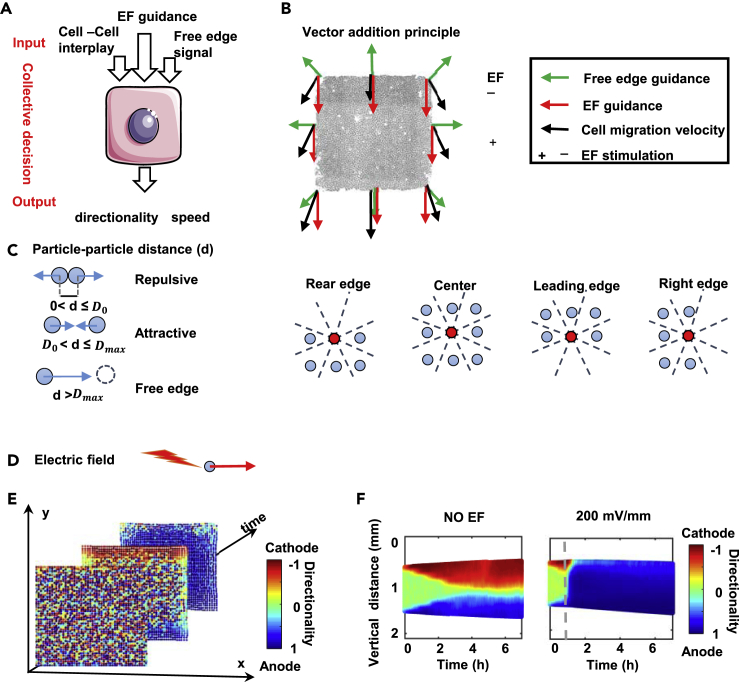
Figure 4.
In silico model captures the propagation dynamics of collective migration
(A and B) Directional cues (EF, free edge, and cell-cell interplay) as inputs, and speed and directionality as outputs. Vector addition as a principle in migration directionality determination.
(C) A elastic ball representing a cell. The cell-cell distance d determines the cellular interaction, where D0 and Dmax denote the threshold of repulsive interactions and the threshold of the free edge effect. Red balls at the rear edge, leading edge and right edge have three vacant neighbor sectors out of eight, which bias the direction of migration.
(D) Directional guidance of EF on the particle. An EF biases the directionality.
(E) A set of snapshots of the computer simulation of collective cell migration of a cell sheet (time = 0, 1, 2 h) of 2500 cells. The snapshots are derived from Video S5.
(F) In silico kymographs of cell migration directionality for NO EF and 200 mV/mm EF groups. Color codes the directionality as shown, compare with Figure 3C. See also Table S1, Figure S4 and Video S5.