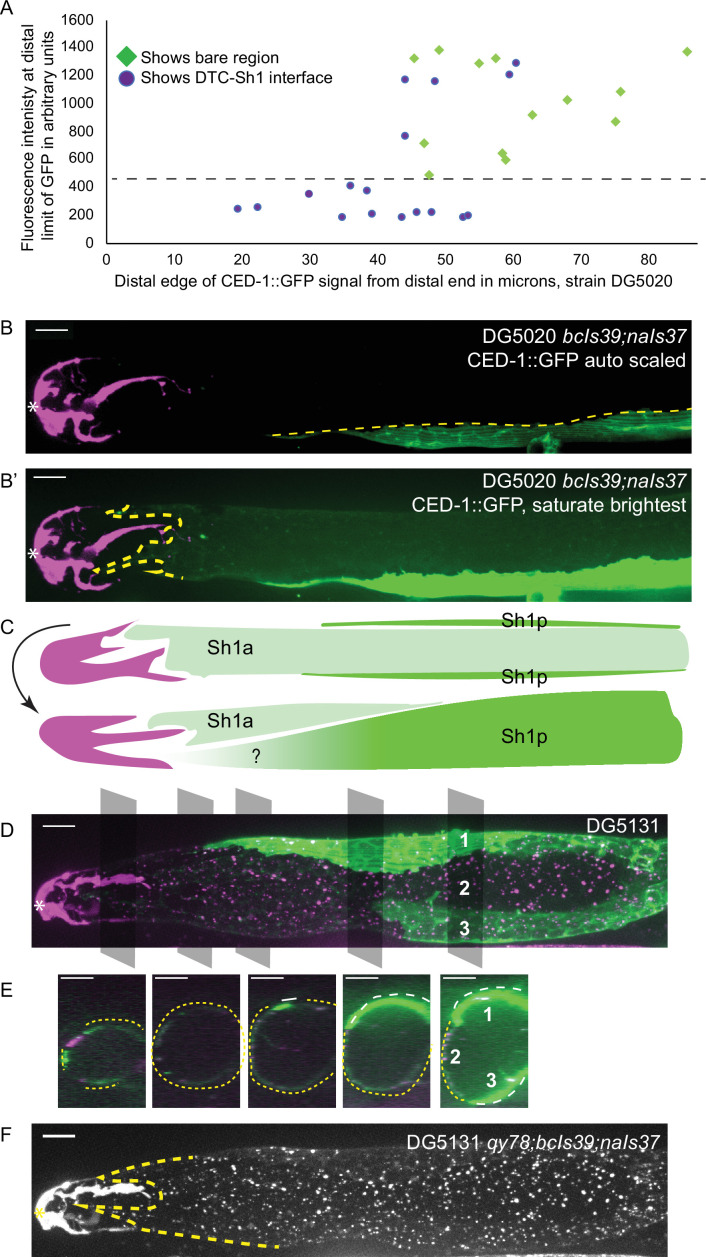
Figure 3. lim-7p::CED-1::GFP has variable expression intensity that conceals distal position of Sh1.
(A) Plot of distal position vs. fluorescence intensity in arbitrary units of CED-1::GFP at the distal limit of its domain in N=30 DG5020 bcIs39[lim-7p::CED-1::GFP]; naIs37[lag-2p::mCherry-PH] animals. Dashed black line: all of the lowly expressing gonads (under ~400 AU, or <30% maximum brightness of brightest sample) have a distal tip cell (DTC)-Sh1 interface detected. (B) DG5020 sample in which disparate expression levels in the two Sh1 cells of a single gonad arm obscure detection of the DTC-Sh1 interface. The GFP channel is scaled automatically in B; B’ is scaled to saturate the brightest pixels and reveal the dim second Sh1 cell. Dashed yellow link marks the edge of the bright Sh1 cell. (C) Schematic showing Sh1 pair configuration over distal germline, with the distal extent of Sh1p uncertain in superficial projection. The two Sh1 cells of a pair descend from the anterior and posterior daughters of Z1 and Z4, so the two Sh1 cells are here labeled Sh1a and Sh1p (arbitrarily). Top, superficial view. Bottom, side view. (D) DG5131 qy78[mKate::inx-8]; bcIs39[lim-7p::CED-1::GFP]; naIs37[lag-2p::mCherry-PH] sample in which one Sh1 cell contacts the DTC around the circumference of the germline and the other Sh1 cell lies at some distance from the distal end. Gray boxes and numbers mark planes and landmarks shown in (E). (E) Five cross sections through gonad in (E) made by projecting through two 1 µm re-slices at the positions shown by gray boxes in (D). Same analysis for DG5020 shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1. (F) Same worm as in (D,E); signal from endogenously tagged allele qy78[mKate::inx-8] more uniformly labels the Sh1 cells, obscuring their individual shapes. All scale bars 10 µm.