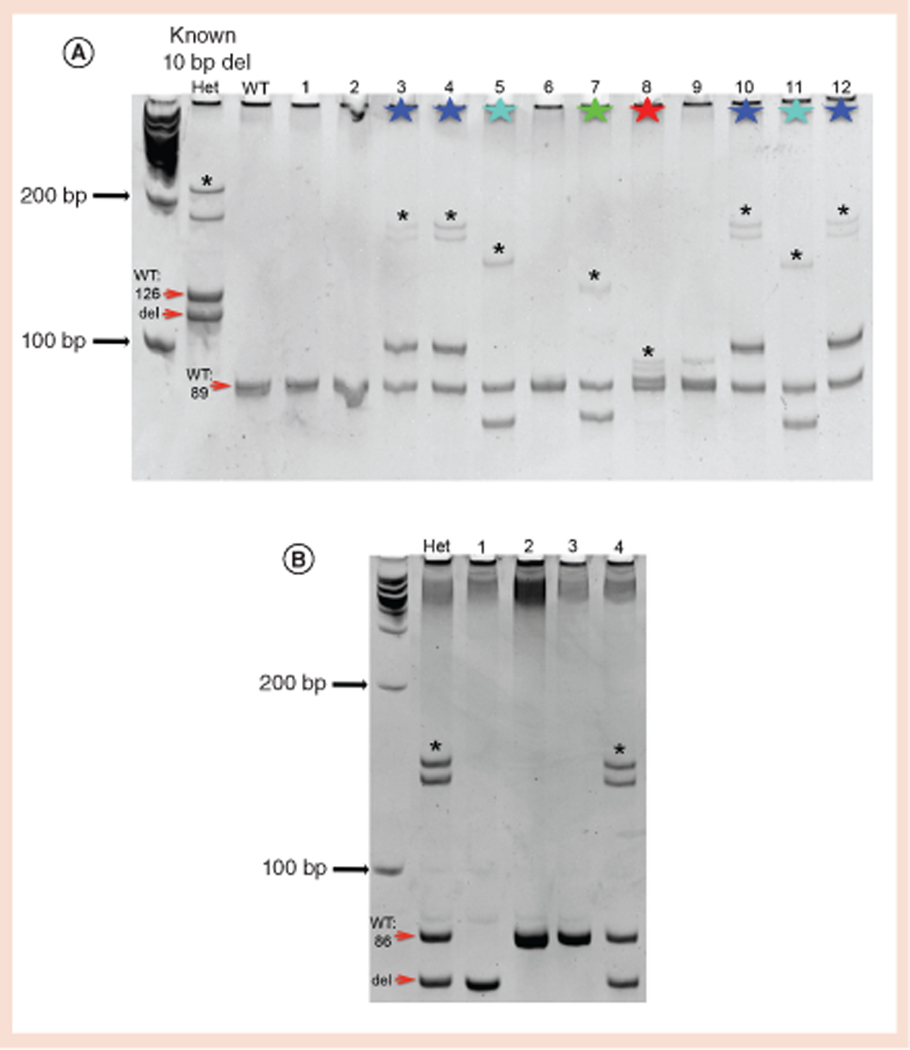
Figure 2. Representative ways in which neutral PAGE can be used to screen at the F1 and F2 generations.
(A) PAGE results showing 12 individual embryos from an outcross in which the F0-injected founder transmits four different germline mutations in gad1a exon 5 at a frequency of ∼67%. The first lane is a known heterozygous zebrafish for a different allele that serves as a positive control. The starred samples were sequenced and determined to have the following types of mutations: embryo numbers 3, 4, 10, 12 have a 14-bp insertion; embryos 5 and 11 have a 10-bp deletion; embryo number 7 has a 9-bp deletion; embryo number 8 has a 2-bp insertion. (B) PAGE results from an incross of a line of fish (gav2501) that are heterozygous for a CRISPR-Cas9-induced 10-bp deletion at gad2 exon 1. Fish number 1 is a homozygous mutant, fish numbers 2 and 3 are wild-type and fish number 4 is a heterozygous mutant. In both gels, the second pair of bands that are noted with an asterisk are heteroduplexes.