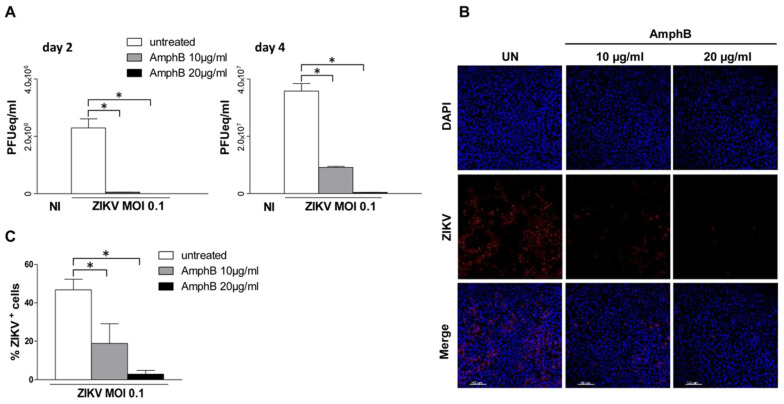
Figure 1.
Disruption of lipid raft architecture by AmphB inhibits ZIKV replication and infection of Vero cells. Vero cells were left untreated or pre-treated with increasing doses of AmphB (10–20 µg/mL) for 30 min and adsorbed with ZIKV at MOI of 0.1 in medium +/− AmphB for 1 h at 37 °C. NI: non-infected. (A) After 2 and 4 days of culture in fresh medium +/−, AmphB viral titre was determined by qRT-PC and expressed as PFU equivalents/mL (PFUeq/mL). Drug treatment significantly inhibited viral replication in a dose-dependent manner. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis after 24 h of culture in fresh medium +/− AmphB. Cells were fixed and stained with anti-pan-flavivirus antibody (ZIKV) followed by donkey anti-mouse AlexaFluo 647 antibody (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar is 100 µm. Images are from one representative experiment out of three. (C) Percentage of infected cells was established for each sample using the Cell Counting tool of MetaMorph software. Data showed a dose-dependent inhibitory effect of the drug on cell infection that decreased from 47% to 19% at 10 µg/mL and 20 µg/mL, respectively. Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments performed. Significance was determined by GraphPad Prism using the nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test. * p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.