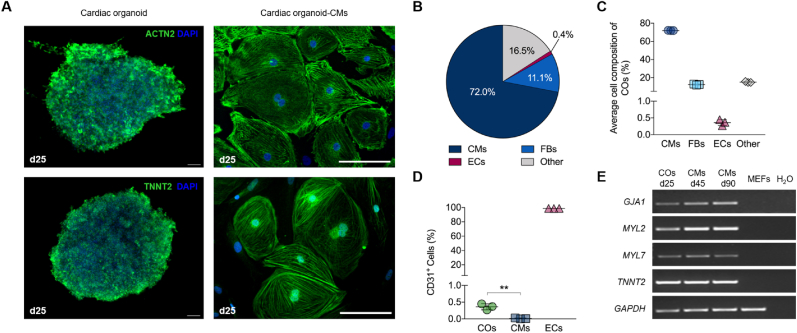
Figure 3.
Characterization of cardiac organoids. (A) Representative images of structures within the cardiac organoids. Immunofluorescence staining in whole cardiac organoids and isolated organoid-derived cardiomyocytes (cardiac organoid-CMs after dissociation) of the following proteins was performed: Z-disc associated marker (ACTN2) and cardiac troponin T (TNNT2). Cell nuclei were stained blue with DAPI. (B) Pie chart of average cell composition in cardiac organoids (COs) using flow cytometry analyses – CMs (TNNT2), fibroblasts (FBs; Vimentin) and endothelial cells (ECs; CD31). (C) Quantification of flow cytometry data showing a robust ratio of CMs with 72%, FBs 11% and ECs <1% in COs. (D) Representative flow cytometry analysis for the endothelial cell marker CD31 in COs, 2D-cultured CMs and human umbilical vein ECs. Results were replicated in 3 experiments. Mean ± SD. One Way ANOVA with Tukey's post test with ∗∗p < 0.01. (E) RT-PCR products separated by gel electrophoresis. The following cardiac-specific marker genes were analyzed for their expression at mRNA level: GJA1 (gap junction protein, 248 bp), MYL2 (ventricular marker, 200 bp), MYL7 (atrial marker, 289 bp) and TNNT2 (cardiac troponin T). GAPDH (258 bp) was used as housekeeping gene and MEFs (mouse embryonic fibroblasts) as negative control. Scale bars: 100 μm.