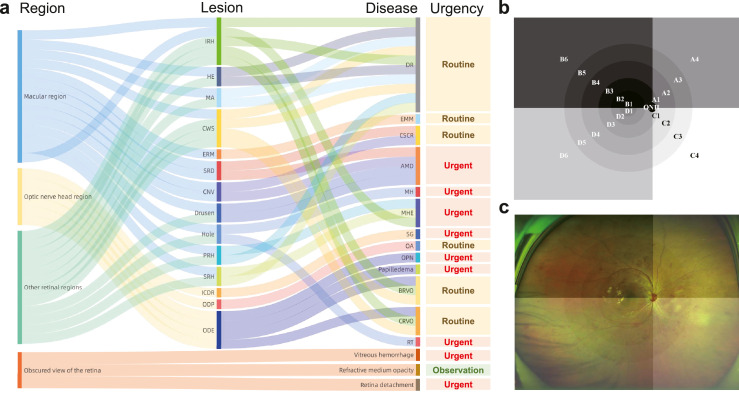
Figure 1.
The clinical logical relation of lesion atlas. The lesion atlas integrated the pathological and anatomical information (a). The anatomical location was determined by dividing the retina into 21 regions as the prototype (b) and the overlaid image (c) displayed. DR, diabetic retinopathy; AMD, age-related macular degeneration; CRVO, central retinal vein occlusion; BRVO, branch retinal vein occlusion; CSCR, central serous chorioretinopathy; RT, retinal tears; EMM, epimacular membrane; MH, macular Hole; MHE, macular hemorrhage; ODE, optic disc edema; OA, optic atrophy; OPN, optic perineuritis; SG, suspected glaucoma; CNV, choroidal neovascularization; HE, hard exudates; CWS, cotton wool spots; MA, microaneurysm; IRH, intraretinal hemorrhage; SRH, subretinal hemorrhage; PRH, preretinal hemorrhage; SRD, serous retinal detachment; ERM, epiretinal membrane; ICDR increased cup-to-disc ratio; ODP, optic disc pallor.