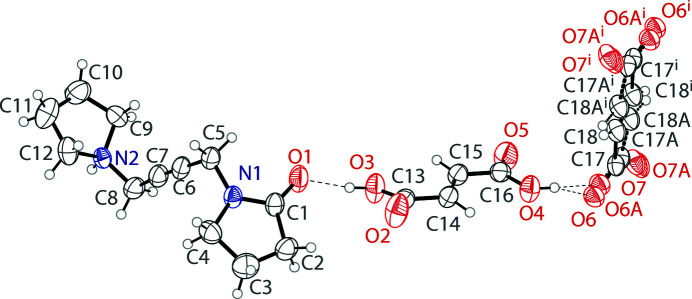
In the title molecular salt, 2C12H19N2O+·C4H2O4 2−·2C4H4O4, the components are held together by N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [001].
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bonding, alkynes, pyrrolidines, fumarates
Abstract
The title compound, bis(oxotremorine) fumarate bis(fumaric acid) {systematic name: 1-[4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)but-2-ynyl]pyrrolidinium (2E)-but-2-enedioate bis[(2E)-but-2-enedioic acid]}, 2C12H19N2O+·C4H2O4
2−·2C4H4O4, has a single oxotremorine monocation protonated at the pyrrolidine nitrogen, one fumaric acid molecule and half of a fumarate dianion in the asymmetric unit. The ions and fumaric acid molecules are held together by N—H⋯O and O–H-⋯O hydrogen bonds in 40-membered rings with graph-set notation R
6
6(40). The fumarate ions join these rings into infinite chains along [001].

Structure description
Oxotremorine is a selective agonist of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, which reproduces many of the symptoms observed in Parkinson’s disease. This property has made it an invaluable tool in studying potential pharmaceuticals for Parkinson’s (Ringdahl & Jenden, 1983 ▸). A salt of oxotremorine that is commonly used in biological studies is produced by treating oxotremorine free base with fumaric acid. The resulting salt is reported as the sesquifumarate, indicating that the compound possesses an empirical formula with a 1:1.5 ratio of cation to fumarate dianion. However, the structure reported here shows that in the solid-state, the compound consists of two monocationic, protonated oxotremorines, one doubly deprotonated dianionic fumarate, and two fully protonated fumaric acid molecules. One half of these ions and molecules are present in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing the atomic labeling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The asymmetric unit contains one half of a fumarate dianion, which is disordered over two positions. The other half of the inversion-generated fumarate dianion is shown. Symmetry code: (i) 2 − x, 1 − y, −z.
The only compound found by searching on ‘sesquifumarate’ in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, version 5.43, update of March 2022; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) is that of the anti-arrhythmic agent tedisamil, which also exists as the bis(cation) bis(fumaric acid) fumarate and not the technical sesquifumarate (Jones et al., 2004 ▸: CSD refcode EYOYUM). There are seven other bis(cation) bis(fumaric acid) fumarate salts (Haynes et al., 2006 ▸: RESGEC, RESGUS; Provins et al., 2006 ▸: SEGSAZ: Li & Zheng, 2005 ▸: QARKOK; Lin & Zheng, 2004 ▸: DAMYIA; Mohamed et al., 2009 ▸: FUTNIS; Fang et al., 2022 ▸: CCDC 2092690), and one bis(cation) bis(fumarate) fumaric acid salt (Collin et al., 1987 ▸: FEMKIR) found in a search of the CSD. Although all of these structures incorporate three equivalents of fumaric acid into their structures relative to two cations, none is a formal sesquifumarate. The only such example in the CSD is that of Λ-cobalt(III) tris(ethylenediamine), which shows all three fumaric acid molecules to be fully deprotonated and in a 3:2 ratio with the tricationic cobalt complex ions (Liebig & Ruschewitz, 2012 ▸: PEJGAO). In general, there is a lack of precision when characterizing salts of fumaric acid, and diffraction studies are invaluable in distinguishing the different forms.
In the structure of the title compound, the pyrrolidinium N—H of oxotremorine has bifurcated hydrogen bonds to two O atoms of a symmetry-generated fumarate dianion. One fumaric acid O—H hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl oxygen of the oxopyrrolidine of oxotremorine. The other fumaric acid O—H hydrogen bonds to one of the fumarate dianion oxygen atoms (Table 1 ▸). These hydrogen bonds connect two oxotremorine cations, two fumaric acid molecules and two fumarate dianions into rings that have graph-set notation
 (40) (Etter et al., 1990 ▸) (Fig. 2 ▸). The fumarate ions connect these rings together into infinite one-dimensional chains along [001]. The crystal packing of the title compound is shown in Fig. 3 ▸.
(40) (Etter et al., 1990 ▸) (Fig. 2 ▸). The fumarate ions connect these rings together into infinite one-dimensional chains along [001]. The crystal packing of the title compound is shown in Fig. 3 ▸.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14—H14⋯O5i | 0.93 | 2.65 | 3.498 (2) | 152 |
| C3—H3B⋯O1i | 0.97 | 2.43 | 3.381 (3) | 166 |
| C5—H5B⋯O2ii | 0.97 | 2.51 | 3.434 (2) | 159 |
| C8—H8A⋯O4iii | 0.97 | 2.54 | 3.191 (2) | 125 |
| C8—H8A⋯O6iii | 0.97 | 2.53 | 3.456 (3) | 161 |
| C8—H8B⋯O5iv | 0.97 | 2.52 | 3.480 (2) | 173 |
| C9—H9A⋯O6iv | 0.97 | 2.56 | 3.228 (3) | 126 |
| C10—H10A⋯O5v | 0.97 | 2.66 | 3.624 (3) | 175 |
| C11—H11A⋯O4vi | 0.97 | 2.64 | 3.553 (3) | 157 |
| C12—H12B⋯O7vii | 0.97 | 2.68 | 3.399 (2) | 132 |
| C12—H12B⋯O7A vii | 0.97 | 2.37 | 3.139 (15) | 135 |
| O4—H4⋯O6 | 0.91 (1) | 1.58 (1) | 2.483 (2) | 167 (2) |
| O3—H3⋯O1 | 0.90 (1) | 1.69 (1) | 2.5739 (16) | 167 (2) |
| N2—H2⋯O6iv | 0.908 (19) | 2.554 (18) | 3.172 (3) | 125.8 (14) |
| N2—H2⋯O7iv | 0.908 (19) | 1.809 (19) | 2.705 (2) | 168.3 (17) |
| N2—H2⋯O6A iv | 0.908 (19) | 2.43 (3) | 3.131 (19) | 133.6 (15) |
| N2—H2⋯O7A iv | 0.908 (19) | 1.61 (2) | 2.489 (15) | 161.7 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 ; (iv)
; (iv)
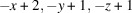 ; (v)
; (v)
 ; (vi)
; (vi)
 ; (vii)
; (vii)
 .
.
Figure 2.
The hydrogen-bonding network forms chains along [001], which consist of
 (40) rings that are joined together by the fumarate dianions. The ring structure is shown above. Hydrogen atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds, and the second component of the disordered fumarate dianion are omitted for clarity.
(40) rings that are joined together by the fumarate dianions. The ring structure is shown above. Hydrogen atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds, and the second component of the disordered fumarate dianion are omitted for clarity.
Figure 3.
The crystal packing of the title compound viewed along the b axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. Hydrogen atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds, and the second component of the disordered fumarate dianion are omitted for clarity.
The fumaric acid and the fumarate dianion are near planar with r.m.s. deviations from planarity of 0.092 and 0.033 Å, respectively. The C—O distances of the fumarate molecules are delocalized with values of 1.270 (3) and 1.243 (2) Å. The C—O distances in the fumaric acid molecules are localized, with the carbonyl distances being 1.209 (2) and 1.203 (2) Å and the carbon–hydroxyl distances being 1.310 (2) and 1.316 (18) Å. The C—O distances and the location of the hydrogen atoms from the difference-Fourier map make the assignment of fumarate and fumaric acid clear.
In the reported structure, the aminobut-2-ynylammonium unit has a near anti conformation, with a N2—C8—C5—N1 torsion angle of 163.17 (13)°. The other known structure of oxotremorine is reported as the sesquioxalate, but is similarly composed of the bis(oxotremorine) bis(oxalic acid) oxalate, and shows a torsion angle of 38.35 (3)° for the equivalent nitrogen and carbon atoms (Clarke et al., 1975 ▸: OXTREO). The other two similar structures reported, trimethyl-[4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)but-2-ynyl]-ammonium iodide (Baker & Pauling, 1973 ▸: MXPBYA), and a related acetylenic imidazole (Moon et al., 1991 ▸: KOGCEO) show equivalent torsion angles of 143.50 (3) and 53.3 (4)°, respectively. The significant separation provided by the but-2-ynyl unit makes it so that there is no significant interaction between the two units, giving no conformational preference.
Synthesis and crystallization
Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction studies were grown by dissolving 15 mg of oxotremorine sesquifumarate purchased from Sigma–Aldrich in 5 ml of water. Solvent was allowed to evaporate at ambient temperature and pressure and crystals formed after 12 h.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The fumarate dianion is disordered over two positions (C17, C18, O6, O7 and C17A, C18A, O6A, O7A), which were modeled using a SAME restraint, as well as EADP instructions. The two components showed a 0.855 (4) to 0.145 (4) occupancy ratio.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | 2C12H19N2O+·C4H2O4 2−·2C4H4O4 |
| M r | 760.78 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 297 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 6.0921 (3), 8.5778 (5), 18.7260 (11) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 94.922 (2), 90.428 (2), 98.945 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 962.88 (9) |
| Z | 1 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.04 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 Venture CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2018 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.717, 0.745 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 27417, 3651, 2975 |
| R int | 0.035 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.612 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.042, 0.109, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 3651 |
| No. of parameters | 269 |
| No. of restraints | 8 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.18, −0.15 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622003649/zl4049sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622003649/zl4049Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622003649/zl4049Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2163782
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Financial statements and conflict of interest: This study was funded by CaaMTech, Inc. ARC reports ownership interest in CaaMTech, Inc., which owns US and worldwide patent applications, covering new tryptamine compounds, compositions, formulations, novel crystalline forms, and methods of making and using the same.
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| 2C12H19N2O+·C4H2O42−·2C4H4O4 | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 760.78 | F(000) = 404 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.312 Mg m−3 |
| a = 6.0921 (3) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 8.5778 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 9070 reflections |
| c = 18.7260 (11) Å | θ = 2.6–25.7° |
| α = 94.922 (2)° | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 90.428 (2)° | T = 297 K |
| γ = 98.945 (2)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 962.88 (9) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.04 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 Venture CMOS diffractometer | 2975 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.035 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2018) | θmax = 25.8°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Tmin = 0.717, Tmax = 0.745 | h = −7→7 |
| 27417 measured reflections | k = −10→10 |
| 3651 independent reflections | l = −22→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.109 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0473P)2 + 0.2757P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3651 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 269 parameters | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 8 restraints | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Hydrogen atoms H2, H3 and H4 were found from a difference-Fourier map and were refined isotropically, using DFIX restraints with O–H distances of 0.90 (1) Å. Isotropic displacement parameters were set to 1.2 Ueq of the parent nitrogen atom and 1.5 Ueq of the parent oxygen atom. All other hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions with C–H = 0.93 Å (sp2) or 0.97 Å (sp3). Isotropic displacement parameters were set to 1.2 Ueq of the parent carbon atom. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O2 | 0.1880 (2) | 0.32007 (19) | 0.36008 (8) | 0.0785 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.5181 (2) | 0.34987 (18) | 0.41423 (7) | 0.0648 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.69301 (19) | 0.57836 (15) | 0.18323 (6) | 0.0575 (3) | |
| O5 | 1.0269 (2) | 0.56449 (19) | 0.22771 (8) | 0.0732 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.7126 (3) | 0.45921 (19) | 0.29059 (8) | 0.0457 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.798508 | 0.415501 | 0.322444 | 0.055* | |
| C13 | 0.3847 (3) | 0.36674 (19) | 0.36123 (9) | 0.0466 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.4977 (3) | 0.44695 (18) | 0.30158 (8) | 0.0453 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.411762 | 0.491313 | 0.269994 | 0.054* | |
| C16 | 0.8265 (3) | 0.53832 (18) | 0.23060 (8) | 0.0445 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.3504 (2) | 0.16999 (17) | 0.50962 (7) | 0.0673 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.12900 (19) | 0.08762 (16) | 0.60010 (6) | 0.0421 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.65707 (19) | 0.00872 (15) | 0.85784 (6) | 0.0380 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.0229 (3) | 0.2911 (2) | 0.54231 (10) | 0.0578 (5) | |
| H2A | −0.043039 | 0.281057 | 0.494497 | 0.069* | |
| H2B | 0.094453 | 0.399740 | 0.553553 | 0.069* | |
| C1 | 0.1861 (2) | 0.17907 (19) | 0.54731 (8) | 0.0445 (4) | |
| C3 | −0.1513 (3) | 0.2442 (3) | 0.59673 (12) | 0.0758 (6) | |
| H3A | −0.168967 | 0.334814 | 0.629641 | 0.091* | |
| H3B | −0.293254 | 0.203854 | 0.572933 | 0.091* | |
| C4 | −0.0716 (3) | 0.1172 (2) | 0.63662 (10) | 0.0576 (4) | |
| H4A | −0.039682 | 0.153881 | 0.686613 | 0.069* | |
| H4B | −0.181912 | 0.022144 | 0.633910 | 0.069* | |
| C5 | 0.2587 (3) | −0.02922 (19) | 0.62190 (8) | 0.0458 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.370750 | −0.043844 | 0.586468 | 0.055* | |
| H5B | 0.162152 | −0.129865 | 0.623917 | 0.055* | |
| C6 | 0.3680 (2) | 0.01937 (19) | 0.69249 (8) | 0.0453 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.4569 (3) | 0.0611 (2) | 0.74894 (9) | 0.0476 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.5696 (3) | 0.1275 (2) | 0.81681 (9) | 0.0526 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.466071 | 0.177765 | 0.846459 | 0.063* | |
| H8B | 0.691969 | 0.208802 | 0.806785 | 0.063* | |
| C9 | 0.8224 (3) | −0.0784 (2) | 0.82116 (8) | 0.0463 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.963732 | −0.010026 | 0.817488 | 0.056* | |
| H9B | 0.769788 | −0.122425 | 0.773541 | 0.056* | |
| C10 | 0.8423 (3) | −0.2081 (3) | 0.86974 (11) | 0.0690 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.867468 | −0.304045 | 0.841843 | 0.083* | |
| H10B | 0.964896 | −0.175271 | 0.903809 | 0.083* | |
| C11 | 0.6245 (3) | −0.2359 (3) | 0.90830 (12) | 0.0729 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.548597 | −0.343053 | 0.896019 | 0.087* | |
| H11B | 0.649915 | −0.220532 | 0.959802 | 0.087* | |
| C12 | 0.4880 (3) | −0.1170 (2) | 0.88405 (9) | 0.0561 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.383755 | −0.164457 | 0.845940 | 0.067* | |
| H12B | 0.406420 | −0.074741 | 0.923545 | 0.067* | |
| H4 | 0.773 (3) | 0.632 (3) | 0.1495 (10) | 0.089 (7)* | |
| H3 | 0.440 (4) | 0.291 (3) | 0.4458 (11) | 0.098 (8)* | |
| H2 | 0.724 (3) | 0.068 (2) | 0.8967 (10) | 0.053 (5)* | |
| O6 | 0.8934 (4) | 0.7598 (3) | 0.10050 (12) | 0.0504 (5) | 0.855 (4) |
| O7 | 1.1822 (4) | 0.7858 (2) | 0.02939 (11) | 0.0519 (4) | 0.855 (4) |
| C17 | 1.0122 (5) | 0.7065 (2) | 0.05155 (12) | 0.0381 (5) | 0.855 (4) |
| C18 | 0.9417 (3) | 0.5389 (2) | 0.02174 (10) | 0.0442 (5) | 0.855 (4) |
| H18 | 0.804798 | 0.487027 | 0.035288 | 0.053* | 0.855 (4) |
| O6A | 0.939 (3) | 0.737 (2) | 0.0861 (11) | 0.0504 (5) | 0.145 (4) |
| O7A | 1.239 (2) | 0.8253 (18) | 0.0278 (9) | 0.0519 (4) | 0.145 (4) |
| C17A | 1.096 (3) | 0.7175 (18) | 0.0433 (9) | 0.0381 (5) | 0.145 (4) |
| C18A | 1.074 (2) | 0.5595 (14) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0442 (5) | 0.145 (4) |
| H18A | 1.189497 | 0.548224 | −0.030918 | 0.053* | 0.145 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O2 | 0.0462 (7) | 0.1052 (12) | 0.0848 (10) | −0.0063 (7) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0461 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0503 (7) | 0.0919 (10) | 0.0556 (7) | 0.0070 (6) | 0.0046 (6) | 0.0340 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0508 (7) | 0.0692 (8) | 0.0536 (7) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0024 (5) | 0.0224 (6) |
| O5 | 0.0460 (7) | 0.0988 (11) | 0.0808 (9) | 0.0140 (7) | 0.0119 (6) | 0.0357 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0460 (8) | 0.0463 (9) | 0.0464 (9) | 0.0088 (7) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0097 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0450 (9) | 0.0450 (9) | 0.0518 (9) | 0.0094 (7) | 0.0042 (7) | 0.0119 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0485 (9) | 0.0434 (8) | 0.0455 (8) | 0.0073 (7) | 0.0010 (7) | 0.0118 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0447 (9) | 0.0417 (8) | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0090 (7) | 0.0054 (7) | 0.0043 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0591 (7) | 0.0944 (10) | 0.0584 (8) | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0389 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0367 (6) | 0.0536 (8) | 0.0374 (7) | 0.0076 (5) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0113 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0371 (6) | 0.0446 (7) | 0.0316 (6) | 0.0043 (5) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0029 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0654 (11) | 0.0583 (11) | 0.0530 (10) | 0.0192 (9) | −0.0103 (8) | 0.0070 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0422 (8) | 0.0542 (9) | 0.0372 (8) | 0.0050 (7) | −0.0054 (6) | 0.0096 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0560 (11) | 0.0972 (16) | 0.0831 (14) | 0.0325 (11) | 0.0053 (10) | 0.0203 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0504 (9) | 0.0678 (11) | 0.0563 (10) | 0.0127 (8) | 0.0130 (8) | 0.0077 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0472 (8) | 0.0510 (9) | 0.0409 (8) | 0.0088 (7) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0115 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0423 (8) | 0.0526 (9) | 0.0438 (9) | 0.0090 (7) | 0.0019 (7) | 0.0178 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0446 (8) | 0.0573 (10) | 0.0439 (9) | 0.0126 (7) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0138 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0626 (10) | 0.0514 (10) | 0.0463 (9) | 0.0166 (8) | −0.0070 (8) | 0.0060 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0411 (8) | 0.0559 (10) | 0.0412 (8) | 0.0090 (7) | 0.0030 (6) | −0.0020 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0741 (13) | 0.0688 (13) | 0.0702 (12) | 0.0277 (10) | −0.0078 (10) | 0.0112 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0741 (13) | 0.0640 (12) | 0.0794 (14) | −0.0056 (10) | −0.0103 (11) | 0.0305 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0410 (8) | 0.0748 (12) | 0.0499 (9) | −0.0049 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0164 (8) |
| O6 | 0.0583 (12) | 0.0436 (10) | 0.0486 (13) | 0.0053 (7) | 0.0167 (7) | 0.0044 (8) |
| O7 | 0.0575 (14) | 0.0492 (13) | 0.0408 (7) | −0.0149 (9) | 0.0115 (9) | −0.0009 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0421 (14) | 0.0411 (9) | 0.0297 (10) | 0.0013 (10) | −0.0020 (11) | 0.0048 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0432 (10) | 0.0447 (11) | 0.0402 (10) | −0.0065 (8) | 0.0062 (8) | 0.0030 (8) |
| O6A | 0.0583 (12) | 0.0436 (10) | 0.0486 (13) | 0.0053 (7) | 0.0167 (7) | 0.0044 (8) |
| O7A | 0.0575 (14) | 0.0492 (13) | 0.0408 (7) | −0.0149 (9) | 0.0115 (9) | −0.0009 (9) |
| C17A | 0.0421 (14) | 0.0411 (9) | 0.0297 (10) | 0.0013 (10) | −0.0020 (11) | 0.0048 (7) |
| C18A | 0.0432 (10) | 0.0447 (11) | 0.0402 (10) | −0.0065 (8) | 0.0062 (8) | 0.0030 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O2—C13 | 1.2026 (19) | C5—H5A | 0.9700 |
| O3—C13 | 1.310 (2) | C5—H5B | 0.9700 |
| O3—H3 | 0.902 (10) | C5—C6 | 1.473 (2) |
| O4—C16 | 1.3016 (19) | C6—C7 | 1.185 (2) |
| O4—H4 | 0.914 (10) | C7—C8 | 1.467 (2) |
| O5—C16 | 1.2092 (19) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C15—H15 | 0.9300 | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C15—C14 | 1.316 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| C15—C16 | 1.483 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| C13—C14 | 1.480 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.515 (3) |
| C14—H14 | 0.9300 | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| O1—C1 | 1.2372 (19) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3293 (19) | C10—C11 | 1.511 (3) |
| N1—C4 | 1.451 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C5 | 1.452 (2) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| N2—C8 | 1.486 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.509 (3) |
| N2—C9 | 1.4833 (19) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| N2—C12 | 1.490 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| N2—H2 | 0.908 (19) | O6—C17 | 1.270 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | O7—C17 | 1.243 (2) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C17—C18 | 1.492 (3) |
| C2—C1 | 1.495 (2) | C18—C18i | 1.295 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.510 (3) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | O6A—C17A | 1.273 (14) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9700 | O7A—C17A | 1.222 (14) |
| C3—C4 | 1.509 (3) | C17A—C18A | 1.502 (14) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C18A—C18Ai | 1.25 (2) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C18A—H18A | 0.9300 |
| C13—O3—H3 | 108.7 (16) | H5A—C5—H5B | 107.9 |
| C16—O4—H4 | 110.0 (15) | C6—C5—H5A | 109.3 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 117.9 | C6—C5—H5B | 109.3 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 124.13 (15) | C7—C6—C5 | 178.83 (17) |
| C16—C15—H15 | 117.9 | C6—C7—C8 | 174.81 (17) |
| O2—C13—O3 | 123.57 (15) | N2—C8—H8A | 108.7 |
| O2—C13—C14 | 122.35 (15) | N2—C8—H8B | 108.7 |
| O3—C13—C14 | 114.08 (14) | C7—C8—N2 | 114.07 (14) |
| C15—C14—C13 | 123.90 (15) | C7—C8—H8A | 108.7 |
| C15—C14—H14 | 118.1 | C7—C8—H8B | 108.7 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 118.1 | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.6 |
| O4—C16—C15 | 114.39 (13) | N2—C9—H9A | 111.2 |
| O5—C16—O4 | 123.90 (15) | N2—C9—H9B | 111.2 |
| O5—C16—C15 | 121.70 (15) | N2—C9—C10 | 102.94 (13) |
| C1—N1—C4 | 114.58 (13) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.1 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 123.48 (13) | C10—C9—H9A | 111.2 |
| C4—N1—C5 | 121.90 (13) | C10—C9—H9B | 111.2 |
| C8—N2—C12 | 116.01 (13) | C9—C10—H10A | 110.5 |
| C8—N2—H2 | 103.0 (11) | C9—C10—H10B | 110.5 |
| C9—N2—C8 | 116.32 (12) | H10A—C10—H10B | 108.7 |
| C9—N2—C12 | 104.70 (13) | C11—C10—C9 | 106.06 (15) |
| C9—N2—H2 | 108.6 (11) | C11—C10—H10A | 110.5 |
| C12—N2—H2 | 107.8 (11) | C11—C10—H10B | 110.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.8 | C10—C11—H11A | 110.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 110.7 | C10—C11—H11B | 110.5 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 110.7 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.7 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 105.11 (15) | C12—C11—C10 | 106.27 (15) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 110.7 | C12—C11—H11A | 110.5 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 110.7 | C12—C11—H11B | 110.5 |
| O1—C1—N1 | 123.90 (15) | N2—C12—C11 | 103.58 (13) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 126.98 (15) | N2—C12—H12A | 111.0 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 109.11 (14) | N2—C12—H12B | 111.0 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 110.4 | C11—C12—H12A | 111.0 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 110.4 | C11—C12—H12B | 111.0 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.6 | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 106.81 (15) | O6—C17—C18 | 116.8 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 110.4 | O7—C17—O6 | 123.1 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3B | 110.4 | O7—C17—C18 | 120.1 (2) |
| N1—C4—C3 | 104.08 (14) | C17—C18—H18 | 117.8 |
| N1—C4—H4A | 110.9 | C18i—C18—C17 | 124.4 (2) |
| N1—C4—H4B | 110.9 | C18i—C18—H18 | 117.8 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 110.9 | O6A—C17A—C18A | 116.1 (16) |
| C3—C4—H4B | 110.9 | O7A—C17A—O6A | 123.5 (16) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 109.0 | O7A—C17A—C18A | 119.4 (16) |
| N1—C5—H5A | 109.3 | C17A—C18A—H18A | 114.6 |
| N1—C5—H5B | 109.3 | C18Ai—C18A—C17A | 130.7 (16) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 111.67 (13) | C18Ai—C18A—H18A | 114.6 |
| O2—C13—C14—C15 | −159.84 (18) | C5—N1—C1—O1 | 2.9 (2) |
| O3—C13—C14—C15 | 19.3 (2) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | −176.77 (14) |
| C14—C15—C16—O4 | −8.4 (2) | C5—N1—C4—C3 | −179.65 (16) |
| C14—C15—C16—O5 | 170.45 (18) | C8—N2—C9—C10 | −169.44 (14) |
| C16—C15—C14—C13 | 179.50 (15) | C8—N2—C12—C11 | 168.12 (15) |
| N2—C9—C10—C11 | 25.88 (19) | C9—N2—C8—C7 | 59.62 (19) |
| C2—C3—C4—N1 | −4.8 (2) | C9—N2—C12—C11 | 38.48 (17) |
| C1—N1—C4—C3 | 2.4 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −2.6 (2) |
| C1—N1—C5—C6 | 109.44 (16) | C10—C11—C12—N2 | −21.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 5.5 (2) | C12—N2—C8—C7 | −64.18 (19) |
| C3—C2—C1—O1 | 176.15 (18) | C12—N2—C9—C10 | −39.98 (16) |
| C3—C2—C1—N1 | −4.2 (2) | O6—C17—C18—C18i | −171.2 (3) |
| C4—N1—C1—O1 | −179.16 (16) | O7—C17—C18—C18i | 7.4 (4) |
| C4—N1—C1—C2 | 1.17 (19) | O6A—C17A—C18A—C18Ai | −1 (3) |
| C4—N1—C5—C6 | −68.36 (19) | O7A—C17A—C18A—C18Ai | −169 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C14—H14···O5ii | 0.93 | 2.65 | 3.498 (2) | 152 |
| C3—H3B···O1ii | 0.97 | 2.43 | 3.381 (3) | 166 |
| C5—H5B···O2iii | 0.97 | 2.51 | 3.434 (2) | 159 |
| C8—H8A···O4iv | 0.97 | 2.54 | 3.191 (2) | 125 |
| C8—H8A···O6iv | 0.97 | 2.53 | 3.456 (3) | 161 |
| C8—H8B···O5v | 0.97 | 2.52 | 3.480 (2) | 173 |
| C9—H9A···O6v | 0.97 | 2.56 | 3.228 (3) | 126 |
| C10—H10A···O5vi | 0.97 | 2.66 | 3.624 (3) | 175 |
| C11—H11A···O4vii | 0.97 | 2.64 | 3.553 (3) | 157 |
| C12—H12B···O7viii | 0.97 | 2.68 | 3.399 (2) | 132 |
| C12—H12B···O7Aviii | 0.97 | 2.37 | 3.139 (15) | 135 |
| O4—H4···O6 | 0.91 (1) | 1.58 (1) | 2.483 (2) | 167 (2) |
| O3—H3···O1 | 0.90 (1) | 1.69 (1) | 2.5739 (16) | 167 (2) |
| N2—H2···O6v | 0.908 (19) | 2.554 (18) | 3.172 (3) | 125.8 (14) |
| N2—H2···O7v | 0.908 (19) | 1.809 (19) | 2.705 (2) | 168.3 (17) |
| N2—H2···O6Av | 0.908 (19) | 2.43 (3) | 3.131 (19) | 133.6 (15) |
| N2—H2···O7Av | 0.908 (19) | 1.61 (2) | 2.489 (15) | 161.7 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x−1, y, z; (iii) −x, −y, −z+1; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (v) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (vi) −x+2, −y, −z+1; (vii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (viii) x−1, y−1, z+1.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: National Science Foundation, Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences (grant No. CHE-1429086); CaaMTech, Inc.
References
- Baker, R. W. & Pauling, P. J. (1973). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. 1247–1249.
- Bruker (2018). APEX3, SAINT, and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Clarke, P. J., Pauling, P. J. & Petcher, T. J. (1975). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. 774–778.
- Collin, S., Norberg, B., Evrard, G. & Durant, F. (1987). Acta Cryst. C43, 572–577.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.-Y., Zhang, B.-X., Xing, W.-H., Jia, H.-L., Wang, X., Gong, N.-B., Lu, Y. & Du, G.-H. (2022). Chin. Lett. Chem. In the press.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Haynes, D. A., Jones, W. & Motherwell, W. D. S. (2006). CrystEngComm, 8, 830–840.
- Jones, P. G., Schön, U. & Finner, E. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, o1285–o1287.
- Li, Z.-F. & Zheng, Y.-Q. (2005). J. Coord. Chem. 58, 883–890.
- Liebig, T. J. & Ruschewitz, U. (2012). Cryst. Growth Des. 12, 5402–5410.
- Lin, J.-L. & Zheng, Y.-Q. (2004). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 219, 230–232.
- Mohamed, S., Tocher, D. A., Vickers, M., Karamertzanis, P. G. & Price, S. L. (2009). Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 2881–2889.
- Moon, M. W., Chidester, C. G., Heier, R. F., Morris, J. K., Collins, R. J., Russell, R. R., Francis, J. W., Sage, G. P. & Sethy, V. H. (1991). J. Med. Chem. 34, 2314–2327. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Provins, L., Christophe, B., Danhaive, P., Dulieu, J., Durieu, V., Gillard, M., Lebon, F., Lengelé, S., Quéré, L. & van Keulen, B. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 1834–1839. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ringdahl, B. & Jenden, D. J. (1983). Life Sci. 32, 2401–2413. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622003649/zl4049sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622003649/zl4049Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622003649/zl4049Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2163782
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report