Figure 2. Sympathoblast cell fate specification.
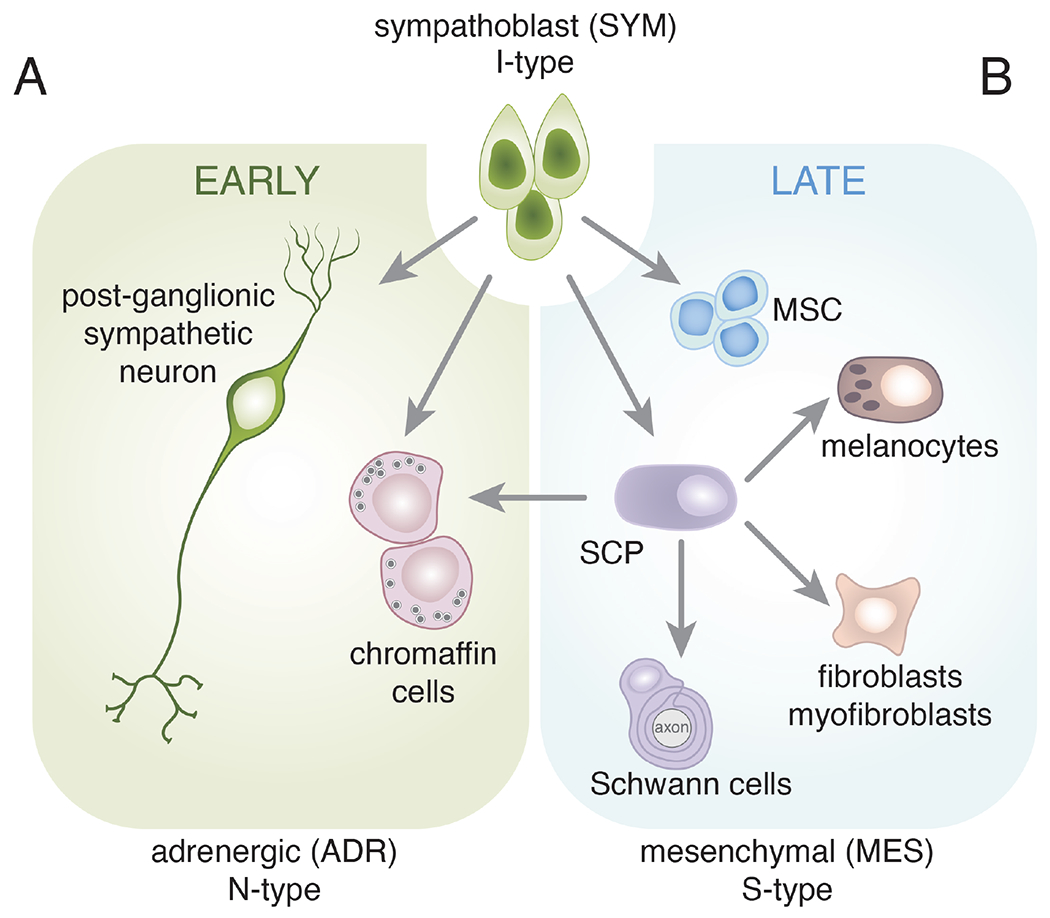
Schematic drawing of major cell fate specification events in the sympathoadrenal lineage and their derivatives. This is not intended to be comprehensive but rather to highlight the multipotency of the sympathoblasts. The neural crest is a transient population and after cells have migrated out of the trunk neural crest along the ventral pathway, a subset of cells commits to become sympathoblasts (I-type). Shortly after the neural crest cells have dispersed and the sympathoblasts have been specified, they form two cell types with neuronal (N-type) features. The post-ganglionic sympathetic neurons may be cholinergic or adrenergic. The chromaffin cells lack traditional dendrites and axons but synthesize catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) and release those neurotransmitters into the circulation from the adrenal medulla. These are some of the first developmental events of the sympathoadrenal lineage and help to establish the patterning of the sympathetic ganglia and developing adrenal gland. B) Later during development, the sympathoblasts produce Schwann cell precursors (SCPs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). The SCPs can produce mature Schwann cells that associate with the axons of the sympathetic neurons. They can also produce mesenchymal cell types such as fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. The MSCs migrate to the bone marrow where they contribute to the hematopoietic stem cell niche. Importantly, SCPs have been shown to be the major source of chromaffin cells in the late stages of adrenal development. This resembles the interconversion of N-type and S-type neuroblastoma cells. Therefore, while individual cell types (e.g., SCPs) are multipotent, the sympathoblasts are the most immature cell population in this lineage and may resemble the I-type neuroblastoma cells. This is not intended to be comprehensive, and each arrow may include several distinct stages of cell fate specification and differentiation. For example, bridge cells are thought to be an intermediate state from SCP to chromaffin cells during the later stages of adrenal medulla development.
