Figure 1.
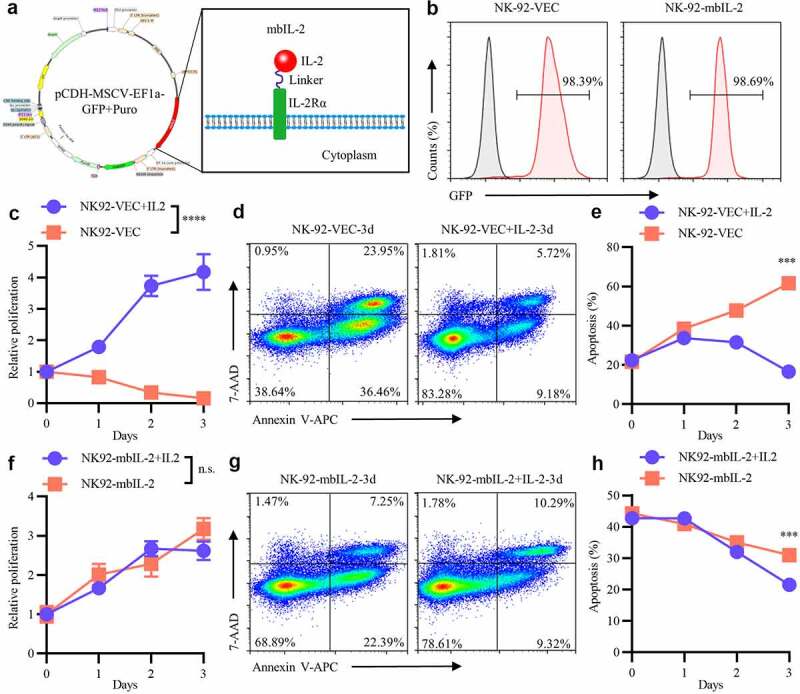
MbIL-2 maintains NK-92 cells survival and proliferation in vitro.
a: Schematic representation of mbIL-2 expression plasmids. b: Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the expression of mbIL-2 in NK-92 cells. NK-92 cells transduced with lentiviral for flow cytometry analysis. c: CCK8 assay of NK-92-VEC cell proliferation (n = 6). NK-92-VEC cells maintained with or without 200 U/ml IL-2 for assays. d–e: Analysis of the proportion of NK-92-VEC apoptotic cells under IL-2 culture conditions. NK-92-VEC cells maintained with or without 200 U/ml IL-2 for assays. d: Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the proportion of NK-92-VEC apoptotic cells under IL-2 condition culture after three days. e: Quantification and statistical analysis of the data (n = 3). f: CCK8 assay of NK-92-mbIL-2 cell proliferation (n = 6). NK-92-mbIL-2 cells maintained with or without 200 U/ml IL-2 for assays. g–h: Analysis of the proportion of NK-92-mbIL-2 apoptotic cells under IL-2 culture conditions. NK-92-mbIL-2 cells maintained with or without 200 U/ml IL-2 for assays. g: Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the proportion of NK-92-mbIL-2 apoptotic cells under IL-2 condition culture after three days. h: Quantification and statistical analysis of the data (n = 3).
