Fig.1. Visual projections are only contralateral in clupeocephalan teleosts.
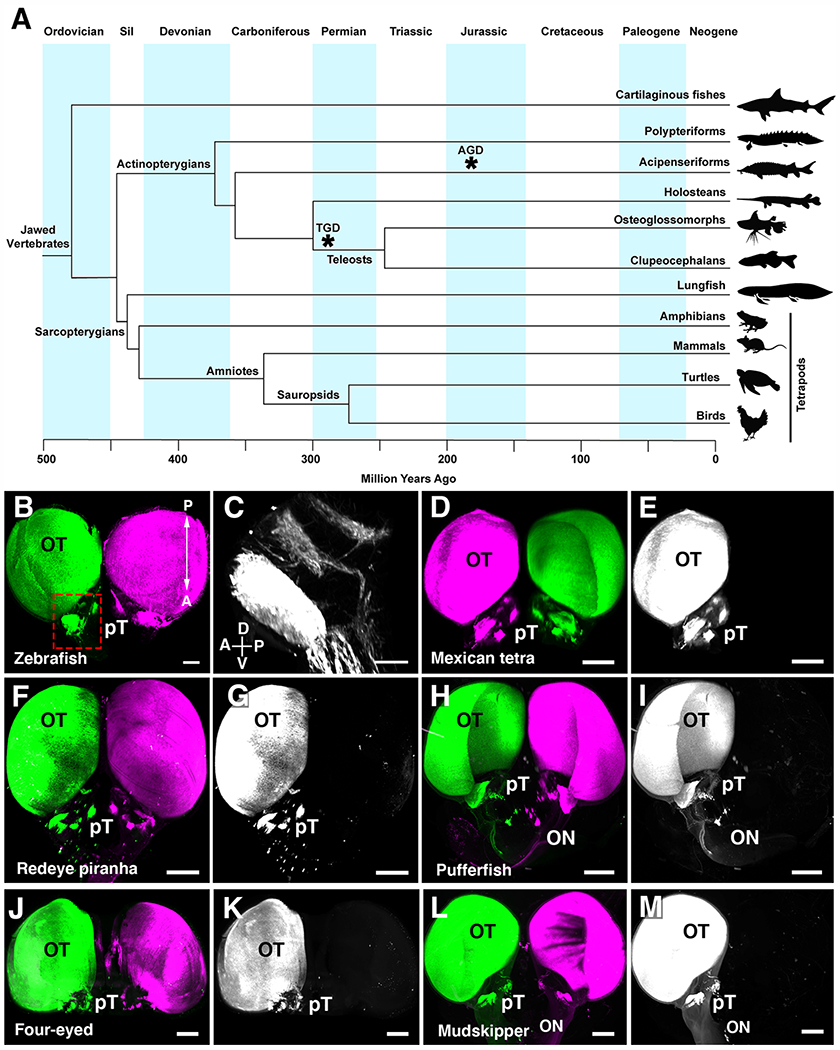
(A) Simplified phylogenetic tree of the major groups of vertebrates. Divergence of each major group is displayed in million years. Asterisks indicate whole genome duplication events in the teleost (TGD) and sturgeon (AGD) ancestors. (B) Whole brain visualization of a juvenile zebrafish injected with an AlexaFluor-555-conjugated CTb (left eye) and AlexaFluor-647-conjugated CTb (right eye) highlighting complete contralateral projections. (C) High magnification showing pre-tectal nuclei. (D to M) 3D rendering of visual projections labelled by injecting AlexaFluor-555-conjugated CTb (left eye) and AlexaFluor-647-conjugated CTb (right eye) followed by iDISCO whole-brain clearing and 3D imaging using light-sheet fluorescence microscopy. (D and E) Mexican tetra. (F and G) Redeye piranha. (H and I) Green-spotted pufferfish. (J and K) Four-eyed fish. (L and M) Atlantic mudskipper. In all species, visual axons only project to the brain on the contralateral side. Abbreviations: A, anterior; Cb, Cerebellum; Ctb, Cholera toxin B; D, dorsal; OB, Olfactory bulb; ON, Optic nerve; P, posterior; V, ventral; Sil, Silurian. Scale bars are 500 μm in (B) and (D) to (M) and 200 μm in (C).
