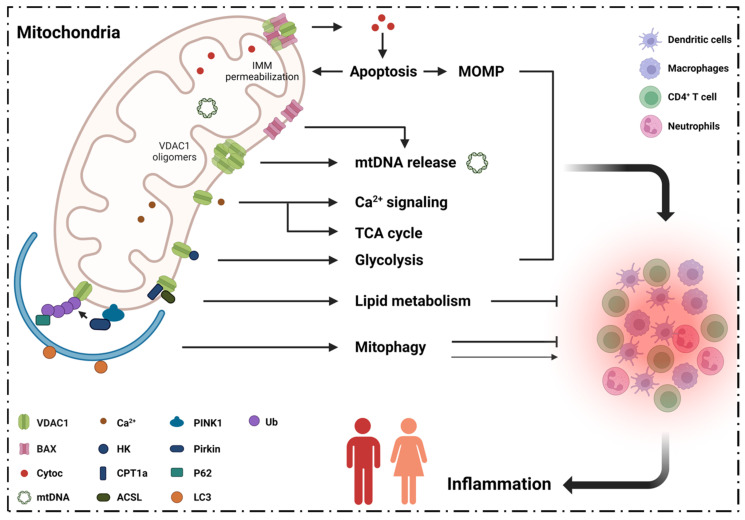
Figure 1.
VDAC1 regulates inflammatory pathogenesis. Mitochondria are the center of energy generation, the TCA cycle, glycolysis and lipid metabolism. VDAC1 is the fundamental component that maintains mitochondrial function. VDAC1 plays an important role in the regulation of apoptosis, mtDNA release, Ca2+ signaling, TCA cycle, glycolysis, lipid metabolism and mitophagy. Impaired mitochondrial homeostasis with dysfunctional signal networks results in inflammatory pathogenesis and mitochondrial diseases. Abbreviations: ACSL: long-chain acyl-CoA synthase; BAX: Bcl-2-associated X protein; CPT1a: carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; Cyto c: cytochrome c; HK: hexokinase; LC3: microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3; IMM: inner mitochondrial membrane; MOMP: mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization; mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA; PINK1: PTEN-induced putative kinase 1; TCA cycle: tricarboxylic acid cycle; Ub: ubiquitin; VDAC1: voltage-dependent anion channel 1.