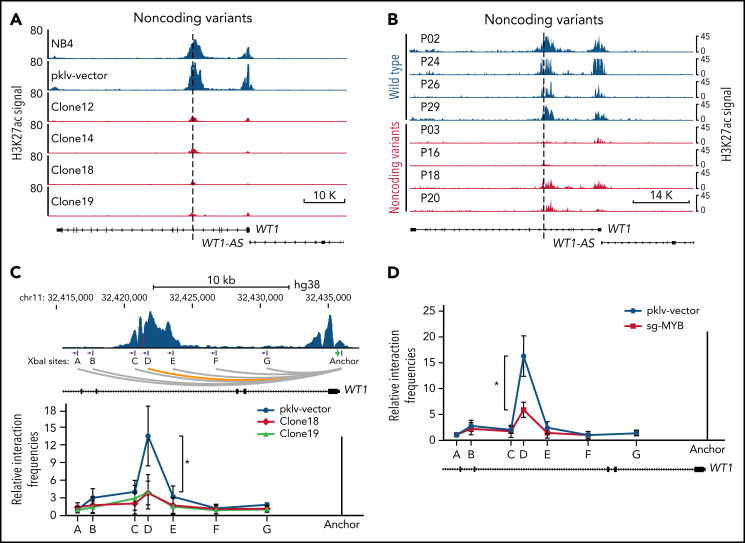
Figure 6.
Alterations in the recurrently mutated site of the WT1 enhancer disrupt the MYB-mediated enhancer-promoter interactions. (A-B) ChIP-seq tracks of H3K27ac signals at the WT1 locus in the MYB motif-mutated clones and the parental cells (A) and APL patients with or without noncoding WT1 variants (B). (C) The relative interaction frequencies between the anchor region (the WT1 promoter) and distal sites (purple bars) in the MYB motif-mutated clones and the parental cells. The relative interaction frequencies were determined by chromatin conformation capture (3C)-qPCR and normalized to the control region (region A). The upper panel is the schematic diagram showing the H3K27ac signals at the WT1 locus and the design of the 3C assay. XbaI restriction sites are indicated by purple blocks, 3C primers are indicated by purple arrows, and the anchor is shown by a green arrow. *P < .05 for comparison between the MYB motif-mutated clones and the parental cells. (D) The relative interaction frequencies analyzed by 3C-qPCR in NB4 cells with or without MYB knockout. *P < .05 for comparison between MYB knockout cells and control cells. pklv-vector, the sgRNA empty vector control; sg-MYB, sgRNA targeting MYB.