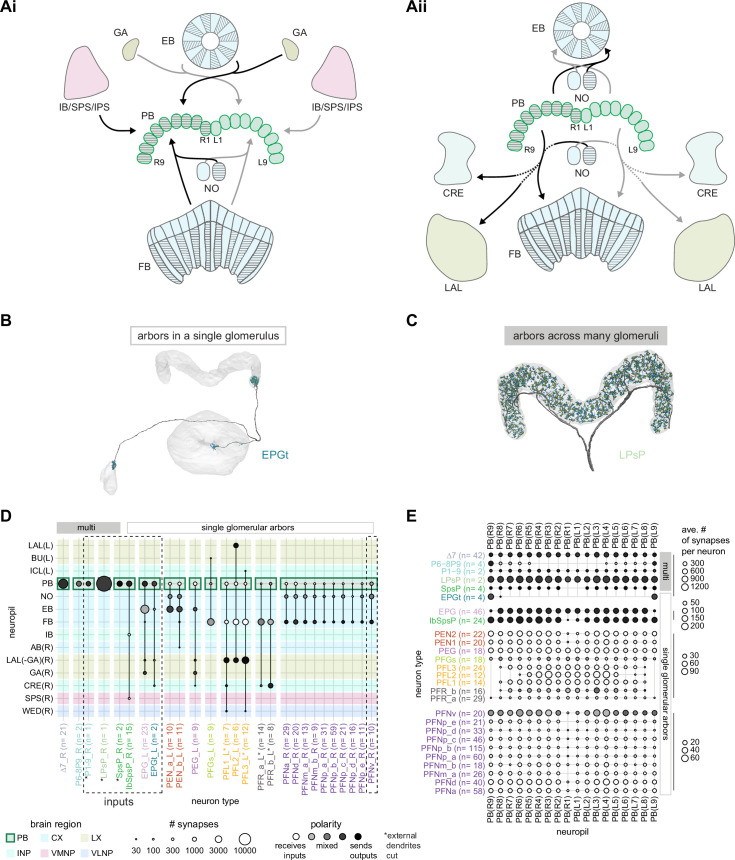
Figure 19. An overview of the protocerebral bridge.
(A) A diagram of the input (Ai) and output (Aii) pathways for the protocerebral bridge (PB). Connected brain regions include the ellipsoid body (EB), the inferior bridge (IB), the superior posterior slope (SPS), the posterior slope (PS), the crepine (CRE), the lateral accessory lobe (LAL), the fan-shaped body (FB), and the noduli (NO). (B) Morphological rendering of an EPGt neuron, which only arborizes in a single glomerulus in the PB. Yellow dots mark presynaptic site. Blue dots mark postsynaptic sites. (C) Morphological rendering as in (B) of an LPsP neuron, which has arbors throughout the PB. Yellow dots mark presynaptic site. Blue dots mark postsynaptic sites. (D) Region arborization plot for each neuron type that contains arbors in the PB. Neuron types that provide input to the PB are denoted by the dashed vertical boxes. The horizontal boxes at top indicate which neurons arborize in multiple glomeruli (filled gray boxes) and which arborize in single glomeruli (gray outline). (E) The average number of synapses per neuron in each PB glomerulus for each neuron type that contains arbors in the PB.