Abstract
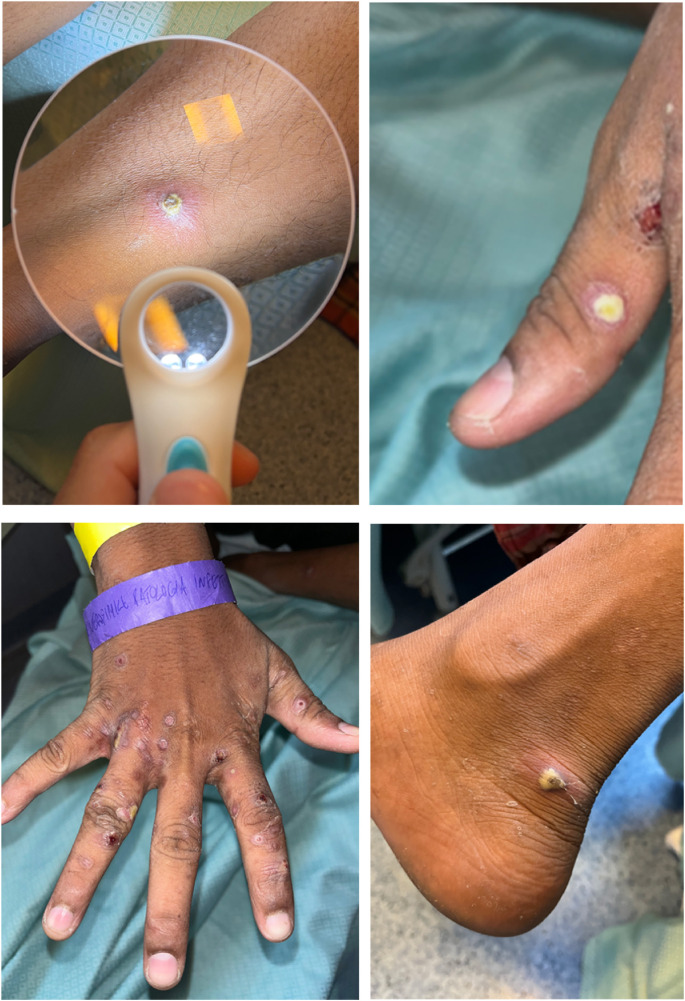
Two teenage illegal migrants from Bangladesh coming from a Libyan port arrived at Lampedusa Island-Italy. The health authorities, having noticed the presence of pustules on the limbs and genitals, suspecting a monkeypox virus infection, have urgently transferred them to the University Hospital of Palermo. They mentioned itching and prior sexual contact. On inspection, itching lesions and pustular lesions with central crusted umbilication and erythematous bases were detected. One of them had also fever and increased c-reactive protein. A real-time polymerase chain reaction assay on vesicle swabs to research monkeypoxvirus DNA and HIV serology was performed for both patients.
Keywords: Monkeypox virus, Pustules, Scabies, Migrants
The tests were negative, so a clinical diagnosis of nodular scabies and impetigo was assumed. In both cases, treatment with benzyl benzoate and amoxicillin-clavulanate resulted in progressive alleviation of symptoms.
Scabies is a contagious skin infection caused by microscopic mites that is prevalent in crowded areas and characterized by an itchy skin eruption that can rarely resemble eczema, nodules, and pustules. In these cases, the presence of itching and the location of the lesions (areas between the fingers, the wrists, axillae, groins, buttocks, and genitals) can aid the clinician in making a differential diagnosis with monkeypox; however, co-infection must be ruled out, particularly in high-risk populations.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or no-for-profit sectors.
Declaration of competing interest
Nothing to declare.
Author's contributions
We consider that all authors equally contribuited on this manuscript.