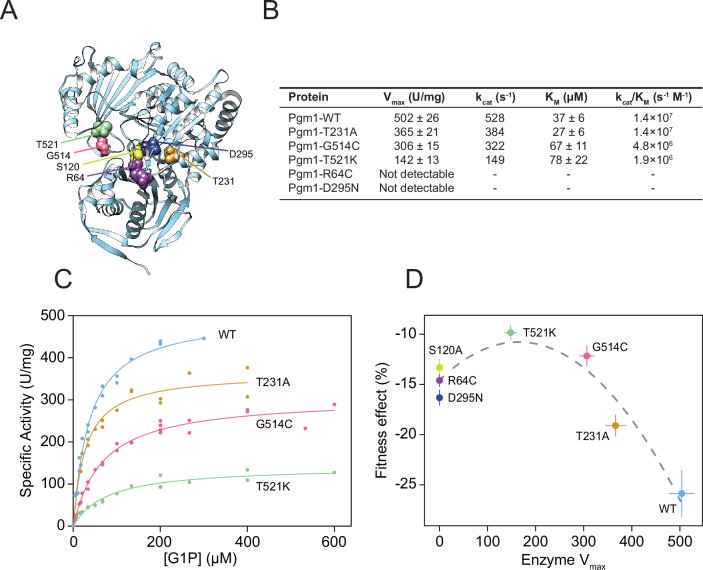
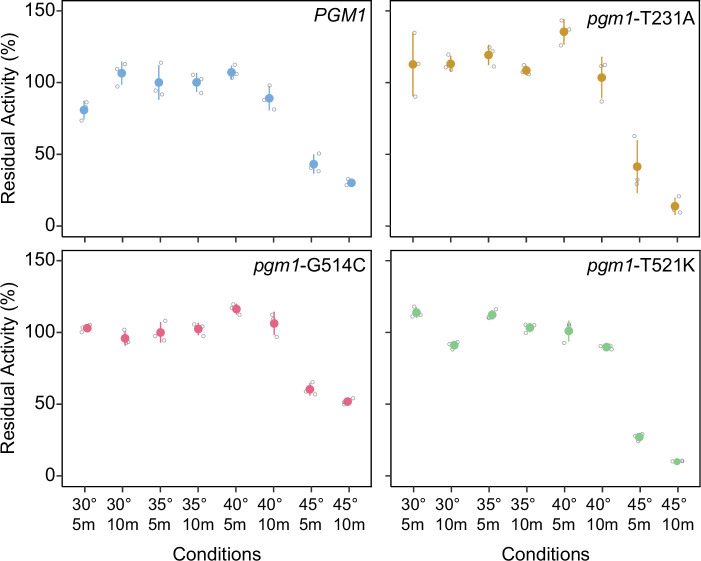
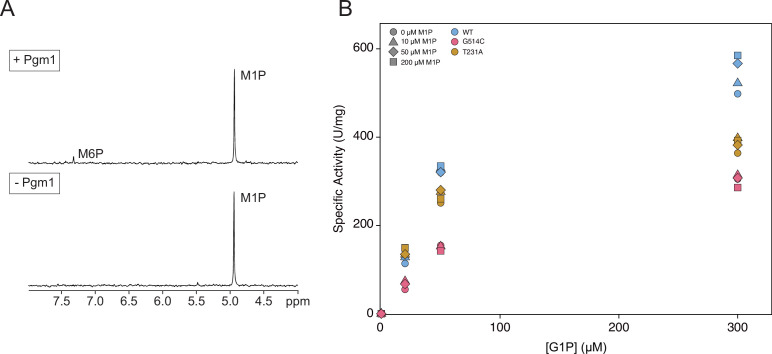
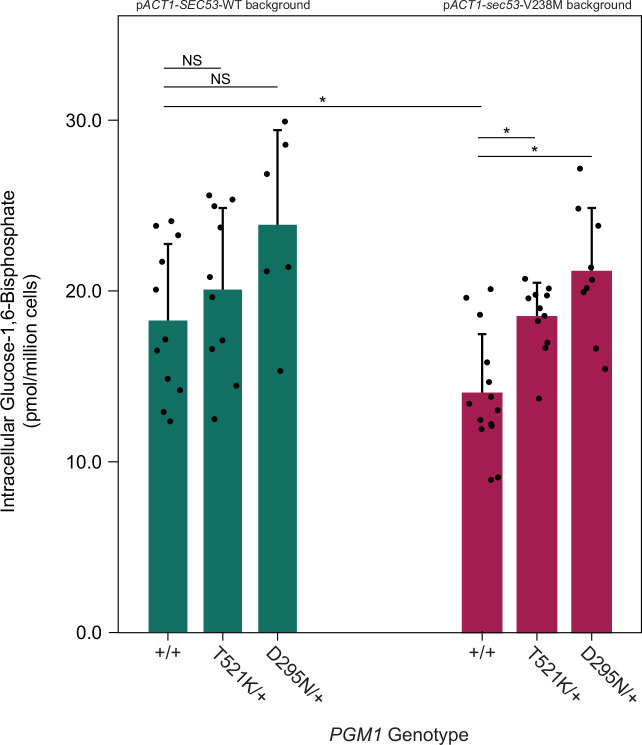
Figure 5. Complete loss of Pgm1 activity overshoots a fitness optimum.
(A) AlphaFold structure of S. cerevisiae Pgm1 (Jumper et al., 2021). Mutated residues shown as spheres. (B) Kinetic parameters of recombinant Pgm1 enzymes as determined by a coupled enzymatic assay. Values ± 95% confidence intervals. (C) Michaelis–Menten curves of wild-type and mutant Pgm1. Replicate measurements are plotted as circles. (D) Pgm1 enzyme Vmax versus the corresponding allele’s fitness effect in the diploid pACT1-sec53-V238M background (as shown in Figure 3A). Horizontal and vertical error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. Best fit regression shown as a dashed curve (y = 14.583 + 0.04613x − 0.00014x2, R2 = 0.907, df = 4, F = 37.34, p = 0.0258, analysis of variance [ANOVA]). Note that we did not measure Pgm1-S120A activity and assume null activity.