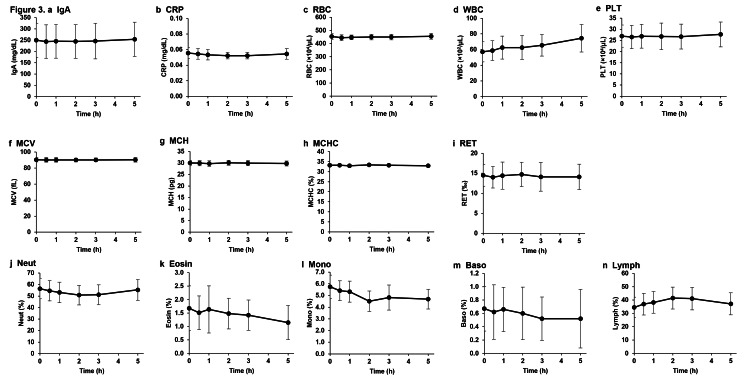
Figure 4. Effects of intravenous NMN administration on immune marker levels and blood cells.
Immune markers (a) IgA and (b) CRP were measured in plasma obtained from patients before and 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 5 h after the intravenous NMN administration. Blood cells, red blood cell markers, and leukocyte fractions were analyzed in blood obtained from patients before and 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 5 h after the intravenous NMN administration. The damage to blood cells was measured based on the number of (c) RBC, (d) WBC, and (e) PLT; the effect of NMN administration on erythrocytes was observed based on (f) MCV, (g) MCH, (h) MCHC, and (i) RET; the effect of NMN administration on the leukocyte fraction was observed in (j) Neut, (k) Eosin, (l) Mono, (m) Basso, and (n) Lymph. The results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 10).
NMN: Nicotinamide mononucleotide; IgA: Immunoglobulin A; CRP: C-reactive protein; RBC: Red blood cell; WBC: White blood cell; PLT: Platelet; MCV: Mean corpuscular volume; MCH: Mean corpuscular hemoglobin; MCHC: Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; RET: Reticulocyte; Neut: Neutrophil; Eosin: Eosinophil; Mono: Monocyte; Basso: Basophil; Lymph: Lymphocyte