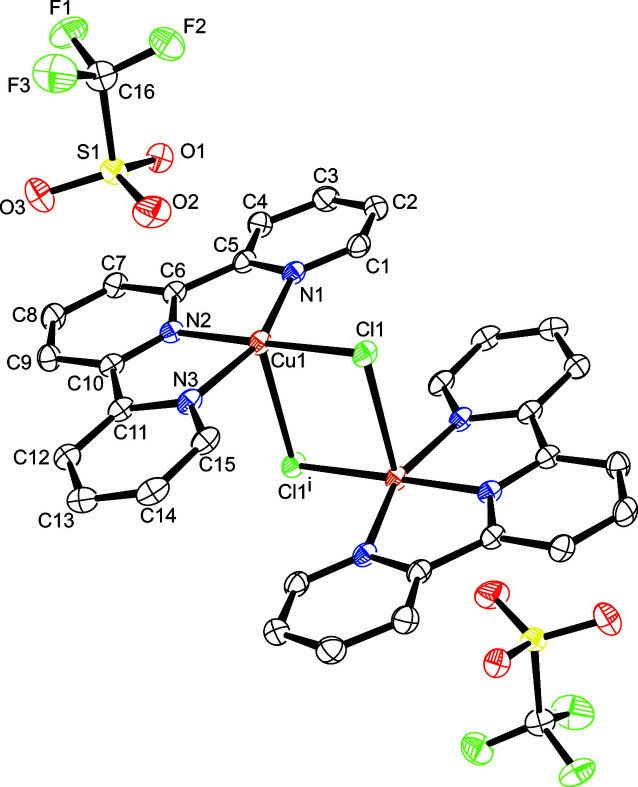
The crystal structure of the centrosymmetric complex [Cu(terpy)2Cl2](OTF)2 consists of a CuII metal center in a distorted square-pyramidal geometry with π–π stacking interactions contributing to the crystal packing.
Keywords: crystal structure, terpyridine, copper, trifluoromethanesulfonate salt, bridging chloride, π–π stacking
Abstract
In the centrosymmetric title complex, [Cu2Cl2(C15H11N3)2](CF3O3S)2, the CuII metal center is fivefold coordinated by two chloride ions and three nitrogen atoms of the terpyridine ligand in a distorted square-pyramidal geometry; two trifluoromethanesulfonate ions complete the outer coordination sphere. π–π stacking interactions between the pyridyl rings in adjacent molecules contribute to the alignment of the complexes in columns along the a-axis. This structure represents the first example of a binuclear dication of formula [Cu(terpy)2Cl2]2+ with trifluoromethanesulfonate as counter-ions.
Structure description
Terpyridines are some of the most studied nitrogen-based tridentate ligands in coordination chemistry, and their metal complexes have found application in catalysis (Wei et al., 2019 ▸; Choroba et al., 2019 ▸), supramolecular chemistry (Wei et al., 2019 ▸), and medicinal chemistry (Glišić et al., 2018 ▸; Malarz et al., 2021 ▸; Li et al., 2020 ▸). Recently, copper(II) terpyridine complexes have received much attention due to their remarkable cytotoxicity and ability to interact with DNA (Karges et al., 2021 ▸); herein, we report the synthesis and structure of the title copper(II) terpyridine complex.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, depicted in Fig. 1 ▸, consists of half of a centrosymmetric dication [Cu(terpy)2Cl2]2+ and one trifluoromethanesulfonate ion completing the outer coordination sphere. The Cu—N, and Cu—Cl distances, as well as, the Cl—Cu—Cl, N—Cu—Cl and N—Cu—N angles are in good agreement with the reported values in similar copper(II) terpyridine complexes currently available in the CSD (version 5.42 with update September 2021; Rojo et al., 1987 ▸; refcode FECJEC; Valdés-Martínez et al., 2002; ▸ refcode HULZAP; Gasser et al., 2004 ▸; refcode HULZAP01). All relevant bond lengths and angles involving the Cu atom are presented in Table 1 ▸.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level; H atoms are omitted for clarity. Symmetry operator for generating equivalent atoms: (i) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z.
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| Cu1—Cl1 | 2.2265 (5) | Cu1—N2 | 1.9420 (17) |
| Cu1—Cl1i | 2.7660 (6) | Cu1—N1 | 2.0397 (18) |
| Cu1—N3 | 2.0278 (19) | ||
| Cl1—Cu1—Cl1i | 89.944 (18) | N2—Cu1—N3 | 80.39 (7) |
| N3—Cu1—Cl1i | 90.30 (5) | N2—Cu1—N1 | 80.11 (7) |
| N3—Cu1—Cl1 | 99.82 (5) | N1—Cu1—Cl1 | 99.60 (5) |
| N3—Cu1—N1 | 159.58 (7) | N1—Cu1—Cl1i | 95.97 (5) |
| N2—Cu1—Cl1i | 90.83 (5) | Cu1—Cl1—Cu1i | 90.056 (18) |
| N2—Cu1—Cl1 | 179.20 (5) |
Symmetry code: (i)
 .
.
In the crystal packing of the title compound, π–π stacking interactions between the N1 and N3 pyridyl ring of adjacent molecules are observed, with a centroid-to-centroid (Cg⋯Cg) distance of 3.658 (1) Å and an offset distance of 1.723 Å. No other supramolecuar interaction is present in the crystal packing of the title compound.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was obtained as product of the reaction of 2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine (0.100 g, 0.429 mmol) with copper(II) chloride dihydrate (0.073 g, 0.429 mmol) in acetonitrile after the addition of silver trifluoromethanesulfonate (0.110 g, 0.429 mmol) and filtration using a 0.45 µm PTFE syringe filter. Crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction of the title compound were obtained by vapor diffusion of diethyl ether over the resulting acetonitrile solution at 278 K.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms were located in a difference map and refined in idealized positions using a riding model with atomic displacement parameters of U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) and with a C—H distance of 0.95 Å.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Cu2Cl2(C15H11N3)2](CF3O3S)2 |
| M r | 962.65 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 98 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.2767 (2), 9.8394 (2), 13.1746 (3) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 106.667 (2), 91.226 (2), 105.453 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 866.08 (4) |
| Z | 1 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.59 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.47 × 0.17 × 0.1 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | XtaLAB AFC12 (RCD3): Kappa single |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2019 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.741, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 33748, 3982, 3889 |
| R int | 0.047 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.650 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.036, 0.094, 1.08 |
| No. of reflections | 3982 |
| No. of parameters | 253 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.55, −0.41 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621010968/bt4119sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621010968/bt4119Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621010968/bt4119Isup3.mol
CCDC reference: 2116881
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Figure 2.
Perspective view of the packing structure of the title complex along the crystallographic a-axis; H atoms are omitted for clarity.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful for the support of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of the Incarnate Word and the X-ray Diffraction Laboratory at The University of Texas at San Antonio.
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| [Cu2Cl2(C15H11N3)2](CF3O3S)2 | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 962.65 | F(000) = 482 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.846 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.2767 (2) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 9.8394 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 14071 reflections |
| c = 13.1746 (3) Å | θ = 3.1–29.5° |
| α = 106.667 (2)° | µ = 1.59 mm−1 |
| β = 91.226 (2)° | T = 98 K |
| γ = 105.453 (2)° | Block, clear bluish green |
| V = 866.08 (4) Å3 | 0.47 × 0.17 × 0.1 mm |
Data collection
| XtaLAB AFC12 (RCD3): Kappa single diffractometer | 3889 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: Rotating-anode X-ray tube, Rigaku (Mo) X-ray Source | Rint = 0.047 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2019) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.741, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −12→12 |
| 33748 measured reflections | l = −16→17 |
| 3982 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0529P)2 + 0.6752P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 3982 reflections | Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3 |
| 253 parameters | Δρmin = −0.41 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. H atoms were located in a difference map and refined in idealized positions using a riding model with atomic displacement parameters of Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) and with a C—H distance of 0.95 Å. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu1 | 0.49265 (4) | 0.41355 (3) | 0.60172 (2) | 0.01772 (10) | |
| Cl1 | 0.62384 (8) | 0.36614 (6) | 0.44902 (4) | 0.02026 (13) | |
| S1 | 0.50126 (8) | 0.15121 (6) | 0.79698 (4) | 0.02142 (13) | |
| F2 | 0.7785 (2) | 0.02432 (18) | 0.78751 (14) | 0.0396 (4) | |
| F1 | 0.6642 (2) | 0.06787 (19) | 0.93864 (12) | 0.0395 (4) | |
| F3 | 0.5041 (2) | −0.11260 (17) | 0.80642 (16) | 0.0478 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.6469 (2) | 0.29199 (17) | 0.83604 (12) | 0.0239 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.3333 (2) | 0.1385 (2) | 0.85354 (15) | 0.0336 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.4661 (3) | 0.0941 (2) | 0.68265 (13) | 0.0360 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.2255 (3) | 0.27262 (19) | 0.55326 (14) | 0.0188 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.3802 (3) | 0.45334 (19) | 0.73563 (14) | 0.0168 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.7290 (3) | 0.55151 (19) | 0.70135 (14) | 0.0184 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.1030 (3) | 0.2851 (2) | 0.62992 (16) | 0.0192 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.6901 (3) | 0.6111 (2) | 0.80261 (16) | 0.0189 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.1958 (3) | 0.3840 (2) | 0.73629 (16) | 0.0186 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.4902 (3) | 0.5499 (2) | 0.82254 (16) | 0.0179 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.1110 (3) | 0.4087 (2) | 0.83124 (17) | 0.0220 (4) | |
| H9 | −0.019262 | 0.358669 | 0.833457 | 0.026* | |
| C15 | 0.1555 (3) | 0.1851 (2) | 0.45439 (17) | 0.0220 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.240897 | 0.174252 | 0.401071 | 0.026* | |
| C14 | −0.0386 (3) | 0.1094 (2) | 0.42706 (18) | 0.0238 (5) | |
| H14 | −0.084305 | 0.047636 | 0.356325 | 0.029* | |
| C12 | −0.0910 (3) | 0.2144 (2) | 0.60811 (17) | 0.0212 (4) | |
| H12 | −0.173957 | 0.225959 | 0.662670 | 0.025* | |
| C13 | −0.1631 (3) | 0.1253 (2) | 0.50390 (18) | 0.0231 (4) | |
| H13 | −0.296333 | 0.076425 | 0.486484 | 0.028* | |
| C7 | 0.4138 (3) | 0.5820 (2) | 0.91921 (16) | 0.0208 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.489630 | 0.651756 | 0.981351 | 0.025* | |
| C4 | 0.8284 (3) | 0.7197 (3) | 0.87846 (17) | 0.0225 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.798549 | 0.759683 | 0.948670 | 0.027* | |
| C8 | 0.2229 (3) | 0.5089 (3) | 0.92254 (17) | 0.0237 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.168203 | 0.527811 | 0.988179 | 0.028* | |
| C2 | 1.0514 (3) | 0.7057 (3) | 0.74756 (18) | 0.0241 (5) | |
| H2 | 1.176548 | 0.735707 | 0.727006 | 0.029* | |
| C16 | 0.6177 (3) | 0.0264 (3) | 0.83346 (19) | 0.0266 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.9066 (3) | 0.5979 (2) | 0.67581 (17) | 0.0216 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.934595 | 0.555208 | 0.605681 | 0.026* | |
| C3 | 1.0114 (3) | 0.7691 (3) | 0.84983 (18) | 0.0254 (5) | |
| H3 | 1.107711 | 0.845362 | 0.899683 | 0.030* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu1 | 0.02295 (16) | 0.01815 (15) | 0.01013 (14) | 0.00641 (11) | 0.00275 (10) | 0.00076 (10) |
| Cl1 | 0.0282 (3) | 0.0213 (2) | 0.0128 (2) | 0.0121 (2) | 0.00591 (19) | 0.00269 (19) |
| S1 | 0.0221 (3) | 0.0223 (3) | 0.0156 (3) | 0.0060 (2) | −0.00080 (19) | −0.0002 (2) |
| F2 | 0.0382 (9) | 0.0427 (9) | 0.0461 (9) | 0.0246 (7) | 0.0131 (7) | 0.0132 (7) |
| F1 | 0.0508 (10) | 0.0437 (9) | 0.0241 (7) | 0.0128 (8) | −0.0061 (7) | 0.0120 (7) |
| F3 | 0.0458 (10) | 0.0206 (7) | 0.0667 (12) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0117 (8) | 0.0074 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0284 (8) | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0056 (6) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0230 (8) | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0075 (7) | 0.0075 (7) | 0.0066 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0400 (10) | 0.0429 (11) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0111 (9) | −0.0078 (7) | −0.0016 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0262 (9) | 0.0162 (8) | 0.0132 (8) | 0.0065 (7) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0028 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0215 (9) | 0.0152 (8) | 0.0130 (8) | 0.0063 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0239 (9) | 0.0182 (8) | 0.0133 (8) | 0.0075 (7) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0038 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0269 (11) | 0.0159 (9) | 0.0149 (9) | 0.0073 (8) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0248 (11) | 0.0190 (10) | 0.0141 (9) | 0.0087 (8) | 0.0032 (8) | 0.0043 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0237 (10) | 0.0167 (9) | 0.0157 (10) | 0.0073 (8) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0039 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0234 (10) | 0.0152 (9) | 0.0144 (9) | 0.0058 (8) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0030 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0227 (11) | 0.0225 (10) | 0.0186 (10) | 0.0053 (9) | 0.0042 (8) | 0.0039 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0332 (12) | 0.0176 (10) | 0.0144 (10) | 0.0080 (9) | 0.0016 (8) | 0.0031 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0362 (12) | 0.0149 (9) | 0.0167 (10) | 0.0056 (9) | −0.0045 (9) | 0.0011 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0247 (11) | 0.0182 (10) | 0.0205 (10) | 0.0065 (8) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0054 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0259 (11) | 0.0158 (10) | 0.0246 (11) | 0.0040 (8) | −0.0045 (9) | 0.0039 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0256 (11) | 0.0210 (10) | 0.0122 (9) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0000 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0261 (11) | 0.0241 (11) | 0.0157 (10) | 0.0088 (9) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0020 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0282 (12) | 0.0277 (11) | 0.0134 (10) | 0.0087 (9) | 0.0055 (8) | 0.0025 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0215 (11) | 0.0285 (11) | 0.0233 (11) | 0.0074 (9) | 0.0034 (8) | 0.0093 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0308 (12) | 0.0197 (10) | 0.0240 (11) | 0.0049 (9) | −0.0022 (9) | 0.0010 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0266 (11) | 0.0250 (11) | 0.0166 (10) | 0.0114 (9) | 0.0055 (8) | 0.0075 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0256 (11) | 0.0275 (11) | 0.0198 (11) | 0.0063 (9) | −0.0014 (9) | 0.0036 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cu1—Cl1 | 2.2265 (5) | C10—C9 | 1.394 (3) |
| Cu1—Cl1i | 2.7660 (6) | C6—C7 | 1.387 (3) |
| Cu1—N3 | 2.0278 (19) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| Cu1—N2 | 1.9420 (17) | C9—C8 | 1.390 (3) |
| Cu1—N1 | 2.0397 (18) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| S1—O1 | 1.4466 (17) | C15—C14 | 1.394 (3) |
| S1—O3 | 1.4409 (18) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| S1—O2 | 1.4392 (17) | C14—C13 | 1.376 (3) |
| S1—C16 | 1.826 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| F2—C16 | 1.331 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.401 (3) |
| F1—C16 | 1.335 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| F3—C16 | 1.337 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C11 | 1.362 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.392 (3) |
| N3—C15 | 1.339 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C10 | 1.335 (3) | C4—C3 | 1.391 (3) |
| N2—C6 | 1.336 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C5 | 1.364 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.336 (3) | C2—C1 | 1.384 (3) |
| C11—C10 | 1.481 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.386 (3) |
| C11—C12 | 1.380 (3) | C1—H1 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.479 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C4 | 1.388 (3) | ||
| Cl1—Cu1—Cl1i | 89.944 (18) | C8—C9—C10 | 117.9 (2) |
| N3—Cu1—Cl1i | 90.30 (5) | C8—C9—H9 | 121.0 |
| N3—Cu1—Cl1 | 99.82 (5) | N3—C15—H15 | 118.9 |
| N3—Cu1—N1 | 159.58 (7) | N3—C15—C14 | 122.2 (2) |
| N2—Cu1—Cl1i | 90.83 (5) | C14—C15—H15 | 118.9 |
| N2—Cu1—Cl1 | 179.20 (5) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.4 |
| N2—Cu1—N3 | 80.39 (7) | C13—C14—C15 | 119.1 (2) |
| N2—Cu1—N1 | 80.11 (7) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.4 |
| N1—Cu1—Cl1 | 99.60 (5) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.7 |
| N1—Cu1—Cl1i | 95.97 (5) | C11—C12—C13 | 118.7 (2) |
| Cu1—Cl1—Cu1i | 90.056 (18) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.7 |
| O1—S1—C16 | 102.05 (10) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.2 (2) |
| O3—S1—O1 | 114.97 (10) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| O3—S1—C16 | 103.57 (11) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| O2—S1—O1 | 114.19 (11) | C6—C7—H7 | 121.0 |
| O2—S1—O3 | 115.73 (12) | C6—C7—C8 | 118.1 (2) |
| O2—S1—C16 | 103.90 (11) | C8—C7—H7 | 121.0 |
| C11—N3—Cu1 | 113.61 (14) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.6 |
| C15—N3—Cu1 | 127.30 (15) | C5—C4—C3 | 118.8 (2) |
| C15—N3—C11 | 118.61 (19) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 |
| C10—N2—Cu1 | 118.38 (14) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.0 (2) |
| C10—N2—C6 | 123.04 (18) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.5 |
| C6—N2—Cu1 | 118.58 (14) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.5 |
| C5—N1—Cu1 | 113.57 (14) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.5 |
| C1—N1—Cu1 | 127.51 (15) | C1—C2—C3 | 119.1 (2) |
| C1—N1—C5 | 118.60 (19) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.5 |
| N3—C11—C10 | 114.06 (19) | F2—C16—S1 | 111.78 (16) |
| N3—C11—C12 | 122.2 (2) | F2—C16—F1 | 107.3 (2) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 123.8 (2) | F2—C16—F3 | 107.8 (2) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 114.01 (18) | F1—C16—S1 | 110.99 (16) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 121.9 (2) | F1—C16—F3 | 106.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 124.13 (19) | F3—C16—S1 | 112.25 (17) |
| N2—C10—C11 | 113.09 (18) | N1—C1—C2 | 122.5 (2) |
| N2—C10—C9 | 119.91 (19) | N1—C1—H1 | 118.7 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 127.0 (2) | C2—C1—H1 | 118.7 |
| N2—C6—C5 | 113.29 (18) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.5 |
| N2—C6—C7 | 120.03 (19) | C2—C3—C4 | 119.1 (2) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 126.68 (19) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 121.0 | ||
| Cu1—N3—C11—C10 | −7.7 (2) | N1—C5—C4—C3 | 0.2 (3) |
| Cu1—N3—C11—C12 | 170.55 (16) | C11—N3—C15—C14 | 1.5 (3) |
| Cu1—N3—C15—C14 | −170.07 (15) | C11—C10—C9—C8 | −178.6 (2) |
| Cu1—N2—C10—C11 | −0.7 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.8 (3) |
| Cu1—N2—C10—C9 | 179.33 (15) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | −1.1 (3) |
| Cu1—N2—C6—C5 | −1.4 (2) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −177.9 (2) |
| Cu1—N2—C6—C7 | 179.33 (15) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | −1.7 (3) |
| Cu1—N1—C5—C6 | 7.0 (2) | C10—N2—C6—C5 | 179.27 (18) |
| Cu1—N1—C5—C4 | −172.78 (16) | C10—N2—C6—C7 | 0.0 (3) |
| Cu1—N1—C1—C2 | 171.97 (16) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 178.98 (19) |
| O1—S1—C16—F2 | −60.24 (18) | C10—C9—C8—C7 | −0.1 (3) |
| O1—S1—C16—F1 | 59.49 (19) | C6—N2—C10—C11 | 178.63 (18) |
| O1—S1—C16—F3 | 178.50 (17) | C6—N2—C10—C9 | −1.4 (3) |
| O3—S1—C16—F2 | −179.95 (16) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −179.6 (2) |
| O3—S1—C16—F1 | −60.22 (19) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −1.1 (3) |
| O3—S1—C16—F3 | 58.8 (2) | C15—N3—C11—C10 | 179.69 (18) |
| O2—S1—C16—F2 | 58.73 (19) | C15—N3—C11—C12 | −2.1 (3) |
| O2—S1—C16—F1 | 178.47 (17) | C15—C14—C13—C12 | −1.5 (3) |
| O2—S1—C16—F3 | −62.5 (2) | C12—C11—C10—N2 | −172.60 (19) |
| N3—C11—C10—N2 | 5.6 (3) | C12—C11—C10—C9 | 7.4 (3) |
| N3—C11—C10—C9 | −174.4 (2) | C4—C5—C6—N2 | 175.9 (2) |
| N3—C11—C12—C13 | 1.0 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −4.9 (3) |
| N3—C15—C14—C13 | 0.3 (3) | C1—N1—C5—C6 | −178.99 (18) |
| N2—C10—C9—C8 | 1.4 (3) | C1—N1—C5—C4 | 1.3 (3) |
| N2—C6—C7—C8 | 1.2 (3) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.9 (3) |
| N1—C5—C6—N2 | −3.8 (3) | C3—C2—C1—N1 | −0.4 (3) |
| N1—C5—C6—C7 | 175.3 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: Welch Foundation (award No. BN0032).
References
- Choroba, K., Machura, B., Kula, S., Raposo, L. R., Fernandes, A. R., Kruszynski, R., Erfurt, K., Shul’pina, L. S., Kozlov, Y. N. & Shul’pin, G. B. (2019). Dalton Trans. 48, 12656–12673. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Gasser, G., Labat, G. & Stoeckli-Evans, H. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, m244–m246. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Glišić, B. Đ., Nikodinovic-Runic, J., Ilic-Tomic, T., Wadepohl, H., Veselinović, A., Opsenica, I. M. & Djuran, M. I. (2018). Polyhedron, 139, 313–322.
- Karges, J., Xiong, K., Blacque, O., Chao, H. & Gasser, G. (2021). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 516, 120137.
- Li, C., Xu, F., Zhao, Y., Zheng, W., Zeng, W., Luo, Q., Wang, Z., Wu, K., Du, J. & Wang, F. (2020). Front. Chem. 8, 210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Malarz, K., Zych, D., Gawecki, R., Kuczak, M., Musioł, R. & Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A. (2021). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 212, 113032. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2019). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Rigaku Corporation, Oxford, England.
- Rojo, T., Arriortua, M. I., Ruiz, J., Darriet, J., Villeneuve, G. & Beltran-Porter, D. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 285–291.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Valdés-Martínez, J., Salazar-Mendoza, D. & Toscano, R. A. (2002). Acta Cryst. E58, m712–m714.
- Wei, C., He, Y., Shi, X. & Song, Z. (2019). Coord. Chem. Rev. 385, 1–19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621010968/bt4119sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621010968/bt4119Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621010968/bt4119Isup3.mol
CCDC reference: 2116881
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report