Abstract
Objectives
Informing an international task force updating the consensus statement on efficacy and safety of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) selectively targeting interleukin-6 (IL-6) pathway in the context of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
Methods
A systematic literature research of all publications on IL-6 axis inhibition with bDMARDs published between January 2012 and December 2020 was performed using MEDLINE, EMBASE and Cochrane CENTRAL databases. Efficacy and safety outcomes were assessed in clinical trials including their long-term extensions and observational studies. Meeting abstracts from ACR, EULAR conferences and results on clinicaltrials.gov were taken into consideration.
Results
187 articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Evidence for positive effect of IL-6 inhibition was available in various inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, giant cell arteritis, Takayasu arteritis, adult-onset Still’s disease, cytokine release syndrome due to chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy and systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Newcomers like satralizumab and anti-IL-6 ligand antibody siltuximab have expanded therapeutic approaches for Castleman’s disease and neuromyelitis optica, respectively. IL-6 inhibition did not provide therapeutic benefits in psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and certain connective tissue diseases. In COVID-19, tocilizumab (TCZ) has proven to be therapeutic in advanced disease. Safety outcomes did not differ from other bDMARDs, except higher risks of diverticulitis and lower gastrointestinal perforations. Inconsistent results were observed in several studies investigating the risk for infections when comparing TCZ to TNF-inhibitors.
Conclusion
IL-6 inhibition is effective for treatment of several inflammatory diseases with a safety profile that is widely comparable to other bDMARDs.
Keywords: Cytokines, Autoimmune Diseases, Inflammation
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
Since the 2013 consensus statement on blocking the effects of interleukin-6 (IL-6) with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), the body of evidence has grown widely.
Data of clinical trials on several novel compounds targeting the IL-6 pathway in various immune-mediated inflammatory diseases have become available. This systematic literature review (SLR) was performed to inform an international consensus task force charged with updating the previous recommendations on pharmacological interventions with bDMARDs specifically targeting the IL-6 pathway.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
Anti-IL-6 bDMARDs were effective in various inflammatory diseases with an emphasis on rheumatic diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic and polyarticular-course juvenile idiopathic arthritis, giant cell arteritis, adult-onset Still’s disease, Takayasu arteritis as well as systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clinically important differences in efficacy were further demonstrated in inflammatory conditions such as Castleman’s disease, neuromyelitis optica and chimeric antigen receptor T cell induced cytokine release syndrome. Use of tocilizumab resulted in better clinical outcomes and reduced mortality in patients with advanced stage of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Targeting IL-6 in osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and certain connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, myositis and Sjogren’s syndrome) was not beneficial.
Safety outcomes regarding cardiovascular events, venous thromboembolism or malignancy did not differ from conventional DMARDs or bDMARDs with other modes of action. Risk of lower gastrointestinal perforations is low, but higher compared with other bDMARDs and in line with previously published reports.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
This SLR was conducted to inform the task force on ‘Consensus statement on blocking IL-6 receptor and IL-6 in inflammatory conditions: An update’ with the emerged evidence published from January 2012 onwards.
Introduction
Basic research identified interleukin-6 (IL-6) as a cytokine with pleotropic activities and underlying abilities to promote inflammation and autoimmunity. The continuing development of biological agents that selectively target the IL-6 pathway has expanded the therapeutic armamentarium for various chronic inflammatory diseases over the last two decades.1 Tocilizumab (TCZ) was the first introduced humanised monoclonal antibody directed to membrane-bound as well as soluble IL-6 receptors (IL-6R), consequently inhibiting IL-6 from interacting with the IL-6R. By demonstrating therapeutic benefits in different clinical trials and indications, TCZ corroborated the concept of IL-6-related research.2 Previous evidence obtained by a systematic literature search in 2012, informed a consensus statement which was published in 2013 and provided points to consider when commencing TCZ and clinically relevant information regarding practical management.3 4 However, these statements addressed recommendations almost exclusively on TCZ and focusing on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and to a minor extent on systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA), as other biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) targeting IL-6 (receptor or ligand) were in development and few or no other clinical data were available at that time.
Within the last decade, the body of evidence on bDMARDs blocking the IL-6-IL-6R axis has undergone a dynamic evolution. Data from clinical trials on novel compounds that target the IL-6 pathway in RA, such as sarilumab (SAR), and also on indications beyond RA and sJIA have become available.5 Furthermore, negative results of IL-6 pathway inhibition in diseases such as psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis or some connective tissue diseases helped to shed more light on the immunopathology of these diseases.6–11 In RA, the body of evidence for using TCZ and other agents in different populations has grown extensively.12–17 Studies with emphasis on exploring tapering or cessation of IL-6 blockade in patients with RA who have achieved clinical remission have provided valuable evidence for clinicians.18–23 Safety data were derived from clinical trials of TCZ or SAR and from large prospective cohorts assessing long-term safety. This systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted to inform a consensus task force charged with developing an update of the original recommendations on pharmacological interventions with biological DMARDs targeting IL-6 pathway to account for the latest developments in indications, efficacy, safety as well as biomarker assessment, patient adherence and health economic aspects. This new SLR is considered an update of the SLR performed for the corresponding 2013 consensus statement.3 4
Methods
Literature search
The framework for this literature search and research questions were defined in the course of a steering group meeting with experts in various medical disciplines on 31 August 2020. A review protocol and definition of PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcomes) were drafted and finally approved by the steering group. Details of the research questions developed by the steering group are provided in online supplemental tables 1.1.1–1.1.4. This SLR was conducted in adherence to the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) standardised operating procedures for recommendations and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement.24 25 Based on the research questions defined, five different searches on IL-6 inhibiting agents were carried out separately, namely: (1) efficacy in approved indications (including biomarker assessment); (2) efficacy in other studied diseases; (3) safety in approved indications; (4) safety in other studied diseases and, finally, (5) adherence, patient preferences and economic aspects. A professional librarian with longstanding experience (EC) conducted the database search using MEDLINE, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library’s Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL). Articles published in full and in English language were eligible for inclusion as well as conference abstracts presented at the EULAR and American College of Rheumatology (ACR) annual meetings from 2019 to 2020 (conference abstracts at ACR 2020 were hand-searched). Preliminary results from ongoing clinical trials, which were neither published in articles nor abstracts, were obtained from clincaltrials.gov insofar as sufficient data were available.26 As this SLR was performed to incorporate evidence since the last SLR for the corresponding 2013 consensus,3 4 articles published from 1 January 2012 to 15 January 2021 (last date searched) were included.
rmdopen-2022-002359supp001.pdf (2.3MB, pdf)
For articles to be eligible for inclusion, the following criteria were defined: (1) Efficacy: randomised, controlled, double-blind phase III trials (RCT) with a study duration of ≥3 months and sample size of ≥50 patients investigating IL-6 receptor or ligand inhibition with bDMARDs. (2) Open label studies addressing strategic, switching or dose-reduction issues or phase II trials if no phase III trial was available. Trials with earlier primary endpoint or trials with smaller sample size were eligible for inclusion if no other study fulfilled inclusion criteria. (3) Safety: observational studies, primarily, cohort studies, case control studies and registry data. (4) Safety data from RCTs, long-term extensions (LTEs) or postmarketing data of compounds of interest were further eligible for extracting safety data if registry data were not available. Description of PICOs and details on complete search strategy are listed in online supplemental section 1: 1.2.1–1.3.5.3.
Study selection, data extraction and risk of bias assessment
During the study selection process, one reviewer (KK) evaluated all retrieved publications by title and abstract screening for eligibility. After the initial screening, a detailed assessment for inclusion of preselected articles was performed. In case of uncertainties, these were discussed with the methodologist (AK). Data of studies selected for inclusion were extracted based on disease-specific variables of interest which were predefined in the review protocol. Risk of bias (RoB) analysis was conducted using the Cochrane Collaboration’s Risk of Bias tool for RCTs and additionally the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for observational studies and case-control studies. Due to high heterogeneity of available studies, the steering group decided that no pooling of efficacy or safety outcomes by meta-analysis should be performed. Thus, the results in this manuscript are reported narratively.
Results
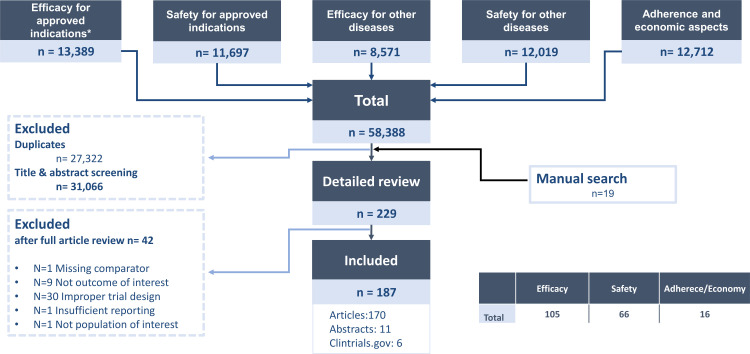
After deduplication, a total of 31 066 records remained for title and abstract screening. A total of 229 articles were selected for full-text review, of which 187 were finally included. Of these, 105 articles were eligible for extraction on efficacy including biomarker assessment, 66 on safety and 16 on adherence and health economic aspects. A flowchart with a detailed description of the selection process is shown in figure 1. Characteristics of each publication eligible for data-extraction, baseline characteristics, outcomes for each intervention group and the respective reference (section 8 in the online supplemental appendix) are shown in the supplement. For most of the RCTs included, RoB was considered as low. However, RoB on open-label studies was classified as high due to their unblinded design. RoB assessment was not performed on ACR/EULAR abstracts, trials available on clinicaltrial.gov or studies on biomarker assessment, patient adherence and economic aspects. Details of all articles and abstracts included and RoB assessment are provided in online supplemental appendix (Section 2: Efficacy for approved indications; Section 3: Efficacy for other studied diseases; Section 4: Safety aspects of interleukin-6 pathway inhibition; Section 5: Biomarkers for prediction of therapeutic response of interleukin-6 pathway inhibition; Section 6: Patient adherence/preferences and economic aspects of interleukin-6 pathway inhibition).
Figure 1.
Flowchart describing the study selection process.
rmdopen-2022-002359supp002.pdf (2.2MB, pdf)
Efficacy for approved indications
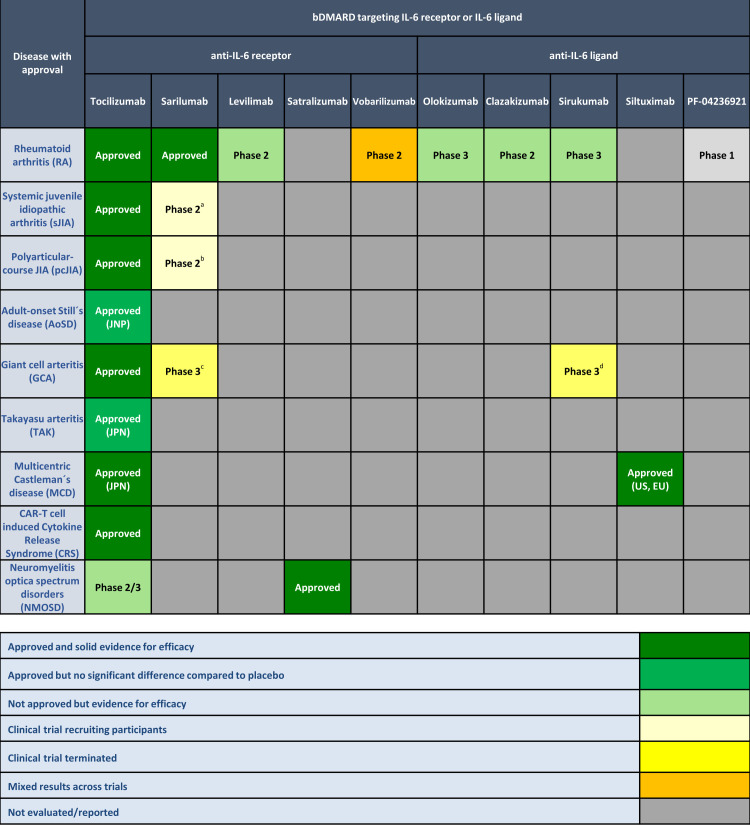
A total 13 389 publications were retrieved for screening and 76 full text publications selected for inclusion regarding efficacy for approved indications. Studies evaluating biomarkers for prediction of therapeutic response of IL-6 pathway inhibition were incorporated in this search and are shown in online supplemental tables S5.1 and S5.2. Figure 2 shows bDMARDs specifically inhibiting IL-6 receptor or ligand and their approved indications based on available data at end of December 2020. At this date, TCZ was approved for RA, sJIA, polyarticular-course juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pcJIA), giant cell arteritis (GCA), chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and in Japan for adult-onset Still’s disease (AoSD), Takayasu arteritis (TAK) as well as multicentric Castleman’s disease (MCD). Among the other anti-IL-6R antibodies, SAR is approved for RA in EU, Japan and USA and satralizumab (SAT) for treatment of seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD). In addition, several compounds selectively binding the IL-6 ligand, including the humanised antibody olokizumab (OKZ) as well as chimeric monoclonal antibody siltuximab (SIL), were developed. OKZ received market authorisation for the treatment of RA in Russia in 2020. SIL is the first anti-IL-6 drug to be licensed for the treatment of MCD in the United States of America (USA) and the European Union (EU).
Figure 2.
Efficacy of biological disease modifying antirheumatic drugs targeting the IL-6 receptor or ligand and their relative efficacy and/or regulatory approvals across immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (based on available data at end of December 2020). aNCT02991469 (recruiting); bNCT02776735 (recruiting); cNCT03600805 (study terminated, results are awaited); d trial terminated early due to sponsor decision. For colorblind readers, figure 2 is provided in the online supplemental appendix (section 7: S7.1). EU, European Union; JPN, Japan; RU: Russian Federation; US: United Stated of America.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
In total, 42 studies investigating bDMARDs selectively inhibiting IL-6 receptor or cytokine in patients with RA were included (low RoB: n=15; unclear RoB: n=7; high RoB: n=13, conference abstracts: n=3; not fully published with available study results on clinicaltrials.gov: n=4; for details of RoB analyses, see online supplemental section S2.2.1. Efficacy data were grouped into (1) efficacy trials (in combination with methotrexate (MTX) or other conventional synthetic DMARD (csDMARD) or as monotherapy); (2) head-to-head trials with other bDMARDs; (3) trials investigating routes of administration; (4) adding versus switching trials; (5) induction/strategic trials; and 6) stopping or dose reduction trials. Patients were grouped based on population (treatment naïve, previous insufficient response to conventional synthetic DMARDs and tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF-i)). Details on study characteristics, baseline characteristics and efficacy outcomes are summarised in online supplemental tables S2.1.1, S2.3.1.1–S2.3.1.12 and S2.4.1.1–S2.4.1.12.
Efficacy trials
Trials comparing bDMARDs specifically inhibiting IL-6 receptor or ligand to placebo in patients with established RA with inadequate response (IR) to methotrexate (MTX) or conventional synthetic disease-modifying drugs (csDMARDs) showed effective reduction of signs and symptoms for several anti-IL-6R agents, including TCZ (Korean patients),13 SAR12 27 28 and BCD-089 (levilimab).29 Baseline characteristics and detailed efficacy outcomes are shown in online supplemental tables S2.3.1.1 and S2.4.1.1. A not yet published study of a phase II trial investigating ALX-0061 (vobarilizumab), an anti-IL-6R nanobody, did not show significant differences from placebo on achieving American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement (ACR20 response) in MTX-IR patients.30 In an early open-label phase II study, vobarilizumab monotherapy had similar numerical ACR response rates compared with TCZ.31 Compounds selectively targeting IL-6 cytokine such as clazakizumab (CLZ) (formerly ALD518 and BMS-945429),32 OKZ33 and sirukumab,34 respectively, were associated with significant improvement in signs, symptoms and physical function compared with placebo in patients with RA refractory to MTX or csDMARDs. Four trials (all with low RoB) studied the efficacy of agents binding IL-6 receptor or ligand in patients with an IR or intolerance to antitumour necrosis factor (TNF) therapy. All showed comparable results with improvements in signs and symptoms of RA, irrespective of the compound used (SAR,35 OKZ36 37 and sirukumab38). Three studies addressed the efficacy of TCZ in patients with previous insufficient treatment response to csDMARDs and TNF-inhibitors. In the BREVACTA study, the subcutaneous formulation of TCZ (TCZ-SC) was superior to placebo (PBO-SC) showing higher ACR responses (ACR20 response: 60.9% vs 31.5%) and inhibition of radiographic joint damage at week 24 in patients who had an IR to ≥1 DMARDs, including anti-TNF agents.15 Intravenous TCZ was more effective than placebo in reducing signs and symptoms in patients with RA who failed to respond adequately to DMARD therapy, among them approximately 38% in both groups with previous use of anti-TNF agents.14 The TORPEDO study failed to achieve its primary endpoint of improvement in Health Assessment Questionnaire—Disability Index (HAQ-DI) at week 4 when comparing intravenous TCZ to placebo in patients with IR to csDMARDs or anti-TNFs. The study was completed in 2014, but has not been published until the timepoint of submission of this manuscript (clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT00977106).39
Head-to-head trials
Three head-to-head studies were included (all three with high RoB). Efficacy results are summarised in table 1 (baseline characteristics and detailed efficacy outcomes are shown in online supplemental tables S2.3.1.4 and S2.4.1.4). TCZ and SAR monotherapy demonstrated clinical and functional superiority compared with adalimumab (ADA) monotherapy in patients who were intolerant or inadequate responders to MTX.40 41 The SIRROUND-H study assessed superiority of sirukumab monotherapy over ADA monotherapy in biologic-naïve patients who did not respond to MTX. The study failed to meet one of its coprimary endpoints with no significant differences in ACR50% response rates at week 24; however, sirukumab showed greater improvements with regard to the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) at week 24.42 Due to pronounced effects of IL-6 inhibition on hepatic acute phase reactant (C reactive protein (CRP)) production and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), an overestimation of improvement or response rates when using composite disease activity measures that include acute-phase reactants, such as the DAS28 or the Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI), can occur. Especially, the ESR is highly weighted in the DAS28, whereas CRP level exhibits low weight in SDAI.43 Thus, studies using composite disease activity measures comprising acute-phase reactants were judged as being at high RoB. In patients who had failed MTX, Weinblatt et al reported significantly greater ACR20 response rates at week 12 of CLZ over placebo in a randomised dose-ranging study. Herein, ADA was included as active reference; however, the study was not powered for head-to-head comparisons between CLZ and ADA.44
Table 1.
Head-to-head studies comparing bDMARDs specifically targeting IL-6 receptor or ligand to tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors
| Population | Study | Design | Risk of bias (RoB) | Treatment arm | No. of patients (n) | Primary endpoint | P value (primary endpoint) |
ACR20 (%) |
ACR50 (%) |
ACR70 (%) |
DAS28 <2.6 (%) |
CDAI≤2.8 (%) |
ACR/EULAR Boolean remission (%) | ΔHAQ (mean) | |
| MTX-IR | Gabay et al (2013) (ADACTA)40 | Superiority trial | High | ADA 40 mg Q2W | 162 | ΔDAS28-ESR at week 24 | −1.8 | <0.0001 | 49.4 | 27.8 | 17.9 | 10.5 | 9.3* | NR | −0.5 |
| TCZ 8 mg/kg Q4W | 163 | −3.3 | 65.0 | 47.2 | 32.5 | 39.9 | 17.2* | NR | −0.7 | ||||||
| MTX-IR | Burmester et al (2017) (MONARCH) 41 | Superiority trial | High | ADA 40 mg Q2W | 185 | ΔDAS28-ESR at week 24 | −2.2 | <0.0001 | 58.4 | 29.7 | 11.9 | 7.0 | 2.7 | NR | −0.43 |
| SAR 200 mg Q2W | 184 | −3.28 | 71.7 | 45.7 | 23.4 | 26.6 | 7.1 | NR | −0.61 | ||||||
| MTX-IR | Taylor et al (2018) (SIRROUND-H)42 | Superiority trial | High | ADA 40 mg Q2W | 186 | ΔDAS28-ESR+ACR 50 (%) at week 24 | −2.19 | Reference | 56.5 | 31.7 | 12.9 | 7.5 | NR | 3.8 | −0.52 |
| SRK 50 mg Q4W | 186 | −2.58 | 0.013 | 53.8 | 26.9 | 11.8 | 12.9 | NR | 3.8 | −0.51 | |||||
| SRK 100 mg Q2W | 187 | −2.96 | <0.001 | 58.8 | 35.3 | 15.5 | 20.3 | NR | 3.7 | −0.53 | |||||
| MTX-IR | Weinblatt et al (2015)44‡ | Dose-ranging study with active comparator (ADA) | Unclear | Placebo+MTX | 61 | ACR 20 (%) at week 12 | 39.3 | Reference | 37.7† | NR | 6.6† | 1.6 | 3.3 | 3.3 | −0.62† |
| ADA 40 mg Q2W+MTX | 59 | 76.3 | <0.05* | 66.1† | NR | 18.6† | 20.3 | 8.5 | 5.1 | −0.66† | |||||
| CLZ 25 mg Q4W+MTX | 59 | 76.3 | <0.05 | 81.4† | NR | 27.1† | 35.6 | 11.9 | 8.5 | −0.68† | |||||
| CLZ 100 mg Q4W+MTX | 60 | 73.3 | <0.05 | 65.0† | NR | 40.0† | 35.0 | 8.3 | 10.0 | −0.79† | |||||
| CLZ 200 mg Q4W+MTX | 60 | 60.0 | <0.05 | 66.7† | NR | 30.0† | 26.7 | 3.3 | 5.0 | −0.71† | |||||
| CLZ 100 mg Q4W+Placebo | 60 | 55.0 | <0.05 | 58.3† | NR | 16.7† | 21.7 | 8.3 | 6.7 | −0.64† | |||||
| CLZ 200 mg Q4W+Placebo | 59 | 61.0 | <0.05 | 57.6† | NR | 25.4† | 25.4 | 3.4 | 1.7 | −0.60† | |||||
Results of secondary efficacy outcomes are depicted at the time point of the primary endpoint. ADACTA-H, MONARCH-H and SIRROUND-H trial were judged as being at high RoB due to inclusion of acute phase reactants in the outcome of the primary endpoint.
*Posthoc analysis.
†Efficacy outcome at week 24.
‡Study not powered to compare CLZ with ADA.
ACR, American College of Rheumatology; ADA, adalimumab; CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; CLZ, clazakizumab; DAS28, Disease Activity Score of 28 joints; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; HAQ, Health Assessment Questionnaire; MTX, methotrexate; NR, not reported; Q2W, every other week; Q4W, once every 4 weeks; SAR, sarilumab; SRK, sirukumab; TCZ, tocilizumab; Δ, change from baseline.
Trials investigating routes of administration
SUMMACTA compared subcutaneous (SC) versus intravenous formulations (IV) of TCZ in cs-/bDMARD-IR RA patients. TCZ-SC 162 mg weekly (QW) was non-inferior to TCZ-IV 8 mg/kg.45 In the multicentre, double-blind MUSASHI study, TCZ-SC every other week (Q2W) confirmed the non-inferiority of TCZ-SC monotherapy to TCZ-IV monotherapy in Japanese patients with an IR to csDMARDs and/or bDMARDs.46 An 84-week open-label extension period of the MUSASHI study evaluated the efficacy of switch from weight-titrated–dose TCZ-IV monotherapy to fixed-dose TCZ-SC monotherapy. Switching to another route of administration (IV to SC) was associated with comparable efficacy in the majority of patients, even though it was somewhat lower in patients with high body weight.47 In patients with RA with IR to TCZ-SC Q2W, TCZ-SC weekly was superior to TCZ-SC Q2W for adjusted mean change in DAS28-ESR from baseline to week 12 in a Japanese study. Therefore, shortening the dosing interval to QW improved efficacy with acceptable tolerability.48 Details on studies investigating route of administration are shown in online supplemental tables S2.3.1.5 and S2.4.1.5.
Adding versus switching trials
Pertaining to switching within the IL-6R blocker class, a posthoc analysis of the EXTEND trial, an open-label extension study of the ASCERTAIN trial, investigated patients switched from double-blind TCZ to open label SAR, showing sustained clinical efficacy over 96 weeks.49 Apart from that, two key studies (one with unclear and another with high RoB due to being not double-blinded and a lower number of patients enrolled as initially planned) compared the effectiveness between TCZ added to MTX and TCZ monotherapy (switched from MTX) in established RA. Clinical data suggested benefit of add-on (TCZ+MTX) over switching to TCZ, and data of radiographic progression were in favour of the add-on strategy in both studies, whereas in patients receiving TCZ monotherapy radiographic progression was numerically higher.50–52 Study details are depicted in online supplemental tables S2.3.1.6–S2.3.1.7 and S2.4.1.6–S2.4.1.7.
Induction and strategic trials
Three trials (two with high RoB due to including acute-phase reactants in the primary outcome and one with high RoB due to open label design) as well as one report with 2-year results on induction therapy with TCZ in early progressive RA were evaluated (for study details, see online supplemental tables S2.3.1.8-S2.3.1.9, S2.4.1.8-S2.4.1.9). The FUNCTION trial demonstrated significantly higher proportions of patients achieving DAS28-ESR≤2.6 when receiving 8 mg/kg TCZ+MTX or 8 mg/kg TCZ monotherapy in comparison with placebo+MTX at week 24 (45% and 39% vs 15%). Patients treated with 8 mg/kg TCZ plus MTX achieved significantly less radiographic progression and better HAQ-DI improvement at week 52 than did patients with MTX monotherapy.16 Furthermore, TCZ 8 mg/kg+MTX compared with TCZ monotherapy was associated with less radiographic progression at week 104 (mean change from baseline in van der Heijde-modified total Sharp score, 0.19 vs 0.62).53 However, treatment induction with TCZ monotherapy in early RA was not superior to MTX alone in FUNCTION in achievement of secondary endpoints, including ACR responses and Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) remission at week 52.16
The U-Act-Early study was a 2-year RCT, in which DMARD-naïve patients with early RA were treated to the target of sustained remission defined as DAS28<2.6 with a swollen joint count less than or equal to four, persisting for at least 24 weeks. Patients were randomised to TCZ+MTX, TCZ monotherapy or MTX monotherapy using a treat-to-target approach. In the primary analysis (proportion of patients achieving sustained DAS28<2.6), significantly more patients achieved the target while being treated with their initial treatment regimen when TCZ was part of the regimen, compared with MTX monotherapy (TCZ+MTX: 86% vs TCZ mono: 84% vs MTX mono: 44%).17 However, following a treatment step-up according to a standardised treatment protocol during the entire study period, initial significant differences in achieving sustained DAS28<2.6 were no longer observed after the addition of TCZ in the MTX monotherapy group (TCZ+MTX: 86% vs TCZ mono: 88% vs MTX mono: 77%).17 A randomised, open-label strategic study (NORD-STAR) compared the proportion of patients with treatment-naïve, early RA achieving CDAI remission with active conventional therapy based on MTX combined with glucocorticoids (GC) with three different biological therapies, including TCZ, certolizumab-pegol (CZP) and abatacept (ABA) with background MTX. Non-inferiority was demonstrated for active conventional treatment regimens (including GC with rapid tapering or intra-articular GC, sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine) versus TCZ or CZP, but not for ABA at week 24.54
Stopping or dose reduction trials
Eight studies (two rated as having low RoB, three with unclear RoB and two judged as being at high RoB due to open-label study-design; one conference abstract) investigated tapering and discontinuation of IL-6 inhibiting agents or concomitant csDMARDs as a concept for achieving a more tailored treatment approach (for details, see online supplemental tables S2.3.1.10-S2.3.1.12, S2.4.1.10-S2.4.1.12). Four studies investigated a tapering and discontinuation strategy of concomitant MTX, one trial of GC in a subset of patients who achieved DAS≤3.2, whereas in three other studies TCZ was discontinued, or the interval of application extended once DAS28<2.6 was reached. The non-inferiority of MTX tapering versus continuation in patients receiving ongoing TCZ therapy without significant worsening of disease activity was demonstrated in three studies.18–20 Tapering or even stopping MTX was possible in some patients, but continuation of MTX led to numerically better results in different outcomes compared with TCZ monotherapy (DAS28-ESR≤3.2 at week 52: TCZ mono: 62.6% versus TCZ+MTX: 68% and DAS28-ESR<2.6 at week 52: TCZ mono: 48.3% vs TCZ+MTX: 55.1%).19 In a COMP-ACT substudy, MRI revealed similar intra-articular inflammation and damage in patients who discontinued MTX versus those who continued TCZ+MTX.55 The SEMIRA trial investigated patients treated with TCZ±csDMARD who achieved DAS28-ESR≤3.2 and had a stable GC dosage of 5 mg per day. Blinded tapering of GCs with continuation of TCZ resulted in a significant increase of disease activity in the discontinuation arm compared with patients who continued GCs (DAS28-ESR difference: 0.613; p<0.001). Sixty-five per cent of patients tapering GC remained in stable disease activity without experiencing a flare versus 77% of patients in the continued group. During tapering of GC, no difference in adverse events (AEs) was observed, especially no differences in the occurrence of adrenal insufficiency were reported.56 Other studies investigated the discontinuation of TCZ after achieving sustained DAS28-ESR<2.6. A follow-up of the ACT-RAY study showed that among patients who reached sustained DAS28-ESR<2.6 and discontinued TCZ, 238 of 472 patients (50.4%) achieved TCZ-free remission. However, a total of 200 patients (82.5%) subsequently flared following TCZ-free remission, with 82.5% of the TCZ+MTX combination group and 88.5% of the TCZ monotherapy group. The median time to flare once TCZ-free remission was reached was 113 days in the add-on group compared with 84 days in the switch group. The majority of patients (n=186; 94 patients from add-on and 92 from switch group) reinitiated TCZ after flaring and responded well to TCZ resumption by demonstrating improvements after restarting TCZ, with mean (SD) DAS28-ESR decreasing to 3.01 (1.25), 2.42 (1.18) and 2.19 (1.04) at three consecutive assessments visits 12 weeks apart after flare. Furthermore, the proportion of patients with high (DAS28-ESR>5.2) or moderate (DAS28-ESR>3.2 to≤5.2) disease activity was 29.7%, 18.6% and 11.7%, respectively, at these visits.21 In the second year of the SURPRISE study, at total of 105 patients who achieved DAS28-ESR<2.6 at week 52 discontinued TCZ. Among patients who had been previously receiving add-on treatment (TCZ+MTX) in the first year continued MTX alone, while patients in the switch arm (MTX switched to TCZ) continued without any DMARD. All patients were followed for additional 52 weeks. Numerically more patients who continued MTX (originally the add-on group) remained TCZ-free compared with patients in the switch group (67.3% vs 53.1%, p=0.22). Sustained DAS28 low disease activity states were observed more frequently in patients receiving MTX (add-on group). Radiological progression was numerically but not significantly higher in patients without DMARDs (switch group) at week 104 (mTSS; 0.37 vs 0.64, p=0.36).22
Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA), polyarticular-course juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pcJIA) and adult-onset Still’s disease (AoSD)
In sJIA, one pivotal RCT of TCZ (TENDER, unclear RoB) including 112 children with IR to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and GC was published (for details, see online supplemental tables S2.2.2, S2.3.2.1 and S2.4.2.1). TENDER confirmed improvements in signs and symptoms of sJIA during TCZ treatment and showed the clinically relevant GC-sparing effect. The primary end point, defined as JIA ACR 30 response and absence of fever at week 12, was met in significantly more patients of the TCZ group (85%) compared with the placebo arm (24%).57
In pcJIA, results of a phase III study (CHERISH, low RoB) demonstrated that TCZ was efficacious for the management of MTX-IR patients (for details, see online supplemental tables S2.2.3, S2.3.3.1 and S2.4.3.1). In the first part of CHERISH, all 188 patients received open-label TCZ, followed by a second part of double-blind, 24-week withdrawal phase in patients who achieved JIA-ACR 30 response. After the first study part, by week 16, a high proportion (89%) of patients achieved JIA-ACR30 response and 26% even achieved JIA-ACR90 response. The CHERISH study met its primary endpoint showing that patients in the placebo group experienced significantly more JIA-flares than TCZ-treated patients during the withdrawal phase. JIA flare occurred in 48.1% of patients on placebo versus 25.6% continuing TCZ at week 40.58 One study investigated radiographic progression over 2 years in the TENDER and CHERISH trial, reporting the potential of TCZ to delay radiographic progression in children with sJIA and pcJIA.59
AoSD is regarded a counterpart of sJIA in adulthood. In a double-blind RCT (low RoB) including 27 patients published in 2018, treatment with TCZ in AoSD-patients refractory to GC did not result in a significant difference concerning the achievement of the primary endpoint (ACR50 response at week 4) compared with placebo (ACR 50 at week 4: 61.5% vs 30.8%; p=0.24). However, TCZ was associated with a therapeutic benefit in systemic symptoms and steroid-sparing effects compared with the placebo group.60 In 2019, this pivotal trial led to the approval of TCZ for the treatment of AoSD in Japan. Study details are shown in online supplemental tables S2.2.4, S2.3.4.1 and S2.4.4.1)
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) and Takayasu arteritis (TAK)
Several studies evaluated the efficacy of bDMARDs targeting IL-6 pathway in systemic large-vessel vasculitides, especially GCA and TAK. In total, four reports on patients suffering from GCA were included in this SLR (for details, see online supplemental tables S2.2.5, S2.3.5.1 and S2.4.5.1). In the phase III GiACTA trial (low RoB), 251 patients were randomly assigned to receive TCZ weekly or every other week combined with a 26-week prednisone taper or placebo combined with a prednisone taper of either 26 weeks or 52 weeks. TCZ was superior to placebo in achievement of GC-free remission at week 52 in patients with GCA. Sustained GC-free remission at 52 weeks was achieved in 56% of the patients treated with TCZ weekly and 53% in the TCZ every other week arm, compared with 14% of patients receiving placebo and a 26-week prednisone taper and 18% of those in the placebo group with the 52-week prednisone taper scheme (p<0.001 active treatments vs placebo). In addition, the cumulative median prednisone dose over the 52-week period was significantly lower in each TCZ group, as compared with placebo (p<0.001 for all comparisons).61 Based on a 3-year analysis of GiACTA (conference abstract), time to first flare favoured TCZ weekly over TCZ every other week in patients with new-onset and relapsing GCA.62 One multicentre study published as a conference abstract compared the efficacy of SC TCZ versus intravenous TCZ. 91.7% patients who received SC TCZ achieved prolonged remission after 12 months of treatment compared with patients receiving intravenous TCZ (61.4%, p=0.043). Patients in the SC TCZ group were able to successfully discontinue prednisone treatment after 24 months, whereas the median GC sparing effect of the intravenous group was 2.4 after 24 months (IQR 0–5).63
Sirukumab was investigated in one phase III RCT (including 161 patients) providing numerically lower proportions of flares at week 52 in the sirukumab arm versus placebo. However, the study was terminated early due to a sponsor decision.64
One key trial, the TAKT study, a double-blind RCT with 36 patients performed in Japan, investigated the efficacy of TCZ in patients with refractory Takayasu arteritis during GC tapering (for details, see online supplemental tables S2.2.6, S2.3.6.1 and S2.4.6.1). The TAKT study suggested efficacy in favour of TCZ over placebo for time to relapse, although the primary endpoint was not statistically different between TCZ and placebo.65
Multicentric Castleman’s disease (MCD)
TCZ has been licensed for the treatment of MCD in Japan since 2005. Studies on TCZ were discussed in the previous SLR and included in the previous consensus statement.3 4 The current SLR identified one new study (low RoB) published after 2013, confirming the efficacy of siltuximab (SIL), a monoclonal antibody selectively targeting the IL-6 cytokine, in MCD (see online supplemental tables S2.2.7, S2.3.7.1 and S2.4.7.1 for details of the included study). In this RCT including 79 patients, SIL in combination with best supportive care demonstrated superiority versus best supportive care alone regarding tumour and symptomatic response in HIV-negative and human herpesvirus-8-seronegative patients with symptomatic MCD.66 This study subsequently led to the approval of SIL in the EU and USA.
CAR-T cell induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)
The approval of TCZ was based on a retrospective analysis of pooled data of adult and paediatric patients who developed CRS after treatment with CTL019 and KTE-C19 in prospective clinical trials including patients with B-cell lymphoma and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. In this analysis, 45 patients with CTL019-induced CRS and 15 patients with CRS due to KTE-C19 were included. Among patients diagnosed with severe or life-threatening CAR T-cell induced CRS, in the majority of patients who developed CRS after receiving CTL019, symptoms resolved on therapy with TCZ (69%, median time to response 4 days). Likewise, of patients receiving TCZ after CRS due to KTE-C19 53% were considered responders (median time to response 4.5 days).67 While data on CAR-T cell induced CRS are rare, due to the retrospective nature and missing comparator arms, this analysis was judged as having a high RoB. Baseline characteristics and efficacy outcomes are depicted in online supplemental tables S2.2.8, S2.3.8.1 and S2.4.8.1, respectively.
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD)
One open-label trial (high RoB) on TCZ and two RCTs (both with low RoB) on satralizumab (SAT) were available for efficacy evaluation in patients with relapsing NMOSD (for details, see online supplemental tables S2.2.9, S2.3.9.1 and S2.4.9.1). In the phase II/III TANGO trial, treatment with TCZ led to a significantly reduced risk of a subsequent NMOSD relapse compared with azathioprine. TCZ demonstrated a longer median time to the first relapse than azathioprine (78.9 vs 56.7 weeks; p=0.0026) as well as lower relapse rates at the end of the study (14% vs 59%; p<0.0001).68 In two phase III trials, SAT added to concomitant immunosuppressants69 or used as monotherapy70 resulted in a significant reduction of relapse rates compared with placebo. No differences in improvement of pain or fatigue with SAT were observed.69
Efficacy for other studied diseases
Of 8571 records from the database search, additional ACR/EULAR conference abstracts and publications found eligible for inclusion after hand search, 26 articles and 2 trials with data available on clinicaltrial.gov were finally included.
Studies in line with the previously formulated inclusion criteria investigating the efficacy of bDMARDs specifically targeting IL-6 pathway in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, remitting seronegative symmetric synovitis with pitting oedema (RS3PE), refractory relapsing polychondritis, TNF-receptor associated periodic fever syndrome (TRAPS) or chronic infantile neurological cutaneous and articular (CINCA) syndrome were not available, as the body of evidence was limited to case reports.
Nevertheless, there is a plethora of immune-mediated diseases in which selective inhibition of IL-6 pathway has been evaluated with or without success in several investigator-initiated studies. Characteristics of each trial including study population, baseline characteristics, risk of bias assessment, results of studies and summary data for each intervention group are elaborated in online supplemental section 3. A summary of the efficacy of bDMARDs selectively inhibiting IL-6 axis across immune-mediated diseases of interest is shown in table 2.
Table 2.
Efficacy outcomes of clinical trials published from 2012 to 2020 investigating bDMARDs specifically inhibiting IL-6 receptor or ligand compared against placebo or control group, shown across other studied immune-mediated diseases
| Disease | Study | Target | Population | Intervention/ Control |
Primary endpoint | Efficacy |
| Psoriatic arthritis | Mease et al6 (2016) phase IIb |
IL-6 | NSAID-IR and/or csDMARD bDMARD naïve | CLZ vs PBO | ACR 20 response at week 16 | |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | Sieper et al7 (2014)(BUILDER) phase II/III | IL-6R | TNFi-naïve | TCZ vs PBO | ASAS 20 response at week 12 | |
| Sieper et al8 (2015) (ALIGN) phase II | NSAID-IR | SAR vs PBO | ASAS 20 response at week 12 | |||
| Osteoarthritis | Richette et al71 (2020) (TIDOA) phase III | IL-6R | Refractory to analgetics | TCZ vs PBO | ΔVAS pain at week 6 | |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | Wallace et al9 (2017)(BUTTERFLY) phase II | IL-6 | Active disease (SLEDAI-2K/BILAG) | PF-04236921 vs PBO | SLE Responder Index (SRI-4) at week 24 | |
| Rovin et al10 (2016) phase II | Class III or class IV Lupus nephritis | SIR vs PBO | Reduction in proteinuria from baseline to week 24 | |||
|
NCT02437890 phase II |
IL-6R | Moderate to severe active SLE | ALX-0061 vs PBO | mBICLA response rate at week 24 | ||
| Myositis |
NCT02043548 phase II |
IL-6R | Refractory PM/DM | TCZ vs PBO | Mean total improvement scores at visits 2–7 | |
| Sjögren’s syndrome | Felten et al11 (2020) (ETAP) phase II/III | IL-6R | ESSDAI≥5 | TCZ vs PBO | Response to treatment at week 24* | |
| Multiple myeloma | San-Miguel et al75 (2014) phase II | IL-6 | Untreated MM and no candidate for stem cell transplantation | SIL+VMP vs VMP | Complete response rate† | |
| Brighton et al76 (2019) phase II | High-risk smouldering multiple myeloma | SIL vs PBO | 1-year progression-free survival rate | |||
| Systemic sclerosis associated ILD | Khanna et al74 (2020) (focuSSced) phase III | IL-6R | Diffuse cutaneous-SSc; mRSS 10–35; inflammatory status | TCZ vs PBO | ΔmRSS from baseline to week 48; secondary outcome: ΔFVC% predicted from baseline to week 48 | |
| Late antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection | Doberer et al77 (2020) phase II |
IL-6 | Kidney transplant recipients with donor-specific, antibody-positive ABMR | CLZ vs PBO | Safety and tolerability; secondary outcomes: course of eGFR, protein/creatinine ratio | |
| AA-amyloidosis | Okuda et al78 79 (2014/2016) retrospective analyses |
IL-6R | Amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis complicating rheumatic diseases | TCZ vs TNFi | Outcomes: retention rate, median ΔSAA, median ΔeGFR, mean ΔCDAI, mean ΔGC dose | |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | Lally et al80 (2016) open label, phase IIa |
IL-6R | PMR treated with GCs for ≤4 weeks | TCZ+GC vs GC | Relapse-free remission without GC treatment at 6 months | |
| Devauchelle-Pensec et al81 (2016) (TENOR) open label, phase II | Active disease defined as PMR-AS >10 | TCZ mono no control group | PMR-AS ≤10 at week 12 | |||
| COVID-19 CRS/pneumonia | Hermine et al90 (2020) (CORIMUNO-TOCI 1), open-label | IL-6R | Moderate to severe pneumonia | TCZ+SOC vs SOC | (1) % patients dead or needing NIV or mechanic ventilation on day 4 (scores>5 on WHO-CPS) and (2) survival without need of ventilation at day 14 | |
| Salvarani et al93 (2020) (RCT-TCZ-COVID-19), open-label | Mild pneumonia | TCZ+SOC vs SOC | Clinical worsening within 14 days‡ | |||
| Stone et al92 (2020) (BACC Bay Tocilizumab Trial), phase III | Mild pneumonia | TCZ+SOC vs PBO+SOC | Mechanical ventilation or death (time frame: 28 days) | |||
| Salama et al91 (2020) (EMPACTA), phase III | Moderate to severe pneumonia | TCZ+SOC vs PBO+SOC | Mechanical ventilation or death by day 28 |
Red denotes no difference comparted to placebo/control group; orange denotes promising results or rather mixed results across groups/trials and green denotes statistically superior compared with placebo or control group. For colorblind readers, table 2 is provided in the online supplemental appendix (section 7: S7.2).
*Response defined by combination of (1) decrease of at least 3 points in ESSDAI, (2) no new moderate/severe activity in any ESSDAI domain and (3) no worsening in physician’s global assessment on a visual numeric scale ≥1/10.
†Complete response (CR) based on European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) criteria
‡Defined by occurrence of 1 of the following events (whichever came first): (a) admission to intensive care unit with mechanical ventilation; (b) death or (c) paO2/FIO2 ratio <150 mm Hg.
ABMR, antibody-mediated rejection; ACR20, American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement criteria; ASAS20, Assessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis 20% response criteria; bDMARD, biological DMARD; BILAG, British Isles Lupus Assessment Group; CLZ, clazakizumab; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; DM, dermatomyositis; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; ESSDAI, EULAR Sjögren’s syndrome disease activity index; GC, glucocorticoids; ILD, interstitial lung disease; IR, inadequate response; mBICLA, modified BILAG-based Composite Lupus Assessment; MM, multiple myeloma; mRSS, modified Rodnan skin score; NIV, noninvasive ventilation; NSAID, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; %patients, proportion of patients; PBO, placebo; PM, polymyositis; PMR-AS, Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) Activity Score; SAR, sarilumab; SIL, siltuximab; SIR, sirukumab; SLEDAI-2K, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000; SOC, standard of care; SRI4, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Responder Index (SRI); TCZ, tocilizumab; TNF-i, tumour necrosis factor inhibitor; VMP, bortezomib-melphalan-prednisone; WHO-CPS, World Health Organization-Clinical Progression Scale; ΔCDAI, change in Clinical Disease Activity Index; ΔFVC%, change in percentage of predicted forced vital capacity; ΔmRSS, change in modified Rodnan skin score; ΔSAA, change in serum amyloid A (SAA) levels; ΔVAS, change in visual analogue scale.
In this context, current evidence indicates that IL-6 blockade does not seem to be effective in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) or axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). In a phase IIb, RCT in patients with active PsA, CLZ resolved musculoskeletal symptoms (arthritis, enthesitis and dactylitis) but did not improve skin manifestations.6 Currently, no further trials investigating the efficacy and appropriate dose of CLZ in PsA have been published. Also, TCZ and SAR failed to demonstrate therapeutic benefit in anti-TNF-naive patients with active axSpA.7 8 A phase III trial investigated the efficacy of TCZ in patients with hand osteoarthritis refractory to analgesics, exhibited no difference of TCZ over placebo to alleviate pain and improve function.71
Compounds specifically targeting IL-6 receptor or cytokine have undergone phase II or III clinical trials in patients with autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), primary Sjogren’s syndrome (pSS) and idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Common to all these trials is the concept of targeting IL-6-mediated signalling did not show superiority in clinical responses versus placebo. In particular, neither PF-04236921 (a fully human antibody specifically binding IL-6 ligand) was superior to placebo in patients with SLE9 nor did sirukumab demonstrate any benefit in patients with active lupus nephritis and persistent proteinuria.10 Inhibiting IL-6R with vobarilizumab (ALX-0061) did not meet the primary endpoint of dose response in patients with active SLE.72 Likewise, TCZ failed to show clinical improvement in patients with refractory adult polymyositis and dermatomyositis73 as well as in patients with pSS with moderate or high systemic disease activity.11
Several studies investigating selective IL-6 pathway inhibition have not formally reached their primary endpoint but implied clinically meaningful benefits across several secondary outcomes. This includes TCZ in systemic sclerosis (SSc) associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD). The primary endpoint of the phase III focuSSced trial was the difference in the mean change in modified Rodnan skin score at week 48. Despite the non-significant improvement of skin thickening as the primary outcome, change from baseline in forced vital capacity (FVC%) at week 48 favoured TCZ over placebo (difference in least squared mean FVC% change from baseline: 4.2; 95% CI 2.0 to 6.4; nominal p=0.0002), indicating a potentially beneficial effect of TCZ on preservation of lung function in SSc-ILD.74
The results of a phase II RCT of SIL in multiple myeloma (MM) did not show improved outcomes such as complete response, progression-free or overall survival in patients with untreated MM ineligible for high dose chemotherapy.75 SIL further failed to delay the transition from high-risk smouldering multiple myeloma to MM according to the prespecified protocol hypothesis criteria of increasing the 1-year progression-free survival rate by at least 14%.76
One phase II primarily safety powered RCT, evaluated the efficacy (secondary endpoint analysis) of clazakizumab versus placebo in late antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection (ABMR). CLZ was associated with an early decrease in donor-specific antibody levels, modulated antibody-mediated rejection activity and delayed the decrease of renal function (eGFR decline: CLZ −0.96; placebo −2.43 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per month; p=0.04), suggesting a clinically meaningful effect in ABMR.77
Only limited data on IL-6 inhibition in amyloidosis are available. Two retrospective analyses compared the clinical utility of TCZ and anti-TNF therapy in patients with Amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis complicating rheumatic diseases.78 79 Compared with TNF-inhibitors, one study found TCZ superior in the suppression of serum-AA levels and improving renal function.78 Both studies indicated favourable results for TCZ, which needs to be confirmed in future randomised studies. However, given the retrospective design and therefore low hierarchy of evidence, efficacy of TCZ in amyloidosis was judged as ‘promising results’ (table 2).
TCZ has been effective in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) according to case reports.3 This SLR yielded two reports on prospective, open-label phase II trials on TCZ emphasising its steroid-sparing effect80 as well as clinical and serological improvement in recent-onset PMR when used as monotherapy.81 In view of the high RoB of both studies and absence of a comparator arm in one report,81 results of phase III trials of TCZ (NCT03263715 and NCT02908217) and SAR (NCT03600818) are awaited as outcomes were not available in the public domain during the SLR’s time frame.
Finally, given the global crisis due to SARS-CoV-2 infection, causing the disease COVID-19 that is associated with heightened cytokine release including IL-6 and hyperinflammation,82 this SLR aimed to summarise the best available evidence on the use of agents selectively targeting IL-6 axis for the management of SARS-CoV-2 infection. A total of 11 studies at variable risk of bias, among them 4 RCTs, evaluating the therapeutic approach of TCZ or SAR in severe or critical COVID-19 were included (online supplemental table S3.1.14). For cohort studies (n=7), RoB was assessed using the validated NOS. Variability in inclusion criteria and therefore illness severity, study design and also size of the population enrolled, timepoint of treatment initiation, observation period, definition of primary endpoint and imbalances in the use of concomitant standard of care (SOC) treatment or rather steroids could affect the interpretation and comparability of the results. Most of the studies included moderately to severely ill patients with hyperinflammatory state requiring oxygen support. Treatment with TCZ was associated with lower hazards regarding intubation or death in two retrospective cohort studies.83 84 In case of requirement of intensive care unit (ICU) support for critically ill patients, three retrospective observational studies demonstrated positive effects of TCZ on hospital-related mortality.85–87 Furthermore, one prospective study with a historical control group investigated the efficacy of high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone (MP) with or without TCZ in hyperinflamed COVID-19 patients with rapid respiratory deterioration and requiring any oxygen support. The historical control group received supportive care only (no steroids) and in the intervention group, and TCZ was added if respiratory condition had not improved sufficiently through MP. Treatment with TCZ demonstrated a benefit of MP and TCZ concerning clinical improvement in respiratory status, likelihood to evolve to IMV, duration of hospitalisation and mortality.88 Conversely, one small prospective trial failed to show any mortality benefit for SAR.89 The promising results of observational studies led to execution of randomised clinical trials; four randomised trials (including two phase III trials) which, however, excluded critically ill patients, were available (table 2). The CORIMUNO-TOCI I trial, in patients requiring at least 3 L/min oxygen therapy but not admitted to the ICU, reported reduced risk of non-invasive ventilation, IMV or death at day 14, when TCZ was added to SOC. However, no difference was found between groups concerning day-28 mortality.90 A similar trial, the EMPACTA trial, a RCT assessing the efficacy of TCZ in ethnic minority populations, showed that TCZ+SOC was more efficacious than SOC alone in reducing a composite outcome of IMV or death, but no reduction in day-28 mortality was observed.91 Two additional randomised trails failed to provide any benefit of treatment strategies including TCZ on disease progression and other efficacy outcomes, respectively.92 93
Safety
In total, 66 publications addressing the safety profile of bDMARDs targeting IL-6R or IL-6 ligand were included in this SLR. Safety data derived mainly from observational studies, such as cohort studies and real-word registries arising from TCZ in patients with RA and JIA, whereas for compounds with no registry data available (eg, SAR and sirukumab), randomised controlled trials and LTEs were applied as primary source of information. Characteristics of each individual article included, namely, inclusion and exclusion criteria, RoB and safety outcomes for each intervention group were extracted in detail and are listed in section 4 in the online supplemental appendix grouped according to the outcome of interest.
Cardiovascular events and venous thromboembolism
Six observational studies and one RCT addressing cardiovascular (CV) events and venous thromboembolism (VTE) were included (online supplemental table S4.1.1.1–S4.1.6.2). Overall, the risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), myocardial infarction, stroke or rather transient ischaemic attack, heart failure and coronary revascularisation was not increased in patients with RA receiving TCZ compared with those on TNFi, abatacept or rituximab.94–100 In ENTRACTE, a randomised controlled head-to-head trial assessing the CV safety of TCZ and etanercept (ETN) in patients with RA, for fatal and nonfatal stroke, 26 events occurred in the TCZ group (n=1538) compared with 16 events in the ETN treatment arm (n=1542). A total of 83 MACE occurred in TCZ recipients during follow-up compared with 78 in the ETN group. The estimated hazard ratio (HR) for occurrence of MACE in the TCZ group relative to the ETN group was 1.05 (95% CI 0.77–1.43). Additionally, risks of developing VTE (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) were evaluated in ENTRACTE, which reported only a small number of events and no increased risk for TCZ compared with ETN-treated patients.97
Infections
In total, 15 observational studies investigated the risk of infections in patients receiving TCZ compared with those treated with TNF-inhibitors or non-TNF bDMARDs including abatacept and rituximab (see online supplemental tables S4.3.1.1–S4.3.5.3 for details of included reports). IL-6 inhibition with TCZ was associated with an increased risk of hospitalisation for overall serious bacterial infections (SI) compared with non-treated patients, which, however, was in line with rates seen with other bDMARDs.101–106 TCZ was found to have a significantly higher rate of SI compared with ETN in both the adjusted and unadjusted models (HR for adjusted models: 1.21, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.46) in a British observational cohort study.107 Similarly, in the above-mentioned ENTRACTE trial, infections (any infections and serious infections) were more frequently observed in the TCZ- than in the ETN-arm (HR for serious infections 1.39, 95% CI 1.08 to 1.79).97 An increased risk of certain types of serious infections (septicaemia, pneumonia, other upper respiratory tract and skin infections) was observed in TCZ versus TNF-i users in two cohort studies. Of note is, that these observations could not be consistently replicated in other studies and the estimates showed significant variability.107 108 Also, according to Pawar et al, the risk of composite serious infections was higher in TCZ initiators compared with abatacept initiators (pooled HR 1.40, 95% CI 1.20 to 1.63). However, composite risk of TCZ for serious infections requiring hospitalisation for infectious AE was comparable to TNF-i.108 Current evidence suggests that TCZ does not show an increased risk for herpes zoster, opportunistic infections or tuberculosis in comparison to TNF-inhibition or ABA.108–114
Malignancies
Data from four large RA observational studies suggested no increased risk of TCZ in total occurrence of malignant neoplasms, nor did TCZ show any signal of a higher risk for specific cancer types (including invasive melanoma and lymphoma) in comparison with csDMARDs, other bDMARDs or the general population.115–118 Details on studies investigating risks of malignancies are depicted in online supplemental tables S4.4.1.1–S4.4.6.3.
Gastrointestinal and hepatic events
The risk for diverticulitis and any gastrointestinal (GI) infections was investigated in three cohort studies (high RoB: n=1; low RoB: n=1; conference abstract: n=1; for details on baseline characteristics, RoB assessment and safety outcomes (see online supplemental tables S4.5.1.1–S4.5.1.3). One study reported an elevated risk of diverticulitis during TCZ treatment compared with TNF inhibitors (HR 2.34, 95% CI 1.64 to 3.34).108 Higher rates of any GI infections were observed with TCZ compared with ETN as reference compound in another study (HR 1.45, 95% CI 0.72 to 2.90).107 Similarly, a conference abstract assessed the risk of diverticulitis in patients with RA: three prospective observational French registries, confirmed an elevated risk of diverticulitis for TCZ compared with RTX-treated or ABA-treated patients.119
Events of GI perforations, in particular diverticular perforations as complications of diverticulitis have been increasingly reported in patients with RA with TCZ exposure.3 The overall risk of gastrointestinal perforations (GIP) including both the upper and lower GI tract was investigated in five cohort studies including populations with long-term exposure of TCZ (low RoB: n=1; high RoB: n=3; conference abstracts: n=1). GI perforations that required hospitalisation were significantly more frequent among TCZ than among TNF-inhibitors, RTX and ABA. In the majority of cases, the lower GI tract was involved.119 120 Overall incidence rates for lower GI perforations (LIP) under TCZ treatment were markedly increased compared with csDMARDs, TNF-inhibitors, RTX121 or the general population.122 Two of the included studies were further adjusted for concomitant treatment with GC and NSAIDs120 121 and two for history of diverticulitis.120 123 Diverticulitis itself was more often associated with perforation in TCZ exposed patients than in patients treated with other agents.119 121 Likewise in the ENTRACTE trial, eight confirmed GI perforation events occurred in the TCZ arm, compared with one event in the ETN arm. The estimated HR for occurrence of GI-perforations in the TCZ group relative to the ETN group was 8.43 (95% CI 1.06–67.26), accepting event numbers were small.97 Additionally, one observational study indicated a pronounced LIP risk for both TCZ (HR 2.55, 95% CI 1.33 to 4.88) and tofacitinib treatment, when compared with TNF-i (HR 3.24, 95% CI 1.05 to 10.04). However, incidence of upper tract GIP remained comparable between TCZ and other bDMARDs in the same study.123 Study details are shown in online supplemental tables S4.5.2.1–S4.5.2.3. Table 3 provides a summary of the data comparing GI perforation risk of TCZ versus other DMARDs stratified by any, upper and lower perforation.
Table 3.
Safety outcomes in observational studies regarding GIP: comparison between TCZ and other bDMARDs/csDMARDs, tsDMARDs and general population
| Study | Treatment group | N patients | N events | Incidence rate (95% CI) |
aHR (I vs C) | |
| Monemi et al (2016)*120 | Combined TNF-i (ADA, ETN, IFX) | 17 333 | 10 | 0.6/1000 PY (0.3 to 1.2) | REF | REF |
| TCZ | 3602 | 6 | 1.8/1000 PY (0.7 to 4.0) | 2.2 (0.7 to 6.6) | 2.2 (0.9 to 5.4) | |
| Monemi et al (2016)†120 | Combined TNF-i (ADA, ETN, IFX) | 17 333 | 6 | 0.4/1000 PY (0.1 to 0.8) | REF | REF |
| TCZ | 3602 | 5 | 1.5/1000 PY (0.5 to 3.6) | 4.0 (1.1 to 14.1) | 3.1 (1.1 to 8.4) | |
| Rempenault et al (2019) (EULAR 2020)*119 | TCZ | 1496 | 9 | 2.3/1000 PY | TCZ vs RTX: 2.8 (1.5 to 5.1) TCZ vs ABA: 5.4 (1.4 to 19.9) |
|
| RTX | 1986 | 8 | 1.3/1000 PY | |||
| ABA | 1019 | 2 | 0.8/1000 PY | |||
| Rempenault et al (2019) (EULAR 2020)§119 | TCZ | 1496 | 6 | 1.5/1000 PY | TCZ vs RTX: 3.8 (1.7 to 8.5) TCZ vs ABA: 6.9 (1.9 to 25.4) |
|
| RTX | 1986 | 3 | 0.5/1000 PY | |||
| ABA | 1019 | 2 | 0.8/1000 PY | |||
| Rempenault et al (2019) (EULAR 2020)¶ 119 |
TCZ | 1496 | 3 | 0.7/1000 PY | TCZ vs RTX: 1.4 (0.5 to 3.9) TCZ vs ABA: NAP |
|
| RTX | 1986 | 5 | 0.8/1000 PY | |||
| ABA | 1019 | 0 | – | |||
| Strangfeld et al (2017)†121 | csDMARD | 4423 | 11 | 0.61/1000 PY (0.3 to 1.1) | REF | |
| TNF-i | 6711 | 13 | 0.52/1000 PY (0.3 to 0.9) | 1.04 (0.48 to 2.26) | ||
| TCZ | 877 | 11 | 2.69/1000 PY (1.4 to 4.8) | 4.48 (2.01 to 9.99) | ||
| other bDMARDs (RTX+ABA) | NR | NR | NR | 0.33 (0.08 to 1.44) | ||
| Barbulescu et al (2020)†122 | General population | 76 304 | 333 | 1.07/1000 PY (0.95 to 1.33) | REF | NAP |
| Bionaïve patients with RA | 62 532 | 570 | 1.60/1000 PY (1.46 to 1.74) | 1.02 | NAP | |
| TNF-i | 17 594 | 57 | 1.84/1000 PY (1.38 to 3.63) | 0.99 | REF | |
| ABA | 2527 | 13 | 3.32/1000 PY (1.66 to 16.6) | 1.41 | 1.07 (0.55 to 2.10) | |
| RTX | 3552 | 22 | 2.02/1000 PY (1.26 to 5.65) | 1.07 | 0.89 (0.50 to 1.58) | |
| TCZ | 2377 | 22 | 4.51/1000 PY (2.68 to 10.4) | 2.36 | 2.20 (1.28 to 3.79) | |
| Xie et al (2016)*123 | Combined TNF-i | 115 044 | 109 | 0.83/1000 PY (0.69 to 1.00) | NR | |
| TCZ | 11 705 | 16 | 1.55/1000 PY (0.95 to 2.54) | NR | ||
| TOFA | 4755 | 3 | 0.86/1000 PY (0.10 to 3.60) | NR | ||
| Xie et al (2016)†123 | Combined TNF-i | 115 044 | 59 | 0.46/1000 PY (0.35 to 0.58) | REF | |
| ABA | 31 214 | 30 | 0.76/1000 PY (0.53 to 1.09) | 1.41 (0.90 to 2.21) | ||
| RTX | 4391 | 2 | 0.48/1000 PY (0.06 to 1.75) | 1.72 (0.52 to 5.69) | ||
| TCZ | 11 705 | 13 | 1.26/1000 PY (0.73 to 2.18) | 2.55 (1.33 to 4.88) | ||
| TOFA | 4755 | 2 | 0.86/1000 PY (0.10 to 3.60) | 3.24 (1.05 to 10.04) | ||
| Xie et al (2016)‡123 | Combined TNF-i | 115 044 | 49 | 0.38/1000 PY (0.28 to 0.50) | NR | |
| ABA | 31 214 | 12 | 0.31/1000 PY (0.17 to 0.54) | NR | ||
| RTX | 4391 | 1 | 0.24/1000 PY (0.01 to 1.35) | NR | ||
| TCZ | 11 705 | 3 | 0.29/1000 PY (0.06 to 0.85) | NR | ||
| TOFA | 4755 | 0 | 0.00/1000 PY (0.00 to 1.58) | NR | ||
Detailed results are shown in online supplemental tables S4.5.2.1–S4.5.2.3.
*Any GIP.
†Lower GIP.
‡Upper GIP.
§GIP due to diverticulitis (diverticular GIP).
¶GIP due to another aetiology.
ABA, abatacept; ADA, adalimumab; aHR, adjusted HR; bDMARD, biological DMARD; C, control; CI, confidence interval; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; DMARD, disease-modifying antirheumatic drug; ETN, etanercept; GIP, gastrointestinal perforations; I, intervention; IFX, infliximab; N, number; NAP, not applicable; NR, not reported; PY, patient years; REF, reference; RTX, rituximab; TCZ, tocilizumab; TNF-i, tumour necrosis factor inhibitor; TOFA, tofacitinib; tsDMARD, target synthetic DMARD.
The risk of hepatic events was investigated in two studies (moderate RoB: n=1; high RoB: n=1) (for details, see online supplemental tables S4.5.3.1–S4.5.3.4). Hepatic transaminase elevations with TCZ were frequent, but rates of hepatic severe AEs were low in a clinical trial setting. Of note, transaminase elevations were observed more frequently when TCZ was combined with MTX/DMARD compared with monotherapy.124 A postmarketing study from Japan investigated patients who had a history of hepatitis B/C virus or were virus carriers—no patient experienced a viral reactivation (with or without hepatitis) after exposure to TCZ.125
Vaccination
In total, five studies (all with high RoB) addressed the safety and efficacy of vaccination during TCZ therapy (online supplemental tables S4.2.1.1–S4.2.1.3). Overall, IL-6 inhibition with TCZ did not hamper antibody response to influenza, pneumococcal and tetanus toxoid vaccines in patients with RA.126–128 Similarly, safety and efficacy of influenza vaccination did not differ significantly between patients with sJIA and healthy controls.129 One study reported a negative impact of MTX on pneumococcal antibody response, when TCZ was used in combination with MTX in patients with RA.130
Adverse events of special interest
Several studies investigating AEs) of special interest could be included (details shown in online supplemental tables S4.6.1.1–S4.6.11.9). For completeness, all RCTs with a valid comparator and LTEs assessing the safety aspects of SAR and sirukumab were evaluated (online supplemental tables S4.6.10.1–S4.6.10.11). In terms of the other IL-6 receptor or ligand targeting compounds without observational data available, the overall safety profile or incidence of major AEs in all clinical trials was comparable to that of to TCZ.
Studies addressing the risk of withdrawals due to AEs and immunological reactions reported results in line with the available evidence of TCZ and other bDMARDs;131–136 however, one study showed a significantly higher discontinuation rate due to AEs in elderly patients with RA receiving TCZ compared with those treated with ABA. Nonetheless, apart from TCZ, several TNF inhibitors comprising ADA, ETN, golimumab and infliximab were associated with significantly higher discontinuation rate by AEs compared with ABA.137
As inhibition of the IL-6 axis is associated with higher risk for dyslipidaemia, two studies investigated the effect of TCZ on lipid-associated CV risk markers, reporting that median total-cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and triglyceride levels increased in TCZ treatment arms when compared with placebo and ADA. Notably, TCZ modified high-density lipoprotein particles changed towards an anti-inflammatory composition and favourably altered some other vascular risk surrogates, such as lipoprotein (a).138 139 The overall net effect on CV risk of TCZ is therefore difficult to predict based on established or novel risk factor changes alone. For this reason, the results of the ENTRACTE trial, suggesting no increased risk of MACE with TCZ versus ETN, are reassuring.97
Moreover, TCZ showed no risk of worsening diabetes status in terms of therapy intensification and switching to insulin in comparison to other bDMARDs.140 Consistent results were observed with SAR in a posthoc analysis, where SAR was associated with a greater reduction in glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) than placebo or ADA in patients with diabetes.141
Safety analyses of TCZ on haematological variables found significant increases in haemoglobin and haematocrit levels in anaemic and non-anaemic patients with RA compared with other biological and non-biological DMARDs. By contrast, TCZ-treated patients had higher rates of grade 1/2 or 3/4 neutropenia than placebo; however, neutropenia was not associated with serious infections and improved after dose reduction or discontinuation of TCZ.142 143
A stable safety and tolerability profile of TCZ in patients with RA was additionally reported in patients exhibiting renal insufficiency, regardless of MTX usage.144 No safety signal could be identified regarding the risk of ILD and its related complications,145 idiopathic facial nerve palsies146 or osteoporotic fractures.147
Only limited data regarding pregnancy outcomes were available. One safety database including clinical trials and postmarketing data as well as case series did not suggest a higher risk for malformations after exposure to TCZ shortly before conception or early pregnancy.148 149 Nevertheless, an increased rate of preterm birth (31.2%) was observed in TCZ users compared with the general population. No signal of adverse pregnancy outcomes was reported in the same analysis with paternal exposure to TCZ in 13 pregnancies.148 Overall, considering the currently insufficient evidence base, it cannot be suggested to continue TCZ therapy in case of pregnancy.
Safety data in terms of SAR were retrieved from three RCTs and one LTE, concluding comparable safety and tolerability profiles to TCZ without new signals emerging (online supplemental tables S4.6.10.1–S4.6.10.6).28 150–152
In contrast, numerical differences in mortality were observed in sirukumab-treated patients compared with control arms34 153 (for details, see online supplemental tables S4.6.10.7–S4.6.10.11). CV events, infections and malignancies were the underlying causes of deaths. In 2017, the FDA declined the approval of SIR for RA demanding ancillary clinical data for further safety evaluation.154 LTE safety outcomes of SAR and SIR are summarised in table 4.
Table 4.
LTEs investigating the safety profile of SAR and SIR
| Study | Trial | Treatment group | N patients | Any serious AEs Events: n (%) |
Serious infections Events: n (%) |
GI-perforations Events: n (%) |
Any major CVE Events: n (%) |
Any malignancy Events: n (%) |
Deaths of any cause Events: n (%) |
| Fleischmann et al152 | MOBILITY TARGET ASCERTAIN ONE COMPARE EASY EXTEND |
SAR 150/200/100 mg Q2W or SAR 100/150 mg QW+DMARD |
2887 | 685 (23.7) | 232 (8.0) | 9 (0.3) | 41 (1.4) | 52 (1.8) | 31 (1.1) |
| SAR Mono | 471 | 52 (11.0) | 7 (1.5) | 0 | 2 (0.4) | 4 (0.8) | 5 (1.1) | ||
| Thorne et al153 | SIRROUND-D (2 years) |
Placebo | 556 | 40 (7.2) | 11 (2.0) | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.2) | 2 (0.4) | 1 (0.2) |
| SIR 50 mg Q4W | 798 | 141 (17.7) | 58 (7.3) | 3 (0.4) | 13 (1.6) | 8 (1.0) | 10 (1.3) | ||
| SIR 100 mg Q2W | 799 | 132 (16.5) | 47 (5.9) | 1 (0.1) | 5 (0.6) | 12 (1.5) | 11 (1.4) | ||
| SIR combined | 1597 | 273 (17.1) | 105 (6.6) | 4 (0.3) | 18 (1.1) | 20 (1.3) | 21 (1.3) |
Detailed results are shown in online supplemental tables S4.6.10.4–S4.6.10.6 and S4.6.10.10–S4.6.10.11.
AE, adverse events; CVE, cardiovascular event; DMARD, disease-modifying antirheumatic drug; GIP, gastrointestinal perforations; LTEs, long-term extension studies; mono, monotherapy; N, number; Q2W, every other week; Q4W, every 4 weeks; QW, every week; SAR, sarilumab; SIR, sirukumab.
In JIA, this SLR presents the pertinent evidence from observational studies suggesting no increased risk of hospitalisation due to overall serious bacterial infections, tuberculosis, malignancies, GI perforations, hepatic events or rare events such as demyelination through TCZ as opposed to TNF-i and other bDMARDs. In addition, studies addressing the risk of withdrawals due to AEs and incidence of macrophage activation syndrome reported comparable results between TCZ and bDMARDs.155–157 Study outcomes are detailed in online supplemental tables S4.6.11.1–S4.6.11.9.
Biomarkers for prediction of therapeutic response
A total of 20 reports (including three conference abstracts) investigating the applicability of predictors of treatment success and clinical outcome of bDMARDs selectively targeting the IL-6 pathway were included. Different variables including CRP,158 serum IL-6 concentration,159–162 baseline anticitrullinated peptide antibody status,163 type I interferon signalling and metallothionein proteins164 as well as cellular and synovial,165–167 cardiac,168–171 genetic markers,172 173 parameters of bone metabolism174 and body mass index175–177 were evaluated as possible predictors of clinical outcomes. Investigated biomarkers and detailed results are listed in online supplemental table S5.1 and S5.2, respectively. Current data suggest, to some extent, a certain association for different markers with clinical response. This includes low pretreatment IL-6 levels—which were predictive for response to TCZ or to sustained success after its cessation.159 160 Apart from that, a high pretreatment CRP level was indicative of good treatment responses in patients receiving TCZ.158 Data regarding obesity and treatment response, on the other hand, were more controversial.175–177 Generally, the quality of currently available evidence is considered as being low and further studies are required to confirm the validity of these analyses.
Patient adherence/ preferences and economic aspects
Eleven studies on patient perspectives were included (online supplemental appendix table S6.1). Treatment with TCZ resulted in meaningful improvements of patient-reported outcomes (PROs), such as pain, physical function, activity impairment and quality of life.178 179 In RCTs, TCZ and SAR monotherapy yielded greater improvements across multiple PROs than csDMARD or TNF-i (ADA).180 181 Among patients with RA who had previously received ≥1 bDMARD, TCZ treated patients showed a similar or significantly better biological persistence than those receiving other bDMARDs.182 Moreover, fatigue and physical function significantly improved in TCZ treated GCA-patients compared with those receiving steroids only.183 In JIA, patients switching route of administration from intravenous to SC reported satisfaction in terms of life quality, school success and reduced school absenteeism.184 On the other side, in patients with RA, TCZ discontinuation was predicted by low initial CRP levels, high scale on the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), high fatigue and pain, smoking and exposure to bDMARD before TCZ therapy.185 186 Finally, five studies addressing the cost-effectiveness related to the usage of TCZ and SAR were included. Details of economic analyses and outcomes are shown in online supplemental appendix table S6.2. Overall, data on adjusted indirect comparison and cost-effectiveness suggested better results for TCZ and SAR compared with other bDMARDs, although these results should be interpreted with caution as quality of evidence is low.
Discussion
With this SLR, we have obtained an update of the emerging evidence on agents that selectively target the IL-6 pathway by including new data from 2012 onwards. In retrospect, the scope of indications, both licensed and off-label, has extended over the past few years, and the availability of large-scale observational studies made it possible to gain a deep insight into long-term safety. Efficacy has been confirmed across various inflammatory diseases, especially in rheumatic diseases such as RA, JIA, AoSD, GCA, TAK and SSc-LD. Especially in RA, new data allowed us to refine the use of TCZ and other agents. Important findings in this SLR are the clinical efficacy of several novel compounds targeting both the IL-6 receptor (SAR) and IL-6 ligand (olokizumab, sirukumab) in patients with RA. Consistent efficacy results led to the approval of SAR as the second IL-6R blocker for RA in 2017. The humanised IL-6 ligand blocker OKZ is currently licensed for the treatment of RA in Russia only. Sirukumab was ultimately not approved by the FDA in 2017 due to safety concerns. Also, based on results from strategic studies, it can be concluded that in patients who are not suitable for csDMARD combination therapy, IL-6 pathway inhibitors may have some advantages over TNF-inhibitors. TCZ monotherapy may be a legitimate option in RA; however, trends for a worse clinical outcome and a more pronounced radiographic progression in the monotherapy group were observed when compared with combination therapy with MTX. Tapering concomitant MTX or steroids was possible in patients who were in sustained low disease activity or remission, but nevertheless constitutes a risk of flare.
In addition, TCZ was used to successfully treat CRS due to T cell therapy, and newcomers like SAT and the licensed anti-IL-6 ligand antibody SIL have expanded the therapeutic approaches for Castleman’s disease and neuromyelitis optica, respectively. Targeting IL-6 in several diseases (including PsA, axSpA or connective tissue diseases, except for ILD in SSc) was not effective in several clinical trials. In COVID-19, TCZ-treated critically ill patients showed a decreased mortality in subgroup analyses. Noteworthy is that the authorisations of TCZ for treatment of hospitalised adults and paediatric patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pneumonia and SSc-associated interstitial lung disease (ILD), respectively, were effectuated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), but this happened after the last literature search update of this SLR.187 188 Likewise, in December 2021, TCZ received rapid European Commission approval for the treatment of COVID-19 in adults treated with systemic corticosteroids and requiring supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation.189 TCZ demonstrated better clinical outcomes and decreased mortality in severely ill patients, particularly those had received previous dexamethasone treatment.190 191 Meanwhile, treating critically ill patients with COVID-19 with either TCZ or baricitinib (a Janus Kinase inhibitor) after failing dexamethasone therapy has become standard of care.
Safety data deriving from observational studies allowed to gain further insights into long-term safety, especially focusing on less frequent or rare AEs. The risk of cardiac events, VTE or malignancy did not differ from other bDMARDs and csDMARDs. Observational studies suggested a potential increased risk for certain infections such as skin infections as well as diverticulitis in TCZ versus TNF-i treated patients. Observational studies on patients receiving TCZ showed that the risk of diverticulitis lower GI perforations is overall low, but higher compared with other bDMARDs and in line with previously published reports. Properly designed studies on other IL-6 blocking agents are required to study whether this increased risk of GI perforations is specific to TCZ or a potential class effect.
This SLR has several limitations: (1) only one researcher (KK) evaluated all retrieved publications by title and abstract screening for eligibility and assessed the risk of bias; however, whenever a question of uncertainty arose, the paper was discussed with the methodologist (AK); (2) due to the heterogeneity of the available studies, no pooling of efficacy or safety outcomes by meta-analysis were performed; (3) safety analyses are mainly based on observational studies on TCZ in patients with RA and JIA, limiting the interpretability of the safety profile with regard to other populations and other bDMARDs selectively targeting IL-6 receptor or cytokine.
The results of this SLR were presented to inform the consensus statement on efficacy and safety of pharmacological treatment with IL-6 pathway inhibition with biological DMARDs in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
Footnotes
Contributors: All authors critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript. KK and DA had access to the data, controlled the decision to publish and accept full responsibility for the finished work of the study. DA is the guarantor of the study. KK: conduction of the literature search, data extraction, manuscript draft and preparation, figure development. DA: planning and conception of the study, interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. GRB: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. EC: literature search, manuscript preparation. CD: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. MD: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. IBM: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. AR: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. NS: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. TAS: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. TT: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. MT: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. DvdH: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. MJHV: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. KW: interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. JSS: planning and conception of the study, interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development. AK: planning and conception of the study, interpretation of results, manuscript preparation, figure development.
Funding: This study was supported by grants from Sanofi. The company had no influence on the selection of the participants, did not attend any meetings and had no influence the contents of the present manuscript.
Competing interests: KK: honoraria for lectures, presentations: Boehringer Ingelheim, UCB Pharma, Eli Lilly and AbbVie; support for attending meetings and/or travel: AbbVie, Gilead, Sandoz, Pfizer, AstraZeneca and Bristol-Myers Squibb. DA: grants: AbbVie, Amgen, Lilly, Novartis, Roche, SoBi and Sanofi; consulting/lecture fees: AbbVie, Amgen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Sandoz. GRB: consulting fees: AbbVie, Galapagos, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi; honoraria for lectures, presentations: AbbVie, Galapagos, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi. EC: has no financial relationship to disclose. CD: grants: FWF Austria and Celgene; consulting fees and honoraria for lectures/presentations: AbbVie, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Janssen, Novartis, Lilly and Galapagos; support for attending meetings and/or travel: AbbVie, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Janssen, Novartis, Lilly and Galapagos; receipt of equipment, materials, drugs, medical writing, gifts or other services: MSD. MD: consulting fees: Roche, Sanofi, Pfizer, AbbVie, Lilly, BMS, Merck, Galapagos and UCB; honoraria fees for participations at symposia and advisory boards: Roche, Sanofi, AbbVie, Pfizer, Lilly, UCB, Merck, Galapagos and Novartis; his department received grants from: Roche, Sanofi, Pfizer, AbbVie, Lilly, BMS, Merck, Galapagos and UCB. IBM: grants: AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Amgen and Novartis; consulting fees: AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi Regeneron, Novartis, Gilead, Amgen, UCB, GSK and Moonlake; honoraria for lectures, presentations: AbbVie; IBM is also vice principal and head of MVLS College of University of Glasgow and board member of NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde and Evelo; stock: Causeway Therapeutics, Compugen, Cabaletta and EveloBio. AR: grants: Pfizer and Novartis; speaker fees/advisory boards: AbbVie, Angelini, BMS, Centocor, Pfizer, Roche, Novartis and Reckitt Benckiser; AR is also president of the Pediatric Rheumatology European Society (PReS). NS: consulting fees: Amgen, AstraZeneca, Affimune, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli-Lilly, Hanmi Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Novartis, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi and his University has received grant funds for research from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis and Roche Diagnostics. TAS: grant/research support: AbbVie and Roche; consulting fees: AbbVie and Sanofi Genzyme; speaker fees: AbbVie, Roche, Sanofi and Takeda. TT: grants: Asahi Kasei Pharma, Chugai Pharmaceutical; speaking and consulting fees: Bristol Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical, Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., R-Pharma, Sanofi.K.K. MT: grants/ research support: Albireo, Cymabay, Falk, Gilead, Intercept, MSD, Takeda, Alnylam, Ultragenyx; speaker and/or consultant and/or advisory board member: Albireo, BioMX, Boehringer Ingelheim, Falk, Genfit, Gilead, Intercept, Jansen, MSD, Novartis, Phenex, Regulus and Shire; travel support: AbbVie, Falk, Gilead and Intercept; MT is also coinventor of patents on the medical use of 24-norursodeoxycholic acid. DvdH: consulting fees: AbbVie, Bayer, BMS, Cyxone, Eisai, Galapagos, Gilead, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB Pharma; DvdH is also director of Imaging Rheumatology bv. MJHV: has no financial relationship to disclose. KW: research funding: BMS and Pfizer; consulting fees: Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB, Eli Lilly & Company, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Roche, Gilead, BMS, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca and Novartis. JSS: grants/consulting and personal fees: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Novartis, Amgen, Astro, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Celltrion, Chugai, Gilead, ILTOO, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis-Sandoz, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung and UCB. AK: honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, UCB and Pfizer.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
References
- 1.Choy EH, De Benedetti F, Takeuchi T, et al. Translating IL-6 biology into effective treatments. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2020;16:335–45. 10.1038/s41584-020-0419-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2014;6:a016295. 10.1101/cshperspect.a016295 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schoels MM, van der Heijde D, Breedveld FC, et al. Blocking the effects of interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory rheumatic diseases: systematic literature review and meta-analysis informing a consensus statement. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:583–9. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202470 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Smolen JS, Schoels MM, Nishimoto N, et al. Consensus statement on blocking the effects of interleukin-6 and in particular by interleukin-6 receptor inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:482–92. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kang S, Tanaka T, Narazaki M, et al. Targeting interleukin-6 signaling in clinic. Immunity 2019;50:1007–23. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mease PJ, Gottlieb AB, Berman A, et al. The efficacy and safety of Clazakizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody, in a phase IIb study of adults with active psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:2163–73. 10.1002/art.39700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sieper J, Porter-Brown B, Thompson L, et al. Assessment of short-term symptomatic efficacy of tocilizumab in ankylosing spondylitis: results of randomised, placebo-controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:95–100. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sieper J, Braun J, Kay J, et al. Sarilumab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: results of a phase II, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (align). Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:1051–7. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204963 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wallace DJ, Strand V, Merrill JT, et al. Efficacy and safety of an interleukin 6 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase II dose-ranging randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:534–42. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209668 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rovin BH, van Vollenhoven RF, Aranow C, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of treatment with Sirukumab (CNTO 136) in patients with active lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:2174–83. 10.1002/art.39722 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Felten R, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Seror R, et al. Interleukin 6 receptor inhibition in primary Sjögren syndrome: a multicentre double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:329–38. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218467 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Huizinga TWJ, Fleischmann RM, Jasson M, et al. Sarilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody against IL-6Rα in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: efficacy and safety results from the randomised SARIL-RA-MOBILITY Part a trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1626–34. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Baek HJ, Lim MJ, Park W, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in Korean patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:917–31. 10.3904/kjim.2017.159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yazici Y, Curtis JR, Ince A, et al. Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients with moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis and a previous inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: the rose study. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:198–205. 10.1136/ard.2010.148700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kivitz A, Olech E, Borofsky M, et al. Subcutaneous tocilizumab versus placebo in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 2014;66:1653–61. 10.1002/acr.22384 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Burmester GR, Rigby WF, van Vollenhoven RF, et al. Tocilizumab in early progressive rheumatoid arthritis: function, a randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:1081–91. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bijlsma JWJ, Welsing PMJ, Woodworth TG, et al. Early rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab, methotrexate, or their combination (U-Act-Early): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, strategy trial. Lancet 2016;388:343–55. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30363-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Edwards CJ, Östör AJK, Naisbett-Groet B, et al. Tapering versus steady-state methotrexate in combination with tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind trial. Rheumatology 2018;57:84–91. 10.1093/rheumatology/kex358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kremer JM, Rigby W, Singer NG, et al. Sustained response following discontinuation of methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with subcutaneous tocilizumab: results from a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018;70:1200–8. 10.1002/art.40493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pablos JL, Navarro F, Blanco FJ. Efficacy of tocilizumab monotherapy after response to combined tocilizumab and methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the randomised JUST-ACT study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2019;37:437–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huizinga TWJ, Conaghan PG, Martin-Mola E, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes at 2 years and the effect of tocilizumab discontinuation following sustained remission in the second and third year of the ACT-RAY study. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:35–43. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205752 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kaneko Y, Kato M, Tanaka Y, et al. Tocilizumab discontinuation after attaining remission in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who were treated with tocilizumab alone or in combination with methotrexate: results from a prospective randomised controlled study (the second year of the surprise study). Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:1268–75. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kedra J, Dieudé P, Marotte H. Towards the lowest efficacious dose (toledo): results of a multicenter non-inferiority randomized open-label controlled trial assessing tocilizumab or abatacept injection spacing in rheumatoid arthritis patients in remission. American College of rheumatology conference: annual meeting, USA, Atlanta, 2019:4916–9. [Google Scholar]
- 24.van der Heijde D, Aletaha D, Carmona L, et al. 2014 update of the EULAR standardised operating procedures for EULAR-endorsed recommendations. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:8–13. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n71. 10.1136/bmj.n71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Available: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ [Accessed 20 Aug 2021].
- 27.Genovese MC, Fleischmann R, Kivitz AJ, et al. Sarilumab plus methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to methotrexate: results of a phase III study. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67:1424–37. 10.1002/art.39093 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tanaka Y, Wada K, Takahashi Y, et al. Sarilumab plus methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to methotrexate: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial in Japan. Arthritis Res Ther 2019;21:79. 10.1186/s13075-019-1856-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mazurov V, Zotkin E, Ilivanova E, et al. FRI0114 EFFICACY OF LEVILIMAB, NOVEL MONOCLONAL ANTI-IL-6 RECEPTOR ANTIBODY, IN COMBINATION WITH METHOTREXATE IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: 1-YEAR RESULTS OF PHASE 2 AURORA STUDY. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:637.2–8. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-eular.5465 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ablynx . A dose-range finding study for ALX-0061 combination therapy in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. available. Available: https://clinicaltrialsgov/ct2/show/NCT02309359 [Accessed 09 Nov 2020].
- 31.Ablynx . A phase IIb study for ALX-0061 monotherapy in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. Available: https://clinicaltrialsgov/ct2/show/study/NCT02287922 [Accessed 09 Nov 2021].
- 32.Mease P, Strand V, Shalamberidze L, et al. A phase II, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study of BMS945429 (ALD518) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to methotrexate. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:1183–9. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200704 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nasonov E, Stoilov R, Tyabut T, et al. OP0021 OLOKIZUMAB, MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY AGAINST IL6, IN PATIENTS WITH MODERATELY TO SEVERELY ACTIVE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS INADEQUATELY CONTROLLED BY METHOTREXATE: EFFICACY AND SAFETY RESULTS OF PHASE III CREDO-1 STUDY. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:16.1–17. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-eular.1688 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Takeuchi T, Thorne C, Karpouzas G, et al. Sirukumab for rheumatoid arthritis: the phase III SIRROUND-D study. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:2001–8. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fleischmann R, van Adelsberg J, Lin Y, et al. Sarilumab and Nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response or intolerance to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:277–90. 10.1002/art.39944 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Genovese MC, Fleischmann R, Furst D, et al. Efficacy and safety of olokizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to TNF inhibitor therapy: outcomes of a randomised phase IIb study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1607–15. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204760 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Takeuchi T, Tanaka Y, Yamanaka H, et al. Efficacy and safety of olokizumab in Asian patients with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis, previously exposed to anti-TNF therapy: results from a randomized phase II trial. Mod Rheumatol 2016;26:15–23. 10.3109/14397595.2015.1074648 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Aletaha D, Bingham CO, Tanaka Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of sirukumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-TNF therapy (SIRROUND-T): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multinational, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017;389:1206–17. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30401-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Roche H-L. Torpedo study: a study on rapid effect of tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or anti-TNF. Available: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00977106 [Accessed 10 Nov 2020].
- 40.Gabay C, Emery P, van Vollenhoven R, et al. Tocilizumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (ADACTA): a randomised, double-blind, controlled phase 4 trial. Lancet 2013;381:1541–50. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60250-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Burmester GR, Lin Y, Patel R, et al. Efficacy and safety of sarilumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy for the treatment of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (MONARCH): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group phase III trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:840–7. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210310 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Taylor PC, Schiff MH, Wang Q, et al. Efficacy and safety of monotherapy with sirukumab compared with adalimumab monotherapy in biologic-naïve patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (SIRROUND-H): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, multinational, 52-week, phase 3 study. Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:658–66. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212496 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Smolen JS, Aletaha D. Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab and attainment of disease remission in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of acute-phase reactants. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63:43–52. 10.1002/art.27740 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Weinblatt ME, Mease P, Mysler E, et al. The efficacy and safety of subcutaneous clazakizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: results from a multinational, phase IIb, randomized, double-blind, placebo/active-controlled, dose-ranging study. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67:2591–600. 10.1002/art.39249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Burmester GR, Rubbert-Roth A, Cantagrel A, et al. A randomised, double-blind, parallel-group study of the safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab versus intravenous tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (SUMMACTA study). Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:69–74. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203523 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ogata A, Tanimura K, Sugimoto T, et al. Phase III study of the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous versus intravenous tocilizumab monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 2014;66:344–54. 10.1002/acr.22110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ogata A, Atsumi T, Fukuda T, et al. Sustainable efficacy of switching from intravenous to subcutaneous tocilizumab monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 2015;67:1354–62. 10.1002/acr.22598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ogata A, Tanaka Y, Ishii T, et al. A randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, phase III study of shortening the dosing interval of subcutaneous tocilizumab monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to subcutaneous tocilizumab every other week: results of the 12-week double-blind period. Mod Rheumatol 2018;28:76–84. 10.1080/14397595.2017.1332507 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Emery P, van Hoogstraten H, Thangavelu K, et al. Subcutaneous Sarilumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who previously received subcutaneous Sarilumab or intravenous tocilizumab: an open-label extension of a randomized clinical trial. ACR Open Rheumatol 2020;2:672–80. 10.1002/acr2.11188 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dougados M, Kissel K, Sheeran T, et al. Adding tocilizumab or switching to tocilizumab monotherapy in methotrexate inadequate responders: 24-week symptomatic and structural results of a 2-year randomised controlled strategy trial in rheumatoid arthritis (ACT-RAY). Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:43–50. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-201282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kaneko Y, Atsumi T, Tanaka Y, et al. Comparison of adding tocilizumab to methotrexate with switching to tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to methotrexate: 52-week results from a prospective, randomised, controlled study (surprise study). Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:1917–23. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dougados M, Kissel K, Conaghan PG, et al. Clinical, radiographic and immunogenic effects after 1 year of tocilizumab-based treatment strategies in rheumatoid arthritis: the ACT-RAY study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:803–9. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Burmester GR, Rigby WF, van Vollenhoven RF, et al. Tocilizumab combination therapy or monotherapy or methotrexate monotherapy in methotrexate-naive patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year clinical and radiographic results from the randomised, placebo-controlled function trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:1279–84. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210561 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hetland ML, Haavardsholm EA, Rudin A, et al. Active conventional treatment and three different biological treatments in early rheumatoid arthritis: phase IV investigator initiated, randomised, observer blinded clinical trial. BMJ 2020;371:m4328. 10.1136/bmj.m4328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Peterfy C, Kremer J, Rigby W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) results following discontinuation of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis treated with subcutaneous tocilizumab: the COMP-ACT MRI substudy. J Rheumatol 2020;47:325–32. 10.3899/jrheum.180953 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Burmester GR, Buttgereit F, Bernasconi C, et al. Continuing versus tapering glucocorticoids after achievement of low disease activity or remission in rheumatoid arthritis (SEMIRA): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020;396:267–76. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30636-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.De Benedetti F, Brunner HI, Ruperto N, et al. Randomized trial of tocilizumab in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. N Engl J Med 2012;367:2385–95. 10.1056/NEJMoa1112802 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Brunner HI, Ruperto N, Zuber Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with polyarticular-course juvenile idiopathic arthritis: results from a phase 3, randomised, double-blind withdrawal trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:1110–7. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205351 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Malattia C, Ruperto N, Pederzoli S, et al. Tocilizumab may slow radiographic progression in patients with systemic or polyarticular-course juvenile idiopathic arthritis: post hoc radiographic analysis from two randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Res Ther 2020;22:211. 10.1186/s13075-020-02303-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kaneko Y, Kameda H, Ikeda K, et al. Tocilizumab in patients with adult-onset still's disease refractory to glucocorticoid treatment: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:1720–9. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213920 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Stone JH, Tuckwell K, Dimonaco S, et al. Trial of tocilizumab in giant-cell arteritis. N Engl J Med 2017;377:317–28. 10.1056/NEJMoa1613849 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Stone J, Spotswood H, Unizony S. Time to flare in patients with new-onset versus relapsing giant cell arteritis treated with tocilizumab or placebo plus prednisone tapering: 3-year results from a randomized controlled phase 3 trial. American College of rheumatology conference: annual meeting, USA, Atlanta, 2019:3278–80. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Calderón-Goercke M, Loricera J, Prieto-Pena D. Tocilizumab in giant cell arteritis: route of administration: intravenous or subcutaneous. American College of rheumatology conference: annual meeting. 71. USA, Atlanta: ACR, 2019: 4744–6. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Schmidt WA, Dasgupta B, Luqmani R, et al. A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Sirukumab in the treatment of giant cell arteritis. Rheumatol Ther 2020;7:25:25. 10.1007/s40744-020-00227-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Nakaoka Y, Isobe M, Takei S, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with refractory Takayasu arteritis: results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in Japan (the TAKT study). Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:348–54. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.van Rhee F, Wong RS, Munshi N, et al. Siltuximab for multicentric Castleman's disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2014;15:966–74. 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70319-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Le RQ, Li L, Yuan W, Shord SS, et al. Fda approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell-induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome. Oncologist 2018;23:943–7. 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zhang C, Zhang M, Qiu W, et al. Safety and efficacy of tocilizumab versus azathioprine in highly relapsing neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (tango): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol 2020;19:391–401. 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30070-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yamamura T, Kleiter I, Fujihara K, et al. Trial of Satralizumab in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. N Engl J Med 2019;381:2114–24. 10.1056/NEJMoa1901747 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Traboulsee A, Greenberg BM, Bennett JL, et al. Safety and efficacy of satralizumab monotherapy in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol 2020;19:402–12. 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30078-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Richette P, Latourte A, Sellam J, et al. Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients with hand osteoarthritis: double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:349–55. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ablynx . A phase II study to evaluate safety and efficacy of ALX-0061 in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus. Available: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02437890 [Accessed 09 Nov 2021].
- 73.Oddis C. Tocilizumab in the treatment of refractory polymyositis and dermatomyositis (TIM). Available: https://clinicaltrialsgov/ct2/show/study/NCT02043548 [Accessed 15 Nov 2020].
- 74.Khanna D, Lin CJF, Furst DE, et al. Tocilizumab in systemic sclerosis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:963–74. 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30318-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.San-Miguel J, Bladé J, Shpilberg O, et al. Phase 2 randomized study of bortezomib-melphalan-prednisone with or without siltuximab (anti-IL-6) in multiple myeloma. Blood 2014;123:4136–42. 10.1182/blood-2013-12-546374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Brighton TA, Khot A, Harrison SJ, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study of siltuximab in high-risk smoldering multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2019;25:3772–5. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Doberer K, Duerr M, Halloran PF, et al. A randomized clinical trial of anti-IL-6 antibody Clazakizumab in late antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection. J Am Soc Nephrol 2021;32:708-722. 10.1681/ASN.2020071106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Okuda Y, Ohnishi M, Matoba K, et al. Comparison of the clinical utility of tocilizumab and anti-TNF therapy in AA amyloidosis complicating rheumatic diseases. Mod Rheumatol 2014;24:137–43. 10.3109/14397595.2013.854048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Okuda Y, Yamada T, Ueda M, et al. First nationwide survey of 199 patients with amyloid A amyloidosis in Japan. Intern Med 2018;57:3351–5. 10.2169/internalmedicine.1099-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lally L, Forbess L, Hatzis C, et al. Brief report: a prospective open-label phase IIA trial of tocilizumab in the treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:2550–4. 10.1002/art.39740 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Devauchelle-Pensec V, Berthelot JM, Cornec D, et al. Efficacy of first-line tocilizumab therapy in early polymyalgia rheumatica: a prospective longitudinal study. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:1506–10. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208742 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Del Valle DM, Kim-Schulze S, Huang H-H, et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat Med 2020;26:1636–43. 10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Rodriguez-Bano J, Pachon J, Carratala J. Treatment with tocilizumab or corticosteroids for COVID-19 patients with hyperinflammatory state: a multicentre cohort study (SAM-COVID-19). Clinical Microbiology & Infection 2020;27:27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Guaraldi G, Meschiari M, Cozzi-Lepri A, et al. Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:e474–84. 10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Ip A, Berry DA, Hansen E, et al. Hydroxychloroquine and tocilizumab therapy in COVID-19 patients-An observational study. PLoS One 2020;15:e0237693. 10.1371/journal.pone.0237693 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Biran N, Ip A, Ahn J, et al. Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study. Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:e603–12. 10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Gupta S, Wang W, Hayek SS, et al. Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19. JAMA Intern Med 2021;181:20:20. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Ramiro S, Mostard RLM, Magro-Checa C, et al. Historically controlled comparison of glucocorticoids with or without tocilizumab versus supportive care only in patients with COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome: results of the chiC study. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:1143–51. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218479 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Della-Torre E, Campochiaro C, Cavalli G, et al. Interleukin-6 blockade with sarilumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia with systemic hyperinflammation: an open-label cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:1277–85. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Hermine O, Mariette X, Tharaux PL. Effect of tocilizumab vs usual care in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 and moderate or severe pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Internal Medicine 2020:20:20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Salama C, Han J, Yau L, et al. Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia. N Engl J Med 2021;384:20–30. 10.1056/NEJMoa2030340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Stone JH, Frigault MJ, Serling-Boyd NJ, et al. Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020;383:2333–44. 10.1056/NEJMoa2028836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Salvarani C, Dolci G, Massari M, et al. Effect of tocilizumab vs standard care on clinical worsening in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2021;181:24–31. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Kim SC, Solomon DH, Rogers JR, et al. Cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab versus tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a Multi-Database cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:1154–64. 10.1002/art.40084 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Kim SC, Solomon DH, Rogers JR, et al. No difference in cardiovascular risk of tocilizumab versus abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis: a multi-database cohort study. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2018;48:399–405. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.03.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Xie F, Yun H, Levitan EB, et al. Tocilizumab and the risk of cardiovascular disease: direct comparison among biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Care Res 2019;71:1004–18. 10.1002/acr.23737 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Giles JT, Sattar N, Gabriel S, et al. Cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab versus etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020;72:31–40. 10.1002/art.41095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Zhang J, Xie F, Yun H, et al. Comparative effects of biologics on cardiovascular risk among older patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:1813–8. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207870 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Lukas C, Redondin M, Pane I, et al. Cardiovascular events and change in cholesterol levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab: data from the REGATE registry. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2021;39:501–7. 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/hfceu3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Generali E, Carrara G, Selmi C, et al. Comparison of the risks of hospitalisation for cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab and etanercept. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2018;36:310–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Carrara G, Bortoluzzi A, Sakellariou G, et al. Risk of hospitalisation for serious bacterial infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologics. analysis from the record linkage on rheumatic disease study of the Italian Society for rheumatology. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2019;37:60–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Mori S, Yoshitama T, Hidaka T, et al. Comparative risk of hospitalized infection between biological agents in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a multicenter retrospective cohort study in Japan. PLoS One 2017;12:e0179179. 10.1371/journal.pone.0179179 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Grøn KL, Arkema EV, Glintborg B, et al. Risk of serious infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in routine care with abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab in Denmark and Sweden. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:320–7. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Grøn KL, Glintborg B, Nørgaard M, et al. Overall infection risk in rheumatoid arthritis during treatment with abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab; an observational cohort study. Rheumatology 2020;59:1949–56. 10.1093/rheumatology/kez530 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Sakai R, Cho S-K, Nanki T, et al. Head-to-head comparison of the safety of tocilizumab and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis patients (RA) in clinical practice: results from the registry of Japanese RA patients on biologics for long-term safety (real) registry. Arthritis Res Ther 2015;17:74. 10.1186/s13075-015-0583-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Yun H, Xie F, Delzell E, et al. Comparative risk of hospitalized infection associated with biologic agents in rheumatoid arthritis patients enrolled in Medicare. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:56–66. 10.1002/art.39399 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Rutherford AI, Subesinghe S, Hyrich KL, et al. Serious infection across biologic-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for rheumatology biologics register for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:905–10. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212825 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Pawar A, Desai RJ, Solomon DH, et al. Risk of serious infections in tocilizumab versus other biologic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multidatabase cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:456–64. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Rutherford AI, Patarata E, Subesinghe S, et al. Opportunistic infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to biologic therapy: results from the British Society for rheumatology biologics register for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2018;57:997–1001. 10.1093/rheumatology/key023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Leon L, Peñuelas M, Candel FJ, et al. Indicator opportunistic infections after biological treatment in rheumatoid arthritis, 10 years follow-up in a real-world setting. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 2019;11:19878004. 10.1177/1759720X19878004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Lim CH, Chen H-H, Chen Y-H, et al. The risk of tuberculosis disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients on biologics and targeted therapy: a 15-year real world experience in Taiwan. PLoS One 2017;12:e0178035. 10.1371/journal.pone.0178035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Wang X, Wong SH, Wang X-S, et al. Risk of tuberculosis in patients with immune-mediated diseases on biological therapies: a population-based study in a tuberculosis endemic region. Rheumatology 2019;58:803–10. 10.1093/rheumatology/key364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Curtis JR, Xie F, Yun H, et al. Real-world comparative risks of herpes virus infections in tofacitinib and biologic-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:1843–7. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Yun H, Xie F, Delzell E, et al. Risks of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis according to biologic disease-modifying therapy. Arthritis Care Res 2015;67:731–6. 10.1002/acr.22470 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Wadström H, Frisell T, Askling J, et al. Malignant neoplasms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, tocilizumab, abatacept, or rituximab in clinical practice: a nationwide cohort study from Sweden. JAMA Intern Med 2017;177:1605–12. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.4332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Kim SC, Pawar A, Desai RJ, et al. Risk of malignancy associated with use of tocilizumab versus other biologics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multi-database cohort study. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2019;49:222–8. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.03.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Hellgren K, Di Giuseppe D, Smedby KE. Lymphoma risks in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological drugs-a Swedish cohort study of risks by time, drug and lymphoma subtype. Rheumatology 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Mercer LK, Askling J, Raaschou P, et al. Risk of invasive melanoma in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologics: results from a collaborative project of 11 European biologic registers. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:386–91. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Rempenault C, Lukas C, Combe B. OP0022 risk of diverticulitis and gastro-intestinal perforation in rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab compared to rituximab and abatacept: a prospective propensity-matched cohort studyRISK OF DIVERTICULITIS AND GASTRO-INTESTINAL PERFORATION IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS TREATED WITH TOCILIZUMAB COMPARED TO RITUXIMAB AND ABATACEPT: A PROSPECTIVE PROPENSITY-MATCHED COHORT STUDY. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:17:17. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Monemi S, Berber E, Sarsour K, et al. Incidence of gastrointestinal perforations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab from clinical trial, postmarketing, and real-world data sources. Rheumatol Ther 2016;3:337–52. 10.1007/s40744-016-0037-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Strangfeld A, Richter A, Siegmund B, et al. Risk for lower intestinal perforations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab in comparison to treatment with other biologic or conventional synthetic DMARDs. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:504–10. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209773 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Barbulescu A, Delcoigne B, Askling J, et al. Gastrointestinal perforations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in Sweden: a nationwide cohort study. RMD Open 2020;6. 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Xie F, Yun H, Bernatsky S, et al. Brief report: risk of gastrointestinal perforation among rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving tofacitinib, tocilizumab, or other biologic treatments. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:2612–7. 10.1002/art.39761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Genovese MC, Kremer JM, van Vollenhoven RF, et al. Transaminase levels and hepatic events during tocilizumab treatment: pooled analysis of long-term clinical trial safety data in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:1751–61. 10.1002/art.40176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Koike T, Harigai M, Inokuma S, et al. Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab: postmarketing surveillance of 7901 patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan. J Rheumatol 2014;41:15–23. 10.3899/jrheum.130466 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Crnkic Kapetanovic M, Saxne T, Jönsson G, et al. Rituximab and abatacept but not tocilizumab impair antibody response to pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2013;15:R171. 10.1186/ar4358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Tsuru T, Terao K, Murakami M, et al. Immune response to influenza vaccine and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine under IL-6 signal inhibition therapy with tocilizumab. Mod Rheumatol 2014;24:511–6. 10.3109/14397595.2013.843743 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Bingham CO, Rizzo W, Kivitz A, et al. Humoral immune response to vaccines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab: results of a randomised controlled trial (VISARA). Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:818–22. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Shinoki T, Hara R, Kaneko U, et al. Safety and response to influenza vaccine in patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis receiving tocilizumab. Mod Rheumatol 2012;22:871–6. 10.1007/s10165-012-0595-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Mori S, Ueki Y, Akeda Y, et al. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving tocilizumab therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:1362–6. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202658 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Brodszky V, Bíró A, Szekanecz Z, et al. Determinants of biological drug survival in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence from a Hungarian rheumatology center over 8 years of retrospective data. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res 2017;9:139–47. 10.2147/CEOR.S124381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Ebina K, Hashimoto M, Yamamoto W, et al. Drug retention and discontinuation reasons between seven biologics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis -The answer cohort study. PLoS One 2018;13:e0194130. 10.1371/journal.pone.0194130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Gottenberg J-E, Morel J, Perrodeau E, et al. Comparative effectiveness of rituximab, abatacept, and tocilizumab in adults with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to TNF inhibitors: prospective cohort study. BMJ 2019;364:l67. 10.1136/bmj.l67 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ebina K, Hirano T, Maeda Y, et al. Drug retention of 7 biologics and tofacitinib in biologics-naïve and biologics-switched patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the answer cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 2020;22:142. 10.1186/s13075-020-02232-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Yun H, Xie F, Beyl RN, et al. Risk of hypersensitivity to biologic agents among Medicare patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 2017;69:1526–34. 10.1002/acr.23141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Salmon J-H, Perotin J-M, Morel J, et al. Serious infusion-related reaction after rituximab, abatacept and tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: prospective registry data. Rheumatology 2018;57:134–9. 10.1093/rheumatology/kex403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Ebina K, Hashimoto M, Yamamoto W, et al. Drug tolerability and reasons for discontinuation of seven biologics in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis -The answer cohort study. PLoS One 2019;14:e0216624. 10.1371/journal.pone.0216624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.McInnes IB, Thompson L, Giles JT, et al. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor blockade on surrogates of vascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: measure, a randomised, placebo-controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:694–702. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Gabay C, McInnes IB, Kavanaugh A, et al. Comparison of lipid and lipid-associated cardiovascular risk marker changes after treatment with tocilizumab or adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:1806–12. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207872 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Chen SK, Lee H, Jin Y, et al. Use of biologic or targeted-synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and risk of diabetes treatment intensification in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus. Rheumatol Adv Pract 2020;4:rkaa027. 10.1093/rap/rkaa027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Genovese MC, Burmester GR, Hagino O, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor blockade or TNFα inhibition for reducing glycaemia in patients with RA and diabetes: post hoc analyses of three randomised, controlled trials. Arthritis Res Ther 2020;22. 10.1186/s13075-020-02229-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Paul SK, Montvida O, Best JH, et al. Effectiveness of biologic and non-biologic antirheumatic drugs on anaemia markers in 153,788 patients with rheumatoid arthritis: new evidence from real-world data. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2018;47:478–84. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2017.08.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Moots RJ, Sebba A, Rigby W, et al. Effect of tocilizumab on neutrophils in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis: pooled analysis of data from phase 3 and 4 clinical trials. Rheumatology 2017;56:541–9. 10.1093/rheumatology/kew370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Mori S, Yoshitama T, Hidaka T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab therapy for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and renal insufficiency: a real-life registry study in Japan (the ACTRA-RI study). Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:627–30. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206695 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Curtis JR, Sarsour K, Napalkov P, et al. Incidence and complications of interstitial lung disease in users of tocilizumab, rituximab, abatacept and anti-tumor necrosis factor α agents, a retrospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 2015;17. 10.1186/s13075-015-0835-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Strangfeld A, Meißner Y, Schaefer M. No confirmation of increased risk of idiopathic facial nerve palsy under tocilizumab. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases Conference: annual european congress of rheumatology of the european league against rheumatism, EULAR 2019, Spain 2019;78:351–2. [Google Scholar]
- 147.Shin A, Dong YH, Shin S. The comparative risk of osteoporotic fractures among patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving TNF inhibitors versus other biologics: a nation-wide cohort study in Korea. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases Conference: annual european congress of rheumatology of the european league against rheumatism, EULAR 2019, Spain 2019;726. [Google Scholar]
- 148.Hoeltzenbein M, Beck E, Rajwanshi R, et al. Tocilizumab use in pregnancy: analysis of a global safety database including data from clinical trials and post-marketing data. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2016;46:238–45. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Weber-Schoendorfer C, Schaefer C. Pregnancy outcome after tocilizumab therapy in early pregnancy-a case series from the German Embryotox pharmacovigilance center. Reprod Toxicol 2016;60:29–32. 10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.01.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Emery P, Rondon J, Parrino J, et al. Safety and tolerability of subcutaneous sarilumab and intravenous tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019;58:849–58. 10.1093/rheumatology/key361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Kameda H, Wada K, Takahashi Y, et al. Sarilumab monotherapy or in combination with non-methotrexate disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in active rheumatoid arthritis: a Japan phase 3 trial (HARUKA). Mod Rheumatol 2020;30:239–48. 10.1080/14397595.2019.1639939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Fleischmann R, Genovese MC, Lin Y, et al. Long-term safety of sarilumab in rheumatoid arthritis: an integrated analysis with up to 7 years' follow-up. Rheumatology 2020;59:292–302. 10.1093/rheumatology/kez265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Thorne C, Takeuchi T, Karpouzas GA, et al. Investigating sirukumab for rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year results from the phase III SIRROUND-D study. RMD Open 2018;4:e000731. 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000731 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Available: https://www.fda.gov/media/106325/download [Accessed 10 Nov 2021].
- 155.Horneff G, Klein A, Klotsche J, et al. Comparison of treatment response, remission rate and drug adherence in polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients treated with etanercept, adalimumab or tocilizumab. Arthritis Res Ther 2016;18:272. 10.1186/s13075-016-1170-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Grönlund M-M, Remes-Pakarinen T, Kröger L, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in a real-life observational cohort of patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology 2020;59:732–41. 10.1093/rheumatology/kez291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Klein A, Klotsche J, Hügle B, et al. Long-term surveillance of biologic therapies in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis: data from the German BIKER registry. Rheumatology 2020;59:2287–98. 10.1093/rheumatology/kez577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Shafran IH, Alasti F, Smolen JS, et al. Implication of baseline levels and early changes of C-reactive protein for subsequent clinical outcomes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:874–82. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215987 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Shimamoto K, Ito T, Ozaki Y, et al. Serum interleukin 6 before and after therapy with tocilizumab is a principal biomarker in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2013;40:1074–81. 10.3899/jrheum.121389 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Nishimoto N, Amano K, Hirabayashi Y, et al. Drug free REmission/low disease activity after cessation of tocilizumab (Actemra) monotherapy (DREAM) study. Mod Rheumatol 2014;24:17–25. 10.3109/14397595.2013.854079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Strand V, Boklage SH, Kimura T, et al. High levels of interleukin-6 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are associated with greater improvements in health-related quality of life for sarilumab compared with adalimumab. Arthritis Res Ther 2020;22:250. 10.1186/s13075-020-02344-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Boyapati A, Schwartzman S, Msihid J, et al. Association of high serum Interleukin‐6 levels with severe progression of rheumatoid arthritis and increased treatment response differentiating Sarilumab from adalimumab or methotrexate in a post hoc analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020;72:1456–66. 10.1002/art.41299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Cappelli LC, Palmer JL, Kremer J, et al. Tocilizumab treatment leads to improvement in disease activity regardless of CcP status in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2017;47:165–9. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2017.03.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Sanayama Y, Ikeda K, Saito Y, et al. Prediction of therapeutic responses to tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: biomarkers identified by analysis of gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells using genome-wide DNA microarray. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014;66:1421–31. 10.1002/art.38400 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Daïen CI, Gailhac S, Audo R, et al. High levels of natural killer cells are associated with response to tocilizumab in patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2015;54:601–8. 10.1093/rheumatology/keu363 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Humby F, Buch MH, Durez P. A randomised, open labelled clinical trial to investigate synovial mechanisms determining response-resistance to rituximab versus tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis patients failing TNF inhibitor therapy. American College of rheumatology conference: annual meeting, USA, Atlanta, 2019:5180–3. [Google Scholar]
- 167.Dulic S, Vásárhelyi Z, Sava F, et al. T-Cell subsets in rheumatoid arthritis patients on long-term anti-TNF or IL-6 receptor blocker therapy. Mediators Inflamm 2017;2017:6894374. 10.1155/2017/6894374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Gabay C, Burmester GR, Strand V, et al. Sarilumab and adalimumab differential effects on bone remodelling and cardiovascular risk biomarkers, and predictions of treatment outcomes. Arthritis Res Ther 2020;22:70. 10.1186/s13075-020-02163-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Gerasimova H, Popkova T, Kirillova I, et al. FRI0094 significant improvement of NT-PROBNP levels in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tocilizumab and tofacitinib. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:625.2–6. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-eular.5859 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Toussirot E, Marotte H, Mulleman D, et al. Increased high molecular weight adiponectin and lean mass during tocilizumab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 12-month multicentre study. Arthritis Res Ther 2020;22:224. 10.1186/s13075-020-02297-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Fioravanti A, Tenti S, Bacarelli MR, et al. Tocilizumab modulates serum levels of adiponectin and chemerin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: potential cardiovascular protective role of IL-6 inhibition. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2019;37:293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Maldonado-Montoro M, Cañadas-Garre M, González-Utrilla A, et al. Genetic and clinical biomarkers of tocilizumab response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Res 2016;111:264–71. 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.06.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Jiménez Morales A, Maldonado-Montoro M, Martínez de la Plata JE, et al. FCGR2A/FCGR3A gene polymorphisms and clinical variables as predictors of response to tocilizumab and rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Pharmacol 2019;59:517–31. 10.1002/jcph.1341 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Gabay C, Msihid J, Zilberstein M, et al. Identification of sarilumab pharmacodynamic and predictive markers in patients with inadequate response to TNF inhibition: a biomarker substudy of the phase 3 target study. RMD Open 2018;4:e000607. 10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Gardette A, Ottaviani S, Sellam J, et al. Body mass index and response to tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: a real life study. Clin Rheumatol 2016;35:857–61. 10.1007/s10067-016-3183-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Schäfer M, Meißner Y, Kekow J, et al. Obesity reduces the real-world effectiveness of cytokine-targeted but not cell-targeted disease-modifying agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2020;59:1916–26. 10.1093/rheumatology/kez535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Davies R, Vivekanantham A, Lunt M. SAT0103 the effect of bodyweight on response to intravenous or subcutaneous tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:985. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-eular.4164 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Tanaka Y, Kameda H, Saito K, et al. Effect of subcutaneous tocilizumab treatment on work/housework status in biologic-naïve rheumatoid arthritis patients using inverse probability of treatment weighting: first ACT-SC study. Arthritis Res Ther 2018;20. 10.1186/s13075-018-1647-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Strand V, Michalska M, Birchwood C, et al. Impact of tocilizumab monotherapy on patient-reported outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from two randomised controlled trials. RMD Open 2017;3:e000496. 10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Strand V, Michalska M, Birchwood C, et al. Impact of tocilizumab administered intravenously or subcutaneously on patient-reported quality-of-life outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open 2018;4:e000602. 10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000602 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Strand V, Gossec L, Proudfoot CWJ, et al. Patient-reported outcomes from a randomized phase III trial of sarilumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2018;20:129. 10.1186/s13075-018-1614-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Best JH, Vlad SC, Tominna L, et al. Real-World persistence with tocilizumab compared to other subcutaneous biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs among patients with rheumatoid arthritis switching from another biologic. Rheumatol Ther 2020;7:345–55. 10.1007/s40744-020-00201-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Strand V, Dimonaco S, Tuckwell K, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with giant cell arteritis treated with tocilizumab in a phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Arthritis Res Ther 2019;21:64. 10.1186/s13075-019-1837-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Ayaz NA, Karadağ Şerife Gül, Koç R, et al. Patient satisfaction and clinical effectiveness of switching from intravenous tocilizumab to subcutaneous tocilizumab in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: an observational study. Rheumatol Int 2020;40:1111–6. 10.1007/s00296-020-04596-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Forsblad-d'Elia H, Bengtsson K, Kristensen LE, et al. Drug adherence, response and predictors thereof for tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Swedish biologics register. Rheumatology 2015;54:1186–93. 10.1093/rheumatology/keu455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Pappas DA, Blachley T, Best JH, et al. FRI0104 persistence of tocilizumab therapy among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: data from the us-based corrona rheumatoid arthritis registry. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:631–2. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-eular.708 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA Authorizes drug for treatment of COVID-19. Available: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-drug-treatment-covid-19 [Accessed 10 Aug 2021].
- 188.Roche’s Actemra/RoActemra becomes the first biologic therapy approved by the FDA for slowing the rate of decline in pulmonary function in adults with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease, a rare, debilitating condition. Available: https://www.roche.com/media/releases/med-cor-2021-03-05b.htm [Accessed 25 Jun 2021].
- 189.Actemra/RoActemra approved by the European Commission to treat patients with severe COVID-19. Available: https://www.roche.com/media/releases/med-cor-2021-12-07.htm [Accessed 30 Dec 2021].
- 190.Shankar-Hari M, Vale CL, WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group, et al. Association between administration of IL-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2021;326:499–518. 10.1001/jama.2021.11330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.RECOVERY Collaborative Group . Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (recovery): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet 2021;397:1637–45. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
rmdopen-2022-002359supp001.pdf (2.3MB, pdf)
rmdopen-2022-002359supp002.pdf (2.2MB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.