Abstract
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty in maintaining sleep and early morning awakenings. Although pharmacotherapies and psychological interventions remain essential for conventional treatment, motivational factors and interest in using complementary and alternative therapies for insomnia have developed over the last two decades. This review aims to comprehensively explore the effects of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) on improving sleep quality to guide evidence-based clinical decision-making and inform future research. Several electronic databases such as MEDLINE, PubMed, Scopus, EMBASE, Clinical key, Cochrane, and Research gate were explored to search the relevant articles. For the systematic review, CAM studies were classified under "manual practices," "natural practices," and "mind-body practices." A total of 35 clinical trials were selected for inclusion in the systematic review, comprising adult samples. The systematic review revealed 11 RCTs with manual practice, 12 with mind-body practice, and 12 with natural medicine practice. The methodological quality of the RCTs was measured using the modified Jadad scale, a scientific quality index of ≥ 5/10 (on the augmented Jadad scale). Effect sizes (Cohen’s d) were calculated and reported in all placebo-controlled studies with the available data. Regardless of systematic reviews, and randomized controlled trials on CAM, acupuncture, acupressure, herbal medicine, yoga, and tai chi, for insomnia, most of the RCTs did not agree with the findings. Further RCT for insomnia should be developed by considering the current advanced studies in the field of CAM.
Keywords: yoga, valerian, kava, tai-chi, insomnia, acupressure, acupuncture
Introduction and background
Insomnia is identified by difficulty in maintaining sleep and early morning awakenings [1]. Consequently, it further causes workplace absenteeism, accidents, and a decline in productivity which imparts tremendous societal and economic impact [2]. One-third of the general population encounter insomnia symptoms across their lifespan [3]. Insomnia should not be confused with sleep deprivation, the former being the inability to sleep adequately, either in length or quality [4]. Most studies suggested predominance rates of insomnia disorder from 5% to 15% [5-7]. Insomnia could be a persistent issue in 31% to 75% of patients, with more than two-thirds revealing side effects for at least one year [6-8]. Due to the increasing work pressure and social challenges in an advanced society, most of the masses cannot get adequate sleep and suffer from sleep disturbance [9-12]. A detailed study shows that around 30% of adults suffer from sleep disturbance [7]. It mainly affects females and is increasing with advancing age [8]. Insomnia may be acute or chronic, and primary or secondary [1]. Primary insomnia can be defined as an individual experiencing a sleep disorder due to stress or emotions, while secondary insomnia can be due to co-morbid conditions or prior illness [1]. Insomnia has been associated with many comorbidities such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, depression, obesity, and diabetes [2]. It can also lead to alterations in attention with episodic memory, and these cognitive impairments are clinically significant [1,2]. Hence, to maintain an individual's overall health, the treatment of insomnia is necessary [9, 10]. Conventional methods of treating insomnia generally involve either pharmacotherapies or psychological interventions [11]. The use of such kinds of drugs can cause serious adverse effects such as cognitive impairment, oversedation, daytime drowsiness, rebound discontinuation, and psychomotor disturbance [12]. In recent years, benzodiazepines (diazepam and related drugs) or nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics (zolpidem or zopiclone} have been chosen over older barbiturates which can cause death in cases of overdose. In older patients, sedating antipsychotics, e.g., olanzapine or quetiapine, and sedating anti-depressants with older tricyclic drugs, are generally regarded as "off label" [11, 12]. The new treatment guidelines evolved for benzodiazepine include low doses of sedating antipsychotics, antidepressants, and mood stabilizers [11]. Although pharmacotherapies and psychological interventions remain essential for conventional treatment, due to various motivational factors, interest in using alternative therapies and products for insomnia has developed over the last two decades.
One common treatment group used by patients with insomnia is complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) [5-7]. Research on adult insomnia patients has found that 4.5% of them practised CAM to treat their condition [9]. CAM use can be seen extensively among patients with mental disorders, commonly for managing depression or insomnia. CAM generally includes extensive therapies based on different geographical regions from various schools of thought [8]. Common CAM therapies for insomnia include herbal and nutritional medicine, acupuncture, acupressure, yoga, tai chi, and mind-body practices [10]. Mind-body interventions such as yoga help manage stress and anxiety, improving sleep quality [10]. Protein source herbal supplement L-tryptophan is also used for the treatment of insomnia [11]. Acupuncture and acupressure have been found to restore the normal sleep-wake process. They can also be employed to increase the γ-amino butyric acid content, enhancing sleep quality [12, 13]. Considering the growing public interest in CAM, these therapies and products have been researched over the past two decades to treat sleep disorders. Although few systematic reviews have been conducted on the use of acupuncture and valerian in treating insomnia, but comprehensive study on all primary CAM treatments has not been conducted. The present systematic review comprehensively explored the effects of CAM on improving sleep quality to guide evidence-based clinical decision-making and inform future research. We have systematically searched and evaluated the evidence for the impact of CAM on insomnia.
Review
Methods
Data Sources
Several electronic databases such as MEDLINE, PubMed, Scopus, EMBASE, Clinical key, Cochrane, and Research gate were explored to search the relevant articles. The references to the articles were also examined. The search strategy was only restricted to research studies in English.
The PubMed search strategy was : (((((((((((INSOMNIA) OR (insomnia[MeSH Terms])) AND (complementary medicine[MeSH Terms])) OR (alternative medicine[MeSH Terms]))) OR (complementary and alternative medicine[MeSH Terms]))) OR Natural practices OR Manual practices OR Mind-body intervention practices OR Acupuncture OR Acupressure OR Yoga OR Tai Chi AND (The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index[MeSH Terms])) OR (PSQI[MeSH Terms])) OR (sleep quality[MeSH Terms])) OR (sleep latency[MeSH Terms])) OR (adjustment sleep disorder[MeSH Terms]) (((("insomnia s"[All Fields] OR "sleep initiation and maintenance disorders"[MeSH Terms] OR ("sleep"[All Fields] AND "initiation"[All Fields] AND "maintenance"[All Fields] AND "disorders"[All Fields]) OR "sleep initiation and maintenance disorders"[All Fields] OR "insomnia"[All Fields] OR "insomnias"[All Fields] OR "sleep initiation and maintenance disorders"[MeSH Terms]) AND "complementary therapies"[MeSH Terms]) OR "complementary therapies"[MeSH Terms] OR (("complementaries"[All Fields] OR "complementary"[All Fields]) AND "complementary therapies"[MeSH Terms])) AND (("Pittsburgh"[All Fields] AND ("sleep quality"[MeSH Terms] OR ("sleep"[All Fields] AND "quality"[All Fields]) OR "sleep quality"[All Fields])) AND OR "sleep quality"[MeSH Terms] OR "sleep latency"[MeSH Terms] OR "dyssomnias"[MeSH Terms]
Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility criteria have been described with the PICO framework. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for participants, intervention, comparison, and outcomes have been mentioned separately in other sections of the article.
Study Design
Randomized controlled trials reporting outcomes of the effects of CAM on insomnia and sleep quality were identified and included. Observational studies, case reports, case series, case presentations, and case-control studies were not included.
Study Participants
Regardless of health issues, adults (18 years or older) were included in the study, except for those working shifts and time zone travellers.
Interventions
For the systematic review, we have included CAM studies, classified under "manual practices," "natural practices," and "mind-body practices." All psychological and psycho-educational interventions were excluded from the review, e.g., cognitive behavioural therapy, relaxation therapy, or mindfulness (regarded as mainstream therapies). Bright-light treatment, exercise, music therapy, sensory art therapies, and aromatherapy were excluded from the study (as these therapies were not considered classical CAM interventions). Melatonin, too, was excluded from the review as the substance is a hormone, not an exogenous natural medicine. A total of eight CAM intervention RCTs met the inclusion criteria.
Comparison
For comparison, we have compared the intervention with a non-active placebo or control.
Outcome Measures
Subjective and objective sleep outcomes were evaluated, including, but not limited to, sleep quality, duration, and latency. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) and Insomnia severity index (ISI) were used as the outcome measure in most of the studies. Duration of intervention should be ≥ 1 week.
Study Eligibility
The authors KV and AS independently screened all titles and abstracts per the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Only full-text articles that were published in English are included. Any discrepancy was resolved with discussion among other authors. The searched files were imported to the Zotero library after removing duplicate items and were freely available, and Rayyan (https:// rayyan.qcri.org), a free web-based software, was used to review articles. From the selected eligible articles, required data, including administration of intervention and control, author, year of publication, study design, follow-up, sample size, outcome measures, results, effect size and quality rating, and primary outcomes, were extracted from eligible studies.
Data Extraction
KV and AS prepared a narrative synthesis for relevant research articles, including their outcomes, variations on intervention, types, and outcomes measurement. The methodological quality assessment of the RCTs was performed using the modified Jadad scale, a scientific quality index of ≥ 5/10 (on the augmented Jadad scale) [14].
Results
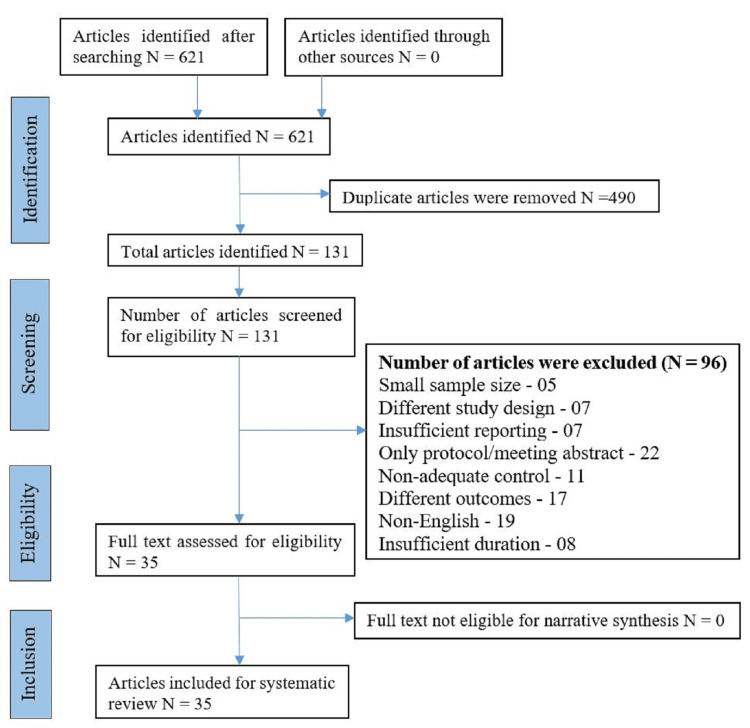
KV and DS systematically searched the articles through different search engines, but as per inclusion and exclusion criteria mentioned previously, we have reviewed the articles through Rayyan (https:// rayyan.qcri.org), free web-based software to be more precise for the inclusion and exclusion criteria. As mentioned in the flow chart, among 621 identified potential studies in the field of CAM and insomnia. A total of 96 studies were removed, due to small sample size (5), different study design (7), insufficient reporting (7), only protocol/meeting abstract available (22), non-adequate control (11), different outcomes (17), non-English (19), short duration (8). This left 35 clinical trials for inclusion, primarily comprising adult samples (except for the tai chi and yoga studies, which used an older population). These CAM studies were grouped under "manual practices," "mind-body," and "natural practices." Eight CAM interventions had RCTs that met the inclusion criteria. DS and KV calculated and reported effect sizes (Cohen’s d) in all placebo-controlled studies with the available data (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Flow Diagram (PRISMA).
Manual Practices
The systematic review revealed 11 RCTs with manual practice intervention [15-25]. These studies involved acupuncture (inserting fine needles to stimulate "acupoints") and acupressure (using digital or blunt pressure on "acupoints"). The trials were between two and 12 weeks, with an average sample size of 70 participants. Seven of the 11 studies measured the outcomes in the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI). The insomnia severity index (ISI) was adequate for the outcome measure in three of the 11 studies. The average quality score was 6.8 out of 10 [15-18]. Out of the four acupressure studies, they all revealed positive results on the PSQI scale with large effect sizes ranging from 1.42 to 2.12 when measured on various PSQI subscales [15-18].
Among these four acupuncture studies, one was negative, equivalent to either placebo acupuncture or basic sleep hygiene. At the same time, one was positive, equal to the positive control (clonazepam), or more effective than placebo acupuncture or positive control (estazolam). Yin et al. stated a large effect size d = 1.14 on sleep quality outcomes [19-25] (Table 1).
Table 1. Manual practices in the treatment of insomnia.
>Statistically significant effect over control (p < 0.05).
N/A, effect size could not be calculated with the data available.
N/S, statistically not significant.
ISI: Insomnia severity index; LSEQ: Leeds Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire; PSQI: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index
a First author; b Intervention dosage is the total dose per day; c Effect size based on modified Cohen’s d; d A quality rating based on the modified Jadad scale; e sleep latency; f sleep duration; g sleep quality; h severity
| Intervention | author a | Study design b | Outcome measures (Insomnia) | Result | Effect size c | Qualitygrading d |
| Acupressure | Yeung (2018)[15] | Two-arm RCT, n = 31, eight weeks | ISI | Self-administered acupressure group had a significantly lower ISI score than the subjects in the sleep hygiene education group | 0.56 | 7/10 |
| Acupressure | Zheng (2014)[16] | Two-arm RCT, n = 75, four weeks | PSQI | Acupressure improves sleep quality more than control | 0.64 | 7/10 |
| Acupressure | Nordio (2008) [17] | Three-arm RCT, n = 44, three weeks | PSQI | Acupressure is more effective than sham acupressure after three weeks on PSQI total score | 1.91h | 9/10 |
| Acupressure | Chen(1999) [18] | Three-arm RCT, n = 84, four weeks acupressure vs. sham acupressure vs. Control (not identified) | PSQI | Acupressure is more effective than sham acupressure and controls on PSQI total score, latency, and duration sub-scores | 2.12e 1.66f 1.52g 1.42h | 8/10 |
| Acupuncture | Bosch (2013) [19] | Five-arm RCT, n=40, three months | PSQI | Acupuncture is more effective than control to improve sleep in both schizophrenia and depression patients | 1.09 | 7/10 |
| Acupuncture | Wang (2020)[20] | Three-arm RCT, n=129, five weeks single acupuncture vs. multi acupuncture vs. sham control | PSQI and Athens Insomnia Scale questionnaire | PSQI scores were significantly decreased in single and multi- acupuncture groups compared to the controlled group. | 0.88 | 6/10 |
| Acupuncture | Wang (2021) [21] | Two-arm RCT, n=82, three weeks | PSQI and ISI | PSQI scores and ISI scores were decreased in the acupuncture group than in the sham-controlled group. | 0.02 | 8/10 |
| Acupuncture | Yin (2017) [22] | Two-arm RCT, n=72, four weeks, | ISI | Acupuncture treatment is more effective than sham acupuncture treatment in increasing sleep quality in insomnia patients | 1.14 | 6/10 |
| Acupuncture | Xuan (2007) [23] | Two-arm RCT, n=46, acupuncture vs. oral administration of estazolam in control group | PSQI | Estazolam was better than acupuncture treatment in prolonging sleeping time. Acupuncture treatment was better than the control group in the improvement of somnipathy and the increase of daytime functional state | N/A | 8/10 |
| Acupuncture | Wang (2008) [24] | Three-arm RCT, n = 44, two-week abdominal acupuncture, seven treatments + placebo pill vs estazolam + sham acupuncture estazolam group) | LSEQ | Acupuncture is more effective than estazolam and sham acupuncture on LSEQ total score | N/A | 7/10 |
| Acupuncture | Da Silva (2005) [25] | Two-arm RCT, n = 30, eight weeks (pregnant women) acupuncture 8-12 treatments vs. sleep hygiene advice | Purpose-designed self-report sleep questionnaire | Acupuncture and sleep hygiene advice affects sleep quality equally after eight weeks. Only effective at follow-up two weeks after stopping acupuncture (10 weeks) | N/A | 7/10 |
Mind-Body Practices
There were 12 mind-body intervention RCTs of sufficient methodological rigour in this review [26-37]. The trial length was between four and 24 weeks, with an average sample size of 90 participants. Five out of the seven studies used PSQI as the outcome measure. The average rating of the quality of the studies was eight out of 10. The yoga intervention studies revealed a positive effect on wait-list control. Manjunath et al. and Mustian et al. studies found large effect sizes (d = 1.52) and d = 2.56 on sleep quality outcome measures [31, 32]. One study (Ward et al.) found no significant difference between yoga and control groups [30].
All five tai chi trials were positive on various PSQI outcome measures compared with health education or low-impact exercise [33-37]. Large effect sizes prevailed in sleep duration d = 2.15 and sleep quality d = 1.05 in Li et al. [35]. At the same time, a marked divergence was observed in Irwin et al. with a large effect size on sleep severity (global score) d = 1.57 compared to small effect sizes on sleep duration d = 0.22, and sleep quality d = 0.44 [37] (Table 2).
Table 2. Mind-body intervention practices in the treatment of insomnia.
>Statistically significant effect over control (p < 0.05).
N/A, effect size could not be calculated with the data available.
N/S, statistically not significant.
CASIS: Asthma and COPD Sleep Impact Scale; PSQI: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; ISI: Insomnia severity index
a First author; b Intervention dosage is the total dose per day; c Effect size based on modified Cohen’s d; d A quality rating based on the modified Jadad scale; e sleep latency; f sleep duration, g sleep quality, h severity
| Interventions | Author a | Study design b | Outcome measures (insomnia) | Result | Effect size c | Qualitygrading d |
| Yoga | Özer (2021) [26] | Two-arm RCT, n = 60, eight weeks Yoga vs. Control | CASIS | Yoga improves sleep in comparison to control | N/A | 7/10 |
| Yoga | Susanti (2022) [27] | Two-arm RCT, n = 104, 20 weeks; yoga vs. control | PSQI | Yoga improved sleep quality significantly in postmenopausal and perimenopausal women in comparison to the control | N/A | 6/10 |
| Yoga | Ghaffarilaleh (2019) [28] | Two-arm RCT, n = 62, 10 weeks; yoga vs. control | PSQI | Yoga helps in improving the quality of sleep, sleep latency and sleep efficiency in patients with premenstrual syndrome in comparison to the control | 0.26 | 6/10 |
| Yoga | Guerra (2020) [29] | Two-arm RCT, N= 64, eight weeks; yoga vs. Control | PSQI | Significant correlation between sleep and yoga; sleep latency was lower in the yoga group | NA | 7/10 |
| Yoga | Ward (2017) [30] | Two-arm RCT, n=26, nine weeks; yoga vs. control | Visual analogue scale, sleep quality, measured using the seven‐item ISI, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index | No significant difference between both groups | 0.06 | 7/10 |
| Yoga | Manjunath (2005) [31] | Three-arm RCT, n =70, six-month (older population) yoga vs. herbal medicine vs. waitlist control | Sleep questionnaire (purpose-designed): Determining latency, waitlist, and herbal medicine formula on sleep quality, total sleep, subsequent day effects, and total latency | Yoga during the six-month evaluation was superior to the waitlist and herbal medicine formulas on sleep latency, full sleep, and “feeling of being rested.” | 1.20e, 1.02 | 8/10 |
| Yoga | Mustian (2013) [32] | Two-arm RCT, n=410, four weeks; yoga vs. control | PSQI | Yoga intervention consists of pranayama (breathing exercises), gentle Hatha and restorative yoga asanas, and meditation > control | 2.56 | 8/10 |
| Tai chi | Siu (2021) [33] | Three-arm RCT, n = 320, 12 weeks; tai chi training vs. exercise vs. control groups | PSQI and ISI | Tai chi training groups significantly reduced the PSQI scores in older adults compared to exercise and control group | 0.65, 0.55 | 6/10 |
| Tai chi | Nguyen (2012) [34] | Three-arm RCT, n = 102, six months; tai chi vs. control | PSQI | Tai chi is effective in improving sleep quality in community-dwelling elderly compared to control | 0.26 | 6/10 |
| Tai chi | Li (2004) [35] | Two-arm RCT, 24-week, n = 118 (older adults); tai chi vs. low-impact exercise | PSQI | Tai chi was more effective than low-impact exercise in increasing sleep duration and improving reported sleep quality, sleep latency, and sleep efficiency | 2.15b, 1.05c | 8/10 |
| Tai chi | McQuade (2017) [36] | Three-arm RCT, n=90, one and three months tai chi vs. light exercise vs. waitlist control | PSQI | Tai chi, light exercise and waitlist control were equally effective in reducing sleep disturbance for those undergoing radiotherapy for prostate cancer | 1.63, 1.23 | 6/10 |
| Tai chi | Irwin(2008) [37] | 25-weeks RCT, n = 112 (older adults) tai chi vs. control | PSQI: sleep quality (primary outcome) | Tai chi had a significant effect on sleep quality, severity, and duration outcomes compared to control | 0.22f , 0.44g, 1.57h | 8/10 |
Natural medicine practices
The review identified 12 RCTs of sufficient methodological rigour [38-48]. Three studies included kava and valerian interventions. Six studies included valerian intervention [38-40]. Three studies included tryptophan intervention [13,47,48]. The trials were from two to eight weeks (commonly two to four weeks) with an average sample size of 150 participants. The herbal medicine kava met the inclusion criteria compared to the placebo. The analysis of Lehrl et al.'s study showed a benefit for kava over placebo on the quality of sleep outcome [40]. The valerian studies exhibited diversified results, with three positive (more effective than placebo and equivalent to oxazepam) and three negative results (equal to placebo) [41-46]. For most of the studies, effect size calculations could not be available. For L-tryptophan trials, the average quality rating was seven out of 10, while herbal medicines studies showed a higher rating of 8 out of 10. Among the three L-tryptophan studies, two were positive on several outcomes. Hudson et al., in their analysis, mentioned a large effect size on increased sleep duration d = 1.16, and a small effect size on sleep quality d = 0.28 [13] (Table 3).
Table 3. Natural medicine practices in the treatment of insomnia.
>Statistically significant effect over control (p < 0.05).
N/A, effect size could not be calculated with the data available.
N/S, statistically not significant.
PSQI: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; ISI: insomnia severity index; VAS: visual analogue scales
a First author; b Intervention dosage is the total dose per day; c Effect size based on modified Cohen’s d; d A quality rating based on the modified Jadad scale; e sleep latency; f sleep duration; g sleep quality; h severity
| Interventions | Author a | Study design b | Outcome measures (insomnia) | Result | Effect size c | Qualitygrading d |
| Kava and Valerian | Wheatley (2001) [38] | RCT, n=24, crossover trial, six weeks | VAS, Wheatley Stress Profile; time to fall asleep, hours slept, and mood on final waking. | Kava, valerian and placebo groups had no significant difference | N/A | 7/10 |
| Kava and Valerian | Jacobs(2005) [39] | Three-arm RCT, n = 391, four weeks | Insomnia Severity Index (ISI): overall score, sleep latency, outcome measures number of awakenings | Neither kava nor valerian relieved anxiety or insomnia more than the placebo | 0.02e | 9/10 |
| Kava and Valerian | Lehrl (2004) [40] | Three-arm RCT, n = 61, four weeks | Görtelmeyer Sleep Questionnaire, quality of sleep SCALE | Kava is more effective than placebo in improving the quality of sleep at the week four endpoint | N/A | 8/10 |
| Valerian | Zare (2021) [41] | Two-arm RCT, n=72, four weeks | PSQI, the prothrombin time (PT), and partial thromboplastin time (PTT) | No significant difference between both groups | N/A | 8/10 |
| Valerian | Oxman (2007) [42] | Two-arm RCT, n = 405, two weeks | Internet sleep diary: sleep onset latency, quality awakenings, assessment; sleep diary quality | Valerian is more effective than placebo on sleep quality | N/A | 9/10 |
| Valerian | Coxeter (2003) [43] | Two-arm RCT, n = 42, six weeks | Sleep diary: sleep latency, self-rated outcomes were ‘poor’ or modest | Valerian had no significant difference from placebo | N/A | 9/10 |
| Valerian | Ziegler (2002) [44] | Two-arm RCT, n = 202, six weeks | Görtelmeyer Sleep outcome; sleep quality, and on all other subscale outcomes | Valerian is more effective than control | N/A | 8/10 |
| Valerian | Koetter (2007) [45] | Two-arm RCT, n = 30, four weeks; valerian-valerian vs. placebo | Sleep monitoring device: sleep awakenings, efficiency; REM sleep stages; Clinical Global Assessment | Sleep latency with valerian-hops and placebo groups had no difference | N/A | 6/10 |
| Valerian | Morin (2005) [46] | Three-arm RCT, n = 184, four weeks | Sleep diary: subjective sleep efficacy, total sleep time, Insomnia Severity Index | Valerian-hops reduced insomnia | 0.81h | 8/10 |
| Tryptophan | Hudson (2005) [13] | Three-arm RCT, n = 57, three weeks 250 mg tryptophan food vs. 250 mg pharmaceutical tryptophan vs. placebo | Sleep diary: sleep efficiency, quality, total, awakening time | Tryptophan food and pharmaceutical tryptophan were more effective than placebo on all outcomes | 1.16 f, 0.28g | 8/10 |
| Tryptophan | Demisch (1987) [47] | RCT crossover, n = 39, eight weeks 2 g tryptophan vs. 0.04 g tryptophan scale) placebo | Sleep quality scale (1-5 Likert scale) | 2 g tryptophan was more effective than 0.04 g tryptophan across groups in phase 1 and within subjects in Group A | N/A | 6/10 |
| Tryptophan | Hartmann (1983) [48] | Four-arm RCT, n = 96, two weeks | Various outcome scales | Sleep latency had a significant difference after treatment with tryptophan | N/A | 6/10 |
A review of all quality studies suggested that CAM may have the potential to improve sleep quality in a variety of patient populations. Although evidence is limited, this systematic review, which includes studies published till Jan. 2022, provides evidence that CAM may be useful for the treatment of both uncomplicated insomnias as well as insomnia co-morbid conditions.
Despite the substantial clinical trial literature, several studies were excluded due to methodological shortcomings. Only 35 English language RCTs met the inclusion criteria. In various RCTs of herbal medicine, mostly involving valerian, researchers employed a short study duration and small sample size, restricting the study's statistical power. Moreover, several acupuncture studies had an 'active' control group, mostly involving another type of acupuncture.
Many studies could not calculate the effect size due to negative results or insufficient data (e.g., no standard deviation). As a result, the effect sizes noted in the positive studies (in natural medicine and manual practices) should be tempered concerning the negative studies. Quality grading of RCTs has been displayed in respective tables of manual, mind body and natural medicine practice. The majority of RCTs for manual practice scored 7/10 for quality of grading. Most RCTs for mind-body practices scored 6/10 while assessing quality grading. Mostly, RCTs with natural medicine practice scored 8/10 score for quality grading.
Discussion
Findings revealed that the evidence for natural medicine practices in treating insomnia was also conflicting. Valerian was one of the most studied soporific natural medicines for its rich folkloric tradition of use in conditions of restlessness, hysteria, headache, nervousness, and mental depression. As detailed in Table 3, the evidence regarding valerian was quite mixed and did not support its use in treating insomnia. These results follow the systematic reviews and meta-analyses done by Bent et al. and Taibi et al. [49, 50]. The study of Bent et al., which included 16 eligible RCTs on valerian and valerian in combination with other herbal medicines, suggests that nine out of 16 studies did not have positive outcomes concerning the improvement of sleep quality [49]. The Taibi et al. review, which included 29 controlled studies, consistently stated that most studies lacked any significant difference between valerian and placebo. Valerian, combined with hops or kava, did not seem to support the available data. Kava may provide a prospective alternative for managing insomnia [50]. However, Lehrl's studies had a different opinion, and presently as kava is withdrawn in several jurisdictions, further studies about its safety and efficacy are much needed [40].
L-tryptophan, an exogenous amino acid converted into serotonin, has been widely studied in treating insomnia and depression [51]. However, the results were encouraging but varied concerning different sleep outcomes. The studies on various animals and humans consistently suggest that L-tryptophan increases sleepiness and decreases sleep latency [51, 52]. It has been observed that the best results seem to occur in cases of mild insomnia with long sleep latency and the absence of any medical or psychiatric comorbidity [51, 52]. A study by Hudson et al. determined a large effect size on increased sleep duration and a negligible effect on sleep quality [13]. A survey by Irwin et al. consistently revealed a substantial effect size for tai chi in reducing insomnia severity. In contrast, sleep duration and quality effects had poor clinical outcomes [37]. The heterogeneous nature of samples throughout the studies made these effect size differences [37].
Acupuncture and acupressure seem to contribute to treating insomnia, probably by the neurochemical modulatory activity of serotonin, dopamine, and endogenous opioids [53]. The review by Cheuk et al. concluded with seven rigorous methodological trials that acupuncture and acupressure help improve sleep quality scores. Still, the evidence for acupuncture as a hypnotic intervention was inconsistent. Compared to control or no treatment, the efficacy of acupuncture and its variants was inconsistent among studies, including many sleep parameters, such as sleep onset latency, time to wake after sleep onset, and total sleep duration [53]. Further, Yeung et al. revealed that definitive conclusions could not be derived on acupuncture's efficacy for insomnia. This conclusion was reached due to the methodological quality of RCTs as the limitations of the study designs hampered studies. For instance, publications of such studies have also provided limited information about inclusion/exclusion criteria, outcomes measured, missing baseline data, randomization methods, and the specific acupuncture approach [54].
Mind-body practices such as yoga and tai chi in insomnia and different sleep disorders are enhancing popularity, particularly in the ageing population who might prefer low-effect exercises [35]. Comparatively, findings supported the benefits of exercise in improving sleep quality and reducing the severity of insomnia in older people. However, a Li et al. study compared tai chi to low-effect exercise and found it superior to low-effect exercises in all outcomes [35]. While Manjunath et al., the yoga study included older participants with sleep issues and noted yoga was superior to both wait-list and herbal medicine on sleep latency and total sleep [31]. Mind-body practices comprise multicomponent interventions, considered to give rise to similar physiological processes to traditional relaxation methods, which have been investigated as treatment options for insomnia [26-37]. Mechanistically, yoga acutely affects the activity of the autonomic nervous system and may decrease the gamma-aminobutyric acid levels and inflammatory markers. Probably by neurobiological pathways, yoga may improve sleep quality [28, 29]. Data from small RCTs suggested that yoga improves subjective and objective sleep quality, reducing insomnia symptoms in adults with chronic medical conditions [26, 28, 29, 31]. One of the largest RCTs of Yoga illustrated reduced hypnotic medication use in cancer survivors with sleep disturbance by 21% in the yoga group compared with 5% in the control group [32]. However, several emerging clinical trials on yoga found that most participants faced a general sleep disturbance. Moreover, yoga studies including pranayama, breathing exercises, gentle hatha, restorative yoga asanas, and meditation assessing sleep outcomes showed common methodological limitations of sample sizes and limited use of objective outcome measures [27-32]. Further studies on yoga are encouraged with participants with a confirmed diagnosis of insomnia using validated sleep assessment scales.
Similarly, in studies for tai chi intervention, the focus was more on sleep quality rather than insomnia. Several RCTs suggested improvement in reported sleep quality, with tai chi intervention, particularly among older adults. Therefore, tai chi may improve sleep quality in different populations, specifically older adults [33-37]. Its impact on objective measures in chronic insomnia needs further explained.
In reference to data from the United States National Health Interview Survey, 17.4% of adults (n= 93 386) reported insomnia or regular sleep disturbance, and 4.5% used CAM therapies to improve their sleep quality. 56% of the individuals said that CAM was essential to maintaining their overall health and well-being, while 72% observed that CAM improved insomnia disorders significantly. Younger and highly qualified persons believe in CAM to improve insomnia symptoms [55]. It has been noticed that traditional Indo-Asian therapies such as acupuncture, acupressure, and yoga were more widely studied compared to standard Western CAM therapies. The broadly researched herbal medicine is valerian in the form of monotherapy or combination with hops or kava [13, 15-48]. Future research in other herbal medications or Western CAM therapies with potential hypnotic effects is recommended as current research in these areas is insufficient.
Strength and limitations
The strengths of this systematic review included the search and synthesis of all relevant studies across several databases, the rigorous methodological inclusion criteria, and a quality assessment of all clinical trials with calculations of the effect size of studies.
This review also had some limitations. These were language constraints, as we excluded non-English publications; several valerian studies were published in German, and acupuncture studies were published in Chinese. Secondly, it lacks appropriate clinical trials with methodological weakness, for instance, adequate sample sizes. While reporting complete data, the long-term efficacy and safety of CAM interventions should have been employed.
Conclusions
This systematic review revealed that CAM interventions might benefit various populations with insomnia and a range of sleep measures. However, clinically relevant conclusions cannot be drawn because of clinical heterogeneity and methodological limitations. Regarding CAM treatments for insomnia, it demonstrates evidence in support of acupressure, yoga, and tai chi; mixed evidence for the use of acupuncture and L-tryptophan; and insufficient evidence for the practice of natural medicines such as valerian. More RCTs with rigorous research design covering a more comprehensive range of CAM interventions with particular consideration for long-term safety and potential side effects are needed to establish the impact of CAM on insomnia, as well as the potential of CAM to be used in interventions for populations with various health conditions or specific demographic groups. Clinical trials exploring the use of CAM adjuvantly with conventional therapies like exercise, psychological interventions, or pharmacotherapies may also promise to improve sleep outcomes and provide clinically relevant evidence. Ultimately, the biological mechanism by which CAM improves sleep quality, and insomnia disorder should be studied to understand the techniques such as yoga and tai chi work on insomnia, in the presence of various health conditions.
Appendices
PubMed Search strategy
The PubMed search strategy was : (((((((((((INSOMNIA) OR (insomnia[MeSH Terms])) AND (complementary medicine[MeSH Terms])) OR (alternative medicine[MeSH Terms]))) OR (complementary and alternative medicine[MeSH Terms]))) OR Natural practices OR Manual practices OR Mind-body intervention practices OR Acupuncture OR Acupressure OR Yoga OR Tai Chi AND (The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index[MeSH Terms])) OR (PSQI[MeSH Terms])) OR (sleep quality[MeSH Terms])) OR (sleep latency[MeSH Terms])) OR (adjustment sleep disorder[MeSH Terms]) (((("insomnia s"[All Fields] OR "sleep initiation and maintenance disorders"[MeSH Terms] OR ("sleep"[All Fields] AND "initiation"[All Fields] AND "maintenance"[All Fields] AND "disorders"[All Fields]) OR "sleep initiation and maintenance disorders"[All Fields] OR "insomnia"[All Fields] OR "insomnias"[All Fields] OR "sleep initiation and maintenance disorders"[MeSH Terms]) AND "complementary therapies"[MeSH Terms]) OR "complementary therapies"[MeSH Terms] OR (("complementaries"[All Fields] OR "complementary"[All Fields]) AND "complementary therapies"[MeSH Terms])) AND (("Pittsburgh"[All Fields] AND ("sleep quality"[MeSH Terms] OR ("sleep"[All Fields] AND "quality"[All Fields]) OR "sleep quality"[All Fields])) AND OR "sleep quality"[MeSH Terms] OR "sleep latency"[MeSH Terms] OR "dyssomnias"[MeSH Terms]
Cochrane search strategy
#1 insomnia: 12861
#2 MeSH descriptor: [Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders] explode all trees: 2818
#3 complementary and alternative medicine: 5768
#4 complementary and alternative therapy: 4452
#5 complementary therapy: 9327
#6 alternative therapy: 32303
#7 MeSH descriptor: [Complementary Therapies] explode all trees: 22054
#8 MeSH descriptor: [Complementary Therapies] explode all trees: 22054
#9 alternative medicine: 18452
#10 complementary medicine: 9033
#11 Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: 3640
#12 PSQI: 2516
#13 MeSH descriptor: [Sleep Quality] explode all trees: 80
#14 sleep duration: 8051
#15 sleep latency: 3033
#16 MeSH descriptor: [Sleep Latency] explode all trees 20
#17 #1 OR #2 AND #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 AND #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16: 77959
#18 #1 OR #2 AND #5 OR #6 AND #11: 12969
The content published in Cureus is the result of clinical experience and/or research by independent individuals or organizations. Cureus is not responsible for the scientific accuracy or reliability of data or conclusions published herein. All content published within Cureus is intended only for educational, research and reference purposes. Additionally, articles published within Cureus should not be deemed a suitable substitute for the advice of a qualified health care professional. Do not disregard or avoid professional medical advice due to content published within Cureus.
Footnotes
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
- 1.A systematic review of insomnia and complementary medicine. Sarris J, Byrne GJ. Sleep Med Rev. 2011;15:99–106. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2010.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sleep patterns and insomnia among adolescents: a population-based study. Hysing M, Pallesen S, Stormark KM, Lundervold AJ, Sivertsen B. J Sleep Res. 2013;22:549–556. doi: 10.1111/jsr.12055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nighttime insomnia symptoms and perceived health in the America Insomnia Survey (AIS) Walsh JK, Coulouvrat C, Hajak G, et al. https://doi.org/10.5665/SLEEP.1150. Sleep. 2011;34:997–1011. doi: 10.5665/SLEEP.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Epidemiology of insomnia: prevalence, course, risk factors, and public health burden. Morin CM, Jarrin DC. Sleep Med Clin. 2022;17:173–191. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2022.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Epidemiological and clinical relevance of insomnia diagnosis algorithms according to the DSM-IV and the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD) Ohayon MM, Reynolds CF 3rd. Sleep Med. 2009;10:952–960. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2009.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chronic insomnia. Morin CM, Benca R. Lancet. 2012;379:1129–1141. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60750-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Professional correlates of insomnia. Léger D, Massuel MA, Metlaine A. Sleep. 2006;29:171–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sleep health: can we define it? Does it matter? Buysse DJ. Sleep. 2014;37:9–17. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Classification and epidemiology of childhood sleep disorders. Owens J. Prim Care. 2008;35:533-46, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2008.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.The effect of meditative movement on sleep quality: A systematic review. Wang F, Eun-Kyoung Lee O, Feng F, et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2015.12.001. Sleep Med Rev. 2016;30:43–52. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2015.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pharmacotherapy for insomnia. Tariq SH, Pulisetty S. Clin Geriatr Med. 2008;24:93-105, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2007.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pharmacologic treatment of disturbed sleep in the elderly. Salzman C. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2008;16:271–278. doi: 10.1080/10673220802432442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Protein source tryptophan versus pharmaceutical grade tryptophan as an efficacious treatment for chronic insomnia. Hudson C, Hudson SP, Hecht T, MacKenzie J. Nutr Neurosci. 2005;8:121–127. doi: 10.1080/10284150500069561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ. Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(95)00134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Self-administered acupressure for insomnia disorder: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Yeung WF, Ho FY, Chung KF, et al. J Sleep Res. 2018;27:220–231. doi: 10.1111/jsr.12597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Effect of acupressure on sleep quality of middle-aged and elderly patients with hypertension. Zheng LW, Chen Y, Chen F, Zhang P, Wu LF. Int J Nurs Sci. 20141;1:334–338. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Efficacy of wrists overnight compression (HT 7 point) on insomniacs: possible role of melatonin? Nordio M, Romanelli F. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19034253/ Minerva Med. 2008;99:539–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.The effectiveness of acupressure in improving the quality of sleep of institutionalized residents. Chen ML, Lin LC, Wu SC, Lin JG. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999;54:0–94. doi: 10.1093/gerona/54.8.m389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sleep ameliorating effects of acupuncture in a psychiatric population. Bosch P, van Luijtelaar G, van den Noort M, Lim S, Egger J, Coenen A. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:969032. doi: 10.1155/2013/969032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Effectiveness and cerebral responses of multi-points acupuncture for primary insomnia: a preliminary randomized clinical trial and fMRI study. Wang YK, Li T, Ha LJ, et al. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020;20:254. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02969-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Impact of acupuncture on sleep and comorbid symptoms for chronic insomnia: a randomized clinical trial. Wang C, Xu WL, Li GW, et al. Nat Sci Sleep. 2021;13:1807–1822. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S326762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Efficacy and safety of acupuncture treatment on primary insomnia: a randomized controlled trial. Yin X, Gou M, Xu J, et al. Sleep Med. 2017;37:193–200. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2017.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Randomized and controlled study on effect of acupuncture on sleep quality in the patient of primary insomnia [article in Chinese] Xuan YB, Guo J, Wang LP, Wu X. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18271228/ Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2007;27:886–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Abdominal acupuncture for insomnia in women: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Wang XY, Yuan SH, Yang HY, Sun YM, Cheng FP, Zhang CL, Huang XC. Acupunct Electrother Res. 2008;33:33–41. doi: 10.3727/036012908803861203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Acupuncture for insomnia in pregnancy--a prospective, quasi-randomised, controlled study. da Silva JB, Nakamura MU, Cordeiro JA, Kulay LJ. Acupunct Med. 2005;23:47–51. doi: 10.1136/aim.23.2.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.The effects of yoga on dyspnea, sleep and fatigue in chronic respiratory diseases. Özer Z, Bahçecioğlu Turan G, Aksoy M. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2021;43:101306. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2021.101306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Effects of yoga on menopausal symptoms and sleep quality across menopause statuses: A randomized controlled trial. Susanti HD, Sonko I, Chang PC, Chuang YH, Chung MH. Nurs Health Sci. 2022;24:368–379. doi: 10.1111/nhs.12931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Effects of yoga on quality of sleep of women with premenstrual syndrome. Ghaffarilaleh G, Ghaffarilaleh V, Sanamno Z, Kamalifard M, Alibaf L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31221931/ Altern Ther Health Med. 2019;25:40–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yogic meditation improves objective and subjective sleep quality of healthcare professionals. Guerra PC, Santaella DF, D'Almeida V, Santos-Silva R, Tufik S, Len CA. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020;40:101204. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yoga for the management of pain and sleep in rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Ward L, Stebbings S, Athens J, Cherkin D, David Baxter G. Musculoskeletal Care. 2018;16:39–47. doi: 10.1002/msc.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Influence of Yoga and Ayurveda on self-rated sleep in a geriatric population. Manjunath NK, Telles S. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15937373/ Indian J Med Res. 2005;121:683–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Multicenter, randomized controlled trial of yoga for sleep quality among cancer survivors. Mustian KM, Sprod LK, Janelsins M, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3233–3241. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.43.7707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Effects of tai chi or exercise on sleep in older adults with insomnia: a randomized clinical trial. Siu PM, Yu AP, Tam BT, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:0. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.A randomized controlled trial of Tai chi for balance, sleep quality and cognitive performance in elderly Vietnamese. Nguyen MH, Kruse A. Clin Interv Aging. 2012;7:185–190. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S32600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tai chi and self-rated quality of sleep and daytime sleepiness in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Li F, Fisher KJ, Harmer P, Irbe D, Tearse RG, Weimer C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:892–900. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Qigong/tai chi for sleep and fatigue in prostate cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy: a randomized controlled trial. McQuade JL, Prinsloo S, Chang DZ, et al. Psychooncology. 2017;26:1936–1943. doi: 10.1002/pon.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Improving sleep quality in older adults with moderate sleep complaints: A randomized controlled trial of Tai Chi Chih. Irwin MR, Olmstead R, Motivala SJ. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18652095/ Sleep. 2008;31:1001–1008. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kava and valerian in the treatment of stress-induced insomnia. Wheatley D. Phytother Res. 2001;15:549–551. doi: 10.1002/ptr.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.An internet-based randomized, placebo-controlled trial of kava and valerian for anxiety and insomnia. Jacobs BP, Bent S, Tice JA, Blackwell T, Cummings SR. Medicine (Baltimore) 2005;84:197–207. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000172299.72364.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Clinical efficacy of kava extract WS 1490 in sleep disturbances associated with anxiety disorders. Results of a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Lehrl S. J Affect Disord. 2004;78:101–110. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0327(02)00238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Efficacy of valerian extract on sleep quality after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a triple-blind randomized controlled trial. Zare Elmi HK, Gholami M, Saki M, Ebrahimzadeh F. Chin J Integr Med. 2021;27:7–15. doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-2727-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.A televised, web-based randomised trial of an herbal remedy (valerian) for insomnia. Oxman AD, Flottorp S, Håvelsrud K, et al. PLoS One. 2007;2:0. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Valerian does not appear to reduce symptoms for patients with chronic insomnia in general practice using a series of randomised n-of-1 trials. Coxeter PD, Schluter PJ, Eastwood HL, Nikles CJ, Glasziou PP. Complement Ther Med. 2003;11:215–222. doi: 10.1016/s0965-2299(03)00122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Efficacy and tolerability of valerian extract LI 156 compared with oxazepam in the treatment of non-organic insomnia--a randomized, double-blind, comparative clinical study. Ziegler G, Ploch M, Miettinen-Baumann A, Collet W. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12568976/ Eur J Med Res. 2002;7:480–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled, prospective clinical study to demonstrate clinical efficacy of a fixed valerian hops extract combination (Ze 91019) in patients suffering from non-organic sleep disorder. Koetter U, Schrader E, Käufeler R, Brattström A. Phytother Res. 2007;21:847–851. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Valerian-hops combination and diphenhydramine for treating insomnia: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Morin CM, Koetter U, Bastien C, Ware JC, Wooten V. Sleep. 2005;28:1465–1471. doi: 10.1093/sleep/28.11.1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Treatment of severe chronic insomnia with L-tryptophan: results of a double-blind cross-over study. Demisch K, Bauer J, Georgi K, Demisch L. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1987;20:242–244. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1017114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chronic insomnia: effects of tryptophan, flurazepam, secobarbital, and placebo. Hartmann E, Lindsley JG, Spinweber C. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;80:138–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00427957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Valerian for sleep: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bent S, Padula A, Moore D, Patterson M, Mehling W. Am J Med. 2006;119:1005–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.02.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.A systematic review of valerian as a sleep aid: safe but not effective. Taibi DM, Landis CA, Petry H, Vitiello MV. Sleep Med Rev. 2007;11:209–230. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2007.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Effects of L-tryptophan on sleepiness and on sleep. Hartmann E. J Psychiatr Res. 1982;17:107–113. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(82)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.L-tryptophan: a rational anti-depressant and a natural hypnotic? Boman B. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 1988;22:83–97. doi: 10.1080/00048678809158946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Acupuncture for insomnia. Cheuk DK, Yeung WF, Chung KF, Wong V. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:0. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005472.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Traditional needle acupuncture treatment for insomnia: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Yeung WF, Chung KF, Leung YK, Zhang SP, Law AC. Sleep Med. 2009;10:694–704. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2008.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Insomnia. [ Jun; 2022 ];https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/insomnia. 2020 [PubMed]