In the crystal structure of the title compound two independent binuclear copper(II) complexes are present, each with site symmetry
 and with the CuII atoms in a square-pyramidal coordination environment.
and with the CuII atoms in a square-pyramidal coordination environment.
Keywords: crystal structure, paddle-wheel structure, binuclear copper complex, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the binuclear title compound, [Cu2(C8H7O3)4(H2O)2], comprises two halves of diaquatetrakis(μ-3-methoxybenzoato-κ2
O
1:O
1′)dicopper(II) units. The paddle-wheel structure of each complex is completed by application of inversion symmetry, with the inversion centre situated at the midpoint between two CuII atoms in each dimer. The two CuII atoms of each centrosymmetric dimer are bridged by four 3-methoxybenzoate anions resulting in Cu⋯Cu separations of 2.5961 (11) and 2.6060 (12) Å, respectively. The square-pyramidal coordination sphere of each CuII atom is completed by an apical water molecule. Intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds of weak nature link the complexes into layers parallel to (100). The three-dimensional network structure is accomplished by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds interlinking adjacent layers.
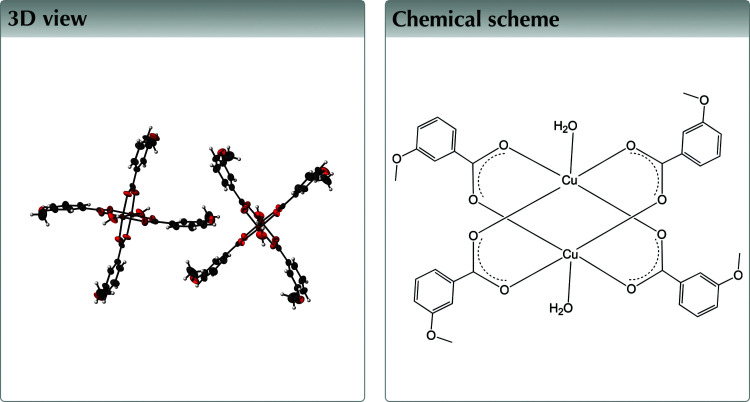
Structure description
A very early structure investigation of cupric acetate monohydrate revealed that it is dimeric in nature, represented by the formula [Cu2(CH3COO)4(H2O)2] (Van Niekerk & Schoening, 1953 ▸). In the dimer, each of the two cupric ions is bonded to four oxygen atoms of four bridging acetate ligands in addition to a terminal aqua ligand. This kind of coordination, wherein a pair of metal cations is bonded to four symmetrically bridging carboxylate anions, is referred to as a paddle-wheel structure and is well documented for several dimeric copper carboxylates (Doedens, 1976 ▸). The Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, version 5.40, update September 2019; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) lists the structures of several dicopper(II) compounds where the cupric cations are symmetrically bridged by four carboxylate ligands. The fifth ligand can be a terminal water molecule or any O– or N-donor ligand. A dinuclear copper compound with a paddle-wheel structure, viz. tetrakis(μ-3-methoxybenzoato- κ2 O 1:O 1′)bis[acetonitrilecopper(II)] (2), was reported previously for the methoxybenzoate anion (Kar et al., 2011 ▸). In the present study, we describe the structure of a related dinuclear copper complex where the acetonitrile ligands are replaced by aqua ligands.
The crystal structure of the title compound, [Cu2(C8H7O3)4(H2O)2], (1), consists of two crystallographically unique cupric cations, four crystallographically independent 3-methoxybenzoate anions and two terminal water molecules that build up two independent halves of a dimeric [Cu2(C8H7O3)4(H2O)2] complex, the other halves being generated by inversion symmetry. The inversion centre is situated at the midpoint of the line connecting two CuII atoms in each of the dimers (Fig. 1 ▸). In each centrosymmetric dimer, a pair of CuII atoms is connected through four syn–syn bis-monodentate 3-methoxybenzoate bridges to generate a binuclear paddle-wheel unit. The fifth ligand, O7 on Cu1 and O14 on Cu2, is a terminal water molecule, defining an overall square-pyramidal coordination sphere around the central metal cation. Bond lengths and angles of the 3-methoxybenzoate anions are in normal ranges and are in agreement with reported data (Kar et al., 2011 ▸). The Cu—Owater bonds [2.171 (4) and 2.126 (4) Å for Cu1 and Cu2, respectively] are elongated as compared to the Cu—Ocarboxylate distances ranging from 1.949 (4) to 1.959 (3) Å for Cu1 and from 1.936 (3) to 1.973 (3) Å for Cu2. The Cu⋯Cu separations in the dimers amount to 2.6060 (12) Å for Cu1 and 2.5961 (11) Å for Cu2, which are shorter than the Cu⋯Cu distance of 2.6433 (3) Å reported for (2) (Kar et al., 2011 ▸).
Figure 1.
The two centrosymmetric binuclear complexes in the crystal structure of [Cu2(C8H7O3)4(H2O)2] with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level. [Symmetry codes: (i) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z; (ii) −x + 2, −y + 1, −z + 1.]
The water molecules, and the phenyl groups C23—H23 and C27—H27, respectively, function as hydrogen-bond donors, while the methoxy oxygen atoms O3, O6 and O13 and the carboxylate oxygen atoms O1, O5, O11 and O14 function as hydrogen-bond acceptors; parts of the O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are bifurcated (Table 1 ▸). Each Cu1 dimer is linked to six other symmetry-related Cu1 dimers with the aid of three O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, and each Cu2 dimer is hydrogen-bonded to six other symmetry-related Cu2 dimers (Fig. 2 ▸). As a result, O—H⋯O hydrogen-bonded layers parallel to (100) are formed. The two C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds interlink adjacent layers into a three-dimensional network (Fig. 3 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O7—H7A⋯O3i | 0.84 (2) | 2.11 (3) | 2.912 (6) | 161 (5) |
| O7—H7B⋯O1ii | 0.83 (2) | 2.42 (5) | 3.107 (6) | 141 (7) |
| O7—H7B⋯O5ii | 0.83 (2) | 2.60 (5) | 3.306 (6) | 144 (6) |
| O14—H14B⋯O13iii | 0.84 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.831 (6) | 169 (8) |
| O14—H14A⋯O11iv | 0.83 (2) | 2.11 (3) | 2.905 (5) | 160 (6) |
| O14—H14A⋯O14iv | 0.83 (2) | 2.57 (5) | 3.055 (8) | 118 (5) |
| C23—H23⋯O6v | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.355 (7) | 149 |
| C27—H27⋯O6vi | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.114 (7) | 117 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 ; (iv)
; (iv)
 ; (v)
; (v)
 ; (vi)
; (vi)
 .
.
Figure 2.
A view along [100] showing the O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) around the Cu1 dimer (left) and the Cu2 dimer (right).
Figure 3.
A view along [001] showing the interlinking of dimeric Cu1 units with adjacent dimeric Cu2 units with the aid of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Synthesis and crystallization
Cupric oxide (100 mg) was added in small portions to a hot aqueous solution of 3-methoxybenzoic acid (0.304 g, 2 mmol) in water (100 ml). The hot reaction mixture was continuously stirred to dissolve the oxide. When most of the oxide had dissolved, the blue reaction mixture was filtered to remove the insoluble matter. The blue filtrate thus obtained was left aside for crystallization. After a few days blue–greenish crystals of (1) slowly separated. The crystals were filtered and dried in air. Yield 35%.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The crystal under investigation was a two-component twin with a refined batch scale factor (BASF) of 0.47. The matrix that was used for overlapping the twin domains is (101 0
 0 00
0 00
 ). H atoms of water molecules were discernible from a difference-Fourier map. To get a reasonable shape, water molecules were refined with a target value of 0.85 (2) Å for O—H bond lengths and of 1.35 (2) Å for H⋯H distances.
). H atoms of water molecules were discernible from a difference-Fourier map. To get a reasonable shape, water molecules were refined with a target value of 0.85 (2) Å for O—H bond lengths and of 1.35 (2) Å for H⋯H distances.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Cu2(C8H7O3)4(H2O)2] |
| M r | 767.65 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 22.515 (3), 7.5349 (6), 21.536 (2) |
| β (°) | 118.429 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 3213.0 (6) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.40 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.15 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker AXS Kappa APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.410, 0.745 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 36309, 6704, 5194 |
| R int | 0.082 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.631 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.043, 0.108, 1.02 |
| No. of reflections | 6704 |
| No. of parameters | 454 |
| No. of restraints | 6 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.90, −0.83 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620004484/wm4126sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620004484/wm4126Isup3.hkl
CCDC reference: 1993956
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
BRS acknowledges the Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility (SAIF), Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Madras, for the single-crystal X-ray data collection.
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| [Cu2(C8H7O3)4(H2O)2] | F(000) = 1576 |
| Mr = 767.65 | Dx = 1.587 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 22.515 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 9989 reflections |
| b = 7.5349 (6) Å | θ = 2.2–26.2° |
| c = 21.536 (2) Å | µ = 1.40 mm−1 |
| β = 118.429 (4)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 3213.0 (6) Å3 | Block, bluish green |
| Z = 4 | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker AXS Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 6704 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5194 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.082 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 26.6°, θmin = 1.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | h = −28→28 |
| Tmin = 0.410, Tmax = 0.745 | k = −9→9 |
| 36309 measured reflections | l = −26→26 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 6 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.108 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0351P)2 + 3.0856P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 6704 reflections | Δρmax = 0.90 e Å−3 |
| 454 parameters | Δρmin = −0.83 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a two-component twin |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu1 | 0.50684 (3) | 0.65510 (8) | −0.02260 (3) | 0.03022 (19) | |
| C1 | 0.5402 (2) | 0.6223 (7) | 0.1219 (3) | 0.0341 (12) | |
| C2 | 0.5610 (2) | 0.7024 (8) | 0.1931 (3) | 0.0352 (12) | |
| C3 | 0.5619 (3) | 0.8829 (7) | 0.2013 (3) | 0.0473 (14) | |
| H3 | 0.553854 | 0.957326 | 0.163685 | 0.057* | |
| C4 | 0.5745 (3) | 0.9535 (8) | 0.2649 (3) | 0.0565 (16) | |
| H4 | 0.572505 | 1.075719 | 0.269696 | 0.068* | |
| C5 | 0.5900 (3) | 0.8450 (8) | 0.3216 (3) | 0.0483 (15) | |
| H5 | 0.598563 | 0.893345 | 0.364783 | 0.058* | |
| C6 | 0.5929 (3) | 0.6635 (7) | 0.3145 (3) | 0.0451 (14) | |
| C7 | 0.5772 (3) | 0.5917 (8) | 0.2496 (3) | 0.0409 (13) | |
| H7 | 0.577578 | 0.469341 | 0.244079 | 0.049* | |
| C8 | 0.6299 (5) | 0.3893 (9) | 0.3737 (4) | 0.095 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.594361 | 0.328194 | 0.334527 | 0.142* | |
| H8B | 0.637957 | 0.332541 | 0.416971 | 0.142* | |
| H8C | 0.670353 | 0.385973 | 0.369359 | 0.142* | |
| C9 | 0.3827 (2) | 0.5945 (7) | −0.0264 (3) | 0.0370 (11) | |
| C10 | 0.3150 (3) | 0.6464 (7) | −0.0354 (3) | 0.0381 (12) | |
| C11 | 0.2869 (3) | 0.8092 (8) | −0.0627 (3) | 0.0465 (14) | |
| H11 | 0.308308 | 0.886444 | −0.079308 | 0.056* | |
| C12 | 0.2266 (3) | 0.8568 (8) | −0.0650 (3) | 0.0604 (17) | |
| H12 | 0.206701 | 0.964655 | −0.085164 | 0.073* | |
| C13 | 0.1958 (3) | 0.7476 (9) | −0.0382 (4) | 0.0584 (19) | |
| H13 | 0.155816 | 0.782540 | −0.038909 | 0.070* | |
| C14 | 0.2244 (3) | 0.5856 (9) | −0.0100 (3) | 0.0526 (15) | |
| C15 | 0.2829 (3) | 0.5331 (8) | −0.0094 (3) | 0.0457 (13) | |
| H15 | 0.301205 | 0.422211 | 0.008402 | 0.055* | |
| C16 | 0.2158 (4) | 0.3189 (9) | 0.0455 (5) | 0.083 (2) | |
| H16A | 0.211575 | 0.238074 | 0.009184 | 0.124* | |
| H16B | 0.191200 | 0.273485 | 0.068286 | 0.124* | |
| H16C | 0.262557 | 0.331491 | 0.079654 | 0.124* | |
| O1 | 0.53588 (19) | 0.7269 (5) | 0.0746 (2) | 0.0403 (10) | |
| O2 | 0.52749 (18) | 0.4584 (4) | 0.11476 (17) | 0.0380 (8) | |
| O3 | 0.6108 (2) | 0.5671 (5) | 0.3743 (2) | 0.0639 (12) | |
| O4 | 0.40388 (17) | 0.4427 (5) | −0.00258 (19) | 0.0419 (9) | |
| O5 | 0.41505 (18) | 0.7099 (5) | −0.04147 (19) | 0.0412 (8) | |
| O6 | 0.1892 (2) | 0.4862 (6) | 0.0153 (2) | 0.0651 (12) | |
| O7 | 0.5378 (3) | 0.9096 (5) | −0.0449 (3) | 0.0582 (11) | |
| H7A | 0.566 (2) | 0.927 (7) | −0.059 (3) | 0.050 (18)* | |
| H7B | 0.530 (3) | 1.005 (5) | −0.031 (4) | 0.10 (3)* | |
| Cu2 | 1.00357 (3) | 0.34185 (7) | 0.52545 (3) | 0.02704 (17) | |
| C17 | 0.8821 (2) | 0.4364 (7) | 0.4052 (3) | 0.0344 (11) | |
| C18 | 0.8143 (2) | 0.3902 (6) | 0.3454 (3) | 0.0335 (11) | |
| C19 | 0.7823 (2) | 0.5098 (7) | 0.2908 (3) | 0.0378 (11) | |
| H19 | 0.800444 | 0.622163 | 0.293246 | 0.045* | |
| C20 | 0.7232 (3) | 0.4598 (7) | 0.2326 (3) | 0.0416 (12) | |
| C21 | 0.6958 (3) | 0.2923 (9) | 0.2304 (3) | 0.0511 (15) | |
| H21 | 0.655720 | 0.258591 | 0.191294 | 0.061* | |
| C22 | 0.7275 (3) | 0.1787 (7) | 0.2854 (3) | 0.0509 (14) | |
| H22 | 0.708932 | 0.067457 | 0.283747 | 0.061* | |
| C23 | 0.7873 (3) | 0.2266 (8) | 0.3437 (3) | 0.0450 (15) | |
| H23 | 0.808799 | 0.148658 | 0.381440 | 0.054* | |
| C24 | 0.7133 (3) | 0.7314 (10) | 0.1710 (4) | 0.073 (2) | |
| H24A | 0.721094 | 0.799866 | 0.211808 | 0.110* | |
| H24B | 0.680916 | 0.791342 | 0.129157 | 0.110* | |
| H24C | 0.754901 | 0.717887 | 0.169388 | 0.110* | |
| C25 | 1.0434 (2) | 0.3824 (7) | 0.4183 (2) | 0.0327 (11) | |
| C26 | 1.0650 (2) | 0.3142 (7) | 0.3676 (3) | 0.0334 (11) | |
| C27 | 1.0786 (3) | 0.1352 (7) | 0.3666 (3) | 0.0438 (13) | |
| H27 | 1.077861 | 0.058767 | 0.400195 | 0.053* | |
| C28 | 1.0931 (3) | 0.0720 (8) | 0.3153 (3) | 0.0532 (16) | |
| H28 | 1.101825 | −0.048261 | 0.314230 | 0.064* | |
| C29 | 1.0948 (3) | 0.1821 (8) | 0.2661 (3) | 0.0499 (15) | |
| H29 | 1.103129 | 0.136388 | 0.230861 | 0.060* | |
| C30 | 1.0841 (3) | 0.3626 (7) | 0.2686 (3) | 0.0400 (13) | |
| C31 | 1.0693 (2) | 0.4274 (7) | 0.3186 (3) | 0.0342 (12) | |
| H31 | 1.061863 | 0.548415 | 0.320089 | 0.041* | |
| C32 | 1.1014 (4) | 0.6486 (8) | 0.2328 (4) | 0.0647 (18) | |
| H32A | 1.063753 | 0.700448 | 0.235440 | 0.097* | |
| H32B | 1.106403 | 0.703643 | 0.195349 | 0.097* | |
| H32C | 1.141820 | 0.666487 | 0.276769 | 0.097* | |
| O8 | 0.91180 (17) | 0.3186 (4) | 0.44982 (19) | 0.0428 (9) | |
| O9 | 0.90509 (18) | 0.5881 (4) | 0.40517 (17) | 0.0416 (9) | |
| O10 | 0.68798 (18) | 0.5618 (5) | 0.1750 (2) | 0.0544 (10) | |
| O11 | 1.0361 (2) | 0.2734 (4) | 0.4584 (2) | 0.0385 (9) | |
| O12 | 1.0316 (2) | 0.5454 (4) | 0.41646 (19) | 0.0408 (9) | |
| O13 | 1.0901 (2) | 0.4638 (5) | 0.2193 (2) | 0.0610 (12) | |
| O14 | 1.0181 (3) | 0.0849 (5) | 0.5712 (2) | 0.0567 (12) | |
| H14B | 1.034 (4) | 0.074 (8) | 0.6150 (11) | 0.10 (3)* | |
| H14A | 0.998 (3) | −0.009 (6) | 0.552 (3) | 0.09 (2)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu1 | 0.0338 (4) | 0.0263 (3) | 0.0275 (4) | 0.0029 (2) | 0.0122 (3) | 0.0011 (2) |
| C1 | 0.019 (2) | 0.050 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.008 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C2 | 0.025 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.027 (3) | −0.004 (2) | 0.010 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C3 | 0.051 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.019 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C4 | 0.066 (4) | 0.043 (3) | 0.059 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.029 (3) | −0.017 (3) |
| C5 | 0.045 (3) | 0.061 (4) | 0.034 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.014 (3) | −0.016 (3) |
| C6 | 0.041 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C7 | 0.045 (3) | 0.047 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.020 (3) | −0.007 (2) |
| C8 | 0.157 (8) | 0.080 (5) | 0.048 (4) | 0.050 (5) | 0.050 (5) | 0.021 (4) |
| C9 | 0.032 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.025 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.009 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C10 | 0.032 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.008 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C11 | 0.038 (3) | 0.056 (4) | 0.038 (3) | 0.011 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.004 (3) |
| C12 | 0.040 (3) | 0.068 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.025 (3) | 0.013 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C13 | 0.033 (4) | 0.086 (5) | 0.056 (4) | 0.008 (3) | 0.020 (3) | −0.016 (3) |
| C14 | 0.034 (3) | 0.075 (4) | 0.048 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.014 (3) |
| C15 | 0.039 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.036 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.012 (2) | −0.010 (3) |
| C16 | 0.080 (5) | 0.078 (5) | 0.103 (7) | −0.007 (4) | 0.053 (5) | 0.010 (5) |
| O1 | 0.047 (3) | 0.0385 (19) | 0.030 (2) | −0.0018 (16) | 0.0142 (19) | −0.0012 (16) |
| O2 | 0.044 (2) | 0.0358 (19) | 0.0291 (19) | −0.0007 (16) | 0.0129 (16) | −0.0034 (15) |
| O3 | 0.095 (3) | 0.066 (3) | 0.035 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| O4 | 0.0324 (18) | 0.044 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.0060 (16) | 0.0161 (16) | 0.0035 (17) |
| O5 | 0.040 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0090 (17) | 0.0218 (18) | 0.0052 (17) |
| O6 | 0.047 (2) | 0.082 (3) | 0.072 (3) | −0.008 (2) | 0.033 (2) | −0.015 (3) |
| O7 | 0.092 (4) | 0.031 (2) | 0.070 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.053 (3) | 0.009 (2) |
| Cu2 | 0.0363 (4) | 0.0242 (3) | 0.0232 (3) | −0.0029 (2) | 0.0163 (3) | −0.0015 (2) |
| C17 | 0.033 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C18 | 0.031 (2) | 0.040 (3) | 0.033 (3) | −0.005 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C19 | 0.033 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.034 (3) | −0.005 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| C20 | 0.033 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.012 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C21 | 0.042 (4) | 0.062 (4) | 0.041 (4) | −0.008 (3) | 0.014 (3) | −0.010 (3) |
| C22 | 0.045 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.046 (3) | −0.019 (3) | 0.015 (3) | −0.005 (3) |
| C23 | 0.045 (4) | 0.051 (3) | 0.034 (3) | −0.009 (3) | 0.016 (3) | −0.005 (3) |
| C24 | 0.065 (4) | 0.065 (4) | 0.070 (5) | −0.001 (4) | 0.016 (4) | 0.018 (4) |
| C25 | 0.036 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.021 (2) | −0.005 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C26 | 0.032 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.033 (3) | −0.007 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.009 (2) |
| C27 | 0.054 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.025 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| C28 | 0.074 (4) | 0.042 (3) | 0.054 (4) | 0.011 (3) | 0.039 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C29 | 0.063 (4) | 0.059 (4) | 0.042 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.037 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C30 | 0.045 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.023 (3) | −0.010 (2) |
| C31 | 0.039 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.029 (3) | −0.004 (2) | 0.016 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C32 | 0.084 (5) | 0.062 (4) | 0.060 (4) | −0.022 (3) | 0.044 (4) | −0.005 (3) |
| O8 | 0.038 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.038 (2) | −0.0101 (17) | 0.0114 (17) | −0.0004 (17) |
| O9 | 0.041 (2) | 0.0380 (18) | 0.0358 (19) | −0.0083 (16) | 0.0105 (17) | −0.0045 (16) |
| O10 | 0.044 (2) | 0.059 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.0012 (18) | 0.0057 (18) | 0.0023 (19) |
| O11 | 0.060 (3) | 0.0358 (18) | 0.033 (2) | −0.0010 (17) | 0.033 (2) | −0.0042 (15) |
| O12 | 0.065 (3) | 0.0319 (19) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0024 (17) | 0.036 (2) | −0.0039 (15) |
| O13 | 0.099 (3) | 0.058 (2) | 0.047 (2) | −0.019 (2) | 0.051 (2) | −0.013 (2) |
| O14 | 0.106 (4) | 0.0252 (19) | 0.036 (2) | −0.012 (2) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0034 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cu1—O1 | 1.949 (4) | Cu2—O8 | 1.936 (3) |
| Cu1—O2i | 1.951 (3) | Cu2—O9ii | 1.953 (3) |
| Cu1—O5 | 1.951 (3) | Cu2—O12ii | 1.964 (3) |
| Cu1—O4i | 1.959 (3) | Cu2—O11 | 1.973 (3) |
| Cu1—O7 | 2.171 (4) | Cu2—O14 | 2.126 (4) |
| Cu1—Cu1i | 2.6060 (12) | Cu2—Cu2ii | 2.5961 (11) |
| C1—O1 | 1.254 (6) | C17—O8 | 1.244 (6) |
| C1—O2 | 1.261 (6) | C17—O9 | 1.255 (6) |
| C1—C2 | 1.500 (7) | C17—C18 | 1.496 (7) |
| C2—C3 | 1.370 (7) | C18—C23 | 1.367 (7) |
| C2—C7 | 1.374 (8) | C18—C19 | 1.381 (7) |
| C3—C4 | 1.367 (9) | C19—C20 | 1.377 (7) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.369 (8) | C20—O10 | 1.351 (6) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C20—C21 | 1.396 (8) |
| C5—C6 | 1.381 (7) | C21—C22 | 1.355 (8) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C6—O3 | 1.362 (7) | C22—C23 | 1.382 (8) |
| C6—C7 | 1.378 (8) | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C23—H23 | 0.9300 |
| C8—O3 | 1.409 (7) | C24—O10 | 1.418 (8) |
| C8—H8A | 0.9600 | C24—H24A | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8B | 0.9600 | C24—H24B | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8C | 0.9600 | C24—H24C | 0.9600 |
| C9—O4 | 1.252 (6) | C25—O12 | 1.253 (6) |
| C9—O5 | 1.272 (6) | C25—O11 | 1.258 (6) |
| C9—C10 | 1.495 (7) | C25—C26 | 1.484 (7) |
| C10—C11 | 1.377 (7) | C26—C27 | 1.385 (7) |
| C10—C15 | 1.397 (7) | C26—C31 | 1.395 (7) |
| C11—C12 | 1.380 (8) | C27—C28 | 1.379 (8) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9300 | C27—H27 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.370 (9) | C28—C29 | 1.361 (8) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | C28—H28 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.379 (9) | C29—C30 | 1.387 (8) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9300 | C29—H29 | 0.9300 |
| C14—C15 | 1.369 (8) | C30—C31 | 1.361 (7) |
| C14—O6 | 1.376 (7) | C30—O13 | 1.365 (7) |
| C15—H15 | 0.9300 | C31—H31 | 0.9300 |
| C16—O6 | 1.414 (8) | C32—O13 | 1.420 (6) |
| C16—H16A | 0.9600 | C32—H32A | 0.9600 |
| C16—H16B | 0.9600 | C32—H32B | 0.9600 |
| C16—H16C | 0.9600 | C32—H32C | 0.9600 |
| O7—H7A | 0.835 (19) | O14—H14B | 0.84 (2) |
| O7—H7B | 0.830 (19) | O14—H14A | 0.832 (19) |
| O1—Cu1—O2i | 169.12 (15) | O8—Cu2—O9ii | 168.91 (14) |
| O1—Cu1—O5 | 86.87 (16) | O8—Cu2—O12ii | 89.02 (16) |
| O2i—Cu1—O5 | 90.77 (15) | O9ii—Cu2—O12ii | 89.57 (16) |
| O1—Cu1—O4i | 91.82 (16) | O8—Cu2—O11 | 88.84 (16) |
| O2i—Cu1—O4i | 88.52 (15) | O9ii—Cu2—O11 | 90.47 (16) |
| O5—Cu1—O4i | 169.26 (15) | O12ii—Cu2—O11 | 169.05 (14) |
| O1—Cu1—O7 | 90.79 (17) | O8—Cu2—O14 | 100.04 (17) |
| O2i—Cu1—O7 | 100.09 (17) | O9ii—Cu2—O14 | 91.05 (17) |
| O5—Cu1—O7 | 100.79 (17) | O12ii—Cu2—O14 | 96.79 (16) |
| O4i—Cu1—O7 | 89.89 (17) | O11—Cu2—O14 | 94.16 (15) |
| O1—Cu1—Cu1i | 83.50 (11) | O8—Cu2—Cu2ii | 84.33 (10) |
| O2i—Cu1—Cu1i | 85.81 (10) | O9ii—Cu2—Cu2ii | 84.59 (10) |
| O5—Cu1—Cu1i | 88.03 (11) | O12ii—Cu2—Cu2ii | 84.78 (10) |
| O4i—Cu1—Cu1i | 81.23 (11) | O11—Cu2—Cu2ii | 84.32 (11) |
| O7—Cu1—Cu1i | 169.25 (15) | O14—Cu2—Cu2ii | 175.37 (14) |
| O1—C1—O2 | 126.3 (5) | O8—C17—O9 | 125.4 (5) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 116.3 (5) | O8—C17—C18 | 116.9 (4) |
| O2—C1—C2 | 117.4 (5) | O9—C17—C18 | 117.6 (5) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 120.4 (5) | C23—C18—C19 | 121.4 (5) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.7 (5) | C23—C18—C17 | 119.4 (5) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 118.9 (5) | C19—C18—C17 | 119.1 (4) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.0 (6) | C20—C19—C18 | 118.8 (5) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C20—C19—H19 | 120.6 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C18—C19—H19 | 120.6 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.2 (5) | O10—C20—C19 | 124.8 (5) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 | O10—C20—C21 | 115.3 (5) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C19—C20—C21 | 119.9 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.9 (5) | C22—C21—C20 | 120.0 (5) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.1 | C22—C21—H21 | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.1 | C20—C21—H21 | 120.0 |
| O3—C6—C7 | 124.6 (5) | C21—C22—C23 | 120.6 (5) |
| O3—C6—C5 | 115.5 (5) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.7 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.9 (5) | C23—C22—H22 | 119.7 |
| C2—C7—C6 | 119.4 (5) | C18—C23—C22 | 119.2 (6) |
| C2—C7—H7 | 120.3 | C18—C23—H23 | 120.4 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 | C22—C23—H23 | 120.4 |
| O3—C8—H8A | 109.5 | O10—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| O3—C8—H8B | 109.5 | O10—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| O3—C8—H8C | 109.5 | O10—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| O4—C9—O5 | 125.2 (5) | O12—C25—O11 | 124.5 (5) |
| O4—C9—C10 | 117.3 (5) | O12—C25—C26 | 117.1 (4) |
| O5—C9—C10 | 117.4 (5) | O11—C25—C26 | 118.4 (4) |
| C11—C10—C15 | 119.7 (5) | C27—C26—C31 | 119.3 (5) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 121.5 (5) | C27—C26—C25 | 119.9 (5) |
| C15—C10—C9 | 118.6 (5) | C31—C26—C25 | 120.7 (4) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 119.4 (6) | C28—C27—C26 | 119.1 (5) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.3 | C28—C27—H27 | 120.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.3 | C26—C27—H27 | 120.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 121.0 (6) | C29—C28—C27 | 121.3 (5) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.5 | C29—C28—H28 | 119.3 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.5 | C27—C28—H28 | 119.3 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 119.5 (6) | C28—C29—C30 | 119.8 (5) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.2 | C28—C29—H29 | 120.1 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 120.2 | C30—C29—H29 | 120.1 |
| C15—C14—O6 | 124.8 (6) | C31—C30—O13 | 124.5 (5) |
| C15—C14—C13 | 120.4 (6) | C31—C30—C29 | 119.7 (5) |
| O6—C14—C13 | 114.8 (5) | O13—C30—C29 | 115.8 (5) |
| C14—C15—C10 | 119.9 (5) | C30—C31—C26 | 120.6 (5) |
| C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 | C30—C31—H31 | 119.7 |
| C10—C15—H15 | 120.0 | C26—C31—H31 | 119.7 |
| O6—C16—H16A | 109.5 | O13—C32—H32A | 109.5 |
| O6—C16—H16B | 109.5 | O13—C32—H32B | 109.5 |
| H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 | H32A—C32—H32B | 109.5 |
| O6—C16—H16C | 109.5 | O13—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 | H32A—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 | H32B—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| C1—O1—Cu1 | 123.6 (3) | C17—O8—Cu2 | 123.5 (3) |
| C1—O2—Cu1i | 120.6 (3) | C17—O9—Cu2ii | 122.0 (3) |
| C6—O3—C8 | 117.0 (5) | C20—O10—C24 | 119.4 (5) |
| C9—O4—Cu1i | 126.7 (3) | C25—O11—Cu2 | 123.2 (3) |
| C9—O5—Cu1 | 118.7 (3) | C25—O12—Cu2ii | 123.2 (3) |
| C14—O6—C16 | 118.1 (5) | C30—O13—C32 | 117.6 (4) |
| Cu1—O7—H7A | 127 (4) | Cu2—O14—H14B | 120 (4) |
| Cu1—O7—H7B | 123 (4) | Cu2—O14—H14A | 128 (4) |
| H7A—O7—H7B | 109 (3) | H14B—O14—H14A | 108 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 12.5 (7) | O8—C17—C18—C23 | 2.6 (7) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | −166.2 (5) | O9—C17—C18—C23 | −179.6 (5) |
| O1—C1—C2—C7 | −169.6 (5) | O8—C17—C18—C19 | −173.4 (5) |
| O2—C1—C2—C7 | 11.8 (7) | O9—C17—C18—C19 | 4.4 (7) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −4.4 (9) | C23—C18—C19—C20 | −2.3 (8) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 173.6 (5) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 173.7 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 3.6 (10) | C18—C19—C20—O10 | −178.2 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 (10) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 1.6 (8) |
| C4—C5—C6—O3 | 178.1 (6) | O10—C20—C21—C22 | 179.4 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −2.9 (10) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −0.4 (9) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 1.4 (8) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | −0.3 (10) |
| C1—C2—C7—C6 | −176.5 (5) | C19—C18—C23—C22 | 1.6 (9) |
| O3—C6—C7—C2 | −178.9 (5) | C17—C18—C23—C22 | −174.3 (5) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | 2.2 (9) | C21—C22—C23—C18 | −0.3 (10) |
| O4—C9—C10—C11 | −178.6 (5) | O12—C25—C26—C27 | −179.6 (5) |
| O5—C9—C10—C11 | 3.5 (7) | O11—C25—C26—C27 | −2.0 (7) |
| O4—C9—C10—C15 | 7.5 (7) | O12—C25—C26—C31 | −2.3 (7) |
| O5—C9—C10—C15 | −170.4 (5) | O11—C25—C26—C31 | 175.4 (5) |
| C15—C10—C11—C12 | −1.2 (8) | C31—C26—C27—C28 | −2.8 (8) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −175.1 (5) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | 174.6 (5) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 2.6 (9) | C26—C27—C28—C29 | 0.5 (10) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.7 (10) | C27—C28—C29—C30 | 2.2 (10) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.6 (9) | C28—C29—C30—C31 | −2.6 (9) |
| C12—C13—C14—O6 | −179.8 (6) | C28—C29—C30—O13 | 176.8 (6) |
| O6—C14—C15—C10 | −179.0 (5) | O13—C30—C31—C26 | −179.1 (5) |
| C13—C14—C15—C10 | 1.9 (8) | C29—C30—C31—C26 | 0.3 (8) |
| C11—C10—C15—C14 | −1.0 (8) | C27—C26—C31—C30 | 2.4 (8) |
| C9—C10—C15—C14 | 173.0 (5) | C25—C26—C31—C30 | −175.0 (5) |
| O2—C1—O1—Cu1 | 0.7 (7) | O9—C17—O8—Cu2 | −4.5 (7) |
| C2—C1—O1—Cu1 | −177.8 (3) | C18—C17—O8—Cu2 | 173.2 (3) |
| O1—C1—O2—Cu1i | −3.4 (7) | O8—C17—O9—Cu2ii | 3.9 (7) |
| C2—C1—O2—Cu1i | 175.1 (3) | C18—C17—O9—Cu2ii | −173.8 (3) |
| C7—C6—O3—C8 | 15.7 (10) | C19—C20—O10—C24 | 2.3 (8) |
| C5—C6—O3—C8 | −165.3 (6) | C21—C20—O10—C24 | −177.5 (6) |
| O5—C9—O4—Cu1i | 3.4 (7) | O12—C25—O11—Cu2 | 0.4 (7) |
| C10—C9—O4—Cu1i | −174.3 (3) | C26—C25—O11—Cu2 | −177.1 (3) |
| O4—C9—O5—Cu1 | −3.0 (7) | O11—C25—O12—Cu2ii | −1.9 (7) |
| C10—C9—O5—Cu1 | 174.7 (3) | C26—C25—O12—Cu2ii | 175.6 (3) |
| C15—C14—O6—C16 | 1.4 (9) | C31—C30—O13—C32 | 19.3 (9) |
| C13—C14—O6—C16 | −179.5 (6) | C29—C30—O13—C32 | −160.1 (5) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O7—H7A···O3iii | 0.84 (2) | 2.11 (3) | 2.912 (6) | 161 (5) |
| O7—H7B···O1iv | 0.83 (2) | 2.42 (5) | 3.107 (6) | 141 (7) |
| O7—H7B···O5iv | 0.83 (2) | 2.60 (5) | 3.306 (6) | 144 (6) |
| O14—H14B···O13v | 0.84 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.831 (6) | 169 (8) |
| O14—H14A···O11vi | 0.83 (2) | 2.11 (3) | 2.905 (5) | 160 (6) |
| O14—H14A···O14vi | 0.83 (2) | 2.57 (5) | 3.055 (8) | 118 (5) |
| C23—H23···O6vii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.355 (7) | 149 |
| C27—H27···O6viii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.114 (7) | 117 |
Symmetry codes: (iii) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (iv) −x+1, −y+2, −z; (v) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (vi) −x+2, −y, −z+1; (vii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (viii) x+1, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
References
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2012). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Doedens, R. J. (1976). Prog. Inorg. Chem. 21, 209–231.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kar, S., Garai, A., Bala, S. & Purohit, C. S. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, m557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Van Niekerk, J. N. & Schoening, F. R. L. (1953). Nature, 171, 36–37.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620004484/wm4126sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620004484/wm4126Isup3.hkl
CCDC reference: 1993956
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





