A novel DyIII complex based on 3-pyridylacetic acid and 1,10-phenanthroline ligands shows a dinuclear structure.
Keywords: crystal structure
Abstract
The title DyIII complex, [Dy2(C7H6NO2)4Cl2(C12H8N2)2] or [Dy2(μ
3-PAA)4(Cl)2(phen)2] (PAA = 3-pyridylacetate, phen = 1,10-phenanthroline), obtained by reaction of Dy(ClO4)3, 3-pyridylacetic acid ligands and 1,10-phenanthroline, exhibits a dinuclear structure. Adjacent binuclear dimers are further connected via face-to-face π–π stacking interactions resulting in supramolecular chains along the c-axis direction.
Structure description
Coordination complexes composed of metal cations and organic ligands have received much attention because of their diverse structures and intriguing properties such as photoluminescence, magnetism, proton conduction and so on. Lanthanide ions are considered to be excellent metal ions for the construction of such systems because of their unique 4f electrons and can show remarkable photoluminescent, magnetic and catalytic properties. Among numerous ligands, pyridinecarboxylate ligands bearing O and N coordination atoms have attracted considerable interest and have proved to be a class of excellent bridging linkers in fabricating metal coordination complexes with appealing structures. The 3-pyridylacetate ligand (3-PAA), one of the most simple pyridinecarboxylate ligands, has attracted particular interest owing to its strong coordination and varied coordination modes, resulting in diverse structures with excellent properties. So far, coordination complexes constructed by the 3-PAA ligand have focused on transition-metal cations, but lanthanide complexes based on the 3-PAA ligand are still rare. Thus, in this work, we prepared the title compound [Dy2(μ 2-PAA)4(Cl)2(phen)2] (1) (3-PAA = 3-pyridylacetate, phen = 1,10-phenanthroline), which displays a dinuclear structure.
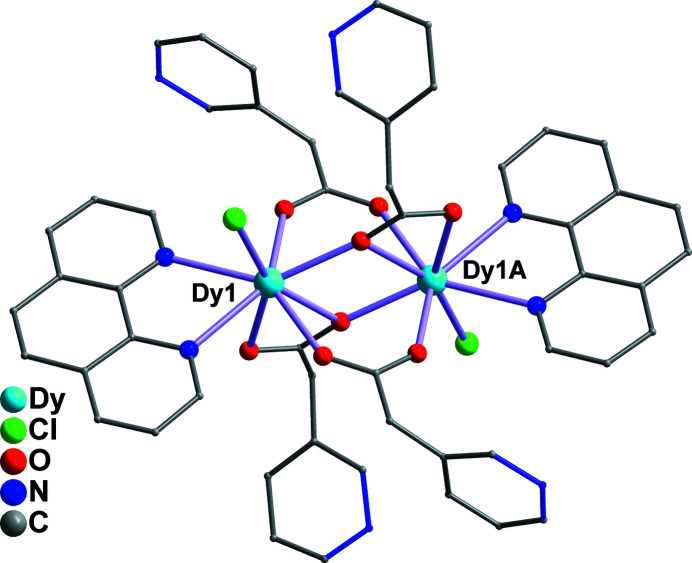
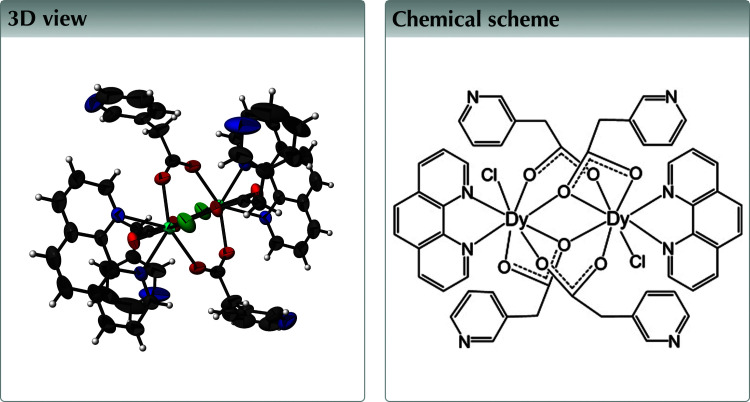
The asymmetric unit of 1 (Fig. 1 ▸) consists of one crystallographically independent DyIII ion, one Cl− anion, two PAA ligands and one phen molecule. The DyIII cation is eight-coordinated by five carboxylate oxygen atoms from four different PAA− ligands, one Cl− ion, and two nitrogen atoms from one chelating phen molecule. The Dy—O bond lengths range from 2.3069 (17) to 2.5170 (15) Å, and the Dy—N bond distances are 2.5386 (18) and 2.5516 (17)Å, which are similar to those in the complex [Zn(μ-L)(μ-dicl)Dy(NO3)2]·H2O {L = N,N′-dimethyl-N,N′-bis(2-hydroxy-3-formyl-5-bromobenzyl, dicl = deprotonated diclofenac = 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino] benzene acetate; Echenique-Errandonea et al., 2019 ▸}. The two PAA− ligands exhibit two different coordination modes. One acts as a tridentate ligand with a μ 2-η1:η2 mode, while the other serves as a bidentate ligand with a μ 2-κO 3:κO 4 mode. It is worth emphasizing that the N atom of the PAA ligand is noncoordinating in 1. As shown in Fig. 2 ▸, two neighboring DyIII ions are linked by four bridging carboxyl groups of four PAA− ligands, forming the binuclear structure of 1, in which the nearest Dy⋯Dy separation is 3.8976 (19) Å. These adjacent binuclear dimers are further connected via face-to-face π–π stacking interactions involving the phenyl and pyridine rings of the phen ligands, the centroid-to-centroid distance being 3.6116 (10) Å, leading to the formation of supramolecular chains along the c-axis direction (Fig. 3 ▸). For background information on the lanthanide ions and the 3-pyridylacetic acid ligand, see: Chakraborty et al. (2021 ▸); Xin et al. (2019 ▸); Ma et al. (2020 ▸); Wang et al. (2011 ▸); Teo et al. (2009 ▸); Adams et al. (2006 ▸).
Figure 1.
The asymmetric unit of 1 with 40% probability displacement ellipsoids. H atoms are omitted for clarity. Symmetry code: (A) 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z.
Figure 2.
The dinuclear structure of 1. H atoms are omitted for clarity. Symmetry code: (A) 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z.
Figure 3.
The supramolecular chain along the c-axis direction formed by face-to-face π–π stacking interactions.
Synthesis and crystallization
Dy(ClO4)3 (0.2 mmol), 3-pyridylacetic acid (3-PAA, 0.25 mmol), 1,10-phenanthroline (0.25 mmol), HCl (0.25mmol) and Et3N were dissolved in 5 mL of acetonitrile and then sealed into a 25 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel vessel. The vessel was kept at 433 K for 3 d under autogenous pressure and then cooled to room temperature at a rate of 5.63 K h−1. Colorless block-shaped crystals were obtained by filtration of the resulting solution. Yield based on Dy: 38%.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1 ▸. The instruction "delu 0.002 0.001 C11 C12" was used during the refinement to limit the displacement parameters of the specified atoms.
Table 1. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Dy2(C7H6NO2)4Cl2(C12H8N2)2] |
| M r | 1300.82 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.8922 (1), 21.5425 (3), 12.9887 (1) |
| β (°) | 101.755 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 2435.94 (5) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 3.22 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.19 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker SAINT CCD area detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.626, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 16420, 4487, 3954 |
| R int | 0.024 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.606 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.021, 0.056, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 4487 |
| No. of parameters | 325 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.59, −0.34 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622002310/vm4049sup1.cif
CCDC reference: 2155088
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| [Dy2(C7H6NO2)4Cl2(C12H8N2)2] | F(000) = 1276 |
| Mr = 1300.82 | Dx = 1.773 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.8922 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 7687 reflections |
| b = 21.5425 (3) Å | θ = 2.5–27.3° |
| c = 12.9887 (1) Å | µ = 3.22 mm−1 |
| β = 101.755 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 2435.94 (5) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 2 | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.19 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SAINT CCD area detector diffractometer | 4487 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3954 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.024 |
| phi and ω scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.626, Tmax = 0.746 | k = −26→23 |
| 16420 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.021 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.056 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.035P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4487 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 325 parameters | Δρmax = 0.59 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.34 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. H atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H = 0.93 Å in phenyl and pyridine rings while C–H = 0.97 Å in CH2 groups and refined in riding mode with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Dy1 | 0.387207 (12) | 0.510416 (5) | 0.855827 (7) | 0.03127 (3) | |
| Cl1 | 0.13833 (7) | 0.58009 (3) | 0.81071 (5) | 0.05938 (19) | |
| O3 | 0.57734 (18) | 0.58550 (8) | 0.90135 (12) | 0.0487 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.4153 (2) | 0.55350 (10) | 0.67882 (13) | 0.0420 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.57990 (18) | 0.44419 (8) | 0.80320 (11) | 0.0472 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.2364 (2) | 0.45183 (9) | 0.69718 (13) | 0.0383 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.6642 (3) | 0.43988 (11) | 0.89307 (17) | 0.0365 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.6799 (3) | 0.60069 (12) | 0.97945 (18) | 0.0455 (6) | |
| C18 | 0.3415 (3) | 0.54877 (14) | 0.48832 (18) | 0.0544 (7) | |
| C26 | 0.3341 (3) | 0.52662 (12) | 0.58975 (17) | 0.0416 (6) | |
| C25 | 0.2402 (3) | 0.47369 (12) | 0.59934 (17) | 0.0420 (6) | |
| C21 | 0.1571 (3) | 0.44537 (15) | 0.50734 (18) | 0.0545 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.8200 (3) | 0.41057 (12) | 0.90869 (18) | 0.0441 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.8755 | 0.4280 | 0.8585 | 0.053* | |
| H6B | 0.8770 | 0.4202 | 0.9788 | 0.053* | |
| C24 | 0.1525 (3) | 0.40185 (12) | 0.7037 (2) | 0.0498 (7) | |
| H24A | 0.1480 | 0.3871 | 0.7702 | 0.060* | |
| C5 | 0.8108 (3) | 0.34153 (13) | 0.8952 (2) | 0.0476 (7) | |
| C19 | 0.2538 (4) | 0.51931 (16) | 0.3983 (2) | 0.0687 (10) | |
| H19A | 0.2583 | 0.5344 | 0.3319 | 0.082* | |
| C22 | 0.0729 (3) | 0.39253 (16) | 0.5185 (2) | 0.0696 (9) | |
| H22A | 0.0181 | 0.3724 | 0.4592 | 0.084* | |
| C12 | 0.7310 (3) | 0.69858 (12) | 0.8813 (2) | 0.0494 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.7993 (3) | 0.70351 (14) | 0.7954 (2) | 0.0662 (9) | |
| H8A | 0.8829 | 0.6781 | 0.7929 | 0.079* | |
| C11 | 0.6079 (3) | 0.73727 (15) | 0.8813 (2) | 0.0690 (9) | |
| H11A | 0.5574 | 0.7359 | 0.9374 | 0.083* | |
| C23 | 0.0701 (3) | 0.36993 (15) | 0.6167 (2) | 0.0657 (9) | |
| H23A | 0.0149 | 0.3343 | 0.6252 | 0.079* | |
| N2 | 0.7518 (3) | 0.74312 (14) | 0.7148 (2) | 0.0894 (9) | |
| C17 | 0.4394 (4) | 0.59840 (15) | 0.4816 (2) | 0.0658 (8) | |
| H17A | 0.4493 | 0.6133 | 0.4161 | 0.079* | |
| C13 | 0.7883 (3) | 0.65317 (14) | 0.9671 (2) | 0.0682 (9) | |
| H13A | 0.8129 | 0.6757 | 1.0331 | 0.082* | |
| H13B | 0.8831 | 0.6352 | 0.9547 | 0.082* | |
| O2 | 0.61601 (17) | 0.46036 (8) | 0.97223 (11) | 0.0421 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.70410 (19) | 0.57482 (8) | 1.06850 (12) | 0.0509 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.5041 (3) | 0.60095 (13) | 0.6677 (2) | 0.0565 (8) | |
| H15A | 0.5597 | 0.6197 | 0.7281 | 0.068* | |
| C20 | 0.1653 (4) | 0.47066 (18) | 0.4064 (2) | 0.0720 (10) | |
| H20A | 0.1078 | 0.4527 | 0.3458 | 0.086* | |
| C16 | 0.5196 (4) | 0.62483 (14) | 0.5697 (2) | 0.0690 (9) | |
| H16A | 0.5842 | 0.6583 | 0.5659 | 0.083* | |
| C1 | 0.7804 (4) | 0.30426 (16) | 0.9734 (3) | 0.0882 (12) | |
| H1A | 0.7679 | 0.3235 | 1.0352 | 0.106* | |
| C10 | 0.5589 (4) | 0.77733 (16) | 0.8009 (3) | 0.0875 (12) | |
| H10A | 0.4759 | 0.8035 | 0.8011 | 0.105* | |
| C4 | 0.8326 (4) | 0.31262 (18) | 0.8051 (3) | 0.0958 (12) | |
| H4A | 0.8526 | 0.3356 | 0.7487 | 0.115* | |
| N1 | 0.7671 (5) | 0.24248 (16) | 0.9688 (3) | 0.1415 (16) | |
| C3 | 0.8239 (5) | 0.2480 (2) | 0.8001 (4) | 0.1398 (18) | |
| H3A | 0.8416 | 0.2267 | 0.7413 | 0.168* | |
| C9 | 0.6330 (5) | 0.77806 (17) | 0.7218 (3) | 0.0939 (13) | |
| H9A | 0.5980 | 0.8055 | 0.6668 | 0.113* | |
| C2 | 0.7889 (5) | 0.2167 (2) | 0.8833 (5) | 0.140 (2) | |
| H2A | 0.7800 | 0.1738 | 0.8781 | 0.168* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Dy1 | 0.03380 (6) | 0.03284 (7) | 0.02427 (6) | 0.00167 (4) | −0.00091 (4) | 0.00130 (4) |
| Cl1 | 0.0556 (4) | 0.0664 (4) | 0.0473 (3) | 0.0255 (3) | −0.0104 (3) | −0.0088 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0544 (10) | 0.0502 (11) | 0.0343 (8) | −0.0156 (8) | −0.0077 (7) | 0.0103 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0500 (11) | 0.0439 (12) | 0.0303 (9) | 0.0042 (10) | 0.0043 (8) | 0.0054 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0509 (9) | 0.0605 (11) | 0.0286 (8) | 0.0160 (9) | 0.0047 (7) | −0.0012 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0372 (10) | 0.0439 (12) | 0.0312 (9) | 0.0055 (9) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0030 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0383 (12) | 0.0338 (13) | 0.0362 (12) | 0.0016 (10) | 0.0051 (10) | 0.0017 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0493 (14) | 0.0429 (15) | 0.0403 (13) | −0.0087 (12) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0052 (11) |
| C18 | 0.0604 (16) | 0.0681 (19) | 0.0349 (13) | 0.0217 (14) | 0.0098 (11) | 0.0097 (12) |
| C26 | 0.0482 (14) | 0.0459 (15) | 0.0290 (11) | 0.0127 (12) | 0.0041 (10) | 0.0035 (10) |
| C25 | 0.0397 (13) | 0.0538 (15) | 0.0303 (12) | 0.0140 (12) | 0.0020 (10) | −0.0057 (11) |
| C21 | 0.0440 (14) | 0.080 (2) | 0.0353 (13) | 0.0073 (14) | −0.0017 (11) | −0.0138 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0365 (12) | 0.0509 (16) | 0.0445 (13) | 0.0049 (11) | 0.0071 (10) | −0.0035 (11) |
| C24 | 0.0494 (14) | 0.0535 (17) | 0.0448 (14) | −0.0060 (13) | 0.0053 (11) | −0.0079 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0319 (12) | 0.0499 (16) | 0.0566 (15) | 0.0096 (11) | −0.0013 (11) | −0.0084 (12) |
| C19 | 0.078 (2) | 0.095 (3) | 0.0318 (14) | 0.0236 (18) | 0.0077 (14) | 0.0053 (14) |
| C22 | 0.0583 (17) | 0.097 (2) | 0.0471 (15) | −0.0097 (18) | −0.0034 (13) | −0.0313 (16) |
| C12 | 0.0444 (13) | 0.0429 (15) | 0.0568 (15) | −0.0134 (10) | 0.0005 (12) | 0.0090 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0567 (17) | 0.0577 (19) | 0.086 (2) | −0.0059 (15) | 0.0176 (16) | 0.0155 (16) |
| C11 | 0.0628 (16) | 0.067 (2) | 0.078 (2) | −0.0037 (13) | 0.0156 (16) | −0.0113 (17) |
| C23 | 0.0564 (16) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0648 (17) | −0.0175 (15) | 0.0045 (14) | −0.0239 (15) |
| N2 | 0.101 (2) | 0.090 (2) | 0.0763 (17) | −0.0263 (18) | 0.0171 (16) | 0.0270 (16) |
| C17 | 0.0842 (19) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0398 (14) | 0.0175 (18) | 0.0187 (13) | 0.0244 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0551 (16) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0658 (18) | −0.0288 (15) | −0.0150 (14) | 0.0267 (15) |
| O2 | 0.0440 (9) | 0.0520 (10) | 0.0284 (8) | 0.0135 (8) | 0.0028 (7) | −0.0033 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0602 (11) | 0.0502 (11) | 0.0347 (8) | −0.0181 (9) | −0.0083 (8) | 0.0070 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0703 (18) | 0.0530 (17) | 0.0455 (14) | −0.0066 (15) | 0.0101 (13) | 0.0103 (12) |
| C20 | 0.072 (2) | 0.111 (3) | 0.0272 (13) | 0.016 (2) | −0.0040 (13) | −0.0135 (16) |
| C16 | 0.094 (2) | 0.0609 (19) | 0.0574 (17) | −0.0034 (17) | 0.0266 (15) | 0.0194 (14) |
| C1 | 0.128 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.065 (2) | −0.012 (2) | −0.016 (2) | 0.0032 (17) |
| C10 | 0.069 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.129 (3) | 0.0161 (17) | −0.011 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C4 | 0.077 (2) | 0.103 (3) | 0.116 (3) | −0.003 (2) | 0.041 (2) | −0.048 (2) |
| N1 | 0.183 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.146 (3) | −0.026 (2) | −0.057 (3) | 0.026 (2) |
| C3 | 0.079 (2) | 0.124 (3) | 0.222 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.044 (3) | −0.118 (3) |
| C9 | 0.103 (3) | 0.060 (2) | 0.100 (3) | −0.015 (2) | −0.025 (2) | 0.026 (2) |
| C2 | 0.082 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.240 (6) | 0.028 (2) | −0.052 (3) | −0.042 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Dy1—O4i | 2.3069 (17) | C19—C20 | 1.327 (5) |
| Dy1—O3 | 2.3275 (16) | C19—H19A | 0.9300 |
| Dy1—O2i | 2.3261 (14) | C22—C23 | 1.371 (4) |
| Dy1—O1 | 2.4323 (16) | C22—H22A | 0.9300 |
| Dy1—O2 | 2.5170 (15) | C12—C11 | 1.376 (4) |
| Dy1—N3 | 2.5386 (18) | C12—C8 | 1.378 (4) |
| Dy1—N4 | 2.5516 (17) | C12—C13 | 1.493 (4) |
| Dy1—Cl1 | 2.6392 (6) | C8—N2 | 1.350 (4) |
| Dy1—C7 | 2.850 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| Dy1—Dy1i | 3.8976 (2) | C11—C10 | 1.356 (4) |
| O3—C14 | 1.261 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| N3—C15 | 1.317 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.9300 |
| N3—C26 | 1.362 (3) | N2—C9 | 1.315 (5) |
| O1—C7 | 1.256 (2) | C17—C16 | 1.346 (4) |
| N4—C24 | 1.323 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| N4—C25 | 1.362 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| C7—O2 | 1.271 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C6 | 1.498 (3) | O2—Dy1i | 2.3261 (14) |
| C14—O4 | 1.262 (3) | O4—Dy1i | 2.3069 (17) |
| C14—C13 | 1.515 (4) | C15—C16 | 1.405 (4) |
| C18—C19 | 1.417 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| C18—C26 | 1.415 (3) | C20—H20A | 0.9300 |
| C18—C17 | 1.393 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C26—C25 | 1.434 (4) | C1—N1 | 1.336 (5) |
| C25—C21 | 1.409 (3) | C1—H1A | 0.9300 |
| C21—C22 | 1.386 (4) | C10—C9 | 1.329 (5) |
| C21—C20 | 1.435 (4) | C10—H10A | 0.9300 |
| C6—C5 | 1.498 (4) | C4—C3 | 1.395 (6) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | N1—C2 | 1.291 (7) |
| C24—C23 | 1.396 (4) | C3—C2 | 1.362 (7) |
| C24—H24A | 0.9300 | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C1 | 1.364 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C4 | 1.374 (4) | C2—H2A | 0.9300 |
| O4i—Dy1—O3 | 138.19 (5) | C25—C21—C20 | 119.7 (3) |
| O4i—Dy1—O2i | 74.46 (6) | C5—C6—C7 | 112.05 (19) |
| O3—Dy1—O2i | 73.64 (6) | C5—C6—H6A | 109.2 |
| O4i—Dy1—O1 | 88.97 (6) | C7—C6—H6A | 109.2 |
| O3—Dy1—O1 | 87.84 (6) | C5—C6—H6B | 109.2 |
| O2i—Dy1—O1 | 125.15 (5) | C7—C6—H6B | 109.2 |
| O4i—Dy1—O2 | 73.42 (6) | H6A—C6—H6B | 107.9 |
| O3—Dy1—O2 | 71.86 (6) | N4—C24—C23 | 124.0 (3) |
| O2i—Dy1—O2 | 72.89 (6) | N4—C24—H24A | 118.0 |
| O1—Dy1—O2 | 52.27 (5) | C23—C24—H24A | 118.0 |
| O4i—Dy1—N3 | 141.73 (6) | C1—C5—C4 | 116.8 (3) |
| O3—Dy1—N3 | 77.03 (6) | C1—C5—C6 | 120.8 (3) |
| O2i—Dy1—N3 | 142.50 (7) | C4—C5—C6 | 122.4 (3) |
| O1—Dy1—N3 | 75.81 (6) | C20—C19—C18 | 121.6 (3) |
| O2—Dy1—N3 | 118.94 (6) | C20—C19—H19A | 119.2 |
| O4i—Dy1—N4 | 77.16 (6) | C18—C19—H19A | 119.2 |
| O3—Dy1—N4 | 141.62 (6) | C21—C22—C23 | 120.1 (3) |
| O2i—Dy1—N4 | 143.32 (6) | C21—C22—H22A | 120.0 |
| O1—Dy1—N4 | 76.54 (5) | C23—C22—H22A | 120.0 |
| O2—Dy1—N4 | 120.04 (6) | C11—C12—C8 | 115.8 (3) |
| N3—Dy1—N4 | 65.29 (6) | C11—C12—C13 | 123.2 (3) |
| O4i—Dy1—Cl1 | 101.26 (5) | C8—C12—C13 | 121.0 (3) |
| O3—Dy1—Cl1 | 101.19 (5) | N2—C8—C12 | 123.8 (3) |
| O2i—Dy1—Cl1 | 83.42 (4) | N2—C8—H8A | 118.1 |
| O1—Dy1—Cl1 | 151.41 (4) | C12—C8—H8A | 118.1 |
| O2—Dy1—Cl1 | 156.30 (4) | C12—C11—C10 | 121.0 (3) |
| N3—Dy1—Cl1 | 79.86 (5) | C12—C11—H11A | 119.5 |
| N4—Dy1—Cl1 | 79.81 (4) | C10—C11—H11A | 119.5 |
| O4i—Dy1—C7 | 82.55 (6) | C24—C23—C22 | 118.2 (3) |
| O3—Dy1—C7 | 76.68 (6) | C24—C23—H23A | 120.9 |
| O2i—Dy1—C7 | 99.24 (6) | C22—C23—H23A | 120.9 |
| O1—Dy1—C7 | 25.99 (5) | C9—N2—C8 | 115.9 (3) |
| O2—Dy1—C7 | 26.47 (5) | C16—C17—C18 | 120.1 (3) |
| N3—Dy1—C7 | 96.17 (6) | C16—C17—H17A | 120.0 |
| N4—Dy1—C7 | 99.62 (6) | C18—C17—H17A | 120.0 |
| Cl1—Dy1—C7 | 175.87 (5) | C12—C13—C14 | 116.1 (2) |
| O4i—Dy1—Dy1i | 69.87 (4) | C12—C13—H13A | 108.3 |
| O3—Dy1—Dy1i | 68.34 (4) | C14—C13—H13A | 108.3 |
| O2i—Dy1—Dy1i | 38.11 (4) | C12—C13—H13B | 108.3 |
| O1—Dy1—Dy1i | 87.04 (3) | C14—C13—H13B | 108.3 |
| O2—Dy1—Dy1i | 34.78 (3) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.4 |
| N3—Dy1—Dy1i | 141.81 (4) | C7—O2—Dy1i | 160.55 (14) |
| N4—Dy1—Dy1i | 143.32 (4) | C7—O2—Dy1 | 91.55 (12) |
| Cl1—Dy1—Dy1i | 121.533 (15) | Dy1i—O2—Dy1 | 107.11 (6) |
| C7—Dy1—Dy1i | 61.17 (4) | C14—O4—Dy1i | 137.13 (15) |
| C14—O3—Dy1 | 138.89 (15) | N3—C15—C16 | 123.7 (3) |
| C15—N3—C26 | 117.5 (2) | N3—C15—H15A | 118.1 |
| C15—N3—Dy1 | 123.72 (16) | C16—C15—H15A | 118.1 |
| C26—N3—Dy1 | 118.73 (16) | C19—C20—C21 | 120.9 (3) |
| C7—O1—Dy1 | 95.93 (14) | C19—C20—H20A | 119.6 |
| C24—N4—C25 | 117.5 (2) | C21—C20—H20A | 119.6 |
| C24—N4—Dy1 | 124.18 (15) | C17—C16—C15 | 118.9 (3) |
| C25—N4—Dy1 | 118.28 (15) | C17—C16—H16A | 120.6 |
| O1—C7—O2 | 119.4 (2) | C15—C16—H16A | 120.6 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 121.2 (2) | N1—C1—C5 | 125.6 (4) |
| O2—C7—C6 | 119.44 (19) | N1—C1—H1A | 117.2 |
| O1—C7—Dy1 | 58.08 (12) | C5—C1—H1A | 117.2 |
| O2—C7—Dy1 | 61.98 (11) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.1 (3) |
| C6—C7—Dy1 | 172.26 (17) | C9—C10—H10A | 120.9 |
| O4—C14—O3 | 125.6 (2) | C11—C10—H10A | 120.9 |
| O4—C14—C13 | 115.7 (2) | C5—C4—C3 | 118.4 (4) |
| O3—C14—C13 | 118.7 (2) | C5—C4—H4A | 120.8 |
| C19—C18—C26 | 119.7 (3) | C3—C4—H4A | 120.8 |
| C19—C18—C17 | 122.6 (3) | C2—N1—C1 | 116.0 (4) |
| C26—C18—C17 | 117.7 (2) | C2—C3—C4 | 118.4 (4) |
| N3—C26—C18 | 122.0 (2) | C2—C3—H3A | 120.8 |
| N3—C26—C25 | 118.8 (2) | C4—C3—H3A | 120.8 |
| C18—C26—C25 | 119.2 (2) | N2—C9—C10 | 125.3 (3) |
| N4—C25—C21 | 122.2 (2) | N2—C9—H9A | 117.4 |
| N4—C25—C26 | 118.8 (2) | C10—C9—H9A | 117.4 |
| C21—C25—C26 | 119.0 (2) | N1—C2—C3 | 124.7 (4) |
| C22—C21—C25 | 117.9 (2) | N1—C2—H2A | 117.6 |
| C22—C21—C20 | 122.4 (3) | C3—C2—H2A | 117.6 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2.
Funding Statement
We acknowledge financial support from the NSF of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (No. GJJ190756).
References
- Adams, C. J., Crawford, P. C., Guy Orpen, A. & Podesta, T. J. (2006). Dalton Trans. pp. 4078–4092. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2008). SMART, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chakraborty, G., Park, I.-H., Medishetty, R. & Vittal, J. J. (2021). Chem. Rev. 121, 3751–3891. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Echenique-Errandonea, E., Zabala-Lekuona, A., Cepeda, J., Rodríguez-Diéguez, A., Seco, J. M., Oyarzabal, I. & Colacio, E. (2019). Dalton Trans. 48, 190–201. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y. J., Hu, J. X., Han, S. D., Pan, J., Li, J. H. & Wang, G. M. (2020). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 2682–2689. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Teo, P., Koh, L. L. & Hor, T. S. A. (2009). Dalton Trans. pp. 5637–5646. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wang, L., Yin, X. H., Hao, H. J., Lin, W., Tan, X. H. & Lin, C. W. (2011). Z. Kristallogr. New. Cryst. Struct. pp. 219–220.
- Xin, Y., Wang, J. H., Zychowicz, M., Zakrzewski, J. J., Nakabayashi, K., Sieklucka, B., Chorazy, S. & Ohkoshi, S. (2019). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 18211–18220. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622002310/vm4049sup1.cif
CCDC reference: 2155088
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report