Key Points
Question
What are the prevalence of and reasons for misrepresentation and nonadherence regarding public health measures against COVID-19?
Findings
In this national survey study of 1733 US adults, nearly half of participants reported misrepresentation and/or nonadherence regarding COVID-19 public health measures. The most common reasons included wanting life to feel normal and wanting to exercise personal freedom.
Meaning
These findings suggest that misrepresentation and nonadherence regarding COVID-19 public health measures constitute a serious public health challenge.
This survey study explores the prevalence of, reasons for, and characteristics associated with misrepresentation and nonadherence regarding COVID-19 public health measures among survey respondents in the US.
Abstract
Importance
The effectiveness of public health measures implemented to mitigate the spread and impact of SARS-CoV-2 relies heavily on honesty and adherence from the general public.
Objective
To examine the frequency of, reasons for, and factors associated with misrepresentation and nonadherence regarding COVID-19 public health measures.
Design, Setting, and Participants
This survey study recruited a national, nonprobability sample of US adults to participate in an online survey using Qualtrics online panels (participation rate, 1811 of 2260 [80.1%]) from December 8 to 23, 2021. The survey contained screening questions to allow for a targeted sample of one-third who had had COVID-19, one-third who had not had COVID-19 and were vaccinated, and one-third who had not had COVID-19 and were unvaccinated.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The survey assessed 9 different types of misrepresentation and nonadherence related to COVID-19 public health measures and the reasons underlying such behaviors. Additional questions measured COVID-19–related beliefs and behaviors and demographic characteristics.
Results
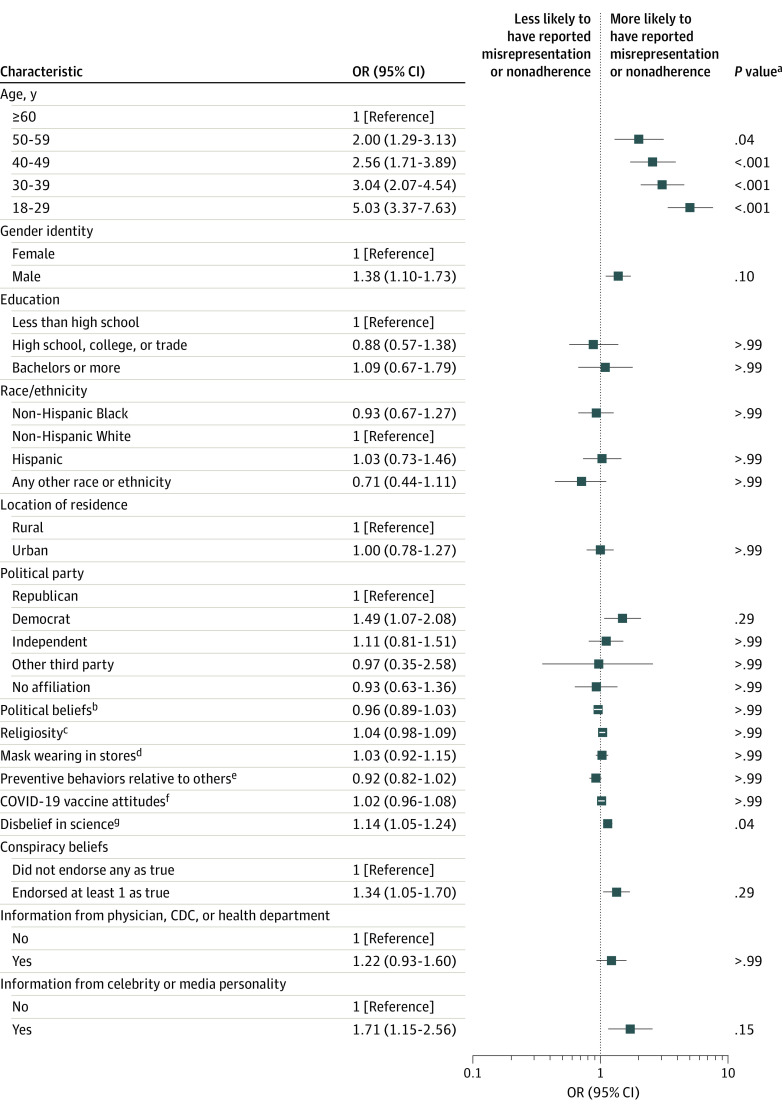
The final sample included 1733 participants. The mean (SD) participant age was 41 (15) years and the sample predominantly identified as female (1143 of 1732 [66.0%]) and non-Hispanic White (1151 of 1733 [66.4%]). Seven hundred twenty-one participants (41.6%) reported misrepresentation and/or nonadherence in at least 1 of the 9 items; telling someone they were with or about to be with in person that they were taking more COVID-19 preventive measures than they actually were (420 of 1726 [24.3%]) and breaking quarantine rules (190 of 845 [22.5%]) were the most common manifestations. The most commonly endorsed reasons included wanting life to feel normal and wanting to exercise personal freedom. All age groups younger than 60 years (eg, odds ratio for those aged 18-29 years, 4.87 [95% CI, 3.27-7.34]) and those who had greater distrust in science (odds ratio, 1.14 [95% CI, 1.05-1.23]) had significantly higher odds of misrepresentation and/or nonadherence for at least 1 of the 9 items.
Conclusions and Relevance
In this survey study of US adults, nearly half of participants reported misrepresentation and/or nonadherence regarding public health measures against COVID-19. Future work is needed to examine strategies for communicating the consequences of misrepresentation and nonadherence and to address contributing factors.
Introduction
SARS-CoV-2 was first identified in December 2019 and rapidly spread around the world, with more than 6 million people worldwide1 and more than 1 million in the US having died.2 In response, governments, organizations, school districts, and businesses worldwide implemented public health measures to mitigate the spread of the disease (eg, health screens, testing, quarantining, and vaccination requirements).
Public health measures have the potential to dramatically reduce the spread and impact of the disease,3,4,5 but their success depends on the public’s willingness to be honest about and adherent to these measures. However, these measures can involve significant psychological,6 social (eg, distancing from friends and family),7,8 financial (eg, loss of employment and/or income),9 and physical (eg, delayed health care appointments leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment)10,11,12 burdens that make adherence difficult.
Given the difficulty and costs associated with many public health measures, members of the public may exercise dishonesty and nonadherence regarding these measures. For example, people may withhold information about having COVID-19 during a health screening to allow them to attend their health care appointment or continue going to work. Reporting being vaccinated when one is not would allow a person to participate in an event restricted to those who are vaccinated or to avoid judgment from vaccinated friends.
Such scenarios are quite plausible given that it is well-established that people often misrepresent or do not disclose information in general,13,14 and specifically regarding their medical information and behaviors, particularly when it is embarrassing or potentially self-serving.15,16,17 For instance, previous research16,17 found that a substantial percentage of US adults withhold important information from their clinicians and that the reasons for doing so include concerns about being judged or lectured and not wanting to have to make a difficult change in behavior. In addition, in a national probability sample of adults receiving medical care for HIV,15 a substantial minority had sex without disclosing their positive HIV status.
Misrepresentation of COVID-19–related health information and nonadherence to public health measures may undermine the effectiveness of these measures. One of the few studies that examined this question early in the pandemic18 found that 55% of respondents reported some concealment of COVID-19 symptoms, and among those instructed to quarantine, 53% reported denying the need to do so when asked. Another study19 found that approximately 10% of full-time in-person employees reported going to work despite having a confirmed case of COVID-19 or a close contact with a confirmed case, and in a study of 69 people who were told to quarantine due to COVID-19 exposure or possible symptoms,20 nearly half (46%) broke quarantine rules.
These few studies were conducted very early in the pandemic, only examined a few types of misrepresentation or nonadherence, and/or did not explore the reasons for these behaviors. Therefore, our understanding of the prevalence of and reasons for these behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic remains limited. To address these limits, the present study explored the prevalence of, reasons for, and characteristics associated with misrepresentation and nonadherence regarding COVID-19 public health measures.
Methods
From December 8 to 23, 2021, we conducted an online survey of US adults that focused on their experiences and challenges throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. Qualtrics online panels were used to send targeted invitations to potential participants, and those interested began the survey. Qualtrics was used in part because of its access to a diversified cohort of US residents. Using an online platform also allowed for additional screening to ensure adequate representation. Specifically, screener questions at the beginning of the survey were used to select a sample in which one-third had had COVID-19, one-third had not had COVID-19 and were at least partially vaccinated (ie, received ≥1 dose of the Ad.26.COV2.S [Johnson & Johnson/Janssen], BNT162b2 [Pfizer], or mRNA-1273 [Moderna] vaccine), and one-third had not had COVID-19 and had not received any COVID-19 vaccinations. Multiple mechanisms were in place to ensure that the survey could not be completed by “bots” or cheaters (eMethods in the Supplement). The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Utah. Consent to participate was given electronically by each participant before starting the survey. Participants were compensated based on the terms of their agreement with Qualtrics. The study followed the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) reporting guideline.
Survey
The survey was developed by the study team, which was composed of health services researchers and psychologists. In addition, pilot testing was conducted and feedback was sought from the lay public to assess the comprehensibility and mechanics of the survey (eMethods in the Supplement). The survey began by asking whether participants had ever had COVID-19 or symptoms that they thought might be COVID-19, had been vaccinated for COVID-19, and had ever been told to follow quarantine rules. Based on these responses, participants were presented with as many as 9 questions assessing misrepresentation and nonadherence that applied to them.
Misrepresentation Items
Participants indicated whether, during the COVID-19 pandemic, they did not mention that they thought they might have or knew they had COVID-19 to someone they were with or were about to be with in person (among those who thought they might have or knew they had COVID-19). The survey also assessed whether, throughout the pandemic, participants did not mention that they thought they might have or knew they had COVID-19 when being screened to enter a clinician’s office or a public place (among those who thought they might have or knew they had COVID-19), told someone they were with or were about to be with that they were taking more COVID-19 prevention measures than they actually were, told someone they were vaccinated for COVID-19 when they were not (among those who were not vaccinated), told someone they were not vaccinated when they were (among those who were vaccinated), and told someone that they did not have to quarantine when they were supposed to (among those who were told to quarantine).
Nonadherence Items
Participants were also asked whether, during the pandemic, they had ever avoided getting tested (among those who thought they might have COVID-19) and if they ever broke quarantine rules (among those who were told to quarantine).
Reasoning
If participants answered affirmatively to any of the misrepresentation or nonadherence items, they were asked to indicate yes or no to a list of reasons for the corresponding behavior. These reasons were consistent across similar items but differed where appropriate. They included items such as: “It’s no one else’s business,” “I didn’t want someone to judge or think badly of me,” “I wanted to exercise my freedom to do what I want,” and “I didn’t think COVID-19 was real.” Participants could say yes to all reasons that applied to them and type additional reasons for each item if desired.
Demographics
Participants also reported their religious beliefs (referred to hereinafter as religiosity), political party affiliation, political social beliefs, vaccine attitudes, where they obtained COVID-19 information, how often they wore a mask in a retail or grocery store, whether they have taken more or fewer COVID-19 prevention measures compared with those with whom they interact, belief in science,21 and conspiracy beliefs about COVID-19.22 Participants self-reported their age, gender identity, race and ethnicity, and location of residence (state and size of town or city). Race and ethnicity were included to allow us to describe the sample and because COVID-19 and its public health measures disproportionately impacted individuals from underserved populations. Finally, participants could provide feedback on the survey in an open text box.
Statistical Analysis
To ensure a conservative estimate of misrepresentation and nonadherence among participants, for those who provided a comment in an open response opportunity that led us to question the validity of their affirmative response to a misrepresentation or nonadherence question, we did not include their affirmative response in the analyses. For instance, a few participants indicated that they did not mention thinking they might have or knowing they had COVID-19 in a health screen for a clinician appointment, but then wrote in an open response text box that they never left home while they had COVID-19.
Analyses were conducted in R Studio,23 version 1.4.1106 (R Program for Statistical Computing) with the use of multiple packages.24,25,26 We report demographic statistics, the percentage of participants who engaged in the 9 misrepresentation and nonadherence behaviors, and the reasons for these behaviors.
We used multiple logistic regression to conduct an exploratory analysis of the characteristics that were associated with whether or not participants reported misrepresentation or nonadherence in any of the 9 items (0, no reported misrepresentation or nonadherence; 1, reported misrepresentation or nonadherence in at least 1 of the 9 items). Separate models for each of the 9 items did not differ substantially from the overall model and are provided in the eTable in the Supplement). Significance was set at 2-sided α = .05. To account for multiple comparisons, P values were adjusted using Holm-Bonferroni correction.27
Results
Participants
Of the 2260 people who received the email invitation and accessed the survey, 1811 completed it (participation rate, 80.1%). We excluded 59 participants who provided indecipherable responses in the open text boxes and 19 participants who completed the survey in less than one-third of the median completion time (2 minutes and 58 seconds), leaving a final analytic sample of 1733 participants. Participants had a mean (SD) age of 41 (15) years (range, 18-87 years); of 1732 with responses available, 1143 identified as female (66.0%), 548 identified as male (31.6%), and 41 provided other gender identity responses (2.4%). Most participants identified as non-Hispanic White (1151 [66.4%]) and most had completed a bachelor’s degree or more (470 [27.1%]). Consistent with sampling quotas, 477 (27.5%) reported having had COVID-19, 499 (28.8%) reported not having had COVID-19 and being at least partially vaccinated, and 509 (29.4%) reported not having had COVID-19 and being unvaccinated. An additional 160 participants (9.2%) were unsure whether they had COVID-19 and were at least partially vaccinated, and 81 (4.7%) were unsure whether they had COVID-19 and were not vaccinated. An additional 7 participants (0.4%) did not respond regarding either their COVID-19 status or their vaccination status. Participant characteristics and additional survey measures are provided in Table 1; the full survey is provided in the eAppendix in the Supplement.
Table 1. Participant Characteristicsa.
| Characteristic | Values for final sample (N = 1733) |
|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) [range], y | 41 (15) [18-87] |
| Age, y | |
| ≥60 | 241/1724 (14.0) |
| 50-59 | 229/1724 (13.3) |
| 40-49 | 325/1724 (18.9) |
| 30-39 | 481/1724 (27.9) |
| 18-29 | 448/1724 (26.0) |
| Gender identity | |
| Female | 1143/1732 (66.0) |
| Male | 548/1732 (31.6) |
| Prefer not to say | 15/1732 (0.9) |
| Nonbinary/third gender | 10/1732 (0.6) |
| Prefer to self-describe | 10/1732 (0.6) |
| Transgender man | 5/1732 (0.3) |
| Transgender woman | 1/1732 (0.1) |
| Race and ethnicity | |
| Hispanic | 193/1733 (11.1) |
| Non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native | 20/1733 (1.1) |
| Non-Hispanic Asian or Asian American | 45/1733 (2.6) |
| Non-Hispanic Black or African American | 279/1733 (16.1) |
| Non-Hispanic Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander | 3/1733 (0.2) |
| Non-Hispanic White or European American | 1151/1733 (66.4) |
| Non-Hispanic multiracial | 26/1733 (1.5) |
| Non-Hispanic other race | 13/1733 (0.7) |
| Otherb | 3/1733 (0.2) |
| Educational attainment | |
| None | 16/1731 (0.9) |
| Elementary school | 5/1731 (0.3) |
| Some high school but no diploma | 95/1731 (5.5) |
| High school (diploma or GED) | 606/1731 (35.0) |
| Some college, but no degree | 425/1731 (24.5) |
| Trade school | 114/1731 (6.6) |
| Bachelor’s degree | 354/1731 (20.5) |
| Master’s degree | 95/1731 (5.5) |
| Doctoral/professional degree | 21/1731 (1.2) |
| Location of residence | |
| Rural | 486/1728 (28.1) |
| Small city (eg, <100 000 people) | 281/1728 (16.3) |
| Suburb | 564/1728 (32.6) |
| Midsized city (100 000 to 1 million people) | 145/1728 (8.4) |
| Large city (>1 million people) | 248/1728 (14.3) |
| Other | 4/1728 (0.2) |
| Political affiliation | |
| Democrat | 596/1733 (34.4) |
| Republican | 462/1733 (26.7) |
| Independent | 425/1733 (24.5) |
| Liberal third party | 23/1733 (1.3) |
| Conservative third party | 5/1733 (0.3) |
| No affiliation | 222/1733 (12.8) |
| COVID-19 infection history | |
| Confident or certain of no COVID-19 infection | 1009/1727 (58.4) |
| Confident or certain of COVID-19 infection | 477/1727 (27.5) |
| Uncertain of COVID-19 infection | 241/1727 (14.0) |
| COVID-19 vaccine status | |
| Not vaccinated | 812/1732 (46.9) |
| Received BNT162b2 (Pfizer) or mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine | |
| 1 dose | 111/1732 (6.4) |
| 2 doses | 466/1732 (26.9) |
| 2 doses and a booster | 244/1732 (14.1) |
| Received Ad.26.COV2.S (Johnson & Johnson/Janssen) vaccine | |
| 1 dose | 51/1732 (2.9) |
| 1 dose and a booster | 48/1732 (2.8) |
| Source of COVID-19 informationc | |
| My physician | 1061/1718 (61.7) |
| Friends | 665/1713 (38.8) |
| Family | 809/1713 (47.2) |
| Local department of health | 864/1710 (50.5) |
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention | 902/1714 (52.6) |
| 730/1716 (42.5) | |
| A certain politician | 109/1671 (6.5) |
| A certain celebrity | 85/1680 (5.1) |
| A certain media personality | 111/1674 (6.6) |
| Survey scores, mean (SD) | |
| Religiosityd | 3.96 (2.16) |
| Political stance on social issuese | 3.96 (1.66) |
| Vaccine attitudesf | 4.67 (2.06) |
| How often they wear a mask in stores, g | 2.88 (1.14) |
| COVID-19 prevention measures taken more or less relative to others with whom they interacth | 3.18 (1.22) |
| Disbelief in science mean (SD)i | 4.01 (1.50) |
| Conspiracy theories about COVID-19j | 2.60 (1.04) |
| The virus causing COVID-19 was purposefully released by a government or a person | 2.94 (1.32) |
| COVID-19 is a biological weapon being tested | 2.80 (1.30) |
| The current COVID-19 outbreak is a form of population control to reduce the number of people in infected countries | 2.73 (1.30) |
| The COVID-19 vaccine has a microchip so the government can track you | 2.38 (1.29) |
| COVID-19 is not real | 2.11 (1.27) |
| The COVID-19 vaccine causes infertility | 2.67 (1.18) |
Abbreviation: GED, General Educational Development.
Unless indicated otherwise, data are expressed as No./total No. (%) of participants. Owing to missing data, numbers of participants may not total 1733 in all categories. Percentages have been rounded and may not total 100.
Includes participants who reported their race (as White or European American [n = 1] or more than 1 race [n = 2]) but did not report their ethnicity.
Includes all that apply.
Scores range from 1 (not at all) to 7 (very).
Scores range from 1 (very liberal) to 7 (very conservative).
Scores range from 1 (very negative) to 7 (very positive).
Scores range from 1 (never) to 4 (every time).
Scores range from 1 (much less) to 5 (much more).
Scores range from 1 (strongly agree) to 7 (strongly disagree) for 6 items (Cronbach α = .94).
Scores range from 1 (definitely false) to 5 (definitely true) for 5 items (Cronbach α = .90).
Frequency of and Reasons for Misrepresentation and Nonadherence
Overall, 721 participants (41.6%) reported misrepresentation or nonadherence for at least 1 of the 9 behaviors (Figure 1). Among the 9 items, the most commonly reported included telling someone they were with or were about to be with in person that they were taking more COVID-19 preventive measures than they actually were (420 of 1726 [24.3%]), followed by breaking quarantine rules (190 of 845 [22.5%]), avoiding getting tested for COVID-19 when they thought they might have it (171 of 814 [21.0%]), and not mentioning that they thought they might have or knew they had COVID-19 when being screened to enter a clinician’s office (193 of 945 [20.4%]).
Figure 1. Frequency With Which Participants Engaged in Misrepresentation and Nonadherence.
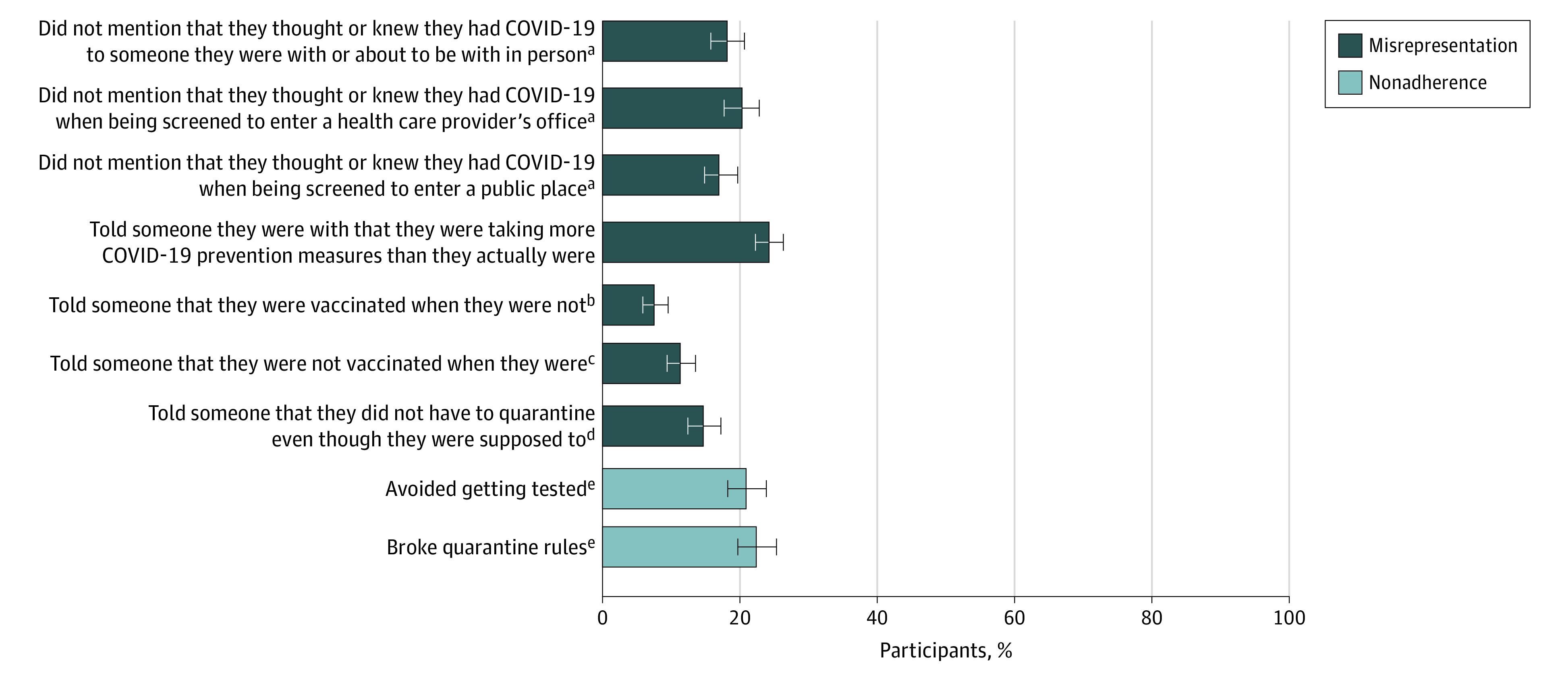
Error bars indicate 95% CIs.
aAmong those who thought or knew they had COVID-19.
bAmong those who were not vaccinated.
cAmong those who were vaccinated.
dAmong those who were told to quarantine.
eAmong those who thought they had COVID-19.
Table 2 reports, among those who reported misrepresentation or nonadherence in a given item (eg, broke quarantine rules), the percentage who endorsed each reason offered for this misrepresentation or nonadherence. “I wanted my life to feel ‘normal’ (ie, how I felt before the COVID-19 pandemic began),” “I wanted to exercise my freedom to do what I want,” “It’s no one else’s business,” “I didn’t feel very sick,” and “I was following guidance from a public figure I trust (eg, politicians, scientists, people on the news, celebrities)” were the most commonly endorsed reasons for misrepresentation and nonadherence to COVID-19 public health measures. A substantial proportion of participants also endorsed reasons such as “I didn’t think COVID-19 was real,” “I didn’t think COVID-19 was a big deal,” and “I didn’t want someone to judge or think badly of me.”
Table 2. Reasons for Misrepresentation and Nonadherence Regarding COVID-19 Public Health Measures Among Study Participantsa.
| Reason | Scenario, No./total No. (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Did not mention having or possibly having COVID-19 | Said they were taking more preventive measures than they were | Said they did not have to quarantine despite requirement to do so | Said they were vaccinated when not vaccinated | Said they were not vaccinated when vaccinated | Did not test when might have COVID-19 | Broke quarantine rules | |||
| When screened to enter a clinician’s office | When screened to enter a public place | When meeting or about to meet someone in person | |||||||
| I wanted my life to feel “normal” (ie, how I felt before the COVID-19 pandemic began) | 101/192 (52.6) | 94/163 (57.7) | 87/171 (50.9) | 222/417 (53.2) | 66/124 (53.2) | 31/62 (50.0) | NA | NA | 105/189 (55.5) |
| I wanted to exercise my freedom to do what I want | 91/191 (47.6) | 81/163 (49.7) | 76/171 (44.4) | 190/417 (45.6) | 68/125 (54.4) | 31/62 (50.0) | NA | 79/170 (46.5) | 100/189 (52.9) |
| I was following guidance from a public figure that I trust (eg, politicians, scientists, people on the news, celebrities) | 88/190 (46.3) | 74/162 (45.7) | 75/171 (43.9) | 174/415 (41.9) | 55/125 (44.0) | 22/61 (36.1) | 54/104 (51.9) | 62/170 (36.5) | 70/189 (37.0) |
| I didn’t feel very sick | 84/191 (44.0) | 82/163 (50.3) | 77/171 (45.0) | NA | 70/123 (56.9) | NA | NA | 80/170 (47.1) | 93/190 (48.9) |
| It’s no one else’s business | 83/191 (43.5) | NA | 66/170 (38.8) | 167/415 (40.2) | 67/126 (53.2) | 33/62 (53.2) | 57/104 (54.8) | 71/169 (42.0) | 112/189 (59.3) |
| I didn’t want to be stopped from doing something I needed to do | 81/192 (42.2) | 78/162 (48.1) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| I didn’t want to have to get tested for COVID-19 | 80/190 (42.1) | 74/161 (46.0) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| I didn’t want someone to judge or think badly of me | 70/192 (36.5) | 64/161 (39.7) | 60/172 (34.9) | 147/416 (35.3) | 48/125 (38.4) | 25/62 (40.3) | 47/103 (45.6) | 54/169 (31.9) | 56/189 (29.6) |
| I didn’t think I really had COVID-19 | 70/192 (36.5) | 71/163 (43.5) | 71/171 (41.5) | NA | 62/125 (49.6) | NA | NA | 63/169 (37.3) | 90/189 (47.6) |
| I didn’t think COVID-19 was a big deal | 67/192 (34.9) | 67/162 (41.3) | 69/171 (40.3) | 107/416 (25.7) | 51/125 (40.8) | 22/62 (35.5) | NA | 52/170 (30.6) | 75/190 (39.5) |
| I didn’t want certain people to know | 66/191 (34.5) | 62/163 (38.0) | 56/171 (32.7) | 133/416 (32.0) | 52/124 (41.9) | 25/62 (40.3) | 51/104 (49.0) | 51/169 (30.2) | 59/189 (31.2) |
| I didn’t think it mattered | 64/191 (33.5) | 57/162 (35.2) | 53/169 (31.4) | 117/417 (28.1) | 53/125 (42.4) | 20/62 (32.3) | 55/104 (52.9) | 47/169 (27.8) | 80/189 (42.3) |
| I didn’t think COVID-19 was real | 60/191 (31.4) | 65/163 (39.9) | 50/170 (29.4) | 104/417 (24.9) | 55/123 (44.7) | 19/61 (31.1) | NA | 50/169 (29.6) | 53/188 (28.2) |
| I was bored or lonely | NA | NA | 70/171 (40.9) | 139/415 (33.5) | 59/125 (47.2) | NA | NA | NA | 77/190 (40.5) |
| I couldn’t miss work to stay home | NA | NA | 66/172 (38.4) | 140/415 (33.7) | 49/125 (39.2) | NA | NA | NA | 70/188 (37.2) |
| I couldn’t miss important nonwork responsibilities to stay home (eg, get groceries, care for loved ones) | NA | NA | 75/170 (44.1) | 172/415 (41.4) | 69/125 (55.2) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| I didn’t want them to be angry at me for exposing them | NA | NA | 60/169 (35.5) | 128/415 (30.8) | 51/124 (41.1) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| I didn’t want to miss an event or fun activity to stay home | NA | NA | 62/171 (36.3) | 136/415 (32.8) | 52/124 (41.9) | NA | NA | NA | 78/189 (41.3) |
| I was confused about the rules for quarantine | NA | NA | 57/170 (33.5) | NA | 46/124 (37.1) | NA | NA | NA | 61/189 (32.3) |
| I wanted to be able to do something where being vaccinated was required (eg, a special event, get together with friends/family who were vaccinated, etc) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 24/62 (38.7) | NA | NA | NA |
| I needed to be able to go to work | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 20/62 (32.3) | NA | NA | NA |
| I needed to be able to attend college classes | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11/62 (17.7) | NA | NA | NA |
| I didn’t want to have to deal with the consequences of a test showing that I had COVID-19 (eg, my family would have to quarantine, I would have to miss work, my child would miss school, etc) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 65/170 (38.2) | NA |
| I was worried it would hurt or be uncomfortable to get tested | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 72/170 (42.3) | NA |
| I wanted to keep COVID-19 rates low in my area so public health measures were not put in place (eg, closing schools, mask mandates) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 55/168 (32.7) | NA |
| I didn’t want the government to have my personal information | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 61/170 (35.9) | NA |
| I thought I couldn’t afford the cost of getting tested | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 51/168 (30.4) | NA |
| I didn’t have time to get tested | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 45/168 (26.8) | NA |
| I didn’t know how or where to get tested | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 41/170 (24.1) | NA |
Abbreviation: NA, not applicable.
Data are presented as No. (%) of participants.
Risk Factors Associated With Misrepresentation and Nonadherence
The exploratory multiple logistic regression28 (Tjur R2 = 0.097; area under the curve, 0.69) indicated that younger participants (odds ratio [OR] for those aged 18-29 years, 4.87 [95% CI, 3.27-7.34]; OR for those aged 30-39 years, 3.16 [95% CI, 2.16-4.70]; OR for those aged 40-49 years, 2.59 [95% CI, 1.73-3.92]; OR for those aged 50-59 years, 2.09 [95% CI, 1.35-3.25]) compared with those 60 years or older and those with greater disbelief in science (OR, 1.14 [95% CI, 1.05-1.23]) had significantly higher odds of reporting misrepresentation or nonadherence in any of the 9 items (Figure 2). Gender identity, educational attainment, race and ethnicity, location of residence, political party affiliation, political beliefs, religiosity, mask use in retail and grocery stores, degree of COVID-19 preventive measures taken relative to others, attitude toward vaccines, COVID-19 conspiracy beliefs, and where COVID-19 information was obtained were not associated with misrepresentation or nonadherence in at least 1 of the 9 items.
Figure 2. Exploratory Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis of Risk Factors Associated With Misrepresentation and Nonadherence.
OR indicates odds ratio.
aHolm-Bonferroni correction applied.
bMean (SD) score, 3.97 (1.66); scores range from 1 (very liberal) to 7 (very conservative).
cMean (SD) score, 3.96 (2.16); scores range from 1 (not at all) to 7 (very).
dMean (SD) score, 2.88 (1.14); scores range from 1 (never) to 4 (every time).
eMean (SD) score, 3.18 (1.22); scores range from 1 (much less) to 5 (much more).
fMean (SD) score, 4.67 (2.06); scores range from 1 (very negative) to 7 (very positive).
gMean (SD) score, 4.01 (1.50); scores range from 1 (strongly agree) to 7 (strongly disagree).
Discussion
The results of this study demonstrate that nearly half of survey participants reported engaging in misrepresentation and/or nonadherence regarding public health measures against COVID-19 during the pandemic. Overstating COVID-19 preventive measures they are taking, breaking quarantine rules, avoiding getting tested for COVID-19 when they thought they might have it, and not mentioning that they thought or knew they had COVID-19 when being screened to enter a clinician’s office were the most common manifestations of misrepresentation and nonadherence. The most common reasons for these behaviors included wanting life to feel normal, wanting to exercise personal freedom, feeling that it is no one else’s business, and not feeling very sick. A substantial minority of participants also explained these behaviors by endorsing statements about COVID-19 not being real or a big deal.
These results are consistent with the little research conducted to date demonstrating misrepresentation and nonadherence regarding COVID-19 public health measures18,19,20 and with research demonstrating nondisclosure of non–COVID-19 medical information such as nondisclosure of HIV-positive status to sexual partners15 and of important medical information (eg, being depressed or suicidal, recreational drug use) to clincians.16,17 Our findings regarding participants’ reasons for misrepresentation and nonadherence (eg, wanting to exercise personal freedom and believing that COVID-19 is not real) are aligned with prior research demonstrating the desire to maintain personal autonomy in response to past governmental health requirements29,30 and denials of reputable medical (specifically regarding COVID-1931,32 as well as other domains33,34) and scientific information.35,36
The results also suggest that younger participants and those with greater disbelief in science may be more likely to engage in misrepresentation or nonadherence. Younger patients have been found to have a higher likelihood of dishonesty regarding disclosure of medical information16,17 and lower likelihood of medical adherence in general37,38 and regarding COVID-19 preventive measures specifically.39,40 Similarly, greater disbelief in science has been an important factor associated with nonadherence to health behaviors during the pandemic (eg, masking, vaccination uptake)41,42 and beyond.34,43 These groups may represent an important focus for efforts to address misrepresentation and nonadherence.
Overall, the results of this study suggest that some participants misrepresented their COVID-19 status and/or vaccination status and did not adhere to public health measures. Although these public health measures can involve tremendous psychological, social, financial, and physical burdens,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 such misrepresentation and nonadherence may have placed others at risk of COVID-19. For example, not disclosing thinking or knowing one has COVID-19 when entering a clinician’s office endangers clinicians, office staff, and other patients who may be at increased risk of severe outcomes from COVID-19.
Limitations
The present research has limitations. First, the online sample is not fully representative of the US population, although it allowed for a larger and more diverse sample size than data collected using other means and ensured the inclusion of sufficient participants differing in COVID-19 history and vaccination status. We also acknowledge that with an online nonprobability sample, the findings from our model do not offer unbiased population level insights and should be interpreted with caution. These findings provide important preliminary insights for hypothesis testing about factors that may be associated with misrepresentation or nonadherence regarding COVID-19 public health guidelines. Second, in a study examining the extent to which people are misrepresenting the truth, participants may have been dishonest in their survey responses. However, if this occurred, participants likely provided answers that were more socially desirable44 (ie, minimizing their misrepresentation or nonadherence), thereby likely making our results an underestimate of how commonly people misrepresent or are nonadherent in this setting. Third, although the study captured the percentage of individuals who misrepresented or were nonadherent, it cannot speak to the frequency or the degree of these behaviors. In addition, indicated reasons for misrepresentation and nonadherence may have been post hoc explanations, rather than the original determinants. Finally, there may have been other reasons why people misrepresented or were nonadherent that we did not measure (eg, prosocial or practical reasons). For instance, participants may have avoided getting a COVID-19 test because they did not want to risk infecting others at the testing site. In addition, participants may not have mentioned a COVID-19 diagnosis or symptoms in a screening because they thought they were no longer contagious and therefore believed it to be irrelevant. This could have led us to overestimate the cases of misrepresentation and nonadherence that are of concern (ie, misrepresentation and nonadherence that may lead to increased spread of the disease). However, screening questions typically include a time frame that preempts this possibility (eg, “Have you had any symptoms of COVID-19 in the last 2 weeks?”). Furthermore, the general public is often uninformed about viral transmission45; therefore, full disclosure is necessary for the medical screener to assess actual risk level.
Conclusions
The results of this survey study reveal a serious public health challenge for the COVID-19 pandemic and any future infectious disease outbreaks. With misrepresentation and nonadherence regarding public health measures being fairly common, the effectiveness of these measures in preventing disease spread may be undermined. This possibility highlights the need for further research examining strategies for educating the public on the importance of honesty and adherence in these situations as well as for addressing the factors (eg, the burden of quarantine, believing that COVID-19 is not real) that drive misrepresentation and nonadherence. It also underscores the importance of public health officials, policy makers, and media personalities fostering trust and engagement in these public health measures to reduce the occurrence and therefore the impact of misrepresentation and nonadherence.
eMethods. Survey Development Information
eTable. Individual Regression Models
eAppendix. Full Study Survey
References
- 1.World Health Organization . WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. March 11, 2022. Accessed March 11, 2022. https://covid19.who.int/
- 2.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . COVID data tracker weekly review. Updated August 26, 2022. Accessed September 9, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/covid-data/covidview/index.html
- 3.Wang Y, Deng Z, Shi D. How effective is a mask in preventing COVID-19 infection? Med Devices Sens. 2021;4(1):e10163. doi: 10.1002/mds3.10163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nunes B, Rodrigues AP, Kislaya I, et al. mRNA vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19-related hospitalisations and deaths in older adults: a cohort study based on data linkage of national health registries in Portugal, February to August 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(38). doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.38.2100833 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pan A, Liu L, Wang C, et al. Association of public health interventions with the epidemiology of the COVID-19 outbreak in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(19):1915-1923. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brooks SK, Webster RK, Smith LE, et al. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence. Lancet. 2020;395(10227):912-920. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Philpot LM, Ramar P, Roellinger DL, Barry BA, Sharma P, Ebbert JO. Changes in social relationships during an initial “stay-at-home” phase of the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal survey study in the US. Soc Sci Med. 2021;274:113779. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.113779 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Krendl AC, Perry BL. The impact of sheltering in place during the COVID-19 pandemic on older adults’ social and mental well-being. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2021;76(2):e53-e58. doi: 10.1093/geronb/gbaa110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cortes GM, Forsythe EC. Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic and the CARES Act on earnings and inequality. Upjohn Institute Working Paper 20-332. W.E. Upjohn Institute for Employment Research. September 8, 2020. Accessed September 9, 2022. https://research.upjohn.org/up_workingpapers/332/
- 10.Czeisler ME, Marynak K, Clarke KEN, et al. Delay or avoidance of medical care because of COVID-19–related concerns—United States, June 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1250-1257. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6936a4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Findling MG, Blendon RJ, Benson JM. Delayed care with harmful health consequences—reported experiences from national surveys during coronavirus disease 2019. JAMA Health Forum. 2020;1(12):e201463. doi: 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2020.1463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Riera R, Bagattini AM, Pacheco RL, Pachito DV, Roitberg F, Ilbawi A. Delays and disruptions in cancer health care due to COVID-19 pandemic: systematic review. JCO Glob Oncol. 2021;7:311-323. doi: 10.1200/GO.20.00639 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.DePaulo BM, Kashy DA, Kirkendol SE, Wyer MM, Epstein JA. Lying in everyday life. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1996;70(5):979-995. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.70.5.979 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.DePaulo BM, Ansfield ME, Kirkendol SE, Boden JM. Serious lies. Basic Appl Soc Psych. 2011;26:147-167. doi: 10.1080/01973533.2004.9646402 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ciccarone DH, Kanouse DE, Collins RL, et al. Sex without disclosure of positive HIV serostatus in a US probability sample of persons receiving medical care for HIV infection. Am J Public Health. 2003;93(6):949-954. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.93.6.949 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Levy AG, Scherer AM, Zikmund-Fisher BJ, Larkin K, Barnes G, Fagerlin A. Prevalence of and factors associated with patient nondisclosure of medically relevant information to clinicians. JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1(7):e185293. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.5293 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Levy AG, Scherer AM, Zikmund-Fisher BJ, Larkin K, Barnes GD, Fagerlin A. Assessment of patient nondisclosures of experiencing imminent threats to clinicians. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(8):e199277. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.9277 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.O’Connor AM, Evans AD. Dishonesty during a pandemic: the concealment of COVID-19 information. J Health Psychol. 2022;27(1):236-245. doi: 10.1177/1359105320951603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shoss M, Min H, Horan K, Schlotzhauer A, Nigam J, Swanson N. The impact of precarious work on going to work sick and sending children to school sick during the COVID-19 pandemic. Paper presented at: Virtual 3rd International Electronic Conference on Environmental Research and Public Health—Public Health Issues in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic; January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tseng C-W, Roh Y, DeJong C, Kanagusuku LN, Soin KS. Patients’ compliance with quarantine requirements for exposure or potential symptoms of COVID-19. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2021;80(11):276-282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hartman RO, Dieckmann NF, Sprenger AM, Stastny BJ, DeMarree KG. Modeling attitudes toward science: development and validation of the credibility of science scale. Basic Appl Soc Psych. 2017;39(6):358-371. doi: 10.1080/01973533.2017.1372284 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Piltch-Loeb R, Zikmund-Fisher BJ, Shaffer VA, et al. Cross-sectional psychological and demographic associations of Zika knowledge and conspiracy beliefs before and after local Zika transmission. Risk Anal. 2019;39(12):2683-2693. doi: 10.1111/risa.13369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.RStudio Team . RStudio: integrated development environment for R. RStudio. PBC; 2021. Accessed September 9, 2022. https://www.rstudio.com/
- 24.Wickham H, Averick M, Bryan J, et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J Open Source Softw. 2019;4(43):1686. doi: 10.21105/joss.01686 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Revelle W. psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research. Northwestern University. Version 2.2.5. 2022. Accessed September 9, 2022. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/psych/index.html
- 26.Wilke CO. cowplot: Streamlined plot theme and plot annotations for 'ggplot2'. R package version 1.1.1. December 30, 2020. Accessed September 9, 2022. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/cowplot/index.html
- 27.Holm S. A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat. 1979;6(2):65-70. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tjur T. Coefficients of determination in logistic regression models—a new proposal: the coefficient of discrimination. Am Stat. 2009;63(4):366-372. doi: 10.1198/tast.2009.08210 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gualano MR, Olivero E, Voglino G, et al. Knowledge, attitudes and beliefs towards compulsory vaccination: a systematic review. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(4):918-931. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1564437 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Smith LE, Hodson A, Rubin GJ. Parental attitudes towards mandatory vaccination: a systematic review. Vaccine. 2021;39(30):4046-4053. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.06.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Miller BL. Science denial and COVID conspiracy theories: potential neurological mechanisms and possible responses. JAMA. 2020;324(22):2255-2256. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.21332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Alsubaie S, Alshahrani H, Alshahrani A, et al. Denial attitude towards COVID-19 among general population in Saudi Arabia. Eur Psychiatry. 2021;64(S1):S296-S297. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.795 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hebert EB, Koulouglioti C. Parental beliefs about cause and course of their child’s autism and outcomes of their beliefs: a review of the literature. Issues Compr Pediatr Nurs. 2010;33(3):149-163. doi: 10.3109/01460862.2010.498331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ophir Y, Jamieson KH. Intentions to use a novel Zika vaccine: the effects of misbeliefs about the MMR vaccine and perceptions about Zika. J Public Health (Oxf). 2018;40(4):e531-e537. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdy042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dunlap RE, Jacques PJ. Climate change denial books and conservative think tanks: exploring the connection. Am Behav Sci. 2013;57(6):691-698. doi: 10.1177/0002764213477097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lewandowsky S. Liberty and the pursuit of science denial. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2021;42:65-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2021.02.024 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Krueger K, Botermann L, Schorr SG, Griese-Mammen N, Laufs U, Schulz M. Age-related medication adherence in patients with chronic heart failure: a systematic literature review. Int J Cardiol. 2015;184:728-735. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.03.042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gast A, Mathes T. Medication adherence influencing factors-an (updated) overview of systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13643-019-1014-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang D, Marmo-Roman S, Krase K, Phanord L. Compliance with preventative measures during the COVID-19 pandemic in the USA and Canada: results from an online survey. Soc Work Health Care. 2021;60(3):240-255. doi: 10.1080/00981389.2020.1871157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lavoie KL, Gosselin-Boucher V, Stojanovic J, et al. ; iCARE Study Team. Determinants of adherence to COVID-19 preventive behaviours in Canada: results from the iCARE Study. medRxiv. Preprint posted online June 13, 2021. doi: 10.1101/2021.06.09.21258634 [DOI]
- 41.Plohl N, Musil B. Modeling compliance with COVID-19 prevention guidelines: the critical role of trust in science. Psychol Health Med. 2021;26(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/13548506.2020.1772988 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Stosic MD, Helwig S, Ruben MA. Greater belief in science predicts mask-wearing behavior during COVID-19. Pers Individ Dif. 2021;176:110769. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2021.110769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lobera J, Rogero-García J. Scientific appearance and homeopathy: determinants of trust in complementary and alternative medicine. Health Commun. 2021;36(10):1278-1285. doi: 10.1080/10410236.2020.1750764 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.King MF, Bruner GC. Social desirability bias: a neglected aspect of validity testing. Psychology & Marketing. 2000;17(2):79-103. doi: [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Saqlain M, Ahmed A, Nabi I, et al. Public knowledge and practices regarding coronavirus disease 2019: a cross-sectional survey from Pakistan. Front Public Health. 2021;9:629015. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.629015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eMethods. Survey Development Information
eTable. Individual Regression Models
eAppendix. Full Study Survey