Abstract
Background
The impact of immunosuppression in solid organ transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection is unknown. The knowledge about the behavior of different immunosuppression schemes in clinical outcomes is scarce. This study aimed to determine the risk of death in kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19 under two different schemes of immunosuppression.
Methods
We describe our experience in kidney transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection in seven transplant centers during the first year of the pandemic before starting the vaccination programs in the city of Bogotá. Demographic characteristics, clinical presentation, immunosuppression schemes at presentation, and global treatment strategies were compared between recovered and dead patients; survival analysis was carried out between calcineurin inhibitors based regimen and free calcineurin inhibitors regimen.
Results
Among 165 confirmed cases, 28 died (17%); the risk factors for mortality identified in univariate analysis were age older than 60 years (p = .003) diabetes (p = .001), immunosuppression based on calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) (p = .025) and patients receiving steroids (p = .041). In multivariable analysis, hypoxemia (p = .000) and calcineurin inhibitors regimen (p = .002) were predictors of death. Survival analysis showed increased mortality risk in patients receiving CNI based immunosuppression regimen vs. CNI free regimens mortality rates were, respectively, 21.7% and 8.5% (p = .036).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that the calcineurin inhibitors probably do not provide greater protection compared to calcineurin inhibitor free schemes being necessary to carry out analyzes that allow us to evaluate the outcomes with different immunosuppression schemes in solid organ transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Abbreviations: CTLA4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein 4; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; RT-PCR, real time polymerase chain reaction; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TH17, T helper 17 cells
Keywords: COVID-19, Immunosuppression, Calcineurin inhibitors, mTOR inhibitors, Belatacept, SARS-CoV-2, Kidney transplantation
Abstract
Introducción
El impacto de los diferentes esquemas de inmunosupresión en receptores de trasplante de órganos sólidos es desconocido. El conocimiento del comportamiento de la enfermedad bajo diferentes esquemas de inmunosupresión es escaso. Nuestra experiencia intenta determinar el riesgo de muerte en receptores de trasplante renal con COVID-19 bajo dos esquemas diferentes de inmunosupresión.
Métodos
Describimos la experiencia en receptores de trasplante renal con infección por SARS-CoV-2 en siete centros de trasplante renal en la ciudad de Bogotá, durante el primer año de pandemia y previo al inicio de los programas de vacunación. Las características demográficas, la presentación clínica, los esquemas de inmunosupresión y las estrategias de tratamiento fueron comparadas entre pacientes recuperados y fallecidos, un análisis de sobrevida fue llevado a cabo entre esquemas basados en inhibidores de calcineurina y esquemas libres de inhibidores de calcineurina.
Resultados
Entre los 165 casos confirmados, 28 murieron (17%), los factores de riesgo identificados para mortalidad en el análisis univariado fueron: edad mayor de 60 años, diabetes, un esquema de inmunosupresión basado en inhibidores de calcineurina y pacientes recibiendo esteroides en el momento del diagnóstico. En el análisis multivariado, la presencia de hipoxemia en el momento del diagnóstico (p = 0,000) y un esquema de inmunosupresión basado en inhibidores de calcineurina (p = 0,002) fueron predictores independientes de mortalidad. El análisis de sobrevida encontró un riesgo mayor de mortalidad en pacientes bajo esquemas de inmunosupresión con inhibidores de calcineurina vs. aquellos libres de inhibidores de calcineurina, con tasas de mortalidad respectivas en 21,7 y 8,5% (p = 0,036).
Conclusiones
Nuestros resultados sugieren que los inhibidores de calcineurina no aportan mayor protección en pacientes con trasplante renal y COVID-19 en comparación con esquemas libres de inhibidores de calcineurina, siendo necesario realizar análisis que permitan evaluar los desenlaces con diferentes esquemas de inmunosupresión en receptores de trasplante renal con infección por SARS-CoV-2.
Palabras clave: COVID-19, Inmunosupresión, Inhibidores de calcineurina, inhibidor mTOR, Belatacept, SARS-CoV-2, Trasplante renal
Introduction
The impact of immunosuppression on SARS-CoV-2 infection in the presence of chronic immunosuppression is unknown. The clinical presentation is minor in the wide majority of the cases; however, it might have a progressive and severe clinical course causing pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, mainly in people older than 60 years or with the presence of comorbidities.1, 2
Solid organ transplant recipients usually present an increased risk of complications due to respiratory viral infections associated with pharmacological immunosuppression, although little else about is known regarding the behavior of SARS-CoV-2 infection.3, 4, 5, 6 In patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection and complicated clinical course, a severe hyperinflammatory state has been described7, 8, 9; this would suggest that the use of immunosuppression schemes could provide protection in solid organ transplant recipients. Expert opinions based on reports of previous coronavirus infections suggest, on one side that calcineurin inhibitors could be protective in severe hyperinflammatory states, and on the other side that they do not represent any impact.10, 11, 12 Series of cohorts, collecting experiences from different centers, have been published, most of them with patients receiving calcineurin inhibitor-based regimens; nevertheless, the analysis of the behavior with immunosuppression regimens free of calcineurin inhibitors, particularly with co-stimulation inhibitors and mTOR inhibitors is scarce. The most common practice in different centers at an overall level was to reduce or suspend antiproliferative drugs or mTOR inhibitors over the reduction or withdrawal of calcineurin inhibitors.13, 14
The published series include a low number of renal transplant patients receiving belatacept, even more so when it is compared to the number of those receiving calcineurin inhibitors or mTOR inhibitors, which does not allow for comparisons between schemes.15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 The drive mechanism of co-stimulation inhibitors and mTOR inhibitors suggests that they might play some role in inflammatory response modulation, compared with schemes based on calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplant recipients and COVID-19.23, 24, 25, 26, 27
In Colombia, the first case of COVID 19 was reported on March 6, 2020; as of mid-February, 2021, when vaccination started (and solid organ transplant recipients were prioritized), 2.2 million cases and 58 thousand cases had been confirmed. According to data from the national official registry, in 2019 there were 1844 renal transplant recipients in active follow-up in 11 transplant centers in the city of Bogotá. We undertook this observational study in 7 transplant centers in Bogota, Colombia in order to describe the clinical presentation, treatment, and outcomes in adult kidney transplant recipients diagnosed with COVID-19, and the possible association between severity of infection and calcineurin inhibitor-based and calcineurin inhibitor-free immunosuppression regimens, before vaccination started.
Materials and methods
This is a multicenter retrospective study involving renal transplant recipients with COVID-19 confirmed by RT PCR via upper respiratory tract sampling. All cases confirmed between March 15, 2020 and February 4, 2021 were included in the analysis, and followed until March 4, 2021 for survival analysis. Demographic variables, comorbidities, body mass index (BMI), renal function, post-transplant time to infection, presenting symptoms, immunosuppression schemes, and chest X-ray imaging findings were collected. The clinical course included admission to hospital, immunosuppression adjustments, treatment strategies, mechanical ventilation, dialysis, and death. The patients were treated according to the local site's standard of care and adjustments in immunosuppressive drugs were made following recommendations of the Colombian Society of Nephrology.28 Each centers received approval from their institutional review board.
Statistical analysis
A univariable analysis was carried out using measures of central tendency and dispersion for each of the quantitative variables studied; frequencies and percentages were utilized for the qualitative variables with mortality as the primary outcome.
Survival curve was plotted using the Kaplan–Meir method and compared between patients under calcineurin inhibitors immunosuppression and calcineurin inhibitors free immunosuppression by log-rank test.
Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis were assessed for independent risk factors of COVID-19 related mortality. In the multivariate analysis, demographic variables and those covariates with a p value <.1 were included. Survival time was considered until death or 30 days after the last case for both Cox and the Kaplan–Meier analysis (March 6, 2021). Results are expressed as hazard ratio with their 95% confidence intervals. A p value <.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient characteristics
Table 1 shows characteristics of the entire cohort; among the 165 patients included in the record, 96% were symptomatic; the remaining 4% were close contacts of confirmed COVID-19 subjects. A total of 82 patients (49.7%) were admitted to the hospital. Patients in the outpatient follow-up group were younger. At the time of diagnosis, calcineurin inhibitors, costimulation inhibitors, mTOR inhibitors, antimetabolites and steroids were received by 62.2%, 21.2%, 15.2%, 92.1% and 78.8% of patients respectively. Modification of immunosuppression occurred in patients receiving calcineurin inhibitors and antimetabolites in 20% and 40% respectively; particularly, the withdrawal of mTOR inhibitors and postponement of the next dose of co-stimulation inhibitors occurred in 7.3% and 9.7% of patients. A small number of patients, among the first confirmed cases, received hydroxychloroquine (3 of 165) and lopinavir/ritonavir (1/165). Antibiotics were received in 40% of patients, 18.8% received ivermectin, and 32.1% dexamethasone. A total of 36 patients (21.8%) were admitted to the intensive care unit and required mechanical ventilation, with acute renal failure needing renal replacement therapy in 15 patients (9.1%). No episode of acute renal graft rejection was reported. Overall mortality 30 days after diagnosis was 17%.
Table 1.
Characteristics of kidney transplant recipients included in the COVID-19 registry.
| All | Recovered | Deceased | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 165 | n = 137 | n = 28 | ||
| Males | 99 (60.0%) | 82 (59.9%) | 17 (60.7%) | .449 |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 49 (14) | 46 (14) | 60 (11) | .000 |
| Median (IQR) | 48 (38–60) | 44 (36–56) | 59 (54–68) | |
| Range | 12–85 | 12–76 | 42–85 | |
| >60 | 40 (24.2%) | 27 (19.7%) | 13 (46.4%) | .003 |
| BMI (kg/cm2) | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 25.5 (3.8) | 25.3 (3.8) | 26.4 (4.0) | .169 |
| Range | 18–45 | 18–45 | 18–36 | |
| Months since transplant | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 6.4 (5.7) | 6.7 (5.6) | 4.8 (5.6) | .103 |
| Range | 0–34.5 | 0.1–34.5 | 0–19.8 | |
| Less than 6 months | 14 (8.5%) | 9 (6.6%) | 5 (17.9%) | .056 |
| Hypertension | 115 (69.7%) | 93 (67.9%) | 22 (78.6%) | .185 |
| Diabetes | 44 (26.7%) | 28 (20.4%) | 16 (57.1%) | .001 |
| BMI > 30 kg/m2 | 14 (8.5%) | 11 (8.0%) | 3 (10.7%) | .463 |
| Immunosuppression | ||||
| CNI | 106 (64.2%) | 83 (60.6%) | 23 (82.1%) | .025 |
| Tacrolimus | 99 (60.0%) | 78 (56.9%) | 21 (75%) | .05 |
| mTor inhibitors | 25 (15.2%) | 23 (16.8%) | 2 (7.1%) | .159 |
| Belatacept | 35 (21.2%) | 31 (22.6%) | 4 (14.3%) | .233 |
| MPA | 152 (92.1%) | 127 (92.7%) | 25 (89.3%) | .41 |
| Azathioprine | 7 (4.2%) | 5 (3.6%) | 2 (7.1%) | .374 |
| Steroids | 130 (78.8%) | 104 (75.9%) | 26 (92.9%) | .041 |
| Presenting symptoms | ||||
| Fever | 98 (59.4%) | 80 (58.4%) | 18 (64.3%) | .357 |
| Cough | 91 (55.2%) | 74 (54.0%) | 17 (60.7%) | .329 |
| Dyspnea | 64 (38.8%) | 48 (35.0%) | 16 (57.1%) | .024 |
| Clinical variables | ||||
| Hypoxemia | 63 (38.2%) | 37 (27.0%) | 26 (92.9%) | <.001 |
| Pulmonary infiltrates | 87 (52.7%) | 61 (44.5%) | 26 (92.9%) | <.001 |
| Hospitalization | 82 (49.7%) | 55 (40.1%) | 27 (96.4%) | <.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 36 (21.8%) | 12 (8.8%) | 24 (85.7%) | <.001 |
| Hemodialysis | 15 (9.1%) | 3 (2.2%) | 12 (42.9%) | <.001 |
| Treatment | ||||
| Hydroxychloroquine | 3 (1.8%) | 3 (2.2%) | 0 (0.0%) | .285 |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir | 1 (0.6%) | 1 (0.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | .321 |
| Ivermectin | 31 (18.8%) | 16 (11.7%) | 15 (53.6%) | <.001 |
| Dexamethasone | 53 (32.1%) | 28 (20.4%) | 25 (89.3%) | <.001 |
| Antibiotics | 66 (40.0%) | 41 (29.9%) | 25 (89.3%) | <.001 |
BMI, body mass index; CNI, calcineurin inhibitors; IQR, inter-quartile range; MPA, mycophenolic acid; SD, standard deviation.
Univariable and multivariable Cox regression analysis for the relationship between risk factors and outcomes
In univariable analysis, age older than 60 years old, history of diabetes, time after transplant to COVID-19 diagnosis less than 6 months, dyspnea, hypoxemia, calcineurin inhibitors, and use of steroids were significantly associated with mortality (Table 2 ).
Table 2.
Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses for death after COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients included in the registry.
| Univariate analysis |
Multivariate analysis |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p value | HR (95% CI) | p value | |
| Age > 60 years | 3.4 (1.6–7.2) | .001 | 1.2 (0.5–3.1) | .647 |
| Diabetes | 4.0 (1.9–8.6) | .000 | 2.3 (0.9–6.0) | .082 |
| Time from KT < 6 months | 2.9 (1.1–7.6) | .034 | 0.7 (0.2–2.0) | .500 |
| Dyspnea | 2.34 (1.1–5.0) | .028 | 0.58 (0.2–1.4) | .220 |
| Hypoxemia | 29.3 (6.9–124.5) | .000 | 41.0 (7.7–218.5) | .000 |
| Steroids | 4.0 (0.9–16.9) | .060 | 1.1 (0.2–5.3) | .898 |
| Calcineurin inhibitors | 3.4 (1.2–9.7) | .026 | 6.1 (1.9–19.4) | .002 |
CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; KT, kidney transplant.
In multivariable Cox regression analysis, hypoxemia and calcineurin inhibitors based immunosuppression remained as independent predictors of death.
Comparison between patients receiving calcineurin inhibitors based regimen and calcineurin inhibitors free regimen
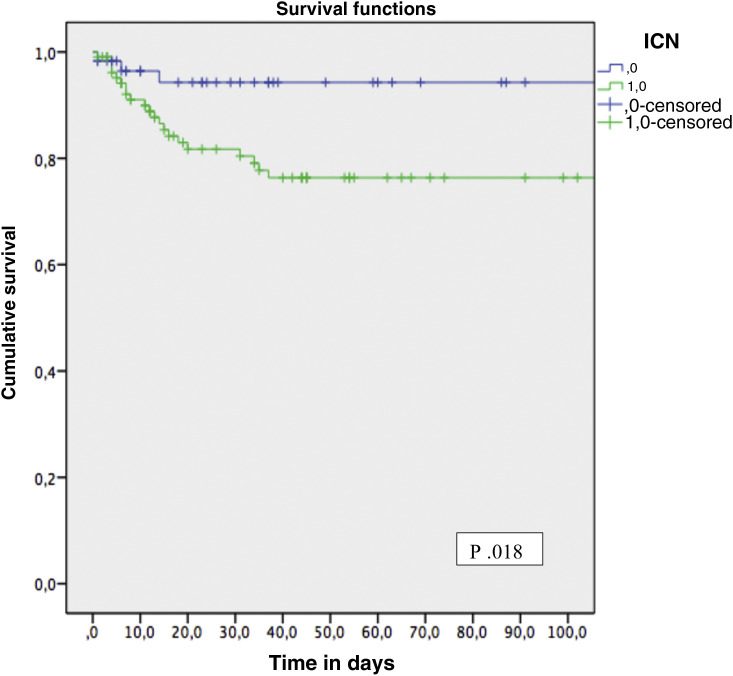
Due to the finding of immunosuppression with calcineurin inhibitors as a risk factor associated with mortality, we have distributed the patients in two subgroups in Table 3 : group 1, under calcineurin inhibitor based immunosuppression regimen and group 2 without calcineurin inhibitor immunosuppression regimen (mTOR inhibitors or belatacept). Most patients in group 1 were males, and they had a time after transplant to COVID-19 diagnosis less than 6 months. Survival analysis showed a significant increasing mortality: group 1, 21.7%; group 2, 8.5% (Fig. 1 ).
Table 3.
Clinical characteristics of kidney transplant recipients according to their immunosuppression regimen at the time of SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis.
| CNI | CNI free | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 106 | n = 59 | ||
| Age (years) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 48.2 | 49.1 | .694 |
| Median (IQR) | 45 | 49.1 | |
| Range | 52 | 73.4 | |
| BMI (kg/cm2) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 25.33 | 25.56 | .71 |
| Median (IQR) | 25.18 | 25.47 | |
| Range | 25.26 | 17.61 | |
| Months since transplant | |||
| Mean (SD) | 7.5 | 5.8 | .082 |
| Median (IQR) | 5.2 | 4.3 | |
| Range | 34.2 | 19.1 | |
| Age > 60 | 25 (23.6) | 15 (25.4) | .109 |
| Males | 64 (60.4) | 35 (59.3) | .004 |
| Less than 6 months | 12 (11.3) | 2 (3.4) | .019 |
| Hypertension | 76 (71.7) | 38 (64.49) | .271 |
| Diabetes | 30 (28.3) | 14 (23.7) | .525 |
| BMI > 30 kg/m2 | 10 (9.4) | 4 (6.8) | .71 |
| Steroids | 85 (80.2) | 45 (76.3) | .556 |
| Presenting symptoms | |||
| Fever | 59 (55.7) | 39 (66.1) | .15 |
| Nasal congestion | 9 (8.5) | 10 (16.9) | .092 |
| Cough | 56 (52.8) | 35 (59.3) | .355 |
| Odynophagia | 24 (22.6) | 13 (22) | .973 |
| Dyspnea | 44 (41.5) | 20 (33.9) | .378 |
| Myalgia | 52 (49.1) | 25 (42.4) | .466 |
| Diarrhea | 37 (34.9) | 14 (23.7) | .156 |
| Fatigue | 56 (52.8) | 19 (32.2) | .015 |
| Anosmia/dysgeusia | 10 (9.4) | 8 (13.6) | .396 |
| Clinical findings | |||
| Hypoxemia | 42 (39.6) | 21 (35.6) | .61 |
| Pulmonary infiltrates | 52 (49.1) | 35 (59.3) | .207 |
| Hospitalization | 54 (50.9) | 28 (47.5) | .668 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 25 (23.6) | 11 (18.6) | .837 |
| Hemodialysis | 10 (9.4) | 5 (8.5) | .462 |
| Treatment | |||
| Hydroxychloroquine | 3 (2.8) | 0 | .99 |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir | 1 (0.9) | 0 | 1 |
| Ivermectin | 21 (19.8) | 10 (16.9) | .652 |
| Dexamethasone | 37 (34.9) | 16 (27.1) | .306 |
| Antibiotics | 43 (40.6) | 24 (40.7) | .995 |
| Death | 23 (21.7) | 5 (8.5) | .036 |
Fig. 1.
Survival function for death according to CNI based immunosuppression regimen and CNI free immunosuppression regimen at the time of SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis.
Discussion
There is limited information regarding the impact of chronic immunosuppression on the outcomes of solid organ transplant recipients or the differences between each of immunosuppression strategy. In this study, clinical presentation of COVID-19 is similar to that reported in the overall population, with fever and cough as the most frequent symptoms.29 It is important to note that the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms (30.9%) is higher than that reported in the general population (5%–10%).30 This situation has been reported in other series with organ transplant patients in France (42%) and Spain (36.7%).15, 31, 32 However, we did not find an association with lower risk of death as was found in a series in Spain.31, 32
The average overall case fatality rate in Colombia has been between 2.5 and 3% depending on the region.33 Multiple experiences have described a higher risk of complications and death in solid organ recipients compared to the overall population, a finding confirmed in our experience.15, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36 In our series, the 30-day case-fatality rate was 17%; the risk of hospitalization was close to half of the patients (49.7%), and mechanical ventilation requirement was also higher (21.8%).
Age over 60, history of diabetes and dyspnea at initial presentation were risk factors for mortality in our cohort, as has been described in the overall population.37 Time to renal transplantation of less than 6 months was not associated with a lower probability of survival although there is a trend in our cohort, which has been described in registries from New York and Spain, probably associated with a higher burden of early.32, 36 Obesity has been previously reported as a risk factor for mortality in solid organ transplant recipients15 but we did not confirm this in our series. On the other hand, we found differences between immunosuppression schemes, with steroids and calcineurin inhibitors as important risk factors for mortality.
In the Brescia cohort, after adjusting with a multivariate model, tacrolimus was associated with risk of death (OR 6.9; 95% CI: 0.99–67, p = .07) although these results could be a consequence of the characteristics of the population studied39; however; in the Spanish Registry tacrolimus showed higher mortality in kidney transplant recipients in the first 6 months after transplantation, probably associated with maximum effect of immunosuppression.32
The capacity of CNI to inhibit viral replication through inhibition of immunophilin pathways independent of their immunosuppressive effect could potentially reduce viral replication of SARS-CoV-2.9, 40, 41 The role in the prophylaxis of graft rejection in a scenario with reduced immunosuppression burden were probably the reasons that positioned CNI as the preferred maintenance immunosuppressants in patients with COVID-19.15, 20, 35, 36
Most studies in patients with solid organ transplants and COVID-19 describe few patients with immunosuppression schemes free of tacrolimus or cyclosporine; fact, which does not allow for comparisons. In our country, the most commonly used immunosuppression scheme is tacrolimus and mycophenolic acid with or without steroids in 69% and 88% of renal transplant recipients, respectively.38
Our search identified 15 publications totaling 1785 cases; 1532 (85.8%) were receiving CNI, 218 (12.2%) mTOR inhibitors, and 29 (1.6%) belatacept.10, 15, 16, 17, 19, 31, 35, 39, 42, 43, 44, 45 A Spanish study of 414 renal transplant recipients, of which 82.6% were receiving tacrolimus and 23% mTOR inhibitors, would be the series with the highest number of cases with CNI-free schemes reported to date (n = 94). It describes a trend toward a higher probability of recovery in the latter group (patients with COVID-19 mortality vs. recovery: mTOR inhibitors p = .069, tacrolimus p = .941).31
Since the clinical behavior in patients with severe COVID-19 could be explained by an excessive activation of the immune system,46 the use of drugs that manage to reduce the mortality of patients with severe COVID-19 could be explained by their activity on the immune system.46
The use of medications that potentially decrease an exaggerated immune response seems reasonable as a treatment strategy to reduce the risk of complications or reduce the likelihood of progression from mild to severe disease. SARS-CoV-2 causes excessive activation of the mTOR signaling pathway in in vitro models; proper functioning of this pathway is necessary for T-cell differentiation. Overactivation of the mTOR pathway can cause an imbalance leading to a reduced accumulation of regulatory T cells and an increased TH1747 response, a scenario that has been described in patients with severe COVID-19.48, 49
mTOR inhibitors inhibit the proliferation of effector T cells and stimulate the accumulation of regulatory T cells.50 Consistent with these observations, mTOR inhibitors could reduce immune-mediated damage and clinical manifestations during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nonetheless, in published series in solid organ transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, mTOR inhibitors were reduced or discontinued in the vast majority of cases.15, 35
In line with current evidence, a reduced level of peripheral regulatory T cells in patients with severe COVID-19 could be part of the reasons for an overactive immune system,49 the expansion of regulatory T cells through immunoregulatory molecules including CTLA4 may explain the role of the immunosuppressant belatacept in a hypothetical control of inflammation in renal transplant recipients with COVID-19.23, 24
Our series includes a large number of cases with immunosuppression schemes free of CNI, with a higher risk of death in those who received CNI. It is important to note that there is no apparent benefit associated with the use of CNI above other immunosuppressants and it seems necessary to carry out further clinical studies that allow us to evaluate outcomes and immunosuppression in renal transplant recipients with COVID-19.
Conflicts of interest
Design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication are the responsibility of the authors alone. The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- 1.Oran D.P., Topol E.J. Prevalence of asymptomatic SARS CoV-2 infection: a narrative review. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:362–367. doi: 10.7326/M20-3012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kumar D., Ferreira V.H., Blumberg E., et al. A 5-year prospective multicenter evaluation of influenza infection in transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67:1322–1329. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ison M.G., Hirsch H.H. Community-acquired respiratory viruses in transplant patients: diversity, impact, unmet clinical needs. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;32:e00042. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00042-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Manuel O., Estabrook M., American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice RNA respiratory viral infections in solid organ transplant recipients: guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin Transplant. 2019;33:e13511. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mombelli M., Kampouri E., Manuel O. Influenza in solid organ transplant recipients: epidemiology, management, and outcomes. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020;18:103–112. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1713098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tay M.Z., Poh C.M., Rénia L., MacAry P.A., Ng L.F.P. The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:363–374. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Petrilli C.M., Jones S.A., Yang J., et al. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1966. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mehta P., McAuley D.F., Brown M., et al. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020;395:1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rodriguez-Cubillo B., Moreno de la Higuera M.A., Lucena R., et al. Should cyclosporine be useful in renal transplant recipients affected by SARS-CoV-2. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:3173–3181. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lubetzky M., Aull M.J., Craig-Schapiro R., et al. Kidney allograft recipients, immunosuppression, and coronavirus disease-2019: a report of consecutive cases from a New York City transplant center. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020;35:1250–1261. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kates O.S., Haydel B.M., Florman S.S., et al. COVID-19 in solid organ transplant: a multi-center cohort study. Clin Infect Dis. 2020:ciaa1097. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen T.Y., Farghaly S., Cham S., et al. COVID-19 pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients: focus on immunosuppression management. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020;22:e13378. doi: 10.1111/tid.13378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Marinaki S., Tsiakas S., Korogiannou M., et al. A systematic review of COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients: a universal effort to preserve patients’ lives and allografts. J Clin Med. 2020;9:2986. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Caillard S., Anglicheau D., Matignon M., et al. An initial report from the French SOT COVID registry suggests high mortality due COVID-19 in recipients of kidney transplant. Kidney Int. 2020;98:1549–1558. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pereira M.R., Mohan S., Cohen D.J., et al. COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: initial report from the US epicenter. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:1800–1808. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mehta S.A., Leonard J., Labella P., et al. Outpatient management of kidney transplant recipients with suspected COVID-19: single-center experience during the New York City surge. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020;22:e13383. doi: 10.1111/tid.13383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chaudhry Z.S., Williams J.D., Vahia A., et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: a cohort study. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:3051–3060. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Benotmane I., Gautier-Vargas G., Wendling M.J. In-depth virological assessment of kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:3162–3172. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Columbia University Kidney Transplant Program Early description of coronavirus 2019 disease in kidney transplant recipients in New York. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31:1150–1156. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020030375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Husain S.A., Dube G., Morris H., et al. Early outcomes of outpatient management of kidney transplant recipients with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;15:1174–1178. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05170420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ahmad S.H., Smith R., Camilleri B. Belatacept, kidney transplantation and COVID-19: successful management of the first reported case within the United Kingdom. Clin Transplant. 2020;34:e14026. doi: 10.1111/ctr.14026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Julia A., Bonafonte I., Gomez A., et al. Blocking of the CD80/86 axis as a therapeutic approach to prevent progression to more severe forms of COVID-19. arXiv: 10055. 2005 [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stephen-Victor E., Das M., Karnam A., Pitard B., Gautier J.F., Bayry J. Potential of regulatory T cell based therapies in the management of severe COVID-19. Eur Respir J. 2020;56:2002182. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02182-2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Study of abatacept in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 participants with respiratory compromise. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04472494.
- 26.Romanelli A., Mascolo S. Sirolimus to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection: an old drug for a new disease. J Res Clin Med. 2020;8:44. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhou Y., Hou Y., Shen J., Huang Y., Martin W., Chen F. Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov. 2020;6:14. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-0153-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Torres Serrano R., Montero C., Benavidez C., et al. Recommendation of the Colombian Association of Nephrology in renal transplantation during the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) Rev Colomb Nefrol. 2020;7(Suppl. 2):70–88. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Goyal P., Choi J.J., Pihneiro L.C., et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in New York City. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:2372–2374. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2010419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Perisetti A., Goyal H., Gajendran M., Boregowda U., Mann R., Sharma N., et al. Prevalence, mechanism, and implications of gastrointestinal symptoms in COVID-19. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020;7:588711. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.588711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Crespo M., Mazuecos A., Rodrigo E., et al. Respiratory and gastrointestinal COVID-19 phenotypes in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2020;104:2225–2233. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Villanego F., Mazuecos A., Prez-Flores I., et al. Predictors of severe COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients in the different epidemic waves: analysis of the Spanish Registry. Am J Transplant. 2021;21:2573–2582. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Iragorri N., Gómez-Restrepo C., Barrett K., et al. COVID-19: adaptation of a model to predict healthcare resource needs in Valle del Cauca, Colombia. Colomb Med. 2020;51:e204534. doi: 10.25100/cm.v51i3.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Caillard S., Chavarot N., Francois H., et al. Is COVID-19 infection more severe in kidney transplant recipients? Am J Transplant. 2021;21:1295–1303. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cravedi P., Mothi S.S., Azzi Y., et al. COVID-19 and kidney transplantation: results from the TANGO International Transplant Consortium. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:3140–3148. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Akalin E., Azzi Y., Bartash R., et al. COVID-19 and kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:2475–2477. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2011117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rosselli D. COVID-19 in Colombia: the first 90 days. Acta Neurol Colomb. 2020;36(Suppl 1):1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Situación de la enfermedad Renal Crónica, la hipertensión arterial y la diabetes mellitus en Colombia 2020. https://cuentadealtocosto.org/site/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/CAC.Co_2021_07_14_Libro_Sit_ERC2020_v4(1).pdf.
- 39.Bossini N., Alberici F., Delbarba E., et al. Kidney transplant patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the Brescia Renal COVID task force experience. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:3019–3029. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Willicombe M., Thomas D., McAdoo S. COVID-19 and calcineurin inhibitors: should they get left out in the storm? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31:1145–1146. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020030348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Carbajo-Lozoya J., Ma-Lauer Y., Malešević M., et al. Human coronavirus NL63 replication is cyclophilin A-dependent and inhibited by non-immunosuppressive cyclosporine A-derivatives including alisporivir. Virus Res. 2014;184:44–53. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pascual J., Melilli E., Jiménez-Martín C., et al. COVID-19-related mortality during the first 60 days after kidney transplantation. Eur Urol. 2020;78:641–643. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.06.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pérez-Sáez M.J., Blasco M., Redondo-Pachón D., et al. Use of tocilizumab in kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:3182–3190. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Demir E., Uyar M., Parmaksiz E., et al. COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients: a multicenter experience in Istanbul. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020;22:e13371. doi: 10.1111/tid.13371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mohamed I.H., Chowdary P.B., Shetty S., et al. Outcomes of renal transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection in the eye of the storm. Transplantation. 2021;105:115–120. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Romanelli A., Mascolo S. Inmmunosuppresion drug-related and clinical manifestations of coronavirus disease 2019: a therapeutical hypothesis. Am J Transplant. 2020;20:1947–1948. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Appelberg S., Gupta S., Svensson A., et al. Dysregulation in Akt/mTOR/HIF-1 signaling identified by proteotranscriptomics of SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:1748–1760. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1799723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xu Z., Shi L., Wang Y., et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:420–422. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chen G., Wu D., Guo W., et al. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:2620–2629. doi: 10.1172/JCI137244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Coquillard C., Vilchez V., Marti F., Gedaly R. mTOR signaling in regulatory T cell differentation and expansion. SOJ Immunol. 2015;3:1–10. [Google Scholar]