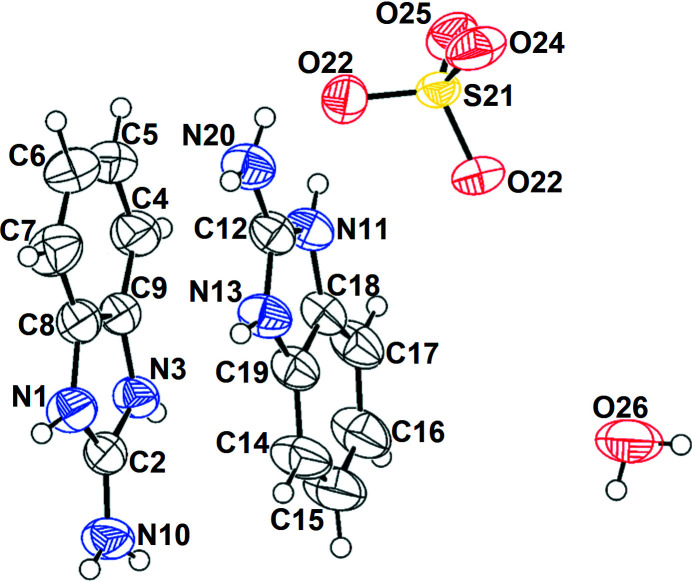
The components of the title molecular salt are linked by N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, 2-aminobenzimidazolium, sulfate
Abstract
In the title hydrated molecular salt, 2C7H8N3
+·SO4
2−·H2O, the components are linked by numerous N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Structure description
2-Aminobenzimidazole has been used for the synthesis of a series of sulfur heterocycles such as 9H-3-thia-1,4a,9-triaza-fluorene-2,4-dithione (1): its potassium thiolate salt was used to prepare metal coordination compounds (Peña-Hueso et al., 2008 ▸), and is the precursor of the title compound. When compound 1 is dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide and strong acids are added, instead of producing the protonated derivative, the thiadiazine ring breaks down, producing 2-aminobenzimidazolium sulfate (2): its crystal structural features are the subject of the present paper.
Compound 2 is formed by the transfer of two protons from sulfuric acid to the heterocycle: the crystal has two 2-aminobenzimidazolium cations, one sulfate anion and one water molecule in its asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸). There is a small asymmetry in the S—O bond lengths of the SO4 2– ion from 1.4596 (16) to 1.4723 (15) Å, probably caused by the hydrogen bonds around the anion (Gagné & Hawthorne, 2018 ▸). Two benzimidazolium cations are stacked in a head-to-tail way, with a distance between C9 of one molecule and C18 of another of 3.441 (3) Å.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of 2 showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level
The sulfate ion accepts seven N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds from four adjacent benzimidazolium cations and one O—H⋯O link from a water molecule (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸). The water molecule accepts one N—H⋯O hydrogen bond and forms two O—H⋯O links to two SO4 2– ions (Fig. 3 ▸). In the extended structure, the benzimidazolium cations form parallel ribbons propagating in the [010] direction (Fig. 4 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O25i | 0.81 (4) | 2.25 (3) | 2.946 (3) | 144 (3) |
| N3—H3⋯O22ii | 0.83 (3) | 1.93 (3) | 2.749 (3) | 172 (3) |
| N11—H11⋯O23 | 0.85 (4) | 1.96 (4) | 2.786 (4) | 166 (3) |
| N13—H13⋯O24iii | 0.83 (4) | 1.91 (4) | 2.720 (3) | 165 (3) |
| N10—H101⋯O23i | 0.87 (4) | 2.03 (4) | 2.894 (5) | 169 (3) |
| N10—H102⋯O25ii | 0.89 (3) | 2.00 (3) | 2.890 (3) | 175 (3) |
| N20—H201⋯O26iii | 0.84 (3) | 2.04 (3) | 2.853 (4) | 165 (3) |
| N20—H202⋯O22iii | 0.93 (4) | 2.09 (4) | 2.973 (4) | 157 (3) |
| O26—H261⋯O24iv | 0.80 (7) | 2.22 (7) | 2.983 (4) | 160 (7) |
| O26—H262⋯O24v | 0.80 (7) | 2.14 (7) | 2.860 (4) | 150 (6) |
| C17—H17⋯O22 | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.272 (3) | 132 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 ; (iv)
; (iv)
 ; (v)
; (v)
 .
.
Figure 2.
Hydrogen-bond environment around the sulfate anion.
Figure 3.
Network of hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) involving the water molecules and sulfate ions.
Figure 4.
The unit-cell packing showing [010] ribbons of cations linked by sulfate anions.
The first crystal structure of a 2-aminobenzimidazolium salt was reported with the nitrate anion (Bats et al., 1999 ▸) and a related structure with hydrogen sulfate as the counter-ion is also known (You et al., 2009 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
The decomposition of 9H-3-thia-1,4a,9-triaza-fluorene-2,4-dithione with dilute aqueous H2SO4 in DMSO afforded the title compound 2, m.p. 287–289°C. IR (KBr), ν (cm−1): 3285 (N—H), 1682 (C=N), 1520 (C=C), 1478 (C—N). NMR (DMSO-d 6, p.p.m.) δ 1H: 7.27 (H4, H7); 7.09 (H5, H6); 13.18 (N1—H, N3—H); 8.70 (NH2). δ 13C: 152.1 (C2); 111.8 (C4, C7); 123.4 (C5, C6); 130.4 (C8, C9). δ 15N: −257.1 (N1, N3); −312.9 (N10). Analysis calculated (%) for C16H16N6SO5: C, 43.97; H, 4.74; N, 21.98. Found: C, 43.50; H, 4.80; N, 21.80. The chemical shifts of C2 (152.1 p.p.m.), C8 and C9 (130.4 p.p.m.) in the 13C NMR spectrum indicate that the endocyclic nitrogen atoms are protonated, in agreement with the crystal structure.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | 2C7H8N3 +·SO4 2−·H2O |
| M r | 382.4 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 12.1115 (2), 10.6282 (2), 17.4772 (3) |
| β (°) | 127.723 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1779.48 (6) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.22 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.25 × 0.17 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Nonius KappaCCD |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 3.0σ(I)] reflections | 9132, 4563, 2429 |
| R int | 0.04 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.675 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.041, 0.050, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 2429 |
| No. of parameters | 265 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.25, −0.31 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001729/hb4397sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001729/hb4397Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001729/hb4397Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1810894
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| 2C7H8N3+·SO42−·H2O | F(000) = 800 |
| Mr = 382.4 | Dx = 1.427 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4784 reflections |
| a = 12.1115 (2) Å | θ = 1–29° |
| b = 10.6282 (2) Å | µ = 0.22 mm−1 |
| c = 17.4772 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 127.723 (1)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 1779.48 (6) Å3 | 0.25 × 0.25 × 0.17 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 2429 reflections with I > 3.0σ(I) |
| Radiation source: Enraf Nonius FR590 | Rint = 0.04 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 28.7°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Detector resolution: 9 pixels mm-1 | h = −15→16 |
| φ & ω scans | k = −14→14 |
| 9132 measured reflections | l = −23→23 |
| 4563 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F2) = 0.050 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | Method, part 1, Chebychev polynomial, (Watkin, 1994, Prince, 1982) [weight] = 1.0/[A0*T0(x) + A1*T1(x) ··· + An-1]*Tn-1(x)] where Ai are the Chebychev coefficients listed below and x = F /Fmax Method = Robust Weighting (Prince, 1982) W = [weight] * [1-(deltaF/6*sigmaF)2]2 Ai are: 0.914 0.838 0.564 0.170 0.849E-01 |
| 2429 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.0002 |
| 265 parameters | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.The positions of all NH and OH hydrogen atoms were refined, and all CH were placed at ideal positions. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C2 | 0.5660 (3) | 0.1533 (2) | −0.12552 (17) | 0.0484 | |
| C4 | 0.5449 (3) | 0.1836 (2) | 0.0688 (2) | 0.0626 | |
| C5 | 0.6271 (4) | 0.1200 (3) | 0.1556 (2) | 0.0725 | |
| C6 | 0.7293 (3) | 0.0372 (3) | 0.1756 (2) | 0.0728 | |
| C7 | 0.7524 (3) | 0.0132 (3) | 0.1090 (2) | 0.0682 | |
| C8 | 0.6705 (3) | 0.0761 (2) | 0.02241 (18) | 0.0503 | |
| C9 | 0.5691 (2) | 0.1616 (2) | 0.00250 (16) | 0.047 | |
| C12 | 0.9604 (2) | 0.2887 (2) | 0.21087 (16) | 0.047 | |
| C14 | 0.8306 (3) | 0.3839 (3) | −0.0275 (2) | 0.0719 | |
| C15 | 0.7199 (4) | 0.4642 (3) | −0.0859 (2) | 0.0819 | |
| C16 | 0.6467 (4) | 0.5164 (3) | −0.0557 (2) | 0.0786 | |
| C17 | 0.6837 (3) | 0.4930 (3) | 0.03457 (18) | 0.0617 | |
| C18 | 0.7951 (2) | 0.4131 (2) | 0.09334 (16) | 0.0479 | |
| C19 | 0.8659 (3) | 0.3583 (2) | 0.06268 (17) | 0.0521 | |
| H1 | 0.700 (3) | 0.023 (3) | −0.073 (2) | 0.0781* | |
| H3 | 0.440 (3) | 0.256 (3) | −0.122 (2) | 0.0603* | |
| H4 | 0.476 | 0.2396 | 0.0553 | 0.0818* | |
| H5 | 0.6134 | 0.1333 | 0.2013 | 0.0945* | |
| H6 | 0.7819 | −0.0041 | 0.2343 | 0.0851* | |
| H7 | 0.82 | −0.0425 | 0.1215 | 0.0843* | |
| H11 | 0.830 (3) | 0.384 (3) | 0.220 (2) | 0.0595* | |
| H13 | 1.021 (3) | 0.235 (3) | 0.136 (2) | 0.0682* | |
| H14 | 0.8797 | 0.3482 | −0.0463 | 0.0925* | |
| H15 | 0.6943 | 0.4849 | −0.1462 | 0.0986* | |
| H16 | 0.5679 | 0.568 | −0.0992 | 0.0857* | |
| H17 | 0.6367 | 0.5309 | 0.0569 | 0.0697* | |
| H101 | 0.580 (3) | 0.137 (3) | −0.227 (2) | 0.0811* | |
| H102 | 0.472 (3) | 0.237 (3) | −0.247 (2) | 0.0806* | |
| H201 | 1.041 (3) | 0.247 (3) | 0.339 (2) | 0.07* | |
| H202 | 1.115 (3) | 0.183 (3) | 0.301 (2) | 0.0698* | |
| H261 | 0.979 (7) | 0.918 (6) | 0.069 (5) | 0.1811* | |
| H262 | 0.925 (6) | 0.838 (6) | 0.005 (5) | 0.1804* | |
| N1 | 0.6657 (2) | 0.0745 (2) | −0.05947 (16) | 0.0562 | |
| N3 | 0.5078 (2) | 0.20819 (19) | −0.08953 (14) | 0.0477 | |
| N10 | 0.5301 (3) | 0.1737 (2) | −0.21296 (17) | 0.0601 | |
| N11 | 0.85749 (19) | 0.3685 (2) | 0.18649 (14) | 0.0479 | |
| N13 | 0.9688 (2) | 0.2826 (2) | 0.13810 (14) | 0.0539 | |
| N20 | 1.0417 (2) | 0.2263 (2) | 0.29315 (16) | 0.0582 | |
| O22 | 0.72767 (16) | 0.64914 (16) | 0.21275 (11) | 0.0506 | |
| O23 | 0.72874 (19) | 0.44104 (15) | 0.26788 (13) | 0.0584 | |
| O24 | 0.8960 (2) | 0.5933 (2) | 0.37860 (12) | 0.0746 | |
| O25 | 0.6554 (2) | 0.61476 (17) | 0.31313 (14) | 0.0657 | |
| O26 | 0.9603 (4) | 0.8443 (3) | 0.06107 (18) | 0.1136 | |
| S21 | 0.75054 (6) | 0.57563 (5) | 0.29273 (4) | 0.0431 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C2 | 0.0604 (14) | 0.0435 (12) | 0.0537 (13) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0411 (12) | −0.0021 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0850 (19) | 0.0550 (15) | 0.0668 (16) | 0.0109 (13) | 0.0563 (16) | 0.0013 (12) |
| C5 | 0.109 (2) | 0.0657 (17) | 0.0641 (17) | 0.0001 (17) | 0.0640 (18) | 0.0001 (14) |
| C6 | 0.087 (2) | 0.0733 (18) | 0.0555 (15) | 0.0049 (16) | 0.0420 (16) | 0.0142 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0703 (17) | 0.0651 (17) | 0.0705 (17) | 0.0194 (14) | 0.0436 (15) | 0.0185 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0577 (14) | 0.0464 (12) | 0.0551 (14) | 0.0060 (11) | 0.0388 (12) | 0.0017 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0580 (13) | 0.0411 (11) | 0.0484 (12) | 0.0015 (10) | 0.0358 (11) | −0.0010 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0421 (11) | 0.0541 (13) | 0.0449 (12) | −0.0005 (10) | 0.0266 (11) | −0.0062 (11) |
| C14 | 0.086 (2) | 0.087 (2) | 0.0555 (16) | 0.0163 (16) | 0.0498 (16) | −0.0027 (14) |
| C15 | 0.107 (3) | 0.085 (2) | 0.0498 (15) | 0.0272 (19) | 0.0461 (17) | 0.0063 (14) |
| C16 | 0.090 (2) | 0.0757 (19) | 0.0485 (15) | 0.0291 (17) | 0.0315 (15) | −0.0001 (14) |
| C17 | 0.0615 (15) | 0.0649 (16) | 0.0475 (14) | 0.0171 (13) | 0.0277 (12) | −0.0065 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0467 (12) | 0.0520 (13) | 0.0425 (12) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0261 (11) | −0.0085 (10) |
| C19 | 0.0542 (14) | 0.0561 (14) | 0.0480 (13) | 0.0051 (11) | 0.0322 (12) | −0.0054 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0716 (14) | 0.0522 (12) | 0.0658 (13) | 0.0182 (11) | 0.0527 (12) | 0.0089 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0555 (11) | 0.0470 (10) | 0.0480 (11) | 0.0102 (9) | 0.0356 (10) | 0.0018 (9) |
| N10 | 0.0807 (16) | 0.0608 (13) | 0.0583 (13) | 0.0140 (11) | 0.0525 (13) | 0.0042 (10) |
| N11 | 0.0440 (10) | 0.0592 (12) | 0.0450 (10) | 0.0050 (9) | 0.0296 (9) | −0.0045 (9) |
| N13 | 0.0522 (12) | 0.0660 (13) | 0.0499 (11) | 0.0139 (10) | 0.0345 (10) | −0.0004 (10) |
| N20 | 0.0551 (12) | 0.0685 (14) | 0.0502 (12) | 0.0098 (11) | 0.0318 (11) | 0.0020 (11) |
| O22 | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0669 (10) | 0.0421 (8) | 0.0040 (7) | 0.0302 (8) | 0.0120 (7) |
| O23 | 0.0752 (12) | 0.0507 (9) | 0.0791 (12) | −0.0031 (8) | 0.0624 (11) | −0.0046 (8) |
| O24 | 0.0619 (11) | 0.1028 (15) | 0.0410 (9) | −0.0251 (11) | 0.0223 (9) | 0.0111 (9) |
| O25 | 0.0948 (14) | 0.0562 (10) | 0.0907 (13) | 0.0093 (9) | 0.0796 (12) | 0.0092 (9) |
| O26 | 0.144 (2) | 0.148 (3) | 0.0652 (14) | −0.069 (2) | 0.0725 (17) | −0.0286 (16) |
| S21 | 0.0483 (3) | 0.0508 (3) | 0.0396 (3) | −0.0046 (3) | 0.0317 (3) | 0.0008 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C2—N1 | 1.336 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.925 |
| C2—N3 | 1.333 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.374 (4) |
| C2—N10 | 1.326 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.95 |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (4) | C17—C18 | 1.379 (3) |
| C4—C9 | 1.377 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.955 |
| C4—H4 | 0.931 | C18—C19 | 1.387 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.379 (4) | C18—N11 | 1.393 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.92 | C19—N13 | 1.389 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.378 (4) | H1—N1 | 0.80 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.922 | H3—N3 | 0.83 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.373 (4) | H11—N11 | 0.85 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.921 | H13—N13 | 0.83 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.390 (3) | H101—N10 | 0.87 (3) |
| C8—N1 | 1.396 (3) | H102—N10 | 0.89 (3) |
| C9—N3 | 1.386 (3) | H201—N20 | 0.83 (3) |
| C12—N11 | 1.343 (3) | H202—N20 | 0.93 (3) |
| C12—N13 | 1.338 (3) | H261—O26 | 0.81 (6) |
| C12—N20 | 1.321 (3) | H262—O26 | 0.79 (6) |
| C14—C15 | 1.376 (4) | O22—S21 | 1.4723 (15) |
| C14—C19 | 1.385 (4) | O23—S21 | 1.4711 (18) |
| C14—H14 | 0.919 | O24—S21 | 1.4680 (19) |
| C15—C16 | 1.394 (4) | O25—S21 | 1.4596 (16) |
| N1—C2—N3 | 109.0 (2) | C16—C17—H17 | 122.5 |
| N1—C2—N10 | 125.7 (2) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.8 |
| N3—C2—N10 | 125.2 (2) | C17—C18—C19 | 121.7 (2) |
| C5—C4—C9 | 117.5 (2) | C17—C18—N11 | 131.6 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 121.5 | C19—C18—N11 | 106.7 (2) |
| C9—C4—H4 | 121 | C18—C19—C14 | 121.6 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.5 (3) | C18—C19—N13 | 106.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.2 | C14—C19—N13 | 131.8 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C8—N1—C2 | 109.08 (19) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.3 (3) | C8—N1—H1 | 127 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C2—N1—H1 | 122 (2) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.4 | C9—N3—C2 | 109.2 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 117.2 (3) | C9—N3—H3 | 128.6 (19) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 122 | C2—N3—H3 | 121.9 (19) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.8 | H102—N10—C2 | 117 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 121.8 (2) | H102—N10—H101 | 124 (3) |
| C7—C8—N1 | 132.3 (2) | C2—N10—H101 | 117 (2) |
| C9—C8—N1 | 106.0 (2) | C18—N11—C12 | 108.65 (18) |
| C8—C9—C4 | 120.7 (2) | C18—N11—H11 | 125.7 (19) |
| C8—C9—N3 | 106.76 (19) | C12—N11—H11 | 125.5 (19) |
| C4—C9—N3 | 132.5 (2) | C19—N13—C12 | 109.13 (19) |
| N11—C12—N13 | 109.0 (2) | C19—N13—H13 | 125 (2) |
| N11—C12—N20 | 126.2 (2) | C12—N13—H13 | 126 (2) |
| N13—C12—N20 | 124.8 (2) | H202—N20—C12 | 114.7 (18) |
| C15—C14—C19 | 116.6 (2) | H202—N20—H201 | 124 (3) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 122.8 | C12—N20—H201 | 118 (2) |
| C19—C14—H14 | 120.7 | H261—O26—H262 | 100 (6) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 121.6 (3) | O22—S21—O23 | 109.89 (10) |
| C14—C15—H15 | 119.2 | O22—S21—O24 | 108.29 (10) |
| C16—C15—H15 | 119.3 | O23—S21—O24 | 108.23 (12) |
| C15—C16—C17 | 121.7 (3) | O22—S21—O25 | 111.26 (10) |
| C15—C16—H16 | 119.2 | O23—S21—O25 | 108.86 (10) |
| C17—C16—H16 | 119.1 | O24—S21—O25 | 110.26 (13) |
| C16—C17—C18 | 116.8 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O25i | 0.81 (4) | 2.25 (3) | 2.946 (3) | 144 (3) |
| N3—H3···O22ii | 0.83 (3) | 1.93 (3) | 2.749 (3) | 172 (3) |
| N11—H11···O23 | 0.85 (4) | 1.96 (4) | 2.786 (4) | 166 (3) |
| N13—H13···O24iii | 0.83 (4) | 1.91 (4) | 2.720 (3) | 165 (3) |
| N10—H101···O23i | 0.87 (4) | 2.03 (4) | 2.894 (5) | 169 (3) |
| N10—H102···O25ii | 0.89 (3) | 2.00 (3) | 2.890 (3) | 175 (3) |
| N20—H201···O26iii | 0.84 (3) | 2.04 (3) | 2.853 (4) | 165 (3) |
| N20—H202···O22iii | 0.93 (4) | 2.09 (4) | 2.973 (4) | 157 (3) |
| O26—H261···O24iv | 0.80 (7) | 2.22 (7) | 2.983 (4) | 160 (7) |
| O26—H262···O24v | 0.80 (7) | 2.14 (7) | 2.860 (4) | 150 (6) |
| C17—H17···O22 | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.272 (3) | 132 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (iii) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iv) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (v) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
Funding Statement
The authors thank Cinvestav for financial support.
References
- Bats, J. W., Gördes, D. & Schmalz, H.-G. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55, 1325–1328.
- Betteridge, P. W., Carruthers, J. R., Cooper, R. I., Prout, K. & Watkin, D. J. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 1487.
- Gagné, O. C. & Hawthorne, F. C. (2018). Acta Cryst. B74, 79–96.
- Nonius (2001). COLLECT. Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(97)76066-X
- Peña-Hueso, A., Esparza-Ruiz, A., Ramos-García, I., Flores-Parra, A. & Contreras, R. (2008). J. Organomet. Chem. 693, 492–504.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Watkin, D. J., Prout, C. K., Carruthers, J. R. & Betteridge, P. W. (1996). CRYSTALS. Chemical Crystallography Laboratory, University of Oxford, England.
- You, W., Fan, Y., Qian, H.-F., Yao, C. & Huang, W. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001729/hb4397sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001729/hb4397Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622001729/hb4397Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1810894
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report