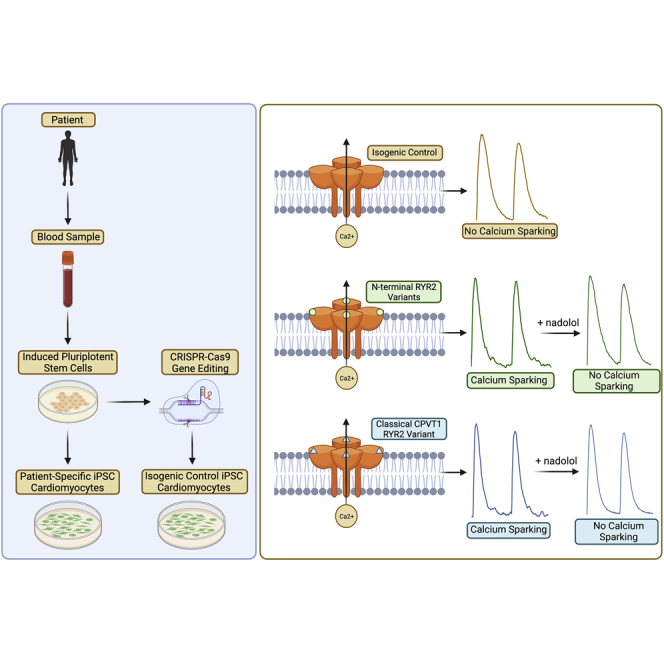
Summary
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is a cardiac channelopathy causing ventricular tachycardia following adrenergic stimulation. Pathogenic variants in RYR2-encoded ryanodine receptor 2 (RYR2) cause CPVT1 and cluster into domains I–IV, with the most N-terminal domain involving residues 77–466. Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs) were generated for RYR2-F13L, -L14P, -R15P, and -R176Q variants. Isogenic control iPSCs were generated using CRISPR-Cas9/PiggyBac. Fluo-4 Ca2+ imaging assessed Ca2+ handling with/without isoproterenol (ISO), nadolol (Nad), and flecainide (Flec) treatment. CPVT1 iPSC-CMs displayed increased Ca2+ sparking and Ca2+ transient amplitude following ISO compared with control. Combined Nad treatment/ISO stimulation reduced Ca2+ amplitude and sparking in variant iPSC-CMs. Molecular dynamic simulations visualized the structural role of these variants. We provide the first functional evidence that these most proximal N-terminal localizing variants alter calcium handling similar to CPVT1. These variants are located at the N-terminal domain and the central domain interface and could destabilize the RYR2 channel promoting Ca2+ leak-triggered arrhythmias.
Keywords: induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, calcium handling, catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, ryanodine receptor, sudden cardiac death
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Extreme N-terminal RyR2 variants alter calcium handling similar to classical CPVT1
-
•
Abnormal Ca2+ kinetics as well as uncontrolled Ca2+ release underlies CPVT1
-
•
In vitro arrhythmia studies with iPSCs show nadolol is an effective treatment
-
•
In silico 3D modeling of RYR2 revealed pathogenicity of N-terminal variants
Ackerman and colleagues provide the first functional evidence that variants N-terminal to the RyR2 mutation hotspot domains alter calcium handling similar to classical CPVT1-causative variants. Using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs), they demonstrated that nadolol is effective in reducing spontaneous calcium release associated with RyR2-F13L, -L14P, and -R15P variants.
Introduction
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is a potentially lethal cardiac channelopathy characterized by exercise- or stress-induced bidirectional or polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) capable of precipitating syncope and sudden cardiac death in the absence of structural heart abnormalities (Leenhardt et al., 1995; Swan et al., 1999; Medeiros-Domingo et al., 2009). Identification of CPVT clinically can be difficult and is complicated by unremarkable resting electrocardiograms (ECGs). Consequently, exercise stress testing is crucial to establishing a CPVT diagnosis as it can unmask bidirectional VT and induce worsening arrhythmias with increased activity (Leenhardt et al., 1995; Liu et al., 2008; Giudicessi and Ackeman, 2019).
Gain-of-function (GOF) variants in the RYR2-encoded ryanodine receptor 2 (RYR2) cause autosomal dominant type 1 CPVT (CPVT1) (Laitinen et al., 2001; Priori et al., 2001). Currently, 60% of CPVT can be explained by variants in established genes, indicating that other unknown genetic causes may exist (Leenhardt et al., 1995; Priori et al., 2002; Medeiros-Domingo et al., 2009). In cardiomyocytes, RYR2 is responsible for systolic calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), which is critical for excitation-contraction coupling (Medeiros-Domingo et al., 2009). Under normal physiological conditions, RYR2 is nearly inactive during diastolic periods (Bers 2002). However, CPVT1-causative RYR2 variants increase diastolic spontaneous Ca2+ release from the SR, which can then trigger ventricular arrythmias (Swan et al., 1999; Wehrens et al., 2003; Lehnart et al., 2004; Paavola et al., 2007).
RYR2 consists of 105 exons, and RYR2 comprises 4,967 amino acids, making it the largest known ion channel in the human cardiomyocyte (Medeiros-Domingo et al., 2009). The transmembrane pore-forming region is located at the C-terminal end, while the majority of the protein is found in the cytoplasm and senses cellular changes. The cytoplasmic domains relay information to the transmembrane region for channel response (Ludtke et al., 2005; Samso et al., 2005; George et al., 2007). Pathogenic variants are most commonly localized to four well-conserved, distinct domains spanning from amino acids 77–466, 2,246–2,534, 3,778–4,201, and 4,497–4,959 (domains I, II, III, and IV, respectively) (George et al., 2007).
RYR2-R176Q, located in hotspot N-terminal domain I, has been previously described as a pathogenic, classical CPVT1-causative variant resulting in increased spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations and VT episodes both with and without adrenergic stimulation in mice (Kannankeril et al., 2006). Despite this, the functional sequelae of missense variants found outside the canonical variant clusters is largely uncharacterized.
Herein, we present three novel N-terminal (N-term) RYR2 variants of uncertain significance (VUSs) located far proximal to the domain I variant hotspot (p.F13L, p.L14P, and p.R15P) identified in three unrelated pedigrees with clinical phenotypes consistent with CPVT1. In this study, we functionally characterized all three of these novel N-term variants compared with a classical CPVT1 variant (p.R176Q). Using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs), we assessed the functional mechanism of disease while evaluating potential variant-specific pharmacological therapies.
Results
Patients with suspected CPVT type 1 index cases and extreme N-term RYR2 VUSs
Three unrelated patients with suspected CPVT were referred to the Mayo Clinic Windland Smith Rice Genetic Heart Rhythm Clinic after commercial genetic testing identified heterozygous RYR2 N-term-localizing missense variants. Each variant was classified originally as a VUS, in part because of their novelty, location outside the 4 established CPVT1-associated hotspots, and lack of either pedigree-based co-segregation or functional evidence for CPVT1 causality.
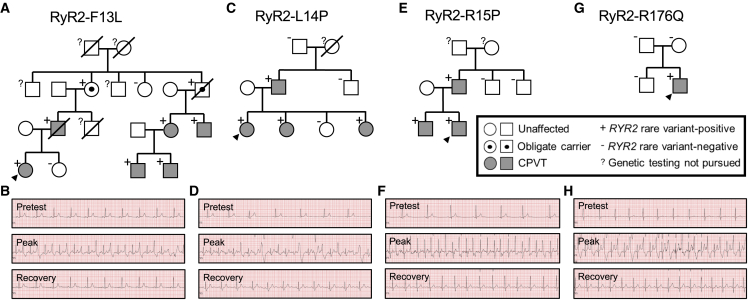
Index case 1 was a 20-year-old female who experienced a sentinel sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) at the age of 17. Of note, this occurred in the context of sudden unexplained deaths of the patient’s mother and maternal uncle before the age of 40 (Figure 1A). Commercial CPVT genetic testing obtained prior to the index case’s Mayo Clinic evaluation identified an ultra-rare VUS in RYR2 (c.37T>C; p.F13L) that was subsequently found in multiple family members (Figure 1B). A treadmill exercise stress test obtained at the time of the index case’s Mayo Clinic evaluation displayed the onset of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) in bigeminy ∼120 beats per minute (bpm) with progression to couplets and bidirectional couplets at peak exercise (∼140 bpm; Figure 1B). The patient is currently well controlled on nadolol and has had no breakthrough events recorded since implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) placement following her sentinel SCA.
Figure 1.
Pedigree co-segregation analysis and clinical stress testing for the three novel CPVT1 variants in index cases I, II, and III and a reference classical, domain I-localizing CPVT1 variant
(A and B) RYR2-F13L co-segregates with a CPVT phenotype (A), and exercise stress testing of index case I demonstrates PVCs in bigeminy progressing to couplets and bidirectional couplets (B).
(C and D) RYR2-L14P co-segregates with a CPVT phenotype (C), and stress testing of index case II demonstrates onset of monomorphic PVCs progressing to bigeminy and couplets (D).
(E and F) RYR2-R15P co-segregates with a CPVT phenotype (E), and stress testing of index case III demonstrates monomorphic PVCs progressing to bigeminy (F).
(G and H) The classical CPVT variant RYR2-R176Q was de novo in the index case (G), and the patient demonstrates the classic stress test findings observed in CPVT (H).
Index case 2 was a 27-year-old female who presented for evaluation after experiencing several swimming-related syncopal episodes. No family history of unexplained SCD was identified, but the patient’s father and two of her sisters were diagnosed subsequently with CPVT (Figure 1C). A treadmill exercise stress test obtained at the time of the index case’s initial Mayo Clinic evaluation displayed the onset of occasional monomorphic PVCs ∼110 bpm with progression to bigeminy and couplets at peak exercise (∼120 bpm; Figure 1D). Commercial CPVT genetic testing subsequently identified an ultra-rare VUS in RYR2 (c.41T>C; p.L14P) that was also present in the patient’s father and two sisters (Figure 1C). Currently, the proband is well controlled after left cardiac sympathetic denervation (LCSD) and nadolol treatment.
The third index case was a 21-year-old male who presented following an exertion-induced syncopal episode at age 17. Commercial genetic testing obtained prior to the index case’s Mayo Clinic evaluation identified an ultra-rare RYR2 VUS (c.44G>C; p.R15P). Of note, RYR2-R15P was also identified in the index case’s father and brother, who were subsequently diagnosed with CPVT on the basis of abnormal exercise stress tests (Figure 1E). A treadmill exercise stress test obtained at the time of the index case’s initial Mayo Clinic evaluation displayed the onset of occasional monomorphic PVCs ∼120 bpm with progression to bigeminy ∼140 bpm (Figure 1F). Following LCSD and ongoing treatment with nadolol, the index case has not experienced any additional cardiac events.
The known classical CPVT1-causative variant, RYR2-R176Q (c.527G>A; p.R176Q), was identified de novo in a 16-year-old male presenting with more than 20 syncopal episodes before the age of 15, when he experienced an exertion-related SCA (Figure 1G). A representative treadmill exercise stress test series for the RYR2-R176Q-positive index case is depicted in Figure 1H for comparison purposes. Following LCSD and ongoing treatment with nadolol and flecainide, the patient has not experienced any additional cardiac events.
Exacerbated Ca2+ amplitude and spontaneous Ca2+ sparking activity in RYR2-L14P compared with its CRISPR-Cas9-corrected isogenic control
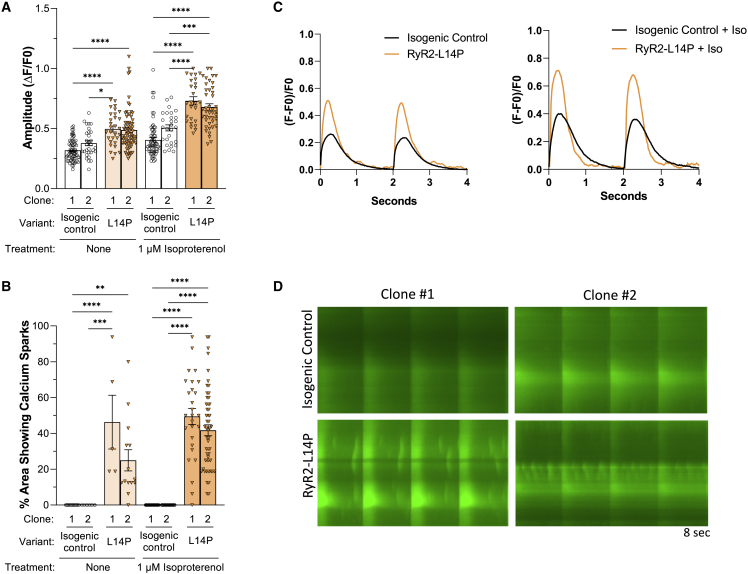
Fluo-4 based Ca2+ imaging was performed using isogenic control and RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs. The calcium transient amplitude normalized by (ΔF/F0) was increased in RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs compared with isogenic control both at baseline (BL; isogenic control clone 1: 0.32 ± 0.01; isogenic control clone 2: 0.38 ± 0.02; L14P clone 1: 0.50 ± 0.03; L14P clone 2: 0.49 ± 0.02) and following treatment with 1 μM isoproterenol (ISO; isogenic control clone 1: 0.40 ± 0.02; isogenic control clone 2: 0.51 ± 0.02; L14P clone 1: 0.73 ± 0.03; L14P clone 2: 0.68 ± 0.03) (Table S1; Figure 2A). Following ISO treatment, RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs displayed faster upstroke velocity than isogenic controls (isogenic control clone 1: 0.83 ± 0.05; isogenic control clone 2: 1.1 ± 0.07; L14P clone 1: 1.3 ± 0.09, n = 26; L14P clone 2: 1.3 ± 0.05) (Table S1; Figure S4A). Peak to 50% and 90% decay and calcium transient duration 50 and 90 were decreased in RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs when compared with isogenic control with/without ISO (Table S1; Figures S4B–S4E). Ca2+ imaging using Fluo-4 indicator displayed elevated spontaneous Ca2+ release (Ca2+ sparks) in RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs before (L14P clone 1: 46% ± 15%; L14P clone 2: 25% ± 6%) and after treatment with ISO (L14P clone 1: 49% ± 5%; L14P clone 2: 42% ± 3%); however, isogenic control iPSC-CMs did not produce sparking activity (isogenic control clone 1: 0% ± 0%,; isogenic control clone 2: 0% ± 0%) (Table S1; Figure 2B). Spontaneous Ca2+ release was highlighted in representative tracings from Ca2+ transients (Figure 2C), representative splice-view images (Figure 2D), and a time-lapse video recording (Videos S1 and S2).
Figure 2.
RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs display changes in Ca2+ transient measurements and sparking activity compared with isogenic control
(A) Calcium transient amplitude normalized by (ΔF/F0).
(B) Percentage of area of 40× microscopic field displaying calcium sparking activity using Fluo-4 Ca2+ imaging at baseline and following treatment with 1 μM ISO.
(C) Representative calcium transient tracings in isogenic control (black) and RYR2-L14P (orange) iPSC-CMs at BL and after ISO.
(D) Representative splice-view images of calcium transients after ISO treatment.
Data presented as mean ± SEM. n = 5–72 per group (Table S1). 3–8 independent experiments were conducted. A two-way ANOVA was performed with post hoc Tukey-Kramer testing. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. iPSC-CMs used were 30 to 50 days old.
See also Figure S4.
Time lapse video recorded at 20ms per frame for 20s at 10% LED power. Isogenic control iPSC-CMs were treated with Fluo-4 calcium dye and paced at 0.5Hz
Time lapse video recorded at 20ms per frame for 20s at 10% LED power. RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs were treated with Fluo-4 calcium dye and paced at 0.5Hz
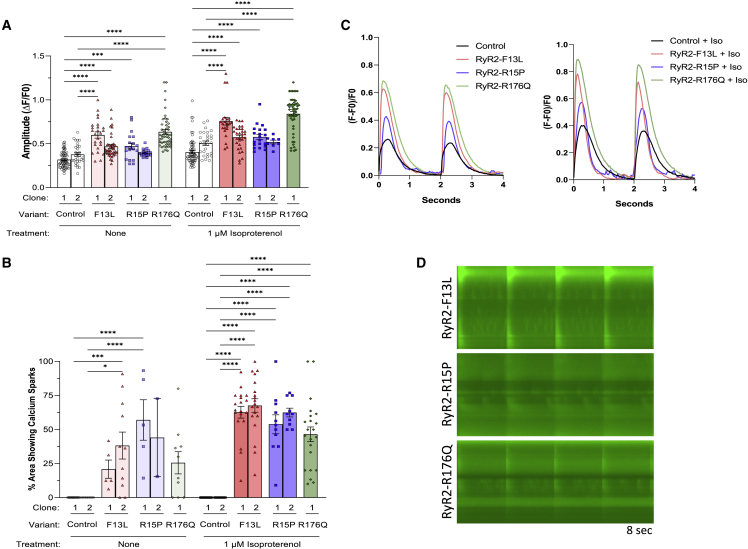
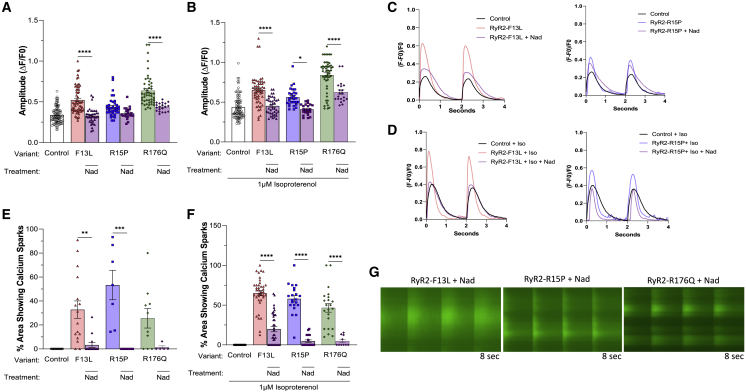
N-term variants RYR2-F13L and -R15P and classical CPVT1 variant RYR2-R176Q showed identical signatures of Ca2+ transient kinetics and Ca2+ sparking activity
Similar to RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs, N-term variants RYR2-F13L and -R15P and classical CPVT variant RYR2-R176Q iPSC-CMs also displayed increased Ca2+ amplitude profiles and upstroke velocity compared with control (L14P variant-corrected isogenic control) at BL (F13L clone 1: 0.60 ± 0.04 and 1.6 ± 0.09; F13L clone 2: 0.47 ± 0.02 and 1.4 ± 0.09; R15P clone 1: 0.47 ± 0.03 and 1.3 ± 0.09; R15P clone 2: 0.40 ± 0.01 and 0.90 ± 0.02; R176Q: 0.63 ± 0.03 and 1.9 ± 0.05) and after ISO treatment (F13L clone 1: 0.76 ± 0.04 and 2.1 ± 0.1; F13L clone 2: 0.57 ± 0.02 and 1.7 ± 0.08; R15P clone 1: 0.58 ± 0.03 and 1.6 ± 0.1; R15P clone 2: 0.52 ± 0.02 and 1.2 ± 0.03; R176Q: 0.84 ± 0.03 and 2.8 ± 0.1) (Table S1; Figures 3A and S5A). Additionally, peak to 50% and 90% decay and calcium transient duration 50 and 90 were decreased in RYR2-F13L, -R15P, and -R176Q, following the same trend as RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs (Table S1; Figures S5B–S5E). Behavior of N-term variants RYR2-F13L and -R15P and classical CPVT variant RYR2-R176Q iPSC-CMs’ spontaneous Ca2+ sparking activity was also comparable to RYR2-L14P at BL (F13L clone 1: 21% ± 7%; F13L clone 2: 38% ± 10%; R15P clone 1: 57% ± 15%; R15P clone 2: 44% ± 29%; R176Q: 26% ± 8%) and with the addition of ISO (F13L clone 1: 63% ± 4%, n = 19; F13L clone 2: 68% ± 5%; R15P clone 1: 54% ± 7%; R15P clone 2: 62% ± 3%; R176Q: 47% ± 5%) (Table S1; Figure 3B). Ca2+ transient representative tracings, splice view images, and a time-lapse videos revealed sparking activity in variant iPSC-CMs (Figures 3B–3D; Video S3).
Figure 3.
Altered Ca2+ handling kinetics and sparking activity in RYR2-F13L, -R15P, and -R176Q iPSC-CMs
(A) Calcium transient amplitude normalized by (ΔF/F0).
(B) Percentage of area of 40× microscopic field displaying calcium sparking activity using Fluo-4 Ca2+ imaging at baseline and following treatment with 1 μM ISO.
(C) Representative calcium transient tracings in control (black), F13L (red), R15P (blue), and R176Q (green) iPSC-CMs at BL and after ISO.
(D) Representative splice-view images of calcium transients after ISO treatment.
Data presented as mean ± SEM. n = 2–67 per group (Table S1). 3–7 independent experiments were conducted. A two-way ANOVA was performed with post hoc Tukey-Kramer testing. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. iPSC-CMs used were 30 to 50 days old.
See also Figure S5.
Time lapse video recorded at 20ms per frame for 20s at 10% LED power. RYR2-R176Q iPSC-CMs were treated with Fluo-4 calcium dye and paced at 0.5Hz
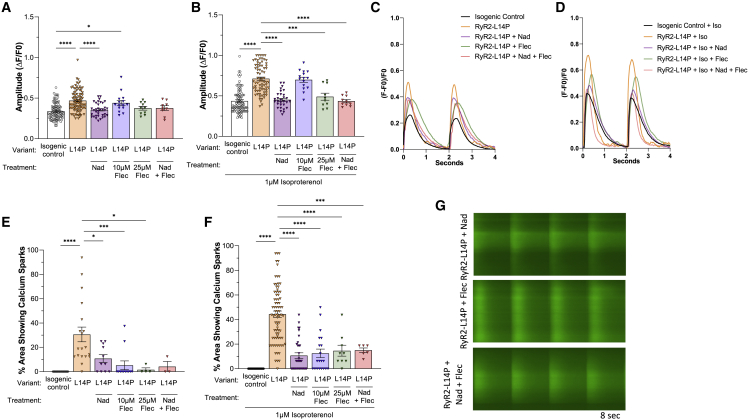
Nadolol, flecainide, and combination treatment rescued Ca2+ handling kinetics in N-term and classical CPVT1 iPSC-CMs
Next, we evaluated the efficacy of nadolol (Nad) and flecainide (Flec) in rescuing abnormal L14P variant-related Ca2+ handling kinetics. Nad significantly reduced Ca2+ transient amplitude both at BL (L14P: 0.47 ± 0.01; L14P + Nad: 0.36 ± 0.01, p < 0.0001) and following ISO stimulation (L14P: 0.70 ± 0.02; L14P + Nad: 0.45 ± 0.02, p < 0.0001). The resulting L14P Ca2+ amplitude was not significantly different from isogenic control (Table S2; Figures 4A and 4B). Flec and combination treatment of Flec and Nad also rescued the Ca2+ amplitude profile after ISO treatment in L14P iPSC-CMs (Figures 4A and 4B). Spontaneous Ca2+ release was reduced following separate Nad and Flec treatment as well as combination treatment before ISO (L14P: 31% ± 6%; L14P + Nad: 11% ± 3%; L14P + 10 μM Flec: 5% ± 4%; L14P + 25 μM Flec: 2% ± 2%; L14P + Nad + Flec: 4% ± 4%) and after ISO (L14P: 44% ± 3%; L14P + Nad: 11% ± 2%; L14P + 10 μM Flec: 13% ± 3%; L14P + 25 μM Flec: 15% ± 4%; L14P + Nad + Flec: 15% ± 2%) (Table S2; Figures 4C–4G).
Figure 4.
Ca2+ transient amplitude and sparking activity in RYR2-L14P compared with its isogenic control after CPVT1 pharmacotherapy
(A–G) Calcium transient amplitude normalized by (ΔF/F0), percentage of area of 40× microscopic field displaying calcium sparking activity, and representative tracings in isogenic control (black); RYR2-L14P (orange); RYR2-L14P + 10 μM Nad (purple); RYR2-L14P + 10 μM Flec (blue); RYR2-L14P + 25 μM Flec (green); and RYR2-L14P + 10 μM Nad +25 μM Flec (red) iPSC-CMs at BL (A, C, and E), and following 1 μM ISO (B, D, F, and G).
Data presented as mean ± SEM. n = 3–97 per group (Table S2). independent experiments were conducted. A one-way ANOVA was performed with post-hoc Tukey-Kramer testing. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. iPSC-CMs used were 30–50 days old.
We further analyzed the rescuing effects of Nad in N-term and classical CPVT iPSC-CMs. Nad treatment of N-term iPSC-CMs reduced Ca2+ transient amplitude to the level of control iPSC-CMs at BL (control: 0.34 ± 0.01; F13L + Nad: 0.33 ± 0.02; R15P + Nad: 0.36 ± 0.02, p > 0.05) and following ISO (control: 0.44 ± 0.02; F13L + Nad: 0.45 ± 0.02; R15P + Nad: 0.41 ± 0.01, p > 0.05) (Table S3; Figures 5A and 5B). Though the Ca2+ amplitude profile in Nad-treated classical CPVT iPSC-CMs was significantly reduced compared with untreated classical CPVT iPSC-CMs, it was not decreased to the control iPSC-CM level at BL or with ISO treatment (Figures 5A and 5B). Following ISO stimulation, all N-term and classical CPVT iPSC-CMs treated with Nad displayed a significant reduction in Ca2+ sparking activity (F13L: 65% ± 3%; F13L + Nad: 20% ± 3%, p < 0.0001; R15P: 58% ± 4%; R15P + Nad: 5% ± 2%, p < 0.0001; R176Q: 47% ± 5%; R176Q + Nad: 5% ± 2%, p < 0.0001) (Table S3; Figures 5C–5G).
Figure 5.
Calcium transient amplitude and sparking activity in RYR2-F13L, -R15P, and -R176Q after nadolol treatment
Calcium transient amplitude normalized by (ΔF/F0) and percent area of 40X microscopic field displaying calcium sparking activity in control, -F13L, -R15P, and -R176Q iPSC-CMs before and after 10μM Nad treatment at BL.
(A and E) and following addition of ISO.
(B, F, and G). Representative tracings shown for control (black), -F13L with (purple) and without (red) 10 μM Nad treatment, and -R15P with (purple) and without (blue) 10 μM Nad treatment at BL (C) and after ISO (D). Data presented as mean ± SEM n = 5–97 per group (Table S3). 3-7 independent experiments were conducted. A one-way ANOVA was performed with post-hoc Tukey-Kramer testing. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. iPSC-CMs used were 30–50 days old.
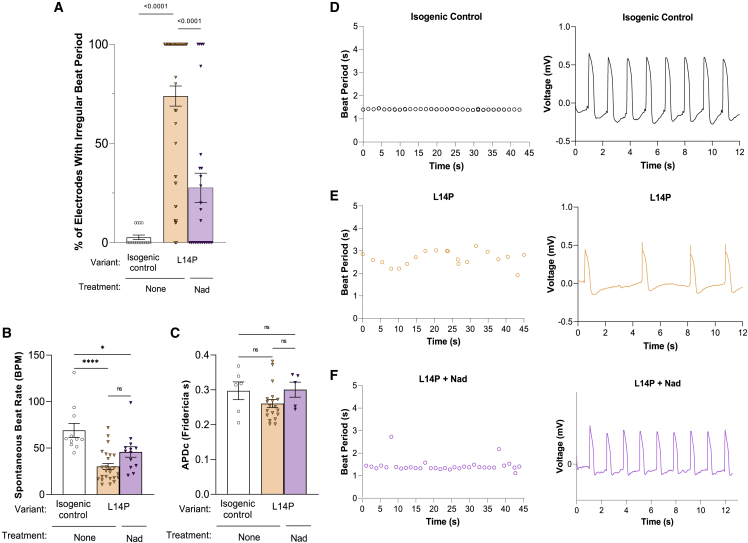
Lastly, we tested the electrophysiological profile of these novel RYR2 variants compared with classical CPVT1 and isogenic control iPSC-CMs using microelectrode array (MEA)-based local extracellular action potential (LEAP) measurements. RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs displayed irregular beating periods significantly more frequently than isogenic control iPSC-CMs (control: 2.7% ± 1.2%; L14P: 73.9% ± 5.1%, p < 0.0001). Irregularities in beat period were significantly decreased in L14P iPSC-CMs after treatment with 10 μM Nad (L14P + Nad: 27.6% ± 7.4%, p < 0.0001) (Figure 6A). Spontaneous beat rate was significantly decreased in L14P iPSC-CMs compared with isogenic control (Figure 6B). Representative tracings of action-potential duration (APD) and beat period displayed inconsistent beating in RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs while showing normal beating patterns in isogenic control iPSC-CMs and RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs treated with Nad (Figures 6D–6F).
Figure 6.
Beat period irregularities in RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs reduced with 10μM nadolol treatment
Percent of irregular 20 s beat periods in isogenic control, L14P, and L14P iPSC-CMs treated with Nad.
(A) Average spontaneous beat rate (B) and Microelectrode Array (MEA) based local extracellular action potential (LEAP) corrected APD (C) for isogenic control, L14P, and L14P + Nad iPSC-CMs. LEAP representative APD tracings and beat period recordings for isogenic control (D), L14P (E), and L14P + Nad (F) iPSC-CMs. Data presented as mean ± SEM. 3 independent experiments were conducted. A two-way ANOVA was performed with post hoc Tukey-Kramer testing. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. iPSC-CMs used were 30 to 50 days old.
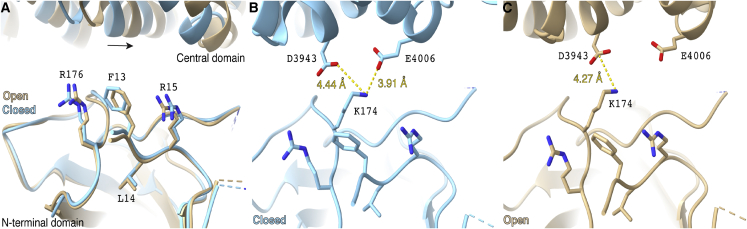
Molecular dynamic simulations demonstrate potential critical function of N-term region
To gain insight into the structural modification of this most proximal N-term region in RYR2 function, we used molecular modeling of RYR2 protein. We hypothesize that the three novel N-term variants (RYR2-F13L, -L14P, and -R15P) we characterized may cause similar biophysical changes as those seen with the classical RYR2-R176Q variant. Previous studies have demonstrated that RYR2-R176Q, which occurs in the β8-β9 loop, results in loss of N-term mediated RYR2 tetramerization (Amador et al., 2013). Although the novel N-term variants we describe are not part of the β8-β9 loop and are in fact more proximal to β1, we predict that this region causes a similar disruption in channel function as seen with variants in the β8-β9 loop (Figure 7A) (Humphrey et al., 1996). The variants studied here also are in the proximity of residue K174 belonging to the β8-β9 loop. K174 is a key residue of the interface between the N-term domain and the central domain. K174 is a modulator of the opening of the channel by interacting with residues D3943 and E4006 of the central domain in the closed conformation (Figure 7B) but only with D3943 in the open conformation (Figure 7C). We observe that F13 is at a distance below 5 Å from both K174 and R176, suggesting that interactions could occur (Figure 7). To test this hypothesis, we performed explicit water and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations of the N-term domain (residues 10–220) for a total simulation time of 0.5 μs (Figure S7; Video S4). The timescale is good enough to investigate the side-chain flexibility of the residues. We observed that there are frequent contacts among the three residues F13, K174, and R176 and that the range of motion of the three side chains is surprisingly narrow. The R176 side chain forms a metastable hydrogen bond with the K174 backbone oxygen (occupancy of 43%), which would limit the dynamics of the K174 backbone (Figure S7C). Also, the F13 aromatic ring interacts, during most of the simulation, with the −CH2 groups of both R176 and K174, limiting the side chains’ range of motion of both residues (Figures S7D and S7E).
Figure 7.
Location of variants in wild-type (WT) RYR2 atomic model
(A) Overlapped atomic models of the open (beige; PDB: 5GOA) and closed (blue; PDB: 5GO9) RYR2 states. The atomic models have been aligned at the N-terminal domain. Relative shift of the central domain is shown with an arrow.
(B and C) Relative position of residue K174 to residues D3943 and E4006 of the central domain, in the open (B) and closed (C) conformations. Alignment and distance measurements were performed with ChimeraX software (Pettersen et al., 2021).
See also Figures S6 and S7.
MDS of the N-terminal domain, focused on the residues of interest F13, K174 and R176
Discussion
RYR2 functions to control calcium-induced calcium release and is mainly active during systole. During the cardiac action potential, small amounts of calcium traversing through voltage-dependent L-type calcium channels (LTCCs) trigger the opening of RYR2s, which consequently release Ca2+ from the SR into the cytoplasm (Medeiros-Domingo et al., 2009; Landstrom et al., 2017). RYR2 GOF variants cause CPVT1, a rare arrhythmogenic syndrome characterized by bidirectional or polymorphic VT following adrenergic stimulation in the setting of a structurally normal heart and resting ECG (Leenhardt et al., 1995; Swan et al., 1999; Medeiros-Domingo et al., 2009). Clinically, CPVT1 presents with premature ventricular complexes or VT manifest during an exercise stress test and progressively worsen as activity level increases, improving as heartrate returns to resting (Leenhardt et al., 1995; Liu et al., 2008). Currently, it is hypothesized that GOF of RYR2 creates an uncontrolled Ca2+ leak from the SR into the cytosol, thereby triggering spontaneous membrane depolarizations leading to ventricular arrhythmias and a CPVT1 phenotype (Swan et al., 1999; Paavola et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2008). Consistent with the typical clinical presentation of patients with CPVT1, several mouse studies have demonstrated that GOF RYR2 variants lead to delayed afterdepolarizations (DADs) at BL with increases in severity following β-adrenergic stimulation (Kannankeril et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2006).
Genetic studies have revealed that CPVT1-associated RYR2 variants cluster in four pathogenic hotspot domains. These four cluster regions have been implicated in domain-domain interaction and calcium handling (George et al., 2007). Although previously characterized pathogenic variants impact channel function, no CPVT1 variants have been discovered in the pore region, suggesting disruptions to the pore itself may result in a non-functional channel and cause calcium-release channel deficiency syndrome (George et al., 2007). Outside the four hotspot domains, several benign polymorphisms are present at high population frequencies; however, no rare pathogenic variants residing outside these domains have thus far been conclusively characterized (Laitinen et al., 2001; Tiso et al., 2001; Milting et al., 2006).
Genetic testing is useful in diagnosis of CPVT1 when pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants are identified. However, a significant number of genetic tests result in the identification of a VUS, which produces a clinical conundrum. Variants identified outside of these aforementioned hotspot domains tend to be classified as VUSs since functional characterization studies have largely not been performed but are necessary to aid in variant interpretation. Here, we characterized the three most proximal RYR2 missense variants identified to date (p.F13L, p.L14P, and p.R15P) compared with a well-established CPVT1-causative variant (p.R176Q) that localizes to the first domain.
RYR2 is a large, homotetrameric ion channel consisting of a large cytoplasmic region (residues 1–4,207) and a transmembrane region (4,486–4,968), also referred to as the channel domain (Peng et al., 2016). The cytoplasmic region contains the N-term domain, the handle domain, two helical domains (HD1 and HD2), the central domain, three SPRY domains, and two RyR domains. The pathogenic CPVT1-associated domains I, II, III, and IV (residues 77–466, 2,246–2,534, 3,778–4,201, and 4,497–4,959) are located inside the N-term domain (residues 1–642), the HD1 domain (residues 2,111–26,79), the central domain (residues 3,593–4,207), and the channel domain (residues 4,486–4,967), respectively. Calmodulin (CaM) interacts with the central domain and the HD1 domain of RYR2 and regulates release of Ca2+ from the SR by inhibiting the channel activity (Balshaw et al., 2001; Gong et al., 2019). Reduced binding of CaM to RYR2 disrupts N-term domain and central domain interactions, leading to spontaneous Ca2+ release and heart failure (Ono et al., 2010).
One proposed mechanism of CPVT1-causing RYR2 GOF variants implicates channel-stabilizing interdomain interactions between the N-term and central domains (Tateishi et al., 2009; Suetomi et al., 2011). In this model, variants found at domain interfaces may disrupt normal stabilizing interactions between domains, leading to channel hypersensitivity (Tateishi et al., 2009; Suetomi et al., 2011). The four variants studied here are located close to the interface between the N-term domain and the central domain and could explain the pathogenic channel hypersensitivity to activation. Prior to this study, no definitive CPVT1-causitive pathogenic variants have been demonstrated to reside more proximally to the variant domain hotspot I (amino acids 77–466). However, there is biological plausibility for variants in this most proximal N-term region (amino acids 1–77) to impact channel function.
RYR2-R176Q is a previously described CPVT1-causitive variant residing in the N-term domain (Kannankeril et al., 2006; Amador et al., 2013). Interestingly, in HEK293 cells, RYR2-R176Q yielded findings consistent with GOF RYR2 variants including decreased Ca2+ content in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) along with increased open probability of RYR2 and increased spontaneous Ca2+ leak; however, there were no significant alterations in the channel’s conformation of the closed RYR2 state (Iyer et al., 2020). Studies using RYR2-R176Q heterozygous mice demonstrated increased VT with adrenergic stimulation, and cardiomyocytes isolated from the mice demonstrated increased spontaneous Ca2+ release with and without ISO (Kannankeril et al., 2006). Taken together, these findings suggest that RYR2-R176Q results in GOF in the channel and thus provide a biological substate for CPVT1 that is also consistent with our findings in IPSC-CMs expressing this classical RYR2-R176Q variant.
Interestingly, our findings for the three novel N-term variants in iPSC-CMs also demonstrate increased Ca2+ sparking activity with and without ISO treatment similar to that seen with the classical RYR2-R176Q variant. Overall, the iPSC-CMs derived from these three most proximal N-term variants displayed alterations in calcium handling kinetics similar to classical CPVT1 variant RYR2-R176Q. These findings provide functional evidence that in iPSC-CMs, these variants result in a significant disruption in channel function analogous to pathogenic CPVT1 variants. Weakening of these interactions, by mutations F13L or R176Q, could result in destabilization of the interaction between the N-term domain and the central domain (due to increased flexibility of K174). Additionally, residues L14 and R15 are necessary to stabilize F13 in the correct position. Mutation of L14 and R15 to proline residues, which are well-known secondary-structure disruptors, would destabilize F13, leading to similar or slightly weaker effects as shown in this study.
Typically, pharmacotherapy for CPVT1 consists of β-blockers and/or Flec (Leren et al., 2016; Preininger et al., 2016). Previous studies in patients have shown Nad treatment to be more effective at decreasing incidence and severity of arrhythmias than β1-selective β-blockers (Leren et al., 2016; Peltenburg et al., 2021). An iPSC-CM study highlighted the efficacy of Flec in cell lines generated from patients with CPVT1 unsuccessfully treated by β-blockers, thereby suggesting that iPSC-CMs are capable of reproducing patient-specific drug responses (Preininger et al., 2016). In our study, all three proximal N-term variant-containing iPSC-CMs displayed reductions in calcium transient amplitude and sparking activity following Nad treatment. Interestingly, all three patients harboring the RYR2-F13L, -L14P, and -R15P variants are currently well controlled with daily Nad treatment. Overall, these novel N-term cardiomyocyte lines displayed rescues in calcium handling kinetics following β-blocker treatment similar to the classical CPVT variant RYR2-R176Q.
Here, we characterized what we believe are the most proximal N-term-localizing RYR2 variants to date found in three unrelated pedigrees with clinical phenotypes consistent with CPVT1 using patient-specific iPSC-CM models. Our functional studies showed convincingly that all three novel variants (p.F13L, p.L14P, and p.R15P) lead to dysfunctional RYR2 channels, thus enabling us to further promote their status from a VUS to a CPVT1-causative pathogenic variant. Similar to the previously well-described pathogenic RYR2-R176Q variant, these novel N-term iPSC-CMs displayed GOF calcium handling alterations, which were resolved in isogenic control iPSC-CMs. Interestingly, 3 dimensionally, these novel N-term variants are located near the classical CPVT variant (RYR2-R176Q). By using patient-specific iPSCs, the functional mechanism and potential pharmacological therapies for these novel CPVT1-causative variants have been established.
These data provide sufficient evidence that these N-term variants have functional implications on channel function and subsequent calcium handling. However, the limitations of the assay used must be acknowledged. Since calcium was measured using Fluo-4 dye, which is a non-ratiometric dye whose emission intensity depends on the calcium concentration, it thus gives a measure of change in calcium concentration by comparing ΔF/F0. This relies on F0 remaining constant between groups. In disease models such as CPVT or with ISO treatment, SR and cytosolic calcium levels may differ, impacting F0. To further evaluate the spontaneous calcium release and diastolic calcium level, a ratiometric calcium-sensitive dye such as Fura-2 must be used. In addition, these findings utilize an in vitro model system with treatment of Flec on a monolayer of cells. The Flec concentration used on cells is not necessarily representative of the concentration in the biophase of patients treated with Flec. Due to inherent variability in iPSC-CMs, additional experimentation is necessary to further evaluate effect of drug treatment on beating rate.
Experimental procedures
Generation of patient-specific iPSCs
Blood (RYR2-F13L, -L14P, and -R15P) or dermal (RYR2-R176Q) samples were obtained from patients following informed consent in accordance to this Mayo Clinic IRB (09-006465) approved study. See supplemental experimental procedures for additional details.
Mutation correction of RYR2-L14P using CRISPR-Cas9
An isogenic control line was generated by correcting patient-derived RYR2-L14P variant iPSCs using a CRISPR-Cas9/PiggyBac gene-correction system. Briefly, a guide RNA (gRNA) was designed online using the GPP sgRNA Designer from Broad Institute (https://portals.broadinstitute.org/gpp/public/analysis-tools/sgrna-design) and was inserted into the pSpCas9(BB)-2A-Puro (v.2.0) vector (Addgene: 62988) using a modified cloning protocol generated by our lab. To construct the targeting vector, a left homologous arm (LHA; ∼500 bp fragment with p.14L) and a right homologous arm (RHA; ∼500 bp fragment) were PCR amplified with P1, P2, and PB1 using Platinum PCR Super-Mix High Fidelity (Invitrogen, 12532-024) and cloned into MV-PGK-Puro-TK PiggyBac vector obtained from System Biosciences (Mountain View, PB200A-1). The schematic strategies of designing gRNA, generating targeting vector, and screening for gene-corrected iPSC colonies are shown in Figure S1.
To produce targeted clones, 3.5 × 105 iPSCs from the patient’s RYR2-L14P-positive cells were seeded into two wells of a Matrigel (Corning, Corning, NY, USA) coated 6-well plate in mTeSR1 media (STEMCELL Technologies, 85,851). The following day, each well was transfected with 1.6 μg CRISPR-Cas9 and 5.4 μg PiggyBac targeting vectors using Lipofectamine 3000 (ThermoFisher, L3000008) according to the protocol. 48 h post transfection, iPSCs were cultured with selection medium containing 0.2 μg/mL puromycin for 10–14 days (Wang et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2018). Surviving colonies were manually picked, expanded, and screened for insertion of PiggyBac cassette. For removal of the PiggyBac cassette, variant-corrected iPSCs were seeded into two wells of a 6-well plate and transfected with 0.9 μg Excision only PiggyBac Transposase Expression Vector (System Biosciences, PB220PA-1) using Lipofectamine 3000 (Wang et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2018). In the next 48 h after transfection, 8 μM Ganciclovir (Sigma, cat#: G2536) was added to medium for 7–10 days to eliminate PiggyBac-cassette-containing cells. Surviving colonies were manually selected for expanding and screening. The established clones were confirmed for removal of PiggyBac cassette by PCR (Figure S1B) and Sanger sequencing (Figure S1D).
Differentiation into iPSC-CMs
iPSCs were differentiated and selected for cardiomyocytes according to previously reported strategies (see supplemental experimental procedures) (Mummery et al., 2012; Burridge et al., 2014; Fuerstenau-Sharp et al., 2015).
Dissociation of iPSC-CMs
iPSCs were dissociated according to previously reported strategies (see supplemental experimental procedures) (Froese et al., 2018).
Quality-control assessment of iPSC lines
Karyotyping was completed by the Mayo Clinic Cytogenetics Laboratory according to Mayo Clinic IRB (1216-97) for each isogenic control and variant-containing iPSC clone. All iPSC clones displayed a normal karyotype (Figure S2A). RYR2 variants were confirmed in patient-derived iPSCs using sanger sequencing (Figure S2C).
Immunocytochemistry of iPSCs and iPSC-CMs
See supplemental experimental procedures for additional details. Briefly, fluorescent intensity within the cell area was quantified, and background fluorescence was subtracted, followed by normalizing to the cell area. Acquisition settings were kept constant across images. All patient clones and isogenic control iPSC clones were confirmed to express Oct4 (ThermoFisher, PA5-27438) and SSEA-4 (ThermoFisher, MA1-021) pluripotent markers (Figure S2B). All N-term lines RYR2-F13L, -L14P, and -R15P, classical CPVT line RYR2-R176Q, and isogenic control were confirmed to express cTnT and RYR2 (Figures S3A and S3B).
Western blot for RYR2 and qRT-PCR of iPSC-CMs
See supplemental experimental procedures for methods. There was no change in RYR2 gene or protein expression between isogenic control and RYR2 missense-variant-containing iPSC-CMs (Figures S3C–S3F).
Live-cell imaging
Fluo-4-based Ca2+ imaging
iPSC-CMs were harvested at 30–50 days post differentiation using the STEMCELL Technologies protocol previously described and plated onto Matrigel-coated 35 mm glass-bottom dishes (MatTek, P35G-1.5-10-C) at a density of 400,000 cells per plate and allowed to grow for 3 to 5 days. Cells were loaded with 5 μM Fluo-4 AM (ThermoFisher, F14201) and 0.02% F-127 (ThermoFisher, P3000MP) in 1 mL Tyrode’s Solution and incubated for 30 min. After incubation, cells were rinsed once with fresh Tyrode’s Solution and then washed with fresh Tyrode’s Solution for a 10 min incubation. Medium was then changed to fresh Tyrode’s solution, and dishes were taken for imaging. Cells were either untreated or treated with Flec, Nad, or combination of the two for 1 h prior to imaging. Tyrode’s Solution was prepared with or without the appropriate drug treatment to allow for continued incubation throughout dyeing and imaging. During imaging, the dishes were kept in a heated 37°C stage-top environment chamber supplied with 5% CO2. Imaging of Ca2+ transients was taken under a 40× objective using a Nikon Eclipse Ti light microscope under BL conditions, and then the same dish was stimulated with ISO for 1 to 10 min. Time-lapse videos of multiple, individual beating isogenic control, RYR2-L14P, RYR2-F13L, RYR2-R15P, and RYR2-R176Q iPSC-CMs, paced at 0.5 Hz, were recorded at a speed of 20 ms per frame for 20 s at 10% LED power. Single regions of interest were selected for every beating iPSC-CM captured in the recordings. The raw data were exported to Excel software (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA) and then analyzed with a custom “in-lab”-developed Excel-based program. Lastly, the data were uploaded to GraphPad Prism 9.01 software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA) for comparison. In the analysis, n represents the regions of interest that correspond to single cells. For each group, an average of 3 to 5 differentiations were used with measurements across different experiments to ensure reproducibility.
MEA
Thirty-day-old iPSC-CMs were harvested using the STEMCELL Technologies protocol previously described and seeded at 50,000 cells per well on 48-well Biocircuit MEA plate (Axion BioSystems, M768-BIO-48) pre-coated with Matrigel. Cells were cultured in a humidified incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 7 to 10 days after dissociation, and media were changed every 2 days. Cells were treated with Nad for 1 h. MEA plate was assessed in Maestro MEA device (Axion BioSystems) with automatically adjusted and controlled environment (37 °C and 5% CO2) and equilibrated for 2 to 5 min. MEA-based APD was recorded after LEAP induction using the AxIS Navigator software (Axion BioSystems,). Data analysis was done using Cardiac Analysis Tool (Axion BioSystems, v.3.1.4).
Statistical analysis
All data points are shown as dots, and bars represent the mean value. Error bars show the standard error of the mean. A Student’s t test was performed to determine statistical significance between two groups. A one-way ANOVA and Tukey-Kramer post hoc test was performed for comparisons among three or more groups, and a two-way ANOVA and Tukey-Kramer post hoc test was performed for comparisons with two or more categorical variables using GraphPad Prism v.9.1.0. A p <0.05 was considered to be significant.
Graphical abstract
The graphical abstract was made using BioRender.com.
Conformational dynamics of RYR2 N-term gomain using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations RYR2 N-term domain structure preparation
We used the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of RYR2 (PDB: 5GO9) to study the conformational changes in RYR2. Due to the large size of the receptor, only the N-term domain with residues in the range 10–220 was used for MD simulations. See supplemental experimental procedures for methods.
MD simulations
We used all-atom explicit solvent MD simulations to investigate the conformational changes of RYR2 N-term domain residues. For these simulations, the CHARMM-GUI solution builder (Lee et al., 2016) was used to prepare the system. See supplemental experimental procedures for methods.
Analysis
MD simulation trajectory analysis was done using Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD 1.9.3) (Humphrey et al., 1996). See supplemental experimental procedures for analysis methods.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, M.J.S., C.S.J.K., D.J.T., J.F., A.R.M., and M.J.A.; methodology, M.J.S., C.S.J.K., D.J.T., S.K.H., M.C.M., and J.B.G.; formal analysis, M.J.S., C.S.J.K., S.M.D., M.C.M., and J.B.C.; investigation, M.J.S., C.S.J.K., M.C.M., and J.B.G.; writing – original draft, M.J.S. and M.C.M.; writing – review & editing, M.J.S., C.S.J.K., D.J.T., A.R.M., and M.J.A.; visualization, M.J.S., M.C.M., and J.B.C.; supervision, J.F., A.R.M., and M.J.A.; project admisinstation, C.S.J.K. and D.J.T.; funding acquisition, A.R.M. and M.J.A.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the team at the Mayo Clinic Microscopy and Cell Analysis Core facility in Rochester, MN, USA, for their assistance and care with the equipment. This work was supported by the Mayo Clinic Windland Smith Rice Comprehensive Sudden Cardiac Death Program and by NIH grants R01HL145473, R01HL142903, R01HL140934, and T32 HL120826 (to A.R.M.).
Conflict of interests
M.J.A. is a consultant for Abbott, ARMGO Pharma, Boston Scientific, Daiichi Sankyo, Invitae, LQT Therapeutics, and Medtronic. M.J.A. and/or Mayo Clinic are involved in an equity/royalty relationship with AliveCor, Anumana, Pfizer, and UpToDate. However, none of these entities were involved in this study in any manner. A.R.M. and Columbia University own shares in ARMGO Pharma, a biotech company developing RyR-targeted therapeutics.
Published: August 4, 2022
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.07.002.
Supplemental information
References
- Amador F.J., Stathopulos P.B., Enomoto M., Ikura M. Ryanodine receptor calcium release channels: lessons from structure-function studies. FEBS J. 2013;280:5456–5470. doi: 10.1111/febs.12194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balshaw D.M., Xu L., Yamaguchi N., Pasek D.A., Meissner G. Calmodulin binding and inhibition of cardiac muscle calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:20144–20153. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010771200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D.M. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 2002;415:198–205. doi: 10.1038/415198a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge P.W., Matsa E., Shukla P., Lin Z.C., Churko J.M., Ebert A.D., Lan F., Diecke S., Huber B., Mordwinkin N.M., et al. Chemically defined generation of human cardiomyocytes. Nat. Methods. 2014;11:855–860. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froese N., Wang H., Zwadlo C., Wang Y., Grund A., Gigina A., Hofmann M., Kilian K., Scharf G., Korf-Klingebiel M., et al. Anti-androgenic therapy with finasteride improves cardiac function, attenuates remodeling and reverts pathologic gene-expression after myocardial infarction in mice. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018;122:114–124. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerstenau-Sharp M., Zimmermann M.E., Stark K., Jentsch N., Klingenstein M., Drzymalski M., Wagner S., Maier L.S., Hehr U., Baessler A., et al. Generation of highly purified human cardiomyocytes from peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0126596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C.H., Jundi H., Thomas N.L., Fry D.L., Lai F.A. Ryanodine receptors and ventricular arrhythmias: emerging trends in mutations, mechanisms and therapies. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2007;42:34–50. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.08.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudicessi J.R., Ackerman M.J. Exercise testing oversights underlie missed and delayed diagnosis of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in young sudden cardiac arrest survivors. Heart Rhythm. 2019;16:1232–1239. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2019.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong D., Chi X., Wei J., Zhou G., Huang G., Zhang L., Wang R., Lei J., Chen S.R.W., Yan N. Modulation of cardiac ryanodine receptor 2 by calmodulin. Nature. 2019;572:347–351. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1377-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey W., Dalke A., Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996;14 doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer K.A., Hu Y., Nayak A.R., Kurebayashi N., Murayama T., Samsó M. Structural mechanism of two gain-of-function cardiac and skeletal RyR mutations at an equivalent site by cryo-EM. Sci. Adv. 2020;6:eabb2964. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannankeril P.J., Mitchell B.M., Goonasekera S.A., Chelu M.G., Zhang W., Sood S., Kearney D.L., Danila C.I., De Biasi M., Wehrens X.H.T., et al. Mice with the R176Q cardiac ryanodine receptor mutation exhibit catecholamine-induced ventricular tachycardia and cardiomyopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:12179–12184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600268103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen P.J., Brown K.M., Piippo K., Swan H., Devaney J.M., Brahmbhatt B., Donarum E.A., Marino M., Tiso N., Viitasalo M., et al. Mutations of the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) gene in familial polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation. 2001;103:485–490. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.4.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landstrom A.P., Dobrev D., Wehrens X.H.T. Calcium signaling and cardiac arrhythmias. Circ. Res. 2017;120:1969–1993. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Cheng X., Swails J.M., Yeom M.S., Eastman P.K., Lemkul J.A., Wei S., Buckner J., Jeong J.C., Qi Y., et al. CHARMM-GUI input generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM simulations using the CHARMM36 additive force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016;12:405–413. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenhardt A., Lucet V., Denjoy I., Grau F., Ngoc D.D., Coumel P. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in children. A 7-year follow-up of 21 patients. Circulation. 1995;91:1512–1519. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.5.1512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnart S.E., Wehrens X.H.T., Laitinen P.J., Reiken S.R., Deng S.X., Cheng Z., Landry D.W., Kontula K., Swan H., Marks A.R. Sudden death in familial polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) leak. Circulation. 2004;109:3208–3214. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000132472.98675.EC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leren I.S., Saberniak J., Majid E., Haland T.F., Edvardsen T., Haugaa K.H. Nadolol decreases the incidence and severity of ventricular arrhythmias during exercise stress testing compared with beta1-selective beta-blockers in patients with catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13:433–440. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.09.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu N., Colombi B., Memmi M., Zissimopoulos S., Rizzi N., Negri S., Imbriani M., Napolitano C., Lai F.A., Priori S.G. Arrhythmogenesis in catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: insights from a RyR2 R4496C knock-in mouse model. Circ. Res. 2006;99:292–298. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000235869.50747.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu N., Ruan Y., Priori S.G. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008;51:23–30. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2007.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludtke S.J., Serysheva I.I., Hamilton S.L., Chiu W. The pore structure of the closed RyR1 channel. Structure. 2005;13:1203–1211. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2005.06.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma N., Zhang J.Z., Itzhaki I., Zhang S.L., Chen H., Haddad F., Kitani T., Wilson K.D., Tian L., Shrestha R., et al. Determining the pathogenicity of a genomic variant of uncertain significance using CRISPR/Cas9 and human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Circulation. 2018;138:2666–2681. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros-Domingo A., Bhuiyan Z.A., Tester D.J., Hofman N., Bikker H., van Tintelen J.P., Mannens M.M.A.M., Wilde A.A.M., Ackerman M.J. The RYR2-encoded ryanodine receptor/calcium release channel in patients diagnosed previously with either catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia or genotype negative, exercise-induced long QT syndrome: a comprehensive open reading frame mutational analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009;54:2065–2074. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milting H., Lukas N., Klauke B., Körfer R., Perrot A., Osterziel K.J., Vogt J., Peters S., Thieleczek R., Varsányi M. Composite polymorphisms in the ryanodine receptor 2 gene associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006;71:496–505. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mummery C.L., Zhang J., Ng E.S., Elliott D.A., Elefanty A.G., Kamp T.J. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells to cardiomyocytes: a methods overview. Circ. Res. 2012;111:344–358. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.227512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Yano M., Hino A., Suetomi T., Xu X., Susa T., Uchinoumi H., Tateishi H., Oda T., Okuda S., et al. Dissociation of calmodulin from cardiac ryanodine receptor causes aberrant Ca(2+) release in heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010;87:609–617. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paavola J., Viitasalo M., Laitinen-Forsblom P.J., Pasternack M., Swan H., Tikkanen I., Toivonen L., Kontula K., Laine M. Mutant ryanodine receptors in catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia generate delayed afterdepolarizations due to increased propensity to Ca2+ waves. Eur. Heart J. 2007;28:1135–1142. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehl543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltenburg P.J., Kallas D., Bos J.M., Lieve K.V.V., Franciosi S., Roston T.M., Denjoy I., Sorensen K.B., Ohno S., Roses-Noguer F., et al. An international multi-center cohort study on beta-blockers for the treatment of symptomatic children with catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation. 2021;145:333–344. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng W., Shen H., Wu J., Guo W., Pan X., Wang R., Chen S.R.W., Yan N. Structural basis for the gating mechanism of the type 2 ryanodine receptor RyR2. Science. 2016;354:aah5324. doi: 10.1126/science.aah5324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen E.F., Goddard T.D., Huang C.C., Meng E.C., Couch G.S., Croll T.I., Morris J.H., Ferrin T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021;30:70–82. doi: 10.1002/pro.3943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preininger M.K., Jha R., Maxwell J.T., Wu Q., Singh M., Wang B., Dalal A., McEachin Z.T., Rossoll W., Hales C.M., et al. A human pluripotent stem cell model of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia recapitulates patient-specific drug responses. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016;9:927–939. doi: 10.1242/dmm.026823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priori S.G., Napolitano C., Memmi M., Colombi B., Drago F., Gasparini M., DeSimone L., Coltorti F., Bloise R., Keegan R., et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of patients with catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation. 2002;106:69–74. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000020013.73106.d8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priori S.G., Napolitano C., Tiso N., Memmi M., Vignati G., Bloise R., Sorrentino V., Danieli G.A. Mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene (hRyR2) underlie catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation. 2001;103:196–200. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samso M., Wagenknecht T., Allen P.D. Internal structure and visualization of transmembrane domains of the RyR1 calcium release channel by cryo-EM. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005;12:539–544. doi: 10.1038/nsmb938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suetomi T., Yano M., Uchinoumi H., Fukuda M., Hino A., Ono M., Xu X., Tateishi H., Okuda S., Doi M., et al. Mutation-linked defective interdomain interactions within ryanodine receptor cause aberrant Ca(2)(+)release leading to catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation. 2011;124:682–694. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.023259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan H., Piippo K., Viitasalo M., Heikkilä P., Paavonen T., Kainulainen K., Kere J., Keto P., Kontula K., Toivonen L. Arrhythmic disorder mapped to chromosome 1q42-q43 causes malignant polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in structurally normal hearts. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999;34:2035–2042. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00461-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi H., Yano M., Mochizuki M., Suetomi T., Ono M., Xu X., Uchinoumi H., Okuda S., Oda T., Kobayashi S., et al. Defective domain-domain interactions within the ryanodine receptor as a critical cause of diastolic Ca2+ leak in failing hearts. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009;81:536–545. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiso N., Stephan D.A., Nava A., Bagattin A., Devaney J.M., Stanchi F., Larderet G., Brahmbhatt B., Brown K., Bauce B., et al. Identification of mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene in families affected with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy type 2 (ARVD2) Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001;10:189–194. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.3.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G., Yang L., Grishin D., Rios X., Ye L.Y., Hu Y., Li K., Zhang D., Church G.M., Pu W.T. Efficient, footprint-free human iPSC genome editing by consolidation of Cas9/CRISPR and piggyBac technologies. Nat. Protoc. 2017;12:88–103. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrens X.H.T., Lehnart S.E., Huang F., Vest J.A., Reiken S.R., Mohler P.J., Sun J., Guatimosim S., Song L.S., Rosemblit N., et al. FKBP12.6 deficiency and defective calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) function linked to exercise-induced sudden cardiac death. Cell. 2003;113:829–840. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Time lapse video recorded at 20ms per frame for 20s at 10% LED power. Isogenic control iPSC-CMs were treated with Fluo-4 calcium dye and paced at 0.5Hz
Time lapse video recorded at 20ms per frame for 20s at 10% LED power. RYR2-L14P iPSC-CMs were treated with Fluo-4 calcium dye and paced at 0.5Hz
Time lapse video recorded at 20ms per frame for 20s at 10% LED power. RYR2-R176Q iPSC-CMs were treated with Fluo-4 calcium dye and paced at 0.5Hz
MDS of the N-terminal domain, focused on the residues of interest F13, K174 and R176