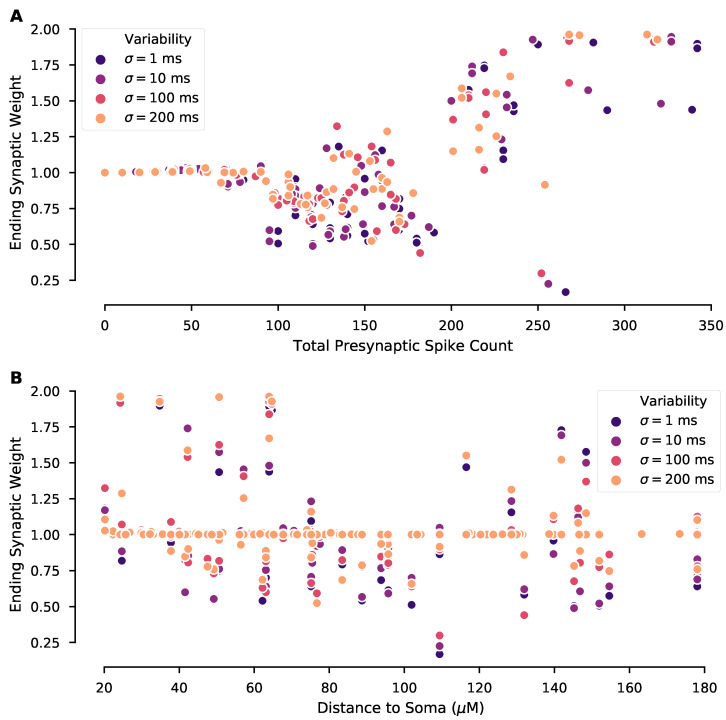
Figure 5.
Ending synaptic weight is partially predicted by total pre-synaptic spike count per synapse. Ending synaptic weight of each synapse is plotted versus (A) its total pre-synaptic spike count across all 10 repeated trials and (B) distance of the synapse from the soma, with experiments separated by the level of trial-to-trial variability. (A) Ending weight exhibits no change for low spike counts, tends toward depression for intermediate spike counts, and exhibits potentiation for high spike counts. This trend is consistent regardless of trial-to-trial variability; however, for intermediate spike counts the ending weight is highly variable. (B) Correlation between ending synaptic weight and distance to soma is not significant for = 100 ms (R = −0.23, p = 0.07) or 200 ms (R = −0.21, p = 0.11), but is significant for = 1 ms (R = −0.25, p = 0.04) and 10 ms (R = −0.25, p = 0.04).