In the crystal, molecules of the title compound are linked into (100) sheets by N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, pyrimidine, N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds
Abstract
In the title compound, C10H13N5, the piperidine ring adopts a chair conformation with the exocyclic N—C bond in an axial orientation, and the dihedral angle between the mean planes of piperidine and pyrimidine rings is 49.57 (11)°. A short intramolecular C—H⋯N contact generates an S(7) ring. In the crystal, N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds link the molecules into (100) sheets and a weak aromatic π-π stacking interaction is observed [centroid–centroid separation = 3.5559 (11) Å] between inversion-related pyrimidine rings.
Structure description
Pyrimidine derivatives exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activities such as GPR119 agonists (Fang et al., 2019 ▸), VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (Sun et al., 2018 ▸) and antitumor activity (Hassan et al., 2017 ▸). As part of our studies in this area, we now describe the synthesis and structure of the title compound.
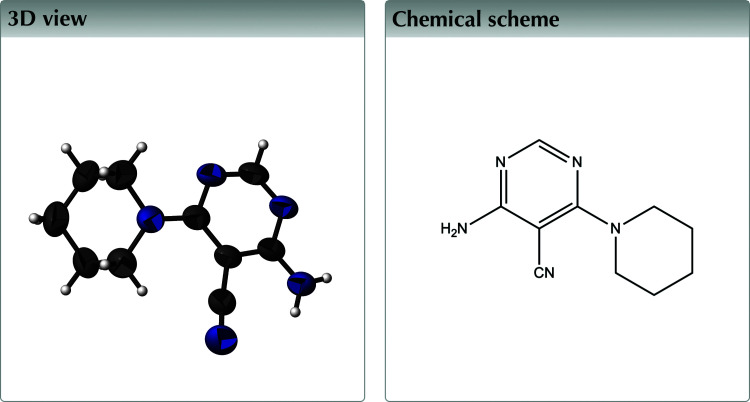
The title compound crystallizes with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸). The piperidine ring adopts a chair conformation, with atoms N3 and C7 displaced from the mean plane of the other four atoms (C5/C6/C8/C9) by −0.2472 (2) and 0.2133 (3) Å, respectively. The exocyclic N3—C4 bond has an axial orientation and the dihedral angle between the piperidine ring mean plane (all atoms) and the pyrimidine ring is 49.57 (11)°. A short intramolecular C9—H9B⋯N5 contact generates an S(7) ring.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. The short C—H⋯N contact is indicated by a double-dashed line.
In the crystal, N4—H4A⋯N1 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) link the molecules into inversion dimers characterized by an
 (8) graph set motif (Fig. 2 ▸) and N4—H4B⋯N5 hydrogen bonds link the dimers into (100) sheets. The packing also features π–π stacking interactions between inversion-related pyrimidine rings at a centroid–centroid distance of 3.5559 (11) Å (Fig. 3 ▸).
(8) graph set motif (Fig. 2 ▸) and N4—H4B⋯N5 hydrogen bonds link the dimers into (100) sheets. The packing also features π–π stacking interactions between inversion-related pyrimidine rings at a centroid–centroid distance of 3.5559 (11) Å (Fig. 3 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4—H4A⋯N1i | 0.86 | 2.12 | 2.983 (2) | 173 |
| N4—H4B⋯N5ii | 0.86 | 2.44 | 3.115 (3) | 135 |
| C9—H9B⋯N5 | 0.97 | 2.61 | 3.484 (1) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 .
.
Figure 2.
Unit-cell packing of the title compound showing N—H⋯N interactions as dotted green and purple lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been excluded.
Figure 3.
A fragment of the packing depicting the π–π interaction as a dashed line.
Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of 4-amino-6-chloro-pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile 1.0 g (0.0065 mol) and piperidine (2.75 g, 0.0325 mol) was refluxed in 20 ml of ethanol for 6 h. The reaction mixture was then cooled and stirred for 2 h at room temperature. The solid obtained was filtered, washed with ethanol and dried giving 0.98 g of white solid (yield 74%), which was recrystallized from acetone solution to obtain colourless blocks of the title compound. IR (ν, cm−1: 3426, 3308 (NH), 2190 (C=N), 1646 (C=N), 1223 (CN). 1H NMR (400 MHz DMSO-d 6): δ 8.01 (s, 1H, pyrimidine CH), 7.21 (br. s, 1 N, NH2), 3.76 (t, 2H, CH2), 1.73–1.48 (m, 6H, 3CH2). 13C NMR (DMSO-d 6): δ 168.5, 164.3, 159.9, 118.1, 58.9, 26.8, 24.9.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C10H13N5 |
| M r | 203.25 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 446 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.7335 (9), 12.4005 (10), 7.9206 (6) |
| β (°) | 93.654 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 1052.09 (15) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.08 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.18 × 0.16 × 0.15 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART APEX CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1998 ▸) |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 12900, 1855, 1452 |
| R int | 0.034 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.595 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.050, 0.180, 1.16 |
| No. of reflections | 1855 |
| No. of parameters | 136 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.21, −0.28 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343Isup2.hkl
IR. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343sup3.pdf
Proton NMR. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343sup4.pdf
C-13 NMR. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343sup5.pdf
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343Isup6.cml
CCDC reference: 1988336
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C10H13N5 | F(000) = 432 |
| Mr = 203.25 | Dx = 1.283 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.7335 (9) Å | Cell parameters from 1855 reflections |
| b = 12.4005 (10) Å | θ = 1.9–25.0° |
| c = 7.9206 (6) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| β = 93.654 (4)° | T = 446 K |
| V = 1052.09 (15) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.18 × 0.16 × 0.15 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 1452 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.034 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1998) | h = −12→12 |
| k = −14→14 | |
| 12900 measured reflections | l = −9→8 |
| 1855 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.180 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.16 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1087P)2 + 0.0972P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1855 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 136 parameters | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. H atoms were placed at calculated positions in the riding-model approximation, with N—H = 0.86 Å and C—H = 0.93 0.96 and 0.97 Å for aromatic, methyl and methine H atoms, respectively. The constraint Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2Ueq(carrier) otherwise was applied. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.81607 (15) | 0.03767 (13) | 0.1080 (2) | 0.0523 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.88239 (16) | 0.02327 (14) | 0.2655 (2) | 0.0549 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.82310 (16) | −0.04487 (14) | −0.0150 (3) | 0.0578 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.95761 (14) | −0.06277 (12) | 0.2958 (2) | 0.0637 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.75761 (15) | −0.04668 (14) | −0.1662 (2) | 0.0722 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.76188 (17) | 0.14099 (15) | 0.0789 (2) | 0.0574 (5) | |
| N4 | 0.87641 (16) | 0.09400 (13) | 0.3914 (2) | 0.0702 (5) | |
| H4A | 0.919123 | 0.083441 | 0.485517 | 0.084* | |
| H4B | 0.829833 | 0.150200 | 0.378499 | 0.084* | |
| N2 | 0.90227 (15) | −0.12859 (13) | 0.0178 (3) | 0.0691 (5) | |
| N5 | 0.72548 (18) | 0.22727 (14) | 0.0646 (3) | 0.0782 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.96377 (18) | −0.12964 (16) | 0.1669 (3) | 0.0691 (6) | |
| H3 | 1.020183 | −0.186103 | 0.184080 | 0.083* | |
| C8 | 0.5344 (2) | −0.0579 (2) | −0.2263 (3) | 0.0902 (8) | |
| H8A | 0.460985 | −0.016619 | −0.263451 | 0.108* | |
| H8B | 0.520469 | −0.087903 | −0.115968 | 0.108* | |
| C5 | 0.7794 (2) | −0.1314 (2) | −0.2914 (3) | 0.0855 (7) | |
| H5A | 0.854903 | −0.170765 | −0.256953 | 0.103* | |
| H5B | 0.790807 | −0.098612 | −0.400522 | 0.103* | |
| C6 | 0.6712 (2) | −0.2074 (2) | −0.3063 (3) | 0.0802 (7) | |
| H6A | 0.665402 | −0.245504 | −0.200085 | 0.096* | |
| H6B | 0.684841 | −0.260338 | −0.393412 | 0.096* | |
| C9 | 0.6452 (2) | 0.01582 (19) | −0.2108 (3) | 0.0776 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.653908 | 0.052850 | −0.317313 | 0.093* | |
| H9B | 0.633297 | 0.069592 | −0.124387 | 0.093* | |
| C7 | 0.5513 (3) | −0.1489 (3) | −0.3494 (4) | 0.1092 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.481912 | −0.198846 | −0.345855 | 0.131* | |
| H7B | 0.551740 | −0.120234 | −0.463297 | 0.131* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0429 (9) | 0.0413 (9) | 0.0733 (12) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0095 (8) | 0.0058 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0461 (9) | 0.0421 (9) | 0.0771 (13) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0087 (8) | 0.0062 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0398 (9) | 0.0528 (10) | 0.0819 (13) | −0.0079 (7) | 0.0118 (8) | −0.0037 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0569 (10) | 0.0484 (9) | 0.0858 (12) | 0.0083 (7) | 0.0045 (8) | 0.0039 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0522 (10) | 0.0749 (12) | 0.0894 (13) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0024 (8) | −0.0172 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0547 (10) | 0.0478 (11) | 0.0695 (12) | −0.0035 (8) | 0.0036 (8) | 0.0065 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0774 (11) | 0.0569 (10) | 0.0753 (12) | 0.0180 (8) | −0.0036 (8) | −0.0008 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0502 (9) | 0.0555 (10) | 0.1022 (14) | 0.0033 (7) | 0.0089 (9) | −0.0119 (9) |
| N5 | 0.0879 (13) | 0.0496 (10) | 0.0955 (15) | 0.0058 (9) | −0.0071 (10) | 0.0081 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0503 (11) | 0.0509 (11) | 0.1066 (17) | 0.0086 (8) | 0.0076 (10) | −0.0009 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0557 (13) | 0.118 (2) | 0.0950 (17) | 0.0059 (12) | −0.0105 (11) | −0.0233 (15) |
| C5 | 0.0727 (14) | 0.1028 (19) | 0.0825 (16) | 0.0020 (13) | 0.0154 (11) | −0.0248 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0959 (17) | 0.0833 (15) | 0.0607 (13) | −0.0066 (13) | 0.0000 (11) | −0.0158 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0793 (15) | 0.0737 (14) | 0.0787 (15) | 0.0076 (11) | −0.0039 (11) | 0.0027 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0790 (17) | 0.137 (3) | 0.109 (2) | −0.0090 (16) | −0.0162 (14) | −0.0462 (19) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.408 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.499 (3) |
| C1—C4 | 1.418 (3) | C8—C7 | 1.510 (4) |
| C1—C10 | 1.420 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C2—N4 | 1.332 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C2—N1 | 1.350 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.495 (3) |
| C4—N3 | 1.350 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9700 |
| C4—N2 | 1.356 (3) | C5—H5B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C3 | 1.321 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.498 (4) |
| N3—C9 | 1.459 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9700 |
| N3—C5 | 1.474 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9700 |
| C10—N5 | 1.142 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| N4—H4A | 0.8600 | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| N4—H4B | 0.8600 | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| N2—C3 | 1.316 (3) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | ||
| C2—C1—C4 | 118.10 (16) | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.8 |
| C2—C1—C10 | 115.91 (16) | N3—C5—C6 | 110.29 (18) |
| C4—C1—C10 | 125.39 (18) | N3—C5—H5A | 109.6 |
| N4—C2—N1 | 116.35 (18) | C6—C5—H5A | 109.6 |
| N4—C2—C1 | 122.27 (16) | N3—C5—H5B | 109.6 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 121.37 (17) | C6—C5—H5B | 109.6 |
| N3—C4—N2 | 116.21 (18) | H5A—C5—H5B | 108.1 |
| N3—C4—C1 | 125.02 (18) | C5—C6—C7 | 111.4 (2) |
| N2—C4—C1 | 118.76 (19) | C5—C6—H6A | 109.4 |
| C3—N1—C2 | 114.68 (18) | C7—C6—H6A | 109.4 |
| C4—N3—C9 | 125.62 (18) | C5—C6—H6B | 109.4 |
| C4—N3—C5 | 120.85 (19) | C7—C6—H6B | 109.4 |
| C9—N3—C5 | 112.34 (18) | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.0 |
| N5—C10—C1 | 174.5 (2) | N3—C9—C8 | 109.6 (2) |
| C2—N4—H4A | 120.0 | N3—C9—H9A | 109.8 |
| C2—N4—H4B | 120.0 | C8—C9—H9A | 109.8 |
| H4A—N4—H4B | 120.0 | N3—C9—H9B | 109.8 |
| C3—N2—C4 | 116.86 (17) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.8 |
| N2—C3—N1 | 129.86 (18) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.2 |
| N2—C3—H3 | 115.1 | C6—C7—C8 | 110.6 (2) |
| N1—C3—H3 | 115.1 | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 112.4 (2) | C8—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 109.1 | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.1 | C8—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8B | 109.1 | H7A—C7—H7B | 108.1 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.1 | ||
| C4—C1—C2—N4 | −176.67 (15) | C1—C4—N3—C5 | 174.72 (17) |
| C10—C1—C2—N4 | 11.7 (2) | N3—C4—N2—C3 | −177.91 (17) |
| C4—C1—C2—N1 | 4.5 (3) | C1—C4—N2—C3 | 3.0 (3) |
| C10—C1—C2—N1 | −167.09 (16) | C4—N2—C3—N1 | 2.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—C4—N3 | 174.67 (16) | C2—N1—C3—N2 | −4.6 (3) |
| C10—C1—C4—N3 | −14.6 (3) | C4—N3—C5—C6 | 108.9 (2) |
| C2—C1—C4—N2 | −6.3 (3) | C9—N3—C5—C6 | −59.3 (3) |
| C10—C1—C4—N2 | 164.43 (16) | N3—C5—C6—C7 | 55.9 (3) |
| N4—C2—N1—C3 | −178.31 (16) | C4—N3—C9—C8 | −109.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—N1—C3 | 0.6 (3) | C5—N3—C9—C8 | 58.3 (3) |
| N2—C4—N3—C9 | 162.23 (19) | C7—C8—C9—N3 | −55.0 (3) |
| C1—C4—N3—C9 | −18.7 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −52.9 (3) |
| N2—C4—N3—C5 | −4.3 (3) | C9—C8—C7—C6 | 52.8 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N4—H4A···N1i | 0.86 | 2.12 | 2.983 (2) | 173 |
| N4—H4B···N5ii | 0.86 | 2.44 | 3.115 (3) | 135 |
| C9—H9B···N5 | 0.97 | 2.61 | 3.484 (1) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y, −z+1; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
References
- Bruker. (1998). SMART, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Fang, Y., Xiong, L., Hu, J., Zhang, S., Xie, S., Tu, L., Wan, Y., Jin, Y., Li, X., Hu, S. & Yang, Z. (2019). Bioorg. Chem. 86, 103–111. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Hassan, A. S., Mady, M. F., Awad, H. M. & Hafez, T. S. (2017). Chin. Chem. Lett. 28, 388–393.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Sun, W., Hu, S., Fang, S. & Yan, H. (2018). Bioorg. Chem. 78, 393–405. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343Isup2.hkl
IR. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343sup3.pdf
Proton NMR. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343sup4.pdf
C-13 NMR. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343sup5.pdf
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620003855/hb4343Isup6.cml
CCDC reference: 1988336
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





