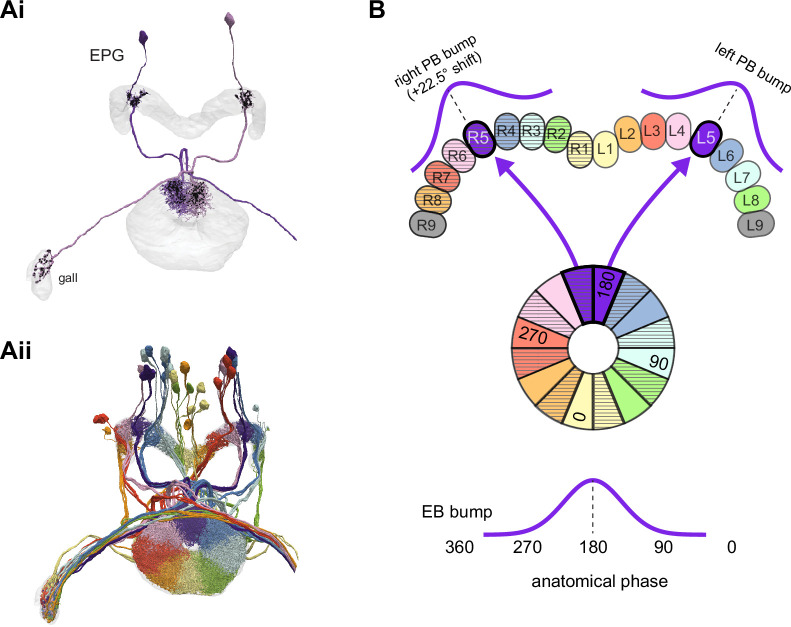
Figure 16. EPGs connect the ellipsoid body (EB) to the protocerebral bridge (PB).
(A, Ai) A morphological rendering of two EPG neurons. Black dots are presynaptic sites. (Aii) A morphological rendering of the entire population of EPG neurons, color-coded by PB glomerulus. (B) Schematic showing where the EPG processes arborize in the EB and in the PB. The EPG neurons map the different locations around the ring of the EB to the right and the left PB. A fictive bump of activity in the EB will therefore split into both a right and a left bump of activity in the PB. Note that the bumps in the PB are slightly shifted with respect to one another due to the 22.5° offset between the right- and left-projecting wedges in the EB.