Important Compound Classes
Title
3-Aminopyrrolidine and Piperidine Macrocyclic Orexin Receptor Agonists
Patent Publication Number
WO 2022/109117 A1
Publication Date
May 27, 2022
Priority Applications
US 63/117,031 and US 63/279,900
Priority Dates
November 23, 2020, and November 16, 2021
Inventors
Bogen, S. L.; Chen, P.; Clausen, D. J.; Liu, J.; Rudd, M. T.; Xiao, L.; Yang, D.; Lin, S.
Assignee Company
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., USA
Disease Area
Sleep disorders
Biological Target
Orexin
Summary
The orexins (hypocretins) comprise two neuropeptides produced in the hypothalamus: orexin A (OX-A) (a 33 amino acid peptide) and orexin B (OX-B) (a 28 amino acid peptide). Orexins regulate states of sleep and wakefulness, potentially opening novel therapeutic approaches for narcolepsy, idiopathic hypersomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, shift work disorder, obstructive sleep apnea, and insomnia. Orexins are found to stimulate food consumption in rats, suggesting a physiological role for these peptides as mediators in the central feedback mechanism that regulates feeding behavior. Orexins have also been indicated as playing roles in arousal, emotion, energy homeostasis, reward, learning, and memory. Two orexin receptors have been cloned and characterized in mammals. They belong to the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors: the orexin-1 receptor (OX or OX1R) is partially selective for OX-A, and the orexin-2 receptor (OX2 or OX2R) is capable of binding OX-A as well as OX-B with similar affinity. The physiological actions in which orexins are presumed to participate are thought to be expressed via one or both of the OX1 receptor and OX2 receptor as the two subtypes of orexin receptors.
The present application describes a series of novel 3-aminopyrrolidine and piperidine macrocycles as orexin receptor agonists for the treatment or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders and diseases, particularly sleep disorders. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, and pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
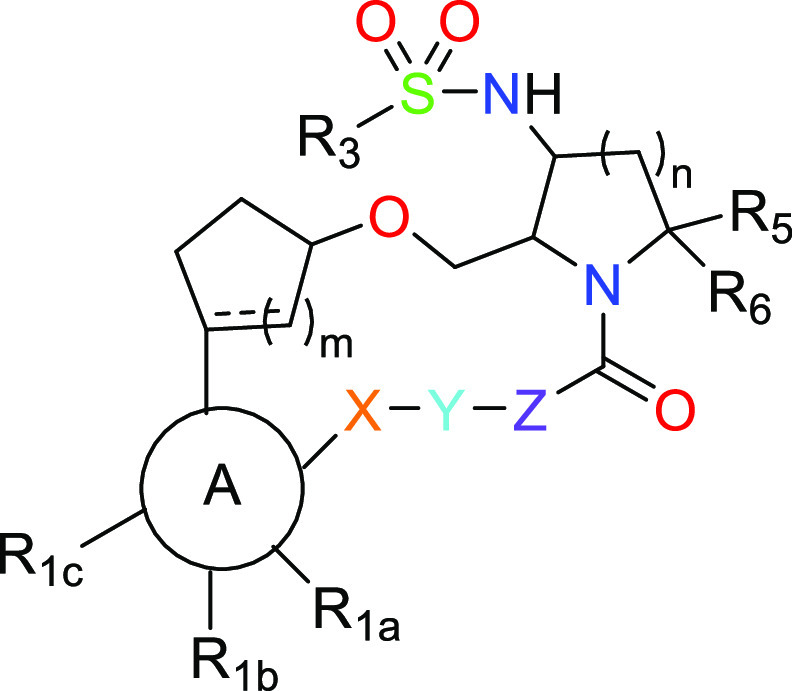
--- = absent or present as a double bond;
X = -O- or -NR- or X may be a direct bond to Y;
Y = C1–6alkyl or C2–6alkenyl;
Z = -O- or -NR- or Z may be a direct bond to Y;
R1a, R1b, and R1c = H, halogen, OH, C1-6alkyl, which is unsubstituted or substituted with 1–3 substituents selected from OH, F, and phenyl, -O-C1-6alkyl, which is unsubstituted or substituted with 1–3 substituents selected from F and phenyl, C3-6cycloalkyl, C2-6alkynyl, -NH2, -NH(C1-6alkyl), -N(C1-6alkyl)2, -(CO)-O-C1-6alkyl, keto, phenyl, pyridyl, and -CN;
R3 = C1-6alkyl, where the alkyl is unsubstituted or substituted with 1–3 F, C3-6cycloalkyl, -NH2, -NH(C1-6alkyl), -N(C1-6alkyl)2, and phenyl;
R5 and R6 = H, C1-6alkyl, where the alkyl is unsubstituted or substituted with OR, NR2, -C(O)NR2, or 1–3 F, and C3-6cycloalkyl;
m = 1 or 2; and n = 1 or 2.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The human orexin-2 receptor IP assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their orexin-2 receptor agonists activity. The hOX2R-IP IC50 (nM) are shown in the table below.
Biological Data
The following table shows representative compounds tested for human
orexin-2 receptor agonists activity and the biological data obtained
from testing representative examples.
Claims
Total claims: 16
Compound claims: 13
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 2
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Special Issue
Published as part of the ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters virtual special issue “New Drug Modalities in Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Translational Science”.
Recent Review Articles. References
- Pizza F.; Barateau L.; Dauvilliers Y.; Plazzi G. The orexin story, sleep and sleep disturbances. J. Sleep Res. 2022, 31, e13665 10.1111/jsr.13665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barateau L.; Pizza F.; Plazzi G.; Dauvilliers Y. Narcolepsy. J. Sleep Res. 2022, 31, e13631 10.1111/jsr.13631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue T.; Wu X.; Chen S.; Yang Y.; Yan Z.; Song Z.; Zhang W.; Zhang J.; Chen Z.; Wang Z. The efficacy and safety of dual orexin receptor antagonists in primary insomnia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2022, 61, 101573. 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian S.; Ravichandran M. Orexin receptors: Targets and applications. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 36, 72. 10.1111/fcp.12723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappa S. L.; Aeschbach D. Sleep and anxiety: From mechanisms to interventions. Sleep Med. Rev. 2022, 61, 101583. 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst S. C.; Landolt H. Sleep-Wake Neurochemistry. Sleep Med. Clin. 2022, 17, 151. 10.1016/j.jsmc.2022.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



