The 100 000 Genomes Project (100KGP) is a UK-wide initiative that has a goal of using whole genome sequencing (WGS) to identify genetic causes of rare inherited diseases and embed the use of this technology within the NHS.1 Using data from this resource alongside international gene-matching efforts, four individuals from two independent families were identified harbouring homozygous frameshift or stop-gain variants in PRKG2, a recently described skeletal dysplasia gene.2 Detailed clinical and radiological assessments helped extend the phenotypic range associated with this autosomal recessive condition while functional studies indicated that both variants had a similar impact on FGF-induced MAPK signalling.
PRKG2 encodes the cyclic guanosine monophosphate dependent protein kinase II (cGKII), which acts downstream of the natriuretic peptide receptor-B/C- natriuretic peptide (NPR-B/CNP). NPR-B is encoded by NPR2, biallelic variants in which are responsible for acromesomelic dysplasia, Maroteaux type (AMDM; MIM 602875). Rodent models further implicate PRKG2 in skeletal development3 4 and cGKII deficiency was shown to be the cause of the dwarfism phenotype observed in Angus cattle.5 Building on support from pathway analysis and model organisms, a recent study showed that biallelic PRKG2 variants can result in acromesomelic dysplasia, PRKG2-type (AMDP) in humans,2 adding PRKG2 to a list of >400 genes associated with genetic skeletal disorders.6 As only two affected individuals were reported, it is important that the full clinical range of this condition is described.
In this study, we searched for rare biallelic PRKG2 variants using data from the 100KGP via the LabKey application available within Genomic England’s research environment. Researchers can apply for access online (www.genomicsengland.co.uk/join-a-gecip-domain). Initial filtering employed a 1% population allele frequency threshold based on data from the 1000 Genomes Project as well as in-house frequency information. An additional family was identified via a network of collaborators and variants were classified using ACMG criteria (online supplemental table 1).
jmedgenet-2021-108027supp001.pdf (248.1KB, pdf)
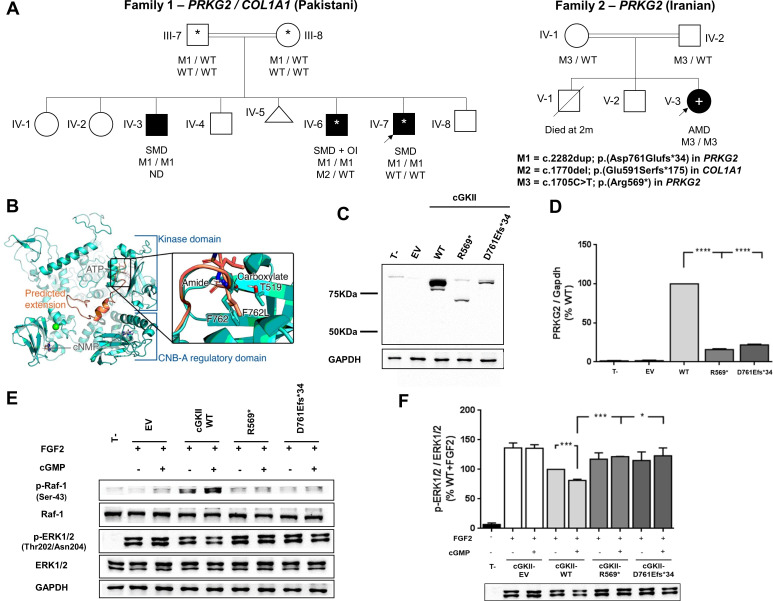
In family 1, WGS and subsequent Sanger sequencing uncovered a homozygous pathogenic PRKG2 variant, NM_006259.3:c.2282dup (p.Asp761Glufs*34; online supplemental figure 1) in three brothers referred with spondylometaphyseal dysplasia (figure 1A). Interestingly, the middle-affected brother (F1-IV-6) also has type I osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). An early clinical exome sequencing study found that for 4.6% of cases with a molecular diagnosis, more than one gene was contributing to a blended phenotype.7 Complex cases such as these are expected to be more common in highly consanguineous families where large regions of homozygosity (ROHs) make up a significant proportion of the genome; however, for F1-IV-6 the secondary diagnosis of OI was due to a COL1A1 frameshift, which had arisen de novo. OI was suspected in this child because of multiple fractures in childhood (arm as an infant, wrist aged 8 and thoracic T6 wedge fracture) combined with blue sclerae. It is certainly possible that the coexistent OI may have had an impact on the severity of the phenotype in this individual, not least because his height was more significantly reduced than for his two brothers and OI (type 1) is a known cause of reduced stature in its own right.
jmedgenet-2021-108027supp002.pdf (3.4MB, pdf)
Figure 1.
Pedigrees, structural modelling and the effects of the PRKG2 variants on cGKII protein levels/MAPK pathway regulation. (A) Simplified pedigrees and segregation of variants in PRKG2 and COL1A1 in two families with rare skeletal dysplasias. More detailed pedigrees are shown in online supplemental figure 4. AMD, acromesomelic dysplasia (mild); ND, not determined; OI, osteogenesis imperfecta; SMD, spondylometaphyseal dysplasia; WT, wild-type; *, WGS performed as part of 100KGP; +, exome sequencing. The COL1A1 variant was initially detected by targeted sequencing in 2011 but confirmed to have arisen de novo by WGS. (B) Structure of cGKII (wild type: turquoise) with overlay of the mutant, p.Asp761Glufs*34 (salmon) extension and inset of Phe762 residue. The protein kinase domain is regulated by two cyclic nucleotides binding (CNB) domains. The predicted C-terminal extension would fall between CNB-A domain and the protein kinase domain and is likely to interfere with the activation of the latter by the former, were it to be stable, a conclusion not supported by in silico predictions. In fact, the extension results in a deleterious amino acid change of a core residue, Phe762, to a leucine (inset). Also visible is the hydrogen bond between the terminal carboxylate and Thr519, whereas the amide bond between Leu762 and Leu763 is forced away in order to best accommodate the subsequent residues. (C) Immunoblotting results for cGKII (upper panel) and GAPDH as an endogenous control (lower panel) of cell lysates extracted from transiently transfected HEK293T cells. Both human cGKII mutants as well as wild-type (WT) proteins were detected at their predicted size: R569*: 65.1 kDa and D761Efs*34: 91.1 kDa (calculated by using the ExPaSy online tool, https://web.expasy.org). (D) Densitometry quantification of cGKII showing that there is an 80% reduction in expression of the two mutants compared with WT. (E) Western blots of phosphorylated Raf-1 and ERK1/2 proteins of the MAPK pathway showed that neither of the mutants were able to phosphorylate c-Raf at Ser43 and therefore downregulate ERK activation compared with WT in response to FGF2 induction in transiently transfected HEKT293 cells. (F) Densitometry quantification of pMAPK 44/42 protein revealed that neither R569* nor D761Efs*34 mutants were able to downregulate FGF2-induced ERK1/2 activation compared with WT, in transiently transfected HEK293 cells in the presence of 8-pCPT-cGMP. Three biological experiments were performed, and significance values are represented as *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 and ****p>0.0001. EV, empty vector; T−, untransfected cells.
In family 2, exome sequencing for a girl with acromesomelic dysplasia revealed a homozygous pathogenic PRKG2 variant c.1705C>T; p.(Arg569*) (online supplemental figure 2), observed previously in a patient with similar clinical and radiological features.2 Comparison of the available genomic data for F2-V-3 and the previously published case was not able to detect a shared haplotype across the PRKG2 locus. However, exome sequencing has limited resolution to detect small regions of identity by descent and so a founder mutation cannot be ruled out. Given the differing ethnicities and the fact that c.1705C>T lies at a CpG dinucleotide, the recurrence of c.1705C>T being due to separate mutational events seems a more likely scenario.
Both variants described here are extremely rare; p.(Asp761Glufs*34) is absent from gnomAD (https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org), while p.(Arg569*) is present as a singleton allele. In both families, the disease-causing variants lay within large ROHs (online supplemental table 2). Pathogenic variants are overrepresented in the largest ROHs and it has been proposed that lying in one of the top 10 such regions can be used as evidence supporting pathogenicity.8 While the p.(Arg569*) variant has already been demonstrated to affect the downstream MAPK pathway,2 the p.(Asp761Glufs*34) in family 1 is likely to be disruptive given the switch of the final Asp-Phe residues for 33 alternative amino acids at the C terminus. In silico modelling highlights the structural importance of this region, in particular the final Phe762 residue (figure 1B, supplementary methods; interactive version at https://michelanglo.sgc.ox.ac.uk/r/prkg2).
To functionally confirm the pathogenicity of the newly identified p.(Asp761Glufs*34) variant, we first analysed cGKII expression by western blot analysis. Plasmid construction for p.(Asp761Glufs*34) involved a sequential PCR strategy (supplemental methods), with the previously characterised p.(Arg569*) variant employed as a positive control. For both variants, cGKII was detected at the predicted size (figure 1C), although at dramatically reduced levels (≥80%) compared with the wild type (figure 1D). Next, we evaluated whether the p.Asp761Glufs*34 mutant was able to inhibit FGF2-induced MAPK pathway by analysing its ability to induce phosphorylation of Raf-1 at Ser-43 and ERK1/2, as described previously.2 Wild-type cGKII downregulated MAPK signalling by reducing ERK1/2 activation through the upstream phosphorylation of Raf-1 at Ser-43 in a cGMP-dependent manner. However, the p.Asp761Glufs*34 mutant failed to phosphorylate Raf-1 at Ser-43 and thus, reduced FGF2-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation (figure 1E–F), similar to results for the p.Arg569* variant.2
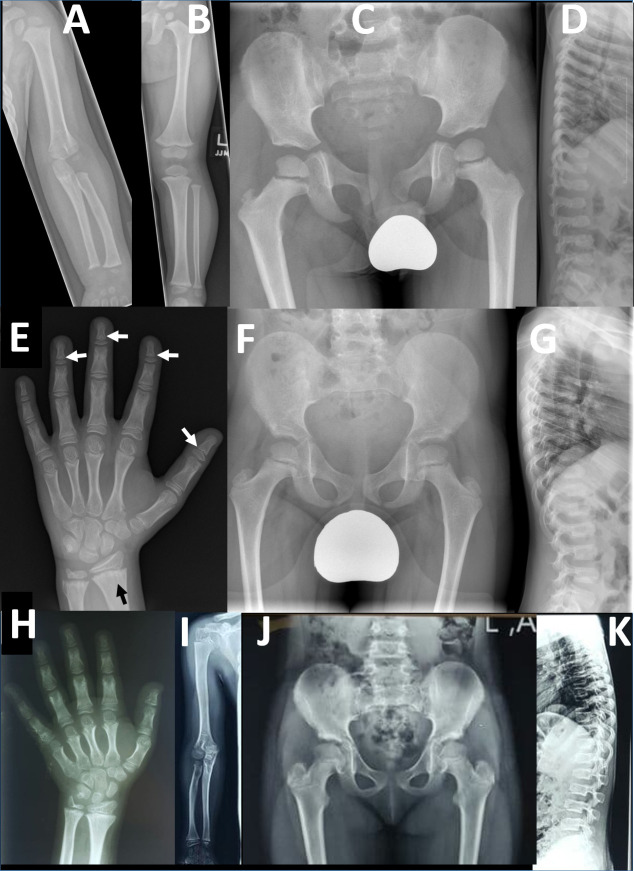
Detailed phenotypic information is provided for both families and compared with the two published cases (online supplemental table 2, figure 3). Radiological findings for F2-V-3 were very similar to those observed for ‘Proband 1’ described previously,2 which is unsurprising given that both individuals harbour the same homozygous p.(Arg569*). In contrast, for PRKG2 family 1 there was a consistent radiological phenotype distinct from previously reported AMDP and AMDM. The three brothers reported here (F1-IV-3, IV-6 and IV-7) had no evidence of acromesomelic shortening, except for mild shortening of toes observed for individual F1-IV-7. The main findings were platyspondyly with anterior vertebral body projections, long slender femoral necks and some metaphyseal irregularity (most evident in the radius and ulna) and striations (figure 2). The metaphyses of the distal phalanges were somewhat cone-shaped in one child, but not pronounced, generalised or associated with shortening, as seen in AMDM.9 In summary, family 1 exhibited a skeletal phenotype characterised by spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, rather than acromesomelic dysplasia as expected in AMDP and AMDM.
Figure 2.
Radiographic findings in two families with PRKG2 variants: radiographs of left upper limb (A) and lower limb (B) in a 26-month-old boy (F1-IV-7) from family 1. The long bones are stocky in appearance but there is no disproportion within the limbs. (C) Pelvic radiograph at age 4 in same child shows development of long, slender femoral necks. (D) Lateral spinal radiograph at age 4 show generalised mild platyspondyly with small central anterior projections of the vertebral bodies, and hypoplasia of the L2 vertebral body. (E) Left hand radiograph at age 11 in same child shows no brachydactyly; there is mild metaphyseal chondrodysplasia evident in the distal radius and particularly the ulna, with some metaphyseal striations (black arrow); subtle coning of the distal phalangeal metaphyses is evident (white arrows), without associated shortening. Pelvic (F) and lateral spine (G) radiographs in middle affected sibling (F1-IV-6) in family 1 showing similar features of long slender femoral necks and platyspondyly with anterior vertebral body projections. Osteopaenia is also evident; this child also has type 1 osteogenesis imperfecta due to a de novo pathogenic variant in COL1A1. Additional radiology is available for F1-IV-3 in online supplemental figure 5 which shows similar results to those for F1-IV-7. (H) Left hand radiograph in female child (F2-V-3, aged 10 years) from family 2 showing generalised brachydactyly. (I) Right upper limb radiograph also from F2-V-3 demonstrates mild disproportionate shortening of the radius and ulna relative to the humerus (mesomelic shortening). (J) Pelvic radiograph from F2-V-3 demonstrates mildly elongated femoral necks. (K) Lateral spine radiograph from the same individual demonstrates mild platyspondyly with small anterior vertebral body projections.
Interestingly, the PRKG2 locus has been identified in several genome-wide association studies on height (www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/genes/PRKG2). Therefore, the description of this now confirmed Mendelian condition constitutes an additional example of rare variants in a gene causing a severe condition, where common variants in the same gene are associated with a related trait.10 In summary, analysis of 100KGP data combined with gene-matching efforts identified four affected individuals with biallelic loss of function variants in PRKG2, extending the phenotypic range of this condition to include spondylometaphyseal dysplasia. The patients described here were the only individuals harbouring severe biallelic PRKG2 variants across all rare disease areas within the 100KGP. These data include 295 patients recruited due to an unexplained skeletal dysplasia and therefore our results are consistent with this condition being extremely rare in humans.
Acknowledgments
We thank the two families for their involvement in our study. This research was made possible through access to the data and findings generated by the 100,000 Genomes Project. The 100KGP is managed by Genomics England Limited (a wholly owned company of the Department of Health and Social Care). The 100KGP uses data provided by patients and collected by the National Health Service as part of their care and support.
Footnotes
Collaborators: The Genomics England Research Consortium (27th May 2021): John C. Ambrose (Genomics England, London, UK); Prabhu Arumugam (Genomics England, London, UK); Roel Bevers (Genomics England, London, UK); Marta Bleda (Genomics England, London, UK); Freya Boardman-Pretty (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Christopher R Boustred (Genomics England, London, UK); Helen Brittain (Genomics England, London, UK); Mark J Caulfield (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Georgia C Chan (Genomics England, London, UK); Greg Elgar (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Tom Fowler (Genomics England, London, UK); Adam Giess (Genomics England, London, UK); Angela Hamblin (Genomics England, London, UK); Shirley Henderson (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Tim J P Hubbard (Genomics England, London, UK); Rob Jackson (Genomics England, London, UK); Louise J Jones (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Dalia Kasperaviciute (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Melis Kayikci (Genomics England, London, UK); Athanasios Kousathanas (Genomics England, London, UK); Lea Lahnstein (Genomics England, London, UK); Sarah E A Leigh (Genomics England, London, UK); Ivonne U S Leong (Genomics England, London, UK); Javier F Lopez (Genomics England, London, UK); Fiona Maleady-Crowe (Genomics England, London, UK); Meriel McEntagart (Genomics England, London, UK); Federico Minneci (Genomics England, London, UK); Loukas Moutsianas (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Michael Mueller (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Nirupa Murugaesu (Genomics England, London, UK); Anna C Need (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Peter O’Donovan (Genomics England, London, UK); Chris A Odhams (Genomics England, London, UK); Christine Patch (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Mariana Buongermino Pereira (Genomics England, London, UK); Daniel Perez-Gil (Genomics England, London, UK); John Pullinger (Genomics England, London, UK); Tahrima Rahim (Genomics England, London, UK); Augusto Rendon (Genomics England, London, UK); Tim Rogers (Genomics England, London, UK); Kevin Savage (Genomics England, London, UK); Kushmita Sawant (Genomics England, London, UK); Richard H Scott (Genomics England, London, UK); Afshan Siddiq (Genomics England, London, UK); Alexander Sieghart (Genomics England, London, UK); Samuel C Smith (Genomics England, London, UK); Alona Sosinsky (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Alexander Stuckey (Genomics England, London, UK); Mélanie Tanguy (Genomics England, London, UK); Ana Lisa Taylor Tavares (Genomics England, London, UK); Ellen R A Thomas (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Simon R Thompson (Genomics England, London, UK); Arianna Tucci (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Matthew J Welland (Genomics England, London, UK); Eleanor Williams (Genomics England, London, UK); Katarzyna Witkowska (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK); Suzanne M Wood (Genomics England, London, UK, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, EC1M 6BQ, UK).
Contributors: ATP and JCT conceived the project. ATP, BB-P, MPF, FD-G, TL, RM and KEH performed data analysis. BB-P and FD-G generated experimental data. The 57 members of GERC performed WGS and provided access data via a secure research environment. MBT, ADC, EGK, MD, AW, PW, KB, KE, RM, HT and DS recruited the patients and collected/interpreted clinical information. ATP drafted the manuscript, which was revised and approved by all.
Funding: This research was supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Oxford Biomedical Research Centre Programme, the Wellcome Trust (203141/Z/16/Z) and the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development and demonstration under grant agreement no. 608473 (to HT). Additional support was from MINECO grant no. SAF2017-84646-R from (to KEH) and via an FPU studentship (to FD-G) from the Spanish Ministry of Education. The 100KGP is funded by the National Institute for Health Research and NHS England. The Wellcome Trust, Cancer Research UK and the Medical Research Council have also funded research infrastructure.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Contributor Information
The Genomics England Research Consortium:
John C Ambrose, Prabhu Arumugam, Roel Bevers, Marta Bleda, Freya Boardman-Pretty, Christopher R Boustred, Helen Brittain, Mark J Caulfield, Georgia C Chan, Greg Elgar, Tom Fowler, Adam Giess, Angela Hamblin, Shirley Henderson, Tim J P Hubbard, Rob Jackson, Louise J Jones, Dalia Kasperaviciute, Melis Kayikci, Athanasios Kousathanas, Lea Lahnstein, Sarah E A Leigh, Ivonne U S Leong, Javier F Lopez, Fiona Maleady-Crowe, Meriel McEntagart, Federico Minneci, Loukas Moutsianas, Michael Mueller, Nirupa Murugaesu, Anna C Need, Peter O’Donovan, Chris A Odhams, Christine Patch, Mariana Buongermino Pereira, Daniel Perez-Gil, John Pullinger, Tahrima Rahim, Augusto Rendon, Tim Rogers, Kevin Savage, Kushmita Sawant, Richard H Scott, Afshan Siddiq, Alexander Sieghart, Samuel C Smith, Alona Sosinsky, Alexander Stuckey, Mélanie Tanguy, Ana Lisa Taylor Tavares, Ellen R A Thomas, Simon R Thompson, Arianna Tucci, Matthew J Welland, Eleanor Williams, Katarzyna Witkowska, and Suzanne M Wood
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Consent obtained from parent(s)/guardian(s)
Ethics approval
The 100K Genomes Project has approval from the HRA Committee East of England (Cambridge South REC: 14/EE/1112).
References
- 1. Turnbull C, Scott RH, Thomas E, Jones L, Murugaesu N, Pretty FB, Halai D, Baple E, Craig C, Hamblin A, Henderson S, Patch C, O'Neill A, Devereau A, Smith K, Martin AR, Sosinsky A, McDonagh EM, Sultana R, Mueller M, Smedley D, Toms A, Dinh L, Fowler T, Bale M, Hubbard T, Rendon A, Hill S, Caulfield MJ, O’Neill A, Genomes P, 100 000 Genomes Project . The 100 000 Genomes Project: bringing whole genome sequencing to the NHS. BMJ 2018;361:k1687. 10.1136/bmj.k1687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Díaz-González F, Wadhwa S, Rodriguez-Zabala M, Kumar S, Aza-Carmona M, Sentchordi-Montané L, Alonso M, Ahmad I, Zahra S, Kumar D, Kushwah N, Shamim U, Sait H, Kapoor S, Roldán B, Nishimura G, Offiah AC, Faruq M, Heath KE. Biallelic cGMP-dependent type II protein kinase gene (PRKG2) variants cause a novel acromesomelic dysplasia. J Med Genet 2022;59:28–38. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2020-107177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Pfeifer A, Aszódi A, Seidler U, Ruth P, Hofmann F, Fässler R. Intestinal secretory defects and dwarfism in mice lacking cGMP-dependent protein kinase II. Science 1996;274:2082–6. 10.1126/science.274.5295.2082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Tsuchida A, Yokoi N, Namae M, Fuse M, Masuyama T, Sasaki M, Kawazu S, Komeda K. Phenotypic characterization of the Komeda miniature rat Ishikawa, an animal model of dwarfism caused by a mutation in Prkg2. Comp Med 2008;58:560–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Koltes JE, Mishra BP, Kumar D, Kataria RS, Totir LR, Fernando RL, Cobbold R, Steffen D, Coppieters W, Georges M, Reecy JM. A nonsense mutation in cGMP-dependent type II protein kinase (PRKG2) causes dwarfism in American Angus cattle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:19250–5. 10.1073/pnas.0904513106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Mortier GR, Cohn DH, Cormier-Daire V, Hall C, Krakow D, Mundlos S, Nishimura G, Robertson S, Sangiorgi L, Savarirayan R, Sillence D, Superti-Furga A, Unger S, Warman ML. Nosology and classification of genetic skeletal disorders: 2019 revision. Am J Med Genet A 2019;179:2393–419. 10.1002/ajmg.a.61366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Yang Y, Muzny DM, Xia F, Niu Z, Person R, Ding Y, Ward P, Braxton A, Wang M, Buhay C, Veeraraghavan N, Hawes A, Chiang T, Leduc M, Beuten J, Zhang J, He W, Scull J, Willis A, Landsverk M, Craigen WJ, Bekheirnia MR, Stray-Pedersen A, Liu P, Wen S, Alcaraz W, Cui H, Walkiewicz M, Reid J, Bainbridge M, Patel A, Boerwinkle E, Beaudet AL, Lupski JR, Plon SE, Gibbs RA, Eng CM. Molecular findings among patients referred for clinical whole-exome sequencing. JAMA 2014;312:1870–9. 10.1001/jama.2014.14601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Wakeling MN, Laver TW, Wright CF, De Franco E, Stals KL, Patch A-M, Hattersley AT, Flanagan SE, Ellard S, Study DDD, DDD Study . Homozygosity mapping provides supporting evidence of pathogenicity in recessive Mendelian disease. Genet Med 2019;21:982–6. 10.1038/s41436-018-0281-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Wang W, Song MH, Miura K, Fujiwara M, Nawa N, Ohata Y, Kitaoka T, Kubota T, Namba N, Jin DK, Kim OH, Ozono K, Cho T-J. Acromesomelic dysplasia, type Maroteaux caused by novel loss-of-function mutations of the NPR2 gene: three case reports. Am J Med Genet A 2016;170A:426–34. 10.1002/ajmg.a.37463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Freund MK, Burch KS, Shi H, Mancuso N, Kichaev G, Garske KM, Pan DZ, Miao Z, Mohlke KL, Laakso M, Pajukanta P, Pasaniuc B, Arboleda VA. Phenotype-specific enrichment of Mendelian disorder genes near GWAS regions across 62 complex traits. Am J Hum Genet 2018;103:535–52. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.08.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
jmedgenet-2021-108027supp001.pdf (248.1KB, pdf)
jmedgenet-2021-108027supp002.pdf (3.4MB, pdf)