To the editor,
Disease from SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19) was first reported in late 2019, in China [1]. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening complication of COVID-19 often requiring long periods of mechanical ventilation and sedation during which delirium occurs in up to 65 % of these patients [2]. Delirium is characterized by an acute onset of a fluctuating course of inattentiveness and either disorganized thought (manifesting as memory, language and orientation difficulties) or altered level of consciousness. This altered mental state is associated with patient and family stress, increased length of hospital stay, escalation of care and hospital costs, and increased morbidity and mortality. [3].
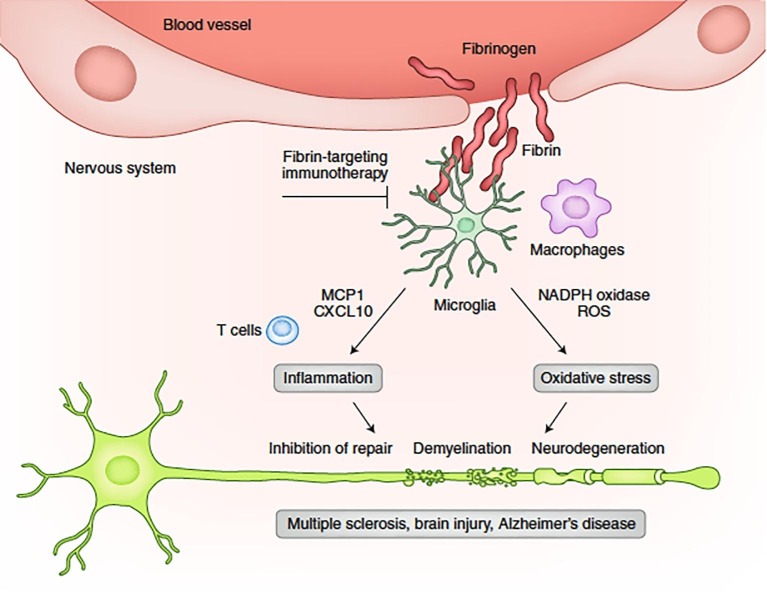
Coagulopathy is another frequent complication of COVID-19 [4]; however, thrombosis observed in COVID patients differ from the consumptive coagulopathy reported in other critically ill patients by virtue of higher, rather than lower, levels of circulating fibrinogen [4]. Recent studies have reported an association between higher plasma fibrinogen levels and post-stroke cognitive impairment [5], [6] Within the CNS, fibrinogen can lead to microglial activation through the CD11b/CD18 pathway, with the activated microglia releasing IL-1β, VEGF and increasing permeability of the BBB [7]. In this way, fibrin (fibrinogen) is deposited in the CNS, causing neuroinflammation, with disruption of synaptic plasticity [6], [7], [8], [9] resulting in cognitive decline [7], [10] (Fig. 1 . [11]). Immunotherapy targeting fibrinogen/fibrin can prevent cognitive impairment in preclinical models of neurodegenerative diseases [12].
Fig. 1.
Fibrin mechanisms and functions in neuroinflammation. Upon BBB disruption, fibrinogen leaks into the brain, and, by activation of the coagulation cascade, it is converted to insoluble fibrin deposits. Fibrin activates microglia and induces the release of CXCL10 and MCP1 to promote recruitment of peripheral immune cells, as well as activation of NADP oxidase to induce oxidative injury, leading to tissue damage. Inhibition of the interaction of fibrin with its cellular receptors or suppression of fibrin's downstream signaling pathways in cells could enable the discovery of selective therapies to the toxic effects of blood leaks in a wide range of diseases that cause vascular damage and inflammation.
From the above, we hypothesize that delirium in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients could be predicted by high plasma fibrinogen levels at ICU admission.
In a retrospective monocentric study, the impact of demographic factors, inflammation -related factors at ICU admission, as well as sedation and treatment strategies, were evaluated for the development of delirium during the ICU management in COVID-19 ARDS patients.
After approval from the Institutional Review Board (P20/64–16/12; CCB B3252020000044; ethical committee from the Intercommunale de Santé Publique du Pays de Charleroi-OM008; chairperson Prof. A. Herchuelz date of approval December 16, 2020), we studied successive adult patients admitted to the 32-bed intensive care unit (ICU) of the CHU de Charleroi, Belgium, between March to December 2020 for invasive mechanical ventilation with sedation due to COVID-19 ARDS. Pregnant patients and patients requiring vv ECMO support were excluded. A standard case report form was used for de-identified data collection. Data were collected from the patients’ medical records by three independent researchers (SS, AW, AK) to determine which factors were associated with an increased risk for the development of delirium.
Data regarding demographic factors and comorbidities, ICU admission inflammation markers, sedation, analgesia and SARS-COV2 treatment strategies as well as confusion/ agitation status were collected.
During mechanical ventilation, severe ARDS patients received sedation/analgesia/paralysis provided by midazolam (titrated to Richmond agitation sedation scale (RASS) of −5), morphine and rocuronium respectively.
During weaning, sedation was provided by propofol to achieve a RASS of 0 to −2. Additionally, sedation was supplemented with clonidine (RASS + 1 to + 4), alprazolam, risperidone or quetiapine when necessary due to hyperactivity.
An altered cognitive state, defined by clinical features of confusion or agitation, was assessed by the nursing staff every 3 h and was considered to be present if found documented at any time during ICU stay.
Data were described using medians and interquartile ranges (IQR) for continuous variables and using absolute counts and percentages for qualitative variables. Inferential methods for variable comparisons included Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon tests and chi-squared tests. A Receiver Operating (ROC) curve for delirium binary classification was calculated, and standard error (SE)and binomial exact confidence intervals were determined. Box plots and violin plots were generated using ggplot2 package for R (R Core Team (2019). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/).
During the study period, 190 patients needed ICU admission for COVID-induced hypoxia. Of these, 102 patients required invasive mechanical ventilation. According to exclusion criteria mentioned above, 78 patients were finally included in this study.
Demographic factors and comorbidities did not have an influence on delirium.
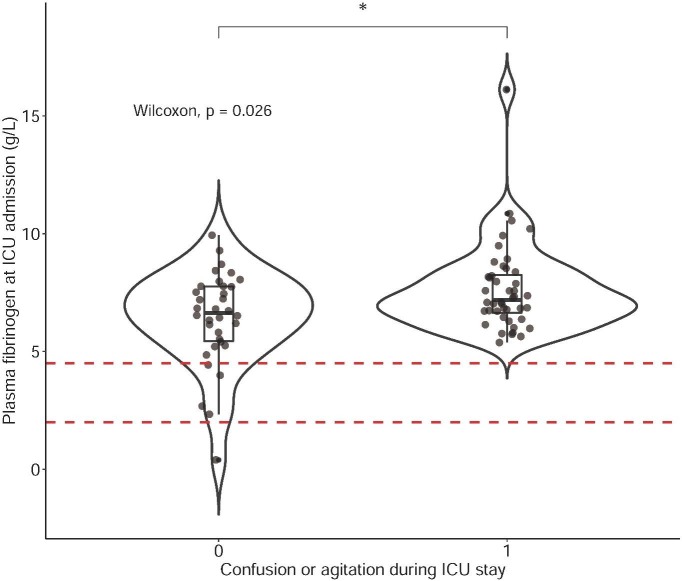
Out of several inflammation markers (ferritin, CRP, white blood cells, lymphocytes, d-dimers, fibrinogen) at ICU admission, only higher fibrinogen levels were associated with an altered cognitive state during ICU stay (7.19 [6.58–8.30] versus 6.63 [5.41–7.77] g/L; p = 0.026) (AUC ROC: 0.65, SE: 0.06, 95 % CI: 0.53 – 0.75, p = 0.02) (Fig. 2 ).
Fig. 2.
Box plot and violin plot for plasma fibrinogen levels at ICU admission in patients with or without confusion/ agitation during ICU stay. Dashed lines denote lower and upper laboratory limits for plasma fibrinogen (2.0–4.5 g/L). Groups were compared using a Wilcoxon test for unpaired data. * denotes a p-value < 0.05 .
Regarding specific treatment for COVID-19, dexamethasone use was not associated with an altered cognitive state; however, the longer patients were exposed to dexamethasone, the more they were likely to suffer from delirium. Patients with altered cognitive state were significantly longer ventilated (p = 0.028) and had a prolonged ICU stay (p = 0.0001).
Major limitations of these data are the use of benzodiazepines (due to propofol shortage) and lack of objective delirium assessment (due to nursing staff shortage).
Nevertheless, these preliminary data support the hypothesis that ICU admission plasma fibrinogen levels could predict an altered cognitive state in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients. Interestingly, Sui J et al. recently described that elevated admission plasma fibrinogen is higher in patients suffering from more severe SARS-COV2 disease [13]. Some neurological symptoms in COVID-19 patients could therefore be due to fibrinogen deposition crossing the altered BBB.
In conclusion, we hypothesize that ICU admission plasma fibrinogen levels could predict the development of cognitive impairment in mechanically ventilated ARDS COVID-19 patients.
Large prospective clinical trials are needed to investigate this hypothesis as well as to compare plasma fibrinogen levels in COVID, versus other ICU, patients with delirium.
Ethics approval.
Ethical committee: Intercommunale de Santé Publique du Pays de Charleroi-OM008.
Chairperson: Prof. A. Herchuelz.
Date of approval December 16, 2020.
Approval number: P20/64-16/12; CCB B3252020000044.
Consent for publication.
Patient consent was not obtained for this retrospective case series.
Availability of data and materials.
In order to protect patient privacy and identity, data analyzed during the current study are available on reasonable request.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the nursing staff of the CHU-Charleroi, Belgium.
References
- 1.Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W; China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 20;382(8):727-733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. Epub 2020 Jan 24. PMID: 31978945; PMCID: PMC7092803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.Helms J, Kremer S, Merdji H, Clere-Jehl R, Schenck M, Kummerlen C, Collange O, Boulay C, Fafi-Kremer S, Ohana M, Anheim M, Meziani F. Neurologic Features in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 4;382(23):2268-2270. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2008597. Epub 2020 Apr 15. PMID: 32294339; PMCID: PMC7179967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 3.Leslie DL, Inouye SK. The importance of delirium: economic and societal costs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011 Nov;59 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S241-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03671.x. PMID: 22091567; PMCID: PMC3415302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Iba T., Levy J.H., Connors J.M., Warkentin T.E., Thachil J., Levi M. The unique characteristics of COVID-19 coagulopathy. Crit Care. 2020 Jun 18;24(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03077-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu Y, Chen H, Zhao K, He W, Lin S, He J. High levels of plasma fibrinogen are related to post-stroke cognitive impairment. Brain Behav. 2019 Oct;9(10):e01391. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1391. Epub 2019 Sep 2. PMID: 31475471; PMCID: PMC6790326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Pyun JM, Ryoo N, Park YH, Kim S. Fibrinogen Levels and Cognitive Profile Differences in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2020;49(5):489-496. doi: 10.1159/000510420. Epub 2020 Nov 3. PMID: 33142286; PMCID: PMC7949208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Obermeier B, Daneman R, Ransohoff RM. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med. 2013 Dec;19(12):1584-96. doi: 10.1038/nm.3407. Epub 2013 Dec 5. PMID: 24309662; PMCID: PMC4080800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Huang X, Hussain B, Chang J. Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021 Jan;27(1):36-47. doi: 10.1111/cns.13569. Epub 2020 Dec 30. PMID: 33381913; PMCID: PMC7804893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.Lersy F, Kremer S. Meningeal inflammation and cerebral vasculitis during acute COVID-19 with spontaneous regression. Intensive Care Med. 2022 Feb;48(2):233-235. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06592-y. Epub 2021 Dec 16. PMID: 34913085; PMCID: PMC8674013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Achar A., Ghosh C. COVID-19-Associated Neurological Disorders: The Potential Route of CNS Invasion and Blood-Brain Relevance. Cells. 2020 Oct 27;9(11):2360. doi: 10.3390/cells9112360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Akassoglou K. Author Correction: The immunology of blood: connecting the dots at the neurovascular interface. Nat Immunol. 2020 Sep;21(9):1134. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0752-z. PMID: 32636513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ryu JK, Rafalski VA, Meyer-Franke A, Adams RA, Poda SB, Rios Coronado PE, Pedersen LØ, Menon V, Baeten KM, Sikorski SL, Bedard C, Hanspers K, Bardehle S, Mendiola AS, Davalos D, Machado MR, Chan JP, Plastira I, Petersen MA, Pfaff SJ, Ang KK, Hallenbeck KK, Syme C, Hakozaki H, Ellisman MH, Swanson RA, Zamvil SS, Arkin MR, Zorn SH, Pico AR, Mucke L, Freedman SB, Stavenhagen JB, Nelson RB, Akassoglou K. Fibrin-targeting immunotherapy protects against neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Nat Immunol. 2018 Nov;19(11):1212-1223. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0232-x. Epub 2018 Oct 15. PMID: 30323343; PMCID: PMC6317891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Sui J., Noubouossie D.F., Gandotra S., Cao L. Elevated Plasma Fibrinogen Is Associated With Excessive Inflammation and Disease Severity in COVID-19 Patients. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Aug;3(11) doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.734005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]