Extended Data Figure 10: Percentage of cases carrying mutations in the BCL6-BLIMP1-BS, BCL2-NR3C1-BS, and CXCR4-NR3C1-BS across lymphoid and non-lymphoid cancers.
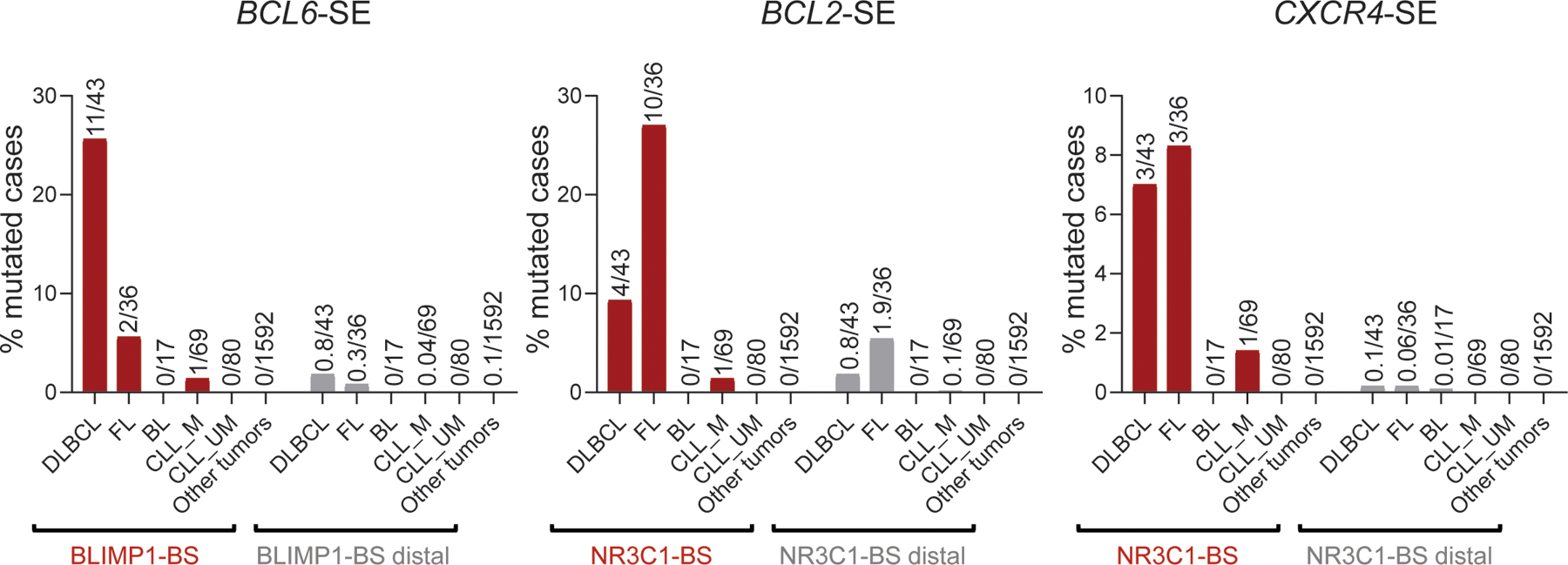
Percentage of cases carrying mutations in the BCL6-, BCL2-, and CXCR4- SE hotspots characterized in Figures 4–6 across an independent panel of GC-derived lymphomas (DLBCL, FL, BL, and IGHV-mutated-CLL), non-GC derived lymphomas (IGHV-unmutated-CLL), and other cancer types from the ICGC pan-cancer project. In further support of the selective pressure for mutating these sequences, 15bp domains located between 0.5kb and 3kb from the BS, within the same SE (BS-distal) were randomly selected with 100 permutations, and the percentage of mutated cases in these regions was calculated (grey bars; mean of 100 permutations). Particularly relevant is the lack of hotspot mutations in M-CLL (which have transited through the GC and therefore represent specific surrogates of normal GC alleles).
