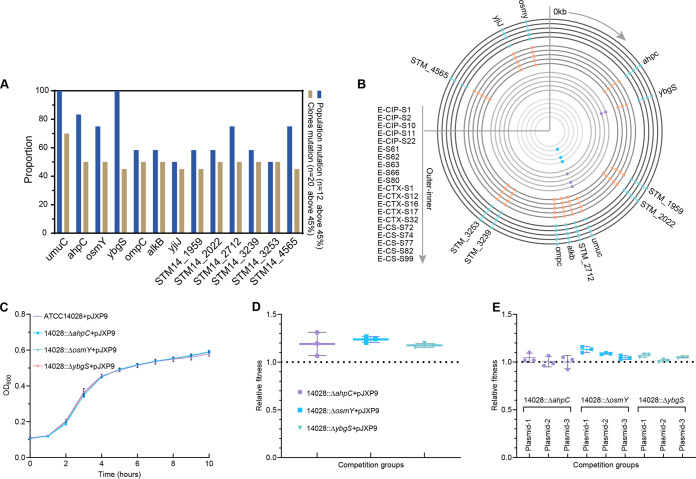
FIG 4.
Chromosomal compensatory mutation analysis and function verification. (A) Frequency analysis of compensatory mutations in chromosomal genes in populations and clones. Mutant frequencies were defined by numbers of occurrences in 12 evolved populations or 20 representative clones. The mutated genes also included mutations at different sites. Cutoffs were set at >0.45, because mutated genes were among the top 25% simultaneously in populations and clones. n, number of populations or individual clones used to detect mutations. (B) Mutants present in 20 evolved clones. Different colors represent different exposure conditions. (C) Growth curves for mutated ATCC 14028+pJXP9 and ancestral ATCC 14028+pJXP9 strains. (D) Relative fitness of mutated ATCC 14028+pJXP9 versus ATCC 14028::lux+pJXP9 by competition assays. (E) Fitness estimation of mutated ATCC 14028 carrying evolved plasmid pJXP9 versus ATCC 14028::lux+pJXP9 strains. Plasmids 1 (from E-S62), 2 (from E-S63), and 3 (from E-CTX-S32) represent three types of evolved pJXP9 plasmids, respectively. All data were derived from at least 3 biological replicates and are presented as the mean ± SD, and levels of significance were determined by nonparametric one-way ANOVA (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001).