The title molecule is essentially flat; in the crystal the molecules are linked by a system of hydrogen bonds formed by the hydrazido group and consisting of chains of fused rings.
Keywords: crystal structure, acyl hydrazide, hydrogen bonding, lattice energy, DFT calculations
Abstract
The title compound, C9H13N3O, crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/c and all non-hydrogen atoms are within 0.1 Å of the molecular mean plane. In the crystal, the hydrogen-bonding pattern results in [001] chains built up from fused R
2
2(6) and R
2
2(10) rings; the former consists of N—H⋯N bonds and the latter N—H⋯O bonds. Electrostatic and dispersion forces are major contributors to the lattice energy, which was estimated by DFT calculations to be −215.7 kJ mol−1.
Structure description
For decades, there has been an interest in aroyl hydrazides because of their numerous applications, for instance, as synthetic precursors to a large number of potential antimicrobial (Popiołek, 2017 ▸) or anticancer (Kumar & Narasimhan, 2013 ▸) drugs, in addition to their own anti-tubercular activities (Sah & Peoples, 1954 ▸). In our search for inhibitors of bacterial virulence factors (Mossine et al., 2016 ▸, 2020 ▸), we turned our attention to the title compound, which can be viewed as a structural analogue of isoniazid (Andrade et al., 2008 ▸) and a potential precursor for pharmacologically active, iron-binding hydrazide-hydrazones. We now report its crystal structure.
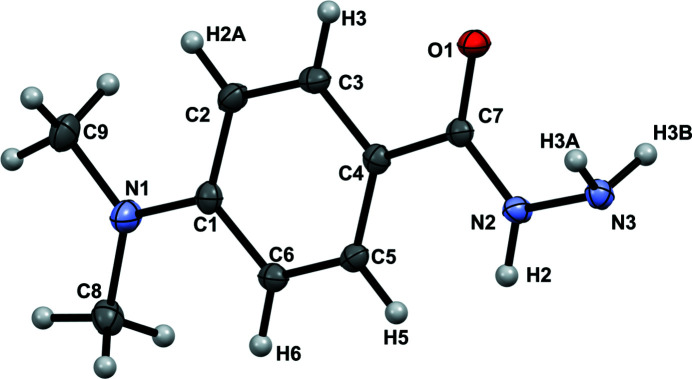
The title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/c, with eight molecules per unit cell. The asymmetric unit contains one molecule of the hydrazide (I), as shown in Fig. 1 ▸. All bond lengths and angles are within their expected ranges. The molecule is essentially flat, with the greatest deviation from the average molecular plane, among the non-hydrogen atoms, found for atom N1 at 0.074 (1) Å. The aromatic ring plane is at 1.08 (4)° to the molecular plane. The spatial arrangement of the hydrazido group, as defined by the torsion angle H2—N2—N3—H3B = 119.3 (15)°, corresponds to the lowest energy conformation that has been calculated for acyl hydrazides (Centore et al., 2010 ▸).
Figure 1.
Atomic numbering and displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level for (I).
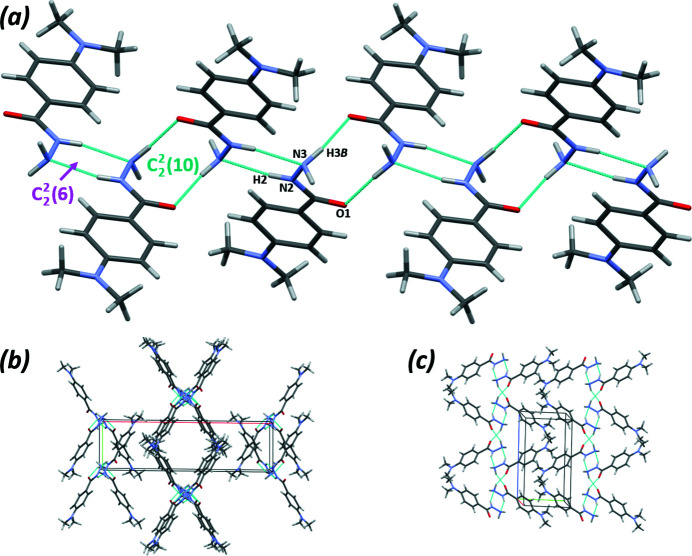
The conventional hydrogen bonding in the extended structure of (I) is limited to two intermolecular heteroatom contacts (Table 1 ▸) involving the hydrazido groups only and is shown in Fig. 2 ▸. The hydrogen-bonding pattern includes infinite chains that propagate in the [001] direction and consist of fused
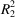 (10) and
(10) and
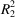 (6) rings (Fig. 2 ▸
a). The
(6) rings (Fig. 2 ▸
a). The
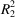 (10) motif is formed by pairs of molecules linked by the N3—H3B⋯O1 hydrogen bonds related by twofold rotation symmetry, while the
(10) motif is formed by pairs of molecules linked by the N3—H3B⋯O1 hydrogen bonds related by twofold rotation symmetry, while the
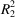 (6) motif is formed by centrosymmetric dimers of (I) linked by the N2—H2⋯N3 hydrogen bonds. In addition, one short intermolecular contact, C6—H6⋯O1, which satisfies the distance and directionality conditions [C6⋯O1iii = 3.4111 (13) Å, C6—H6⋯O1iii = 172°; symmetry code: (iii) x, 1 − y, ½ + z], and which is shown in Fig. 3 ▸ as a dotted line, may also contribute to the stability of the molecular packing in the crystal. The intermolecular non-polar interactions are dominated by hydrogen–hydrogen contacts between the methyl groups; the shortest of these contacts, H8C⋯H9B, is about 0.1 Å less than the sum of the VdW radii. These interactions form a pattern of infinite chains, propagating in the [001] direction, in parallel to the hydrogen-bonded chains (Fig. 2 ▸
b and 2c). The crystal structure lacks any strong π–π stacking interactions. However, a short N3—H3A⋯Cg1 [H3A⋯Cg1iv = 2.614 (15) Å; symmetry code: (iv) x, y − 1, z] contact is present.
(6) motif is formed by centrosymmetric dimers of (I) linked by the N2—H2⋯N3 hydrogen bonds. In addition, one short intermolecular contact, C6—H6⋯O1, which satisfies the distance and directionality conditions [C6⋯O1iii = 3.4111 (13) Å, C6—H6⋯O1iii = 172°; symmetry code: (iii) x, 1 − y, ½ + z], and which is shown in Fig. 3 ▸ as a dotted line, may also contribute to the stability of the molecular packing in the crystal. The intermolecular non-polar interactions are dominated by hydrogen–hydrogen contacts between the methyl groups; the shortest of these contacts, H8C⋯H9B, is about 0.1 Å less than the sum of the VdW radii. These interactions form a pattern of infinite chains, propagating in the [001] direction, in parallel to the hydrogen-bonded chains (Fig. 2 ▸
b and 2c). The crystal structure lacks any strong π–π stacking interactions. However, a short N3—H3A⋯Cg1 [H3A⋯Cg1iv = 2.614 (15) Å; symmetry code: (iv) x, y − 1, z] contact is present.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯N3i | 0.89 (2) | 2.11 (2) | 2.9203 (13) | 151 (1) |
| N3—H3B⋯O1ii | 0.92 (2) | 2.09 (1) | 2.9516 (11) | 157 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i)
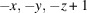 ; (ii)
; (ii)
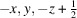 .
.
Figure 2.
Molecular packing and hydrogen bonding in (I). (a) Hydrogen-bonding motifs; (b) and (c) molecular packing views down [001] and [100], respectively. Hydrogen bonds are shown as cyan dotted lines.
Figure 3.
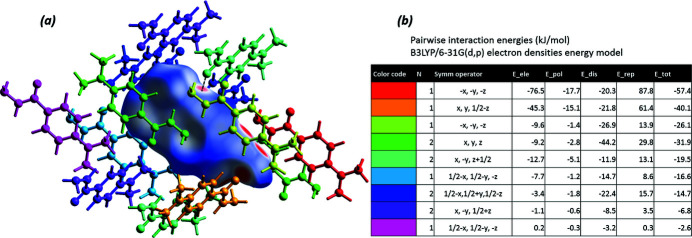
Interaction energies in crystal structure of (I). (a) A view of interactions between a central molecule, shown as its Hirshfeld surface, and 13 molecules that share the interaction surfaces with the central molecule. Red areas on the Hirshfeld surface encode the closest intermolecular contacts, which are hydrogen bonds involving the hydrazido groups, a short C—H⋯O type contact is shown as a dotted line; (b) Calculated energies (electrostatic, polarization, dispersion, repulsion, and total) of pairwise interactions between the central molecule and those indicated by respective colours.
To account for all interactions involved in the build-up of the crystal structure of (I) we have performed DFT calculations, at the B3LYP/6–31 G(d,p) theory level (Mackenzie et al., 2017 ▸; Thomas et al., 2018 ▸), of the electrostatic, dispersion, polarization, and repulsion energies. According to these calculations, the interactions between hydrogen-bonded pairs of molecules contribute about 50% to the lattice energy, with the dispersion energy providing most of the attractive forces between non-hydrogen-bonded molecules of (I) (i.e. E ele = −9.2 kJ mol−1, E dis = −44.2 kJ mol−1 for symmetry code = x, y, z). To estimate the lattice energy, all total energies of unique pairwise interactions between molecules were summed up, thus yielding E l (l = lattice) = −216 kJ mol−1 for the crystal of (I). The calculated contributions to the overall lattice energy (kJ mol−1) are as follows: E ele = −165.3; E pol = −46.0; E dis = −173.9; E rep = 234.1. The spatial distribution of the energetically most significant interactions is illustrated in Fig. 4 ▸, showing the interactions energy frameworks as cylinders penetrating the molecular packing of (I). As expected, the most extensive intermolecular interactions occur in the hydrogen-bonded chain direction parallel to [001].
Figure 4.
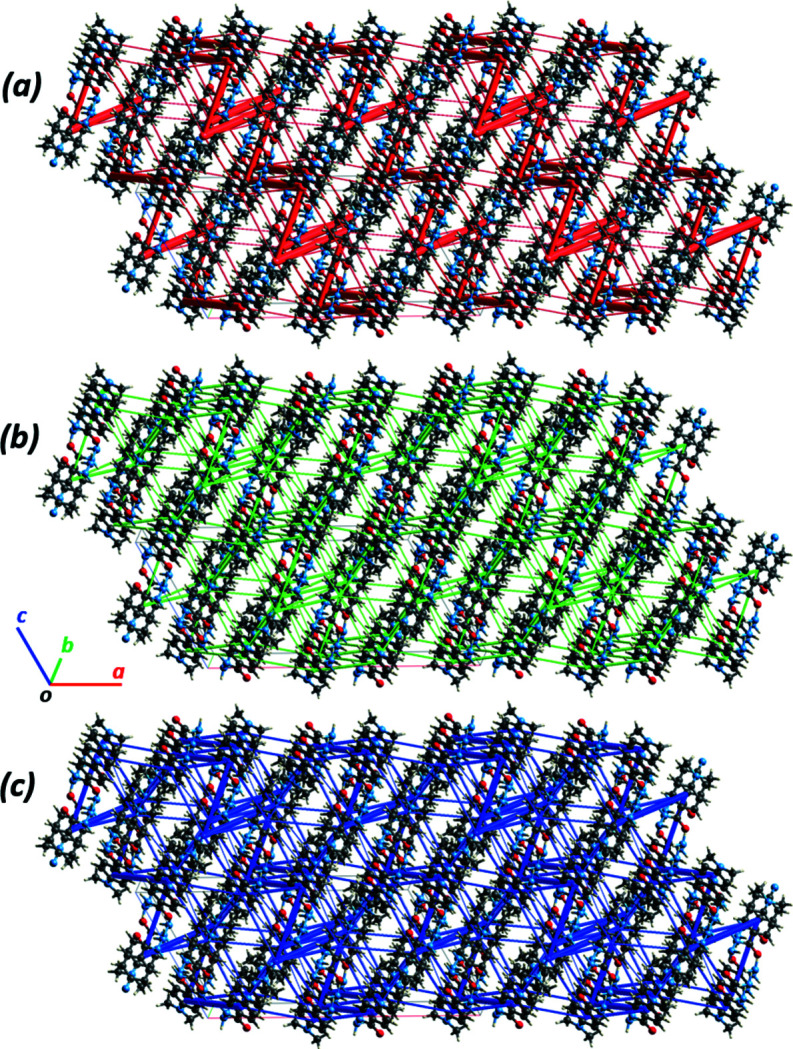
Energy frameworks for separate (a) electrostatic and (b) dispersion contributions to the (c) total pairwise interaction energies in (I). The cylinders link molecular centroids, and the cylinder thickness is proportional to the magnitude of the energies (see Fig. 3 ▸). For clarity, the cylinders corresponding to energies <5 kJ mol−1 are not shown. The directionality of the crystallographic axes is the same for all three diagrams.
Synthesis and crystallization
A sample of commercial 4-dimethylaminobenzhydrazide was recrystallized from hot 95% ethanol solution, affording colorless needles.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C9H13N3O |
| M r | 179.22 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2/c |
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 24.7018 (6), 6.3093 (1), 13.2103 (3) |
| β (°) | 118.0496 (8) |
| V (Å3) | 1817.01 (7) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.72 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.24 × 0.23 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (AXScale; Bruker, 2016 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.684, 0.754 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 15813, 1786, 1770 |
| R int | 0.019 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.618 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.036, 0.098, 1.07 |
| No. of reflections | 1786 |
| No. of parameters | 130 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.22, −0.22 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620013103/hb4366sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620013103/hb4366Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620013103/hb4366Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2032776
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C9H13N3O | F(000) = 768 |
| Mr = 179.22 | Dx = 1.310 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 24.7018 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 9928 reflections |
| b = 6.3093 (1) Å | θ = 4.1–72.3° |
| c = 13.2103 (3) Å | µ = 0.72 mm−1 |
| β = 118.0496 (8)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1817.01 (7) Å3 | Irregular, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.25 × 0.24 × 0.23 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1786 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Incoatec IMuS microfocus Cu tube | 1770 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Multi-layer optics monochromator | Rint = 0.019 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 72.4°, θmin = 4.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (AXScale; Bruker, 2016) | h = −29→26 |
| Tmin = 0.684, Tmax = 0.754 | k = −7→7 |
| 15813 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.098 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0541P)2 + 1.3587P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.07 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1786 reflections | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 130 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL2017/1 (Sheldrick 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0036 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. The hydrazide H2, H3A, and H3B atoms were located in difference-Fourier maps while all other hydrogen atoms were initially placed in calculated positions with their coordinates constrained to ride on their carrier atoms [C—H(aromatic) = 0.95?Å, C—H(methyl) = 0.98?Å]. The constraint Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(carrier) or 1.5Ueq(methyl carrier) was applied in all cases. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.07812 (3) | 0.16597 (12) | 0.32634 (6) | 0.0191 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.03227 (4) | 0.11655 (14) | 0.43722 (7) | 0.0155 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.0261 (6) | 0.151 (2) | 0.4964 (12) | 0.023* | |
| N3 | 0.00327 (4) | −0.07477 (14) | 0.38183 (7) | 0.0155 (2) | |
| H3A | 0.0319 (7) | −0.162 (2) | 0.3826 (12) | 0.023* | |
| H3B | −0.0235 (6) | −0.037 (2) | 0.3076 (13) | 0.023* | |
| N1 | 0.18614 (4) | 0.97723 (15) | 0.64989 (8) | 0.0218 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.08706 (4) | 0.50333 (16) | 0.56022 (8) | 0.0147 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.060886 | 0.428200 | 0.582134 | 0.018* | |
| C6 | 0.11601 (4) | 0.68522 (16) | 0.61942 (8) | 0.0155 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.109206 | 0.733294 | 0.680648 | 0.019* | |
| C1 | 0.15565 (4) | 0.80037 (16) | 0.58975 (8) | 0.0156 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.16280 (5) | 0.72556 (17) | 0.49598 (9) | 0.0174 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.188258 | 0.801208 | 0.472528 | 0.021* | |
| C4 | 0.09528 (4) | 0.42708 (16) | 0.46894 (8) | 0.0144 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.13326 (5) | 0.54379 (17) | 0.43786 (9) | 0.0166 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.138925 | 0.496951 | 0.375132 | 0.020* | |
| C7 | 0.06791 (4) | 0.22760 (16) | 0.40464 (8) | 0.0141 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.17404 (5) | 1.06515 (18) | 0.73873 (9) | 0.0210 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.131656 | 1.116555 | 0.704356 | 0.032* | |
| H8B | 0.202237 | 1.183084 | 0.776385 | 0.032* | |
| H8C | 0.180052 | 0.955197 | 0.795469 | 0.032* | |
| C9 | 0.22406 (5) | 1.09916 (18) | 0.61407 (10) | 0.0222 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.258398 | 1.011548 | 0.620994 | 0.033* | |
| H9B | 0.239960 | 1.224711 | 0.662961 | 0.033* | |
| H9C | 0.199403 | 1.143461 | 0.534079 | 0.033* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0220 (4) | 0.0209 (4) | 0.0193 (4) | −0.0049 (3) | 0.0137 (3) | −0.0052 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0196 (4) | 0.0142 (4) | 0.0150 (4) | −0.0038 (3) | 0.0101 (4) | −0.0026 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0172 (4) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0148 (4) | −0.0023 (3) | 0.0071 (4) | −0.0015 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0217 (5) | 0.0240 (5) | −0.0086 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | −0.0071 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0157 (5) | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0077 (4) | 0.0024 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0157 (5) | 0.0171 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0016 (4) | 0.0075 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0130 (5) | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0160 (5) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0049 (4) | 0.0007 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0167 (5) | 0.0182 (5) | 0.0194 (5) | −0.0023 (4) | 0.0103 (4) | 0.0012 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0145 (5) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0058 (4) | 0.0012 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0176 (5) | 0.0188 (5) | 0.0165 (5) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0105 (4) | −0.0001 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0125 (5) | 0.0159 (5) | 0.0133 (5) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0055 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0214 (5) | 0.0185 (5) | 0.0225 (5) | −0.0020 (4) | 0.0098 (4) | −0.0054 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0197 (5) | 0.0199 (6) | 0.0270 (6) | −0.0059 (4) | 0.0109 (5) | −0.0024 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.2371 (12) | N2—H2 | 0.891 (15) |
| N2—N3 | 1.4187 (12) | N3—H3A | 0.892 (17) |
| N2—C7 | 1.3444 (13) | N3—H3B | 0.920 (15) |
| N1—C1 | 1.3715 (14) | C2—H2A | 0.95 |
| N1—C8 | 1.4506 (14) | C3—H3 | 0.95 |
| N1—C9 | 1.4526 (14) | C5—H5 | 0.95 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3835 (14) | C6—H6 | 0.95 |
| C5—C4 | 1.3989 (14) | C8—H8A | 0.98 |
| C6—C1 | 1.4146 (14) | C8—H8B | 0.98 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4120 (14) | C8—H8C | 0.98 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3821 (15) | C9—H9A | 0.98 |
| C4—C3 | 1.3976 (14) | C9—H9B | 0.98 |
| C4—C7 | 1.4909 (14) | C9—H9C | 0.98 |
| C7—N2—N3 | 121.75 (8) | H3A—N3—H3B | 109.9 (13) |
| C1—N1—C8 | 120.93 (9) | C1—C2—H2A | 120 |
| C1—N1—C9 | 120.31 (9) | C3—C2—H2A | 120 |
| C8—N1—C9 | 118.09 (9) | C2—C3—H3 | 119 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.76 (9) | C4—C3—H3 | 119 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.70 (9) | C4—C5—H5 | 119 |
| N1—C1—C6 | 121.36 (9) | C6—C5—H5 | 119 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 121.27 (9) | C1—C6—H6 | 120 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.37 (9) | C5—C6—H6 | 120 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.90 (9) | N1—C8—H8A | 109 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 124.79 (9) | N1—C8—H8B | 109 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.50 (9) | N1—C8—H8C | 109 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 117.69 (9) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.73 (9) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109 |
| O1—C7—N2 | 121.71 (10) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109 |
| O1—C7—C4 | 121.71 (9) | N1—C9—H9A | 109 |
| N2—C7—C4 | 116.58 (9) | N1—C9—H9B | 109 |
| N3—N2—H2 | 114.0 (9) | N1—C9—H9C | 109 |
| C7—N2—H2 | 124.2 (9) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109 |
| N2—N3—H3A | 108.3 (10) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109 |
| N2—N3—H3B | 105.4 (8) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109 |
| C8—N1—C1—C2 | 173.90 (10) | C1—N1—C9—H9A | −64 |
| C8—N1—C1—C6 | −6.35 (15) | C1—N1—C9—H9B | 176 |
| C9—N1—C1—C2 | 3.50 (16) | C1—N1—C9—H9C | 56 |
| C9—N1—C1—C6 | −176.75 (10) | C8—N1—C9—H9A | 125 |
| N3—N2—C7—O1 | −1.50 (15) | C8—N1—C9—H9B | 5 |
| N3—N2—C7—C4 | 179.43 (9) | C8—N1—C9—H9C | −115 |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.16 (11) | C7—N2—N3—H3A | 54.0 (10) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.60 (16) | C7—N2—N3—H3B | −63.6 (11) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −177.96 (10) | H2—N2—N3—H3A | −123.2 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.79 (15) | H2—N2—N3—H3B | 119.3 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.07 (18) | H2—N2—C7—O1 | 175.4 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.28 (16) | H2—N2—C7—C4 | −3.7 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −177.07 (10) | N1—C1—C2—H2A | −2 |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.08 (15) | C6—C1—C2—H2A | 178 |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 177.14 (10) | N1—C1—C6—H6 | 2 |
| C3—C4—C7—O1 | −0.02 (15) | C2—C1—C6—H6 | −178 |
| C3—C4—C7—N2 | 179.06 (10) | C1—C2—C3—H3 | −180 |
| C5—C4—C7—O1 | −178.23 (10) | H2A—C2—C3—C4 | −180 |
| C5—C4—C7—N2 | 0.84 (15) | H2A—C2—C3—H3 | 0 |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.47 (16) | H3—C3—C4—C5 | −179 |
| C1—N1—C8—H8A | −65 | H3—C3—C4—C7 | 3 |
| C1—N1—C8—H8B | 175 | C3—C4—C5—H5 | 179 |
| C1—N1—C8—H8C | 55 | C7—C4—C5—H5 | −3 |
| C9—N1—C8—H8A | 106 | C4—C5—C6—H6 | 180 |
| C9—N1—C8—H8B | −14 | H5—C5—C6—C1 | 180 |
| C9—N1—C8—H8C | −134 | H5—C5—C6—H6 | 0 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···N3i | 0.89 (2) | 2.11 (2) | 2.9203 (13) | 151 (1) |
| N3—H3B···O1ii | 0.92 (2) | 2.09 (1) | 2.9516 (11) | 157 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x, y, −z+1/2.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: National Institute of Food and Agriculture (award No. Hatch 1023929); University of Missouri, Agriculture Experiment Station Chemical Laboratories .
References
- Andrade, C. H., Salum, L. de B., Castilho, M. S., Pasqualoto, K. F. M., Ferreira, E. I. & Andricopulo, A. D. (2008). Mol. Divers. 12, 47–59. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2016). APEX3, SAINT and AXScale. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Centore, R., Carella, A., Tuzi, A., Capobianco, A. & Peluso, A. (2010). CrystEngComm, 12, 1186–1193.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Kumar, P. & Narasimhan, B. (2013). Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 13, 971–987. [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, C. F., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). IUCrJ, 4, 575–587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Sovago, I., Cottrell, S. J., Galek, P. T. A., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Platings, M., Shields, G. P., Stevens, J. S., Towler, M. & Wood, P. A. (2020). J. Appl. Cryst. 53, 226–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Mossine, V. V., Kelley, S. P. & Mawhinney, T. P. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 557–561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Mossine, V. V., Waters, J. K., Chance, D. L. & Mawhinney, T. P. (2016). Toxicol. Sci. 154, 403–415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Popiołek, Ł. (2017). Med. Chem. Res. 26, 287–301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sah, P. P. T. & Peoples, S. A. (1954). J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 43, 513–524. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Thomas, S. P., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2018). J. Chem. Theory Comput. 14, 1614–1623. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620013103/hb4366sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620013103/hb4366Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620013103/hb4366Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2032776
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report