficiencies in cell surface expression, hormone binding, and hormone signalling. Neuroendocrinology (2021) 111(5):451–64. doi: 10.1159/000508000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171. Janovick JA, Maya-Nunez G, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Huhtaniemi IT, Dias JA, Verbost P, et al. Increased plasma membrane expression of human follicle-stimulating hormone receptor by a small molecule thienopyr(im)idine. Mol Cell Endocrinol (2009) 298(1-2):84–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.09.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172. Janovick JA, Ulloa-Aguirre A. Cellular high-throughput screening. In: Pey AL, editor. Protein homeostasis deseases. London, UK: Academic Press; (2020). p. 343–58. [Google Scholar]
- 173. Maya-Nunez G, Janovick JA, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Soderlund D, Conn PM, Mendez JP. Molecular basis of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: restoration of mutant (E(90)K) GnRH receptor function by a deletion at a distant site. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2002) 87(5):2144–9. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.5.8386 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174. Jardon-Valadez E, Castillo-Guajardo D, Martinez-Luis I, Gutierrez-Sagal R, Zarinan T, Ulloa-Aguirre A. Molecular dynamics simulation of the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor. understanding the conformational dynamics of receptor variants at positions N680 and D408 from in silico analysis. PloS One (2018) 13(11):e0207526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207526 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175. Lin X, Janovick JA, Brothers S, Blomenrohr M, Bogerd J, Conn PM. Addition of catfish gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor intracellular carboxyl-terminal tail to rat GnRH receptor alters receptor expression and regulation. Mol Endocrinol (1998) 12(2):161–71. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.2.0056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176. Zarinan T, Mayorga J, Jardon-Valadez E, Gutierrez-Sagal R, Maravillas-Montero JL, Mejia-Dominguez NR, et al. A novel mutation in the FSH receptor (I423T) affecting receptor activation and leading to primary ovarian failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2021) 106(2):e534–e50. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa782 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177. Arora KK, Chung HO, Catt KJ. Influence of a species-specific extracellular amino acid on expression and function of the human gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor. Mol Endocrinol (1999) 13(6):890–6. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.6.0291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178. Stewart MD, Deng JM, Stewart CA, Mullen RD, Wang Y, Lopez S, et al. Mice harboring gnrhr E90K, a mutation that causes protein misfolding and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in humans, exhibit testis size reduction and ovulation failure. Mol Endocrinol (2012) 26(11):1847–56. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179. Jaquette J, Segaloff DL. Temperature sensitivity of some mutants of the lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor. Endocrinology (1997) 138(1):85–91. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.1.4902 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180. Jeyaraj SC, Chotani MA, Mitra S, Gregg HE, Flavahan NA, Morrison KJ. Cooling evokes redistribution of alpha2C-adrenoceptors from golgi to plasma membrane in transfected human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Mol Pharmacol (2001) 60(6):1195–200. doi: 10.1124/mol.60.6.1195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181. Machamer CE, Rose JK. Vesicular stomatitis virus G proteins with altered glycosylation sites display temperature-sensitive intracellular transport and are subject to aberrant intermolecular disulfide bonding. J Biol Chem (1988) 263(12):5955–60. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)60659-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182. Yu R, Chen CR, Liu X, Kodra JT. Rescue of a pathogenic mutant human glucagon receptor by pharmacological chaperones. J Mol Endocrinol (2012) 49(2):69–78. doi: 10.1530/JME-12-0051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183. Denning GM, Anderson MP, Amara JF, Marshall J, Smith AE, Welsh MJ. Processing of mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is temperature-sensitive. Nature. (1992) 358(6389):761–4. doi: 10.1038/358761a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184. Filipeanu CM, de Vries R, Danser AH, Kapusta DR. Modulation of alpha(2C) adrenergic receptor temperature-sensitive trafficking by HSP90. Biochim Biophys Acta (2011) 1813(2):346–57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.11.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Zarinan T, Gutierrez-Sagal R, Dias JA. Intracellular trafficking of gonadotropin receptors in health and disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol (2018):245:1–39. doi: 10.1007/164_2017_49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186. Arakawa T, Ejima D, Kita Y, Tsumoto K. Small molecule pharmacological chaperones: From thermodynamic stabilization to pharmaceutical drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta (2006) 1764(11):1677–87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2006.08.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187. Castro-Fernandez C, Maya-Nunez G, Conn PM. Beyond the signal sequence: protein routing in health and disease. Endocr Rev (2005) 26(4):479–503. doi: 10.1210/er.2004-0010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188. Perlmutter DH. Chemical chaperones: a pharmacological strategy for disorders of protein folding and trafficking. Pediatr Res (2002) 52(6):832–6. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200212000-00004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189. Gorbatyuk MS, Knox T, LaVail MM, Gorbatyuk OS, Noorwez SM, Hauswirth WW, et al. Restoration of visual function in P23H rhodopsin transgenic rats by gene delivery of BiP/Grp78. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2010) 107(13):5961–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911991107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190. Dandage R, Bandyopadhyay A, Jayaraj GG, Saxena K, Dalal V, Das A, et al. Classification of chemical chaperones based on their effect on protein folding landscapes. ACS Chem Biol (2015) 10(3):813–20. doi: 10.1021/cb500798y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191. Janovick JA, Patney A, Mosely R, Goulet M, Altman M, Rush T, et al. Molecular mechanism of action of pharmacoperone rescue of misrouted GPCR mutants: the GnRH receptor. Mol Endocrinol (2009) 23(2):157–68. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0384 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Conn PM. Pharmacoperones as a new therapeutic approach: In vitro identification and In vivo validation of bioactive molecules. Curr Drug Targets (2016) 17(13):1471–81. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160307143345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193. Conn PM, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Janovick JA. "Pharmacoperone": What's in a word? Pharmacol Res (2013) 83:1–2. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.11.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194. Leidenheimer NJ, Ryder KG. Pharmacological chaperoning: a primer on mechanism and pharmacology. Pharmacol Res (2014) 83:10–9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.01.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195. Wuller S, Wiesner B, Loffler A, Furkert J, Krause G, Hermosilla R, et al. Pharmacochaperones post-translationally enhance cell surface expression by increasing conformational stability of wild-type and mutant vasopressin V2 receptors. J Biol Chem (2004) 279(45):47254–63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408154200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196. Janovick JA, Stewart MD, Jacob D, Martin LD, Deng JM, Stewart CA, et al. Restoration of testis function in hypogonadotropic hypogonadal mice harboring a misfolded GnRHR mutant by pharmacoperone drug therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2013) 110(52):21030–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315194110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197. Conn PM, Smithson DC, Hodder PS, Stewart MD, Behringer RR, Smith E, et al. Transitioning pharmacoperones to therapeutic use: in vivo proof-of-principle and design of high throughput screens. Pharmacol Res (2014) 83:38–51. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.12.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198. Janovick JA, Goulet M, Bush E, Greer J, Wettlaufer DG, Conn PM. Structure-activity relations of successful pharmacologic chaperones for rescue of naturally occurring and manufactured mutants of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2003) 305(2):608–14. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.048454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199. Jean-Alphonse F, Perkovska S, Frantz MC, Durroux T, Mejean C, Morin D, et al. Biased agonist pharmacochaperones of the AVP V2 receptor may treat congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. J Am Soc Nephrol (2009) 20(10):2190–203. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008121289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200. Birnbaumer M. V2R structure and diabetes insipidus. Receptors Channels (2002) 8(1):51–6. doi: 10.3109/10606820212134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201. Robben JH, Knoers NV, Deen PM. Cell biological aspects of the vasopressin type-2 receptor and aquaporin 2 water channel in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol (2006) 291(2):F257–70. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00491.2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202. Bichet DG. [Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus]. Nephrol Ther (2006) 2(6):387–404. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2006.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203. Birnbaumer M. Vasopressin receptor mutations and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Arch Med Res (1999) 30(6):465–74. doi: 10.1016/S0188-4409(99)00063-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204. Oksche A, Schulein R, Rutz C, Liebenhoff U, Dickson J, Muller H, et al. Vasopressin V2 receptor mutants that cause X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: analysis of expression, processing, and function. Mol Pharmacol (1996) 50(4):820–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205. Moeller HB, Rittig S, Fenton RA. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: essential insights into the molecular background and potential therapies for treatment. Endocr Rev (2013) 34(2):278–301. doi: 10.1210/er.2012-1044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206. Sangkuhl K, Schulz A, Rompler H, Yun J, Wess J, Schoneberg T. Aminoglycoside-mediated rescue of a disease-causing nonsense mutation in the V2 vasopressin receptor gene in vitro and in vivo . Hum Mol Genet (2004) 13(9):893–903. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207. Barton-Davis ER, Cordier L, Shoturma DI, Leland SE, Sweeney HL. Aminoglycoside antibiotics restore dystrophin function to skeletal muscles of mdx mice. J Clin Invest (1999) 104(4):375–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI7866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208. Renquist BJ, Lippert RN, Sebag JA, Ellacott KL, Cone RD. Physiological roles of the melanocortin MC(3) receptor. Eur J Pharmacol (2011) 660(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.12.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209. Fan ZC, Tao YX. Functional characterization and pharmacological rescue of melanocortin-4 receptor mutations identified from obese patients. J Cell Mol Med (2009) 13(9B):3268–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00726.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210. Huang H, Wang W, Tao YX. Pharmacological chaperones for the misfolded melanocortin-4 receptor associated with human obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta (2017) 1863(10 Pt A):2496–507. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211. Rene P, Lanfray D, Richard D, Bouvier M. Pharmacological chaperone action in humanized mouse models of MC4R-linked obesity. JCI Insight (2021) 6(4):e132778. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.132778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212. Huang Y, Breitwieser GE. Rescue of calcium-sensing receptor mutants by allosteric modulators reveals a conformational checkpoint in receptor biogenesis. J Biol Chem (2007) 282(13):9517–25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609045200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213. Sykiotis GP, Hoang XH, Avbelj M, Hayes FJ, Thambundit A, Dwyer A, et al. Congenital idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: evidence of defects in the hypothalamus, pituitary, and testes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2010) 95(6):3019–27. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-2582 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214. Monnier C, Dode C, Fabre L, Teixeira L, Labesse G, Pin JP, et al. PROKR2 missense mutations associated with kallmann syndrome impair receptor signalling activity. Hum Mol Genet (2009) 18(1):75–81. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn318 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215. Ulloa-Aguirre AZ T, Lira-Albarrán S. Mutations of gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor gene. In: Huhtaniemi IML, editor. Encyclopedia of endocrine diseases, 2nd. Edition. Oxford, UK: Academic Press; (2019). p. 704–12. [Google Scholar]
- 216. Chevrier L, Guimiot F, de Roux N. GnRH receptor mutations in isolated gonadotropic deficiency. Mol Cell Endocrinol (2011) 346(1-2):21–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.04.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Timossi C. Biochemical and functional aspects of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone and gonadotrophins. Reprod BioMed Online (2000) 1(2):48–62. doi: 10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61901-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218. Janovick JA, Maya-Nunez G, Conn PM. Rescue of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism-causing and manufactured GnRH receptor mutants by a specific protein-folding template: misrouted proteins as a novel disease etiology and therapeutic target. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2002) 87(7):3255–62. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.7.8582 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Zarinan T, Gutierrez-Sagal R, Dias JA. Intracellular trafficking of gonadotropin receptors in health and disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol (2018) 245:1–39. doi: 10.1007/164_2017_49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220. Huhtaniemi IT, Themmen AP. Mutations in human gonadotropin and gonadotropin-receptor genes. Endocrine. (2005) 26(3):207–17. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:26:3:207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221. Tapanainen JS, Aittomaki K, Min J, Vaskivuo T, Huhtaniemi IT. Men homozygous for an inactivating mutation of the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) receptor gene present variable suppression of spermatogenesis and fertility. Nat Genet (1997) 15(2):205–6. doi: 10.1038/ng0297-205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222. Beau I, Touraine P, Meduri G, Gougeon A, Desroches A, Matuchansky C, et al. A novel phenotype related to partial loss of function mutations of the follicle stimulating hormone receptor. J Clin Invest (1998) 102(7):1352–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI3795 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223. Aittomaki K, Lucena JL, Pakarinen P, Sistonen P, Tapanainen J, Gromoll J, et al. Mutation in the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor gene causes hereditary hypergonadotropic ovarian failure. Cell. (1995) 82(6):959–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90275-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224. Aittomaki K, Tapanainen J, Huhtaniemi I, de la Chapelle A. [Inherited primary amenorrhea. the first gynecological disease of Finnish heritage]. Duodecim. (1996) 112(1):9–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225. Newton CL, Whay AM, McArdle CA, Zhang M, van Koppen CJ, van de Lagemaat R, et al. Rescue of expression and signaling of human luteinizing hormone G protein-coupled receptor mutants with an allosterically binding small-molecule agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2011) 108(17):7172–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015723108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226. van Straten NC, Schoonus-Gerritsma GG, van Someren RG, Draaijer J, Adang AE, Timmers CM, et al. The first orally active low molecular weight agonists for the LH receptor: thienopyr(im)idines with therapeutic potential for ovulation induction. Chembiochem. (2002) 3(10):1023–6. doi: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Crepieux P, Poupon A, Maurel MC, Reiter E. Novel pathways in gonadotropin receptor signaling and biased agonism. Rev Endocr Metab Disord (2011) 12(4):259–74. doi: 10.1007/s11154-011-9176-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228. Conn PM, Janovick JA. Pharmacoperone identification for therapeutic rescue of misfolded mutant proteins. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) (2011) 2(6). doi: 10.3389/fendo.2011.00006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229. Conn PM, Smith E, Hodder P, Janovick JA, Smithson DC. High-throughput screen for pharmacoperones of the vasopressin type 2 receptor. J Biomol Screen (2013) 18(8):930–7. doi: 10.1177/1087057113483559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230. Hou S, Madoux F, Scampavia L, Janovick JA, Conn PM, Spicer TP. Drug library screening for the identification of ionophores that correct the mistrafficking disorder associated with oxalosis kidney disease. SLAS Discov (2017) 22(7):887–96. doi: 10.1177/2472555217689992 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231. Madoux F, Janovick JA, Smithson D, Fargue S, Danpure CJ, Scampavia L, et al. Development of a phenotypic high-content assay to identify pharmacoperone drugs for the treatment of primary hyperoxaluria type 1 by high-throughput screening. Assay Drug Dev Technol (2015) 13(1):16–24. doi: 10.1089/adt.2014.627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232. Smithson DC, Janovick JA, Conn PM. Therapeutic rescue of Misfolded/Mistrafficked mutants: Automation-friendly high-throughput assays for identification of pharmacoperone drugs of GPCRs. Methods Enzymol (2013) 521:3–16. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391862-8.00001-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233. Janovick JA, Spicer TP, Bannister TD, Smith E, Ganapathy V, Scampavia L. Chemical validation and optimization of pharmacoperones targeting vasopressin type 2 receptor mutant. Biochem J (2018) 475(18):2941–53. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234. Ulloa-Aguirre A, Janovick JA. Modulation of proteostasis and protein trafficking: a therapeutic avenue for misfolded G protein-coupled receptors causing disease in humans. Emerg Top Life Sci (2019) 3:39–52. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20180055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235. Sharma M, Pampinella F, Nemes C, Benharouga M, So J, Du K, et al. Misfolding diverts CFTR from recycling to degradation: quality control at early endosomes. J Cell Biol (2004) 164(6):923–33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200312018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236. Welsh MJ, Smith AE. Molecular mechanisms of CFTR chloride channel dysfunction in cystic fibrosis. Cell (1993) 73(7):1251–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90353-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237. Jensen TJ, Loo MA, Pind S, Williams DB, Goldberg AL, Riordan JR. Multiple proteolytic systems, including the proteasome, contribute to CFTR processing. Cell. (1995) 83(1):129–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90241-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238. Meacham GC, Patterson C, Zhang W, Younger JM, Cyr DM. The Hsc70 co-chaperone CHIP targets immature CFTR for proteasomal degradation. Nat Cell Biol (2001) 3(1):100–5. doi: 10.1038/35050509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239. Ward CL, Omura S, Kopito RR. Degradation of CFTR by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cell. (1995) 83(1):121–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90240-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240. Birault V, Solari R, Hanrahan J, Thomas DY. Correctors of the basic trafficking defect of the mutant F508del-CFTR that causes cystic fibrosis. Curr Opin Chem Biol (2013) 17(3):353–60. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.04.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241. Eckford PD, Ramjeesingh M, Molinski S, Pasyk S, Dekkers JF, Li C, et al. VX-809 and related corrector compounds exhibit secondary activity stabilizing active F508del-CFTR after its partial rescue to the cell surface. Chem Biol (2014) 21(5):666–78. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.02.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242. Keating D, Marigowda G, Burr L, Daines C, Mall MA, McKone EF, et al. VX-445-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis and one or two Phe508del alleles. N Engl J Med (2018) 379(17):1612–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1807120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243. Loo TW, Bartlett MC, Wang Y, Clarke DM. The chemical chaperone CFcor-325 repairs folding defects in the transmembrane domains of CFTR-processing mutants. Biochem J (2006) 395(3):537–42. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244. Loo TW, Clarke DM. Corrector VX-809 promotes interactions between cytoplasmic loop one and the first nucleotide-binding domain of CFTR. Biochem Pharmacol (2017) 136:24–31. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.03.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245. Pettit RS, Fellner C. CFTR modulators for the treatment of cystic fibrosis. P T (2014) 39(7):500–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246. Wainwright CE, Elborn JS, Ramsey BW, Marigowda G, Huang X, Cipolli M, et al. Lumacaftor-ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis homozygous for Phe508del CFTR. N Engl J Med (2015) 373(3):220–31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1409547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247. Paul D, Sanap G, Shenoy S, Kalyane D, Kalia K, Tekade RK. Artificial intelligence in drug discov and development. Drug Discovery Today (2021) 26(1):80–93. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.10.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248. Bender A, Cortes-Ciriano I. Artificial intelligence in drug discovery: what is realistic, what are illusions? part 2: a discussion of chemical and biological data. Drug Discov Today (2021) 26(4):1040–52. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.11.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249. Bender A, Cortes-Ciriano I. Artificial intelligence in drug discovery: what is realistic, what are illusions? part 1: Ways to make an impact, and why we are not there yet. Drug Discov Today (2021) 26(2):511–24. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.12.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250. Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A, Green T, Figurnov M, Ronneberger O, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature (2021) 596(7873):583–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251. Noorwez SM, Ostrov DA, McDowell JH, Krebs MP, Kaushal S. A high-throughput screening method for small-molecule pharmacologic chaperones of misfolded rhodopsin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci (2008) 49(7):3224–30. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1539 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252. Pey AL, Ying M, Cremades N, Velazquez-Campoy A, Scherer T, Thony B, et al. Identification of pharmacological chaperones as potential therapeutic agents to treat phenylketonuria. J Clin Invest (2008) 118(8):2858–67. doi: 10.1172/JCI34355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253. Smith E, Janovick JA, Bannister TD, Shumate J, Ganapathy V, Scampavia L, et al. Rescue of mutant gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor function independent of cognate receptor activity. Sci Rep (2020) 10(1):10579. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67473-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]