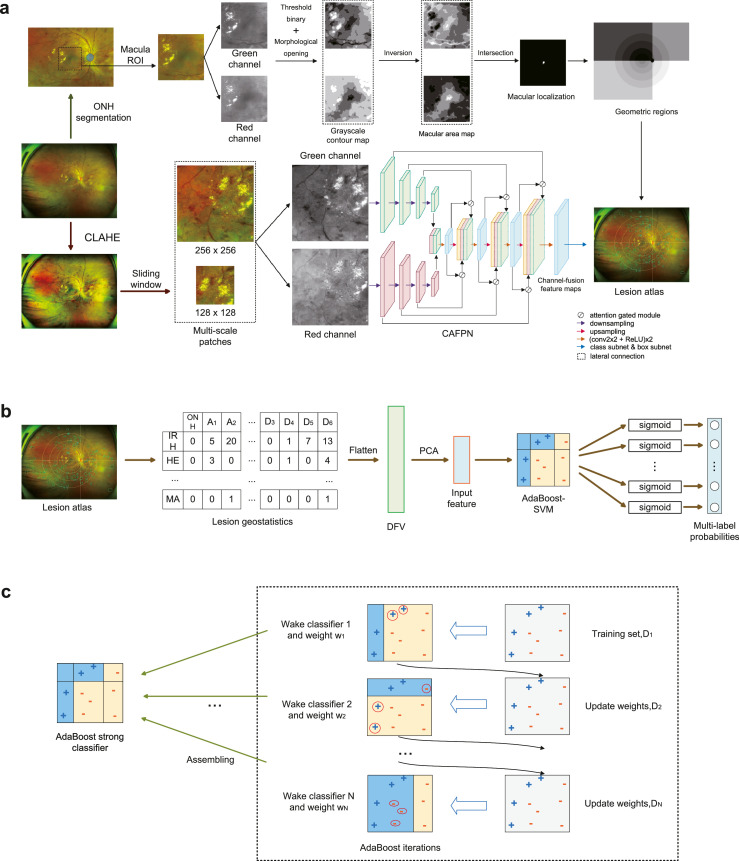
Figure 3.
Overview pipeline of Interpretable eye diseases screening system (IEDSS). There were two paths in the lesion atlas mapping module. In the upper path, geometric regions were generated after ONH segmentation and macula localization. In the lower path, multi-scale patches were cropped from a CLAHE-ed UWF image, and sent into the CAFPN. Results of the lesion detection were output from the CAPFN, and summarized into the lesion atlas with geometric regions (a). The lesion geostatisitcs showed the lesion distribution in the lesion atlas and was flatten to get the DFV. The input feature was generated by DFV dimensionality reduction through PCA and input into the AdaBoost-SVM to get multi-label probabilities in the mass screening system (b). In the training process of the AdaBoost-SVM, Weak classifiers were trained iteratively, and assembled to the strong classifier (c). ONH, optic nerve head; HE, hard exudates; MA, microaneurysm; IRH, intraretinal hemorrhage; CAFPN, channel-attention feature pyramid network; CLAHE, contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization; AdaBoost-SVM, AdaBoost-support vector machine; DFV, discrimination feature vectors; PCA, principal components analysis; ROI, region of interest.