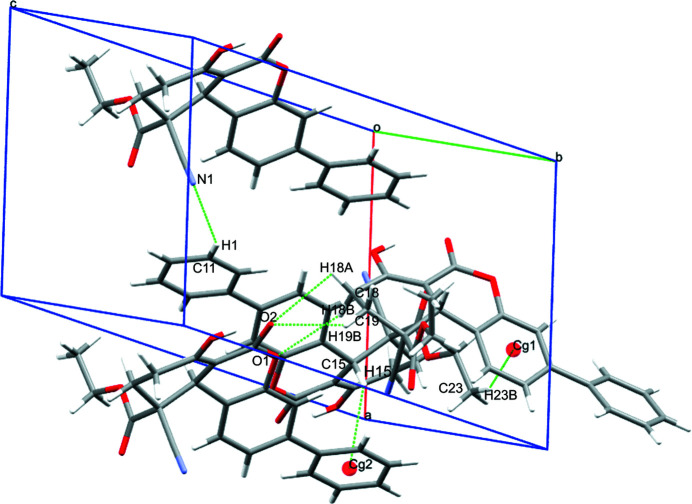
The packing of the title compound is consolidated by C—H⋯O interactions.
Keywords: dibenzopyran, C—H⋯π interaction, C—H⋯O interaction, crystal structure
Abstract
In the title compound, C23H19NO5, the cyano group adopts an axial orientation and the ester group an equatorial orientation. The dihedral angle between the pendant phenyl group and the benzene ring of the fused-ring system is 25.97 (8)°. Intramolecular O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are observed and the packing is consolidated by C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions.
Structure description
Dibenzopyran-6-ones (also called 6H-benzo[c]chromen-6-ones or 3,4,5,6-dibenzo-α-pyranones) form an important group of biologically active natural products that occur in bacteria, fungi, lichens, higher plants and animal waste (Bialonska et al., 2009 ▸). Elsamitrucin, a dibenzopyran-6-one derived drug, is an efficient topoisomerase II inhibitor (Fiocchi et al., 2011 ▸). As well as their biological activities, some dibenzopyran-6-ones have served as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic compounds (see, for example, Coghlan et al., 2001 ▸). As a part of our ongoing studies in this area, we now describe the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
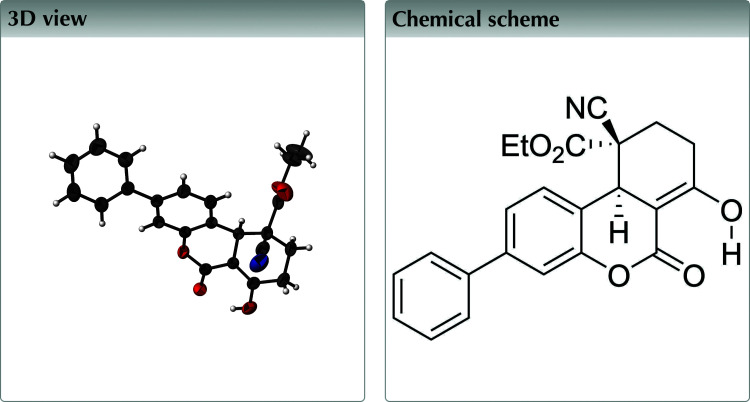
The title compound has a dibenzopyran moiety decorated by several substituents, as shown in Fig. 1 ▸. There are two stereogenic centres: in the arbitrarily chosen asymmetric molecule, C15 and C20 have S and R configurations, respectively, but crystal symmetry generates a racemic mixture. The nitrile group attached to C20 occupies an axial position and is anti to the hydrogen atom attached to C19. The dihedral angle between the pendant C1–C6 phenyl group and the C7–C12 benzene ring of the fused-ring system is 25.97 (8)°. The Cremer–Pople puckering parameters of the O1/C9/C10/C13–C15 and C14/C15/C17–C20 rings indicate half-chair conformations in each case with puckering amplitudes Q = 0.359 Å; θ = 104.52°; φ = 9.27° and Q = 0.49 Å; θ = 134.17°; φ = 327.35°, respectively. The O atom attached to C17 is stabilized in its enol (hydroxy) form, presumably as a result of forming a strong intramolecular hydrogen bond to O2. The packing is consolidated by weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions (Table 1 ▸) and an intramolecular C—H⋯O interaction is also observed (Fig. 2 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom-numbering scheme and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. Intramolecular hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C7–C12 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O2 | 0.82 | 1.86 | 2.5702 (16) | 145 |
| C11—H11⋯O4 | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.399 (2) | 154 |
| C18—H18B⋯O1i | 0.97 | 2.60 | 3.4289 (19) | 144 |
| C19—H19B⋯O2i | 0.97 | 2.60 | 3.285 (2) | 128 |
| C15—H15⋯Cg2ii | 0.98 | 2.95 | 3.7685 (17) | 142 |
| C23—H23B⋯Cg3iii | 0.96 | 2.82 | 3.686 (3) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
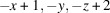 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 .
.
Figure 2.
Intermolecular interactions in the title compound.
From a Cambridge Structural Database search (Groom et al., 2016 ▸), we found compounds identified by refcodes OKEYUB (Xiao et al., 2021 ▸), QABVEY (Wang et al., 2021 ▸), ALTENU (McPhail et al., 1973 ▸), AMUYIS (Alzaydi et al., 2016 ▸), ANOVEG (Sosnovskikh et al., 2016 ▸), ANOVIK (Sosnovskikh et al., 2016 ▸), BUWJEK (Parveen et al., 2015 ▸), BUXLOW (Fatunsin et al., 2010 ▸), DIPTUR (Casiraghi et al., 1986 ▸), DISJAS (Lee et al., 2013 ▸), SEDFEN (Appel et al., 2006 ▸), SIVQIZ (Poudel & Lee, 2014 ▸), SIJZER (Hussain et al., 2007 ▸), TUPJOE (Siegel et al., 2010 ▸), ZAQHIK (Dasari et al., 2012 ▸) and IZACIY (Duan et al., 2021 ▸) to be similar to the title compound.
Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of ethyl 10-cyano-7-hydroxy-6-oxo-3-{[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]oxy}-8,9,10,10a-tetrahydro-6H-benzo[c]chromene-10-carboxylate (100 mg, 0.22 mmol), phenylboronic acid (34 mg, 0.28 mmol, 1.3 equiv.), K3PO4 (73 mg, 0.34 mmol, 1.6 equiv.) and Pd(PPh3)4 (3 mg, 3 mol%) in degassed 1,4-dioxane (10 mL) was stirred at 100° C for 12 h under nitrogen. After completion of the coupling reaction (TLC), the mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with dichloromethane (DCM, 10 mL) and decanted. The residue was extracted with DCM (10 mL × 2) twice. The solvent was removed from the combined DCM layers and the residue was subjected to column chromatography on silica gel (100–200 mesh) by using increasing amounts of ethyl acetate in hexane (5% to 15%) as eluent to afford the title compound as a light-yellow solid in 90% yield (84 mg); R f = 0.4 (hexanes:ethyl acetate, 7:3); m.p. 155–158° C. A sample suitable for single-crystal X-ray analysis was obtained by recrystallization the 50 mg of the solid from a mixture of 1 mL of distilled chloroform and 0.5 mL of distilled methanol.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C23H19NO5 |
| M r | 389.39 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.7089 (8), 14.3510 (12), 14.2749 (15) |
| β (°) | 106.946 (10) |
| V (Å3) | 1902.6 (3) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.75 × 0.44 × 0.42 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Xcalibur, Eos |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.932, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 10689, 4413, 3119 |
| R int | 0.026 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.686 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.046, 0.157, 0.95 |
| No. of reflections | 4413 |
| No. of parameters | 264 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.19, −0.20 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001997/hb4401sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001997/hb4401Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001997/hb4401Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2153368
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the DST–FIST Single Crystal XRD facility at the Department of Chemistry, Pondicherry University, for the diffraction data and Dr Clara Gomes (FCT–UNL, Portugal) for the CSD database survey. MP thanks the Department of Chemistry for facilities. JM thanks Dr Amit Kumar Singh (Sharda University, India) for support.
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C23H19NO5 | F(000) = 816 |
| Mr = 389.39 | Dx = 1.359 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.7089 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 2883 reflections |
| b = 14.3510 (12) Å | θ = 3.0–29.1° |
| c = 14.2749 (15) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 106.946 (10)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1902.6 (3) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.75 × 0.44 × 0.42 mm |
Data collection
| Xcalibur, Eos diffractometer | 4413 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 3119 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 15.9821 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.026 |
| ω scans | θmax = 29.2°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysalisPro; Agilent, 2014) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.932, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −18→17 |
| 10689 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: iterative |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.157 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.95 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4413 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.010 |
| 264 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. The hydrogen atoms in title compound were placed in calculated positions, with C—H = 0.93–0.97 A° and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(C-methyl). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.53859 (10) | 0.16733 (8) | 0.92065 (7) | 0.0410 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.63028 (12) | 0.27465 (8) | 0.84841 (8) | 0.0509 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.44382 (14) | 0.18379 (10) | 0.74486 (11) | 0.0347 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.27716 (13) | −0.06937 (8) | 0.61784 (10) | 0.0595 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.36436 (14) | 0.09212 (10) | 0.73953 (10) | 0.0332 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.431514 | 0.042889 | 0.734017 | 0.040* | |
| O3 | 0.50815 (13) | 0.31695 (9) | 0.66833 (9) | 0.0588 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.561932 | 0.325224 | 0.723781 | 0.088* | |
| C9 | 0.42029 (14) | 0.11197 (10) | 0.92053 (11) | 0.0337 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.32907 (15) | 0.07558 (10) | 0.83485 (11) | 0.0347 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.29134 (15) | 0.04148 (11) | 1.02203 (11) | 0.0366 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.27309 (15) | 0.02080 (11) | 1.11980 (11) | 0.0382 (4) | |
| C19 | 0.28311 (17) | 0.11903 (13) | 0.55664 (11) | 0.0447 (4) | |
| H19A | 0.360887 | 0.079214 | 0.550748 | 0.054* | |
| H19B | 0.203779 | 0.112652 | 0.497179 | 0.054* | |
| C16 | 0.11816 (17) | 0.14945 (12) | 0.65498 (12) | 0.0450 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.54193 (15) | 0.21194 (11) | 0.83729 (11) | 0.0375 (4) | |
| C20 | 0.23367 (15) | 0.08697 (11) | 0.64512 (11) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.40422 (15) | 0.09584 (10) | 1.01183 (11) | 0.0366 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.469369 | 0.121527 | 1.066950 | 0.044* | |
| C21 | 0.17320 (17) | −0.01170 (12) | 0.62229 (11) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.05006 (13) | −0.03278 (10) | 0.60776 (10) | 0.0649 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.19570 (17) | 0.00624 (12) | 0.93635 (12) | 0.0443 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.117331 | −0.029036 | 0.940506 | 0.053* | |
| C18 | 0.33369 (17) | 0.21905 (12) | 0.56740 (12) | 0.0467 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.381800 | 0.232559 | 0.518170 | 0.056* | |
| H18B | 0.250752 | 0.259856 | 0.555766 | 0.056* | |
| C17 | 0.43402 (16) | 0.23902 (11) | 0.66616 (12) | 0.0410 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.21487 (17) | 0.02259 (12) | 0.84563 (12) | 0.0443 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.149569 | −0.002549 | 0.790253 | 0.053* | |
| C6 | 0.20395 (18) | −0.05906 (13) | 1.13558 (13) | 0.0507 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.166517 | −0.099657 | 1.083600 | 0.061* | |
| C3 | 0.32765 (18) | 0.08032 (12) | 1.19927 (12) | 0.0466 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.375026 | 0.134713 | 1.191218 | 0.056* | |
| C2 | 0.2424 (2) | −0.02057 (16) | 1.30377 (15) | 0.0627 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.231601 | −0.034154 | 1.364935 | 0.075* | |
| C1 | 0.1887 (2) | −0.08045 (15) | 1.22642 (15) | 0.0637 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.142442 | −0.135050 | 1.235243 | 0.076* | |
| C5 | 0.3116 (2) | 0.05875 (15) | 1.29030 (14) | 0.0579 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.348412 | 0.098916 | 1.342756 | 0.070* | |
| C22 | 0.2376 (2) | −0.16616 (14) | 0.59282 (18) | 0.0714 (6) | |
| H22A | 0.150569 | −0.169084 | 0.538150 | 0.086* | |
| H22B | 0.220030 | −0.197877 | 0.648226 | 0.086* | |
| C23 | 0.3565 (3) | −0.21069 (18) | 0.5666 (2) | 0.1099 (10) | |
| H23A | 0.372605 | −0.179133 | 0.511451 | 0.165* | |
| H23B | 0.333040 | −0.274743 | 0.550071 | 0.165* | |
| H23C | 0.442123 | −0.207456 | 0.621170 | 0.165* | |
| N1 | 0.03398 (17) | 0.20167 (13) | 0.66178 (13) | 0.0658 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0360 (5) | 0.0501 (7) | 0.0321 (6) | −0.0093 (5) | 0.0023 (4) | 0.0025 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0501 (7) | 0.0508 (7) | 0.0448 (7) | −0.0184 (6) | 0.0029 (5) | 0.0017 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0322 (7) | 0.0351 (8) | 0.0334 (8) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0018 (6) |
| O5 | 0.0520 (7) | 0.0435 (7) | 0.0799 (10) | −0.0124 (6) | 0.0143 (6) | −0.0140 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0349 (8) | 0.0296 (8) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0016 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0606 (8) | 0.0537 (8) | 0.0516 (8) | −0.0181 (6) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0162 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0306 (7) | 0.0323 (8) | 0.0347 (8) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0024 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0364 (7) | 0.0323 (8) | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0029 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0385 (7) | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0338 (9) | 0.0056 (6) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0026 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0365 (7) | 0.0410 (9) | 0.0375 (9) | 0.0092 (6) | 0.0115 (6) | 0.0034 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0431 (8) | 0.0569 (11) | 0.0311 (9) | −0.0059 (8) | 0.0060 (6) | 0.0023 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0375 (8) | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0396 (10) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0056 (6) | 0.0104 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0334 (7) | 0.0373 (8) | 0.0383 (9) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0051 (6) | 0.0039 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0341 (7) | 0.0448 (9) | 0.0307 (8) | −0.0029 (6) | 0.0039 (6) | 0.0012 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0379 (7) | 0.0349 (8) | 0.0324 (8) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0028 (6) | −0.0005 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0431 (9) | 0.0534 (10) | 0.0307 (9) | −0.0102 (8) | 0.0049 (6) | −0.0038 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0483 (7) | 0.0789 (10) | 0.0652 (9) | −0.0248 (7) | 0.0132 (6) | −0.0154 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0437 (8) | 0.0481 (10) | 0.0389 (9) | −0.0103 (7) | 0.0086 (7) | 0.0044 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0430 (9) | 0.0564 (11) | 0.0361 (9) | −0.0032 (7) | 0.0045 (7) | 0.0121 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0377 (8) | 0.0423 (9) | 0.0399 (9) | −0.0027 (7) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0052 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0444 (8) | 0.0481 (10) | 0.0344 (9) | −0.0110 (7) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0010 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0548 (10) | 0.0529 (11) | 0.0485 (11) | −0.0025 (8) | 0.0214 (8) | 0.0004 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0476 (9) | 0.0504 (10) | 0.0426 (10) | 0.0034 (8) | 0.0144 (7) | −0.0021 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0683 (12) | 0.0819 (15) | 0.0468 (12) | 0.0071 (11) | 0.0307 (10) | 0.0081 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0711 (12) | 0.0699 (14) | 0.0602 (13) | −0.0059 (11) | 0.0348 (10) | 0.0087 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0591 (11) | 0.0746 (13) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0072 (10) | 0.0185 (8) | −0.0082 (9) |
| C22 | 0.0747 (13) | 0.0481 (12) | 0.0924 (17) | −0.0228 (10) | 0.0258 (11) | −0.0196 (11) |
| C23 | 0.100 (2) | 0.0564 (15) | 0.188 (3) | −0.0203 (13) | 0.065 (2) | −0.0405 (17) |
| N1 | 0.0558 (9) | 0.0742 (11) | 0.0700 (12) | 0.0198 (9) | 0.0222 (8) | 0.0222 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C13 | 1.3599 (18) | C7—C4 | 1.487 (2) |
| O1—C9 | 1.3961 (17) | C4—C6 | 1.379 (2) |
| O2—C13 | 1.2212 (18) | C4—C3 | 1.395 (2) |
| C14—C17 | 1.355 (2) | C19—C18 | 1.510 (2) |
| C14—C13 | 1.442 (2) | C19—C20 | 1.546 (2) |
| C14—C15 | 1.516 (2) | C16—N1 | 1.134 (2) |
| O5—C21 | 1.321 (2) | C16—C20 | 1.474 (2) |
| O5—C22 | 1.457 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.531 (2) |
| C15—C10 | 1.516 (2) | C21—O4 | 1.1913 (18) |
| C15—C20 | 1.5604 (19) | C12—C11 | 1.381 (2) |
| O3—C17 | 1.3255 (19) | C18—C17 | 1.489 (2) |
| C9—C8 | 1.377 (2) | C6—C1 | 1.382 (2) |
| C9—C10 | 1.386 (2) | C3—C5 | 1.388 (2) |
| C10—C11 | 1.390 (2) | C2—C5 | 1.363 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.387 (2) | C2—C1 | 1.376 (3) |
| C7—C12 | 1.397 (2) | C22—C23 | 1.460 (3) |
| C13—O1—C9 | 119.76 (11) | O1—C13—C14 | 119.40 (13) |
| C17—C14—C13 | 117.57 (14) | C16—C20—C21 | 109.13 (13) |
| C17—C14—C15 | 123.65 (13) | C16—C20—C19 | 108.83 (12) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 118.68 (13) | C21—C20—C19 | 107.00 (13) |
| C21—O5—C22 | 117.30 (14) | C16—C20—C15 | 109.78 (13) |
| C14—C15—C10 | 109.62 (12) | C21—C20—C15 | 113.11 (12) |
| C14—C15—C20 | 111.00 (12) | C19—C20—C15 | 108.88 (12) |
| C10—C15—C20 | 115.36 (12) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.33 (13) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 123.53 (14) | O4—C21—O5 | 125.08 (16) |
| C8—C9—O1 | 114.50 (12) | O4—C21—C20 | 125.09 (16) |
| C10—C9—O1 | 121.96 (13) | O5—C21—C20 | 109.79 (13) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 115.70 (14) | C11—C12—C7 | 121.50 (15) |
| C9—C10—C15 | 118.66 (13) | C17—C18—C19 | 112.50 (13) |
| C11—C10—C15 | 125.57 (13) | O3—C17—C14 | 124.59 (14) |
| C8—C7—C12 | 117.11 (14) | O3—C17—C18 | 112.66 (13) |
| C8—C7—C4 | 121.65 (13) | C14—C17—C18 | 122.73 (14) |
| C12—C7—C4 | 121.25 (14) | C12—C11—C10 | 121.79 (14) |
| C6—C4—C3 | 117.61 (15) | C4—C6—C1 | 121.87 (18) |
| C6—C4—C7 | 121.05 (15) | C5—C3—C4 | 120.32 (17) |
| C3—C4—C7 | 121.33 (15) | C5—C2—C1 | 119.68 (18) |
| C18—C19—C20 | 111.65 (14) | C2—C1—C6 | 119.68 (19) |
| N1—C16—C20 | 176.08 (18) | C2—C5—C3 | 120.84 (18) |
| O2—C13—O1 | 115.36 (13) | O5—C22—C23 | 107.97 (17) |
| O2—C13—C14 | 125.24 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C7–C12 rings, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O2 | 0.82 | 1.86 | 2.5702 (16) | 145 |
| C11—H11···O4 | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.399 (2) | 154 |
| C18—H18B···O1i | 0.97 | 2.60 | 3.4289 (19) | 144 |
| C19—H19B···O2i | 0.97 | 2.60 | 3.285 (2) | 128 |
| C15—H15···Cg2ii | 0.98 | 2.95 | 3.7685 (17) | 142 |
| C23—H23B···Cg3iii | 0.96 | 2.82 | 3.686 (3) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+2; (iii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
References
- Agilent (2014). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Alzaydi, K. M., Abojabal, N. S. & Elnagdi, M. H. (2016). Tetrahedron Lett. 57, 3596–3599.
- Appel, B., Saleh, N. N. R. & Langer, P. (2006). Chem. Eur. J. 12, 1221–1236. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bialonska, D., Kasimsetty, S. G., Khan, S. I. & Ferreira, D. (2009). J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 10181–10186. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, G., Cornia, M., Casnati, G., Fava, G. G. & Belicchi, M. F. (1986). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. pp. 271–273.
- Coghlan, M. J., Kym, P. R., Elmore, S. W., Wang, A. X., Luly, J. R., Wilcox, D., Stashko, M., Lin, C. W., Miner, J., Tyree, C., Nakane, M., Jacobson, P. & Lane, B. C. (2001). J. Med. Chem. 44, 2879–2885. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S., Bhadbhade, M. & Neilan, B. A. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Duan, J., He, X., Choy, P. Y., Wang, Q., Xie, M., Li, R., Xu, K., Shang, Y. & Kwong, F. Y. (2021). Org. Lett. 23, 6455–6460. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Fatunsin, O., Iaroshenko, V. O., Dudkin, S., Mkrtchyan, S., Villinger, A. & Langer, P. (2010). Tetrahedron Lett. 51, 4693–4695.
- Fiocchi, S. C., Selting, K. A., Rosenberg, M. P., Kolli, P., Lenaz, G. & Henry, C. (2011). J. Vet. Int. Med. 25, 897–902. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hussain, I., Nguyen, V. T. H., Yawer, M. A., Dang, T. T., Fischer, C., Reinke, H. & Langer, P. (2007). J. Org. Chem. 72, 6255–6258. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lee, T., Jayakumar, J., Cheng, C. & Chuang, S. (2013). Chem. Commun. 49, 11797. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Sovago, I., Cottrell, S. J., Galek, P. T. A., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Platings, M., Shields, G. P., Stevens, J. S., Towler, M. & Wood, P. A. (2020). J. Appl. Cryst. 53, 226–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- McPhail, A. T., Miller, R. W., Harvan, D. & Pero, R. W. (1973). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. p. 682.
- Parveen, M., Malla, A. M., Ali, A., Nami, S. A. A., Silva, P. S. P. & Silva, M. R. (2015). Chem. Nat. Compd. 51, 62–66.
- Poudel, T. N. & Lee, Y. R. (2014). Org. Biomol. Chem. 12, 919–930. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Siegel, D., Troyanov, S., Noack, J., Emmerling, F. & Nehls, I. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sosnovskikh, V. Y., Korotaev, V. Y., Kutyashev, I. B., Barkov, A. Y. & Safrygin, A. V. (2016). RSC Adv. 6, 58188–58202.
- Spek, A. L. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wang, B., Constantin, M., Singh, S., Zhou, Y., Davis, R. L. & West, F. G. (2021). Org. Biomol. Chem. 19, 399–405. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y., Zhou, L., Hao, H., Bao, Y., Yin, Q. & Xie, C. (2021). Cryst. Growth Des. 21, 1202–1217.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001997/hb4401sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001997/hb4401Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001997/hb4401Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2153368
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report